Properties of zinc
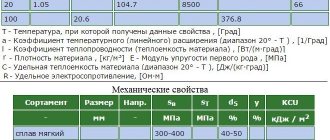
The metal has weak mechanical properties. It is brittle and brittle at normal temperatures, and when it rises to 100–150 degrees Celsius, it becomes malleable and easily deformed: it is forged and rolled into sheets. To increase the strength and melting point, copper, lead, tin, aluminum, and magnesium are added to zinc.
It is a reactive metal. In open air at a temperature of 100 degrees Celsius, a film appears on the surface and the zinc takes on a dull appearance. High humidity and carbon dioxide contribute to the destruction of the element. It is easily corroded by acids and alkalis, so only alloys are used for industrial use.
Zinc (Zn) for door handles
Rarely used in its pure form, because when exposed to air, it naturally reacts to carbon dioxide and forms a layer of Zn carbonate, but is instead used to form numerous metal casting alloys, including brass, bronze, nickel silver, soft solder, German silver, spring brass, and aluminum solder. The most popular of them are called by the abbreviation ZAMAK or TsAM (zinc, aluminum, magnesium and copper). This is the most common basis for the production of door hardware: handles and locks. Multilayer galvanic coating not only protects the product from scratches, but also increases its anti-corrosion properties.
Probably the best known of these is brass, which is made by adding 55% or more copper to Zn. Brass is commonly used today for corrosion resistance. This layer serves as a protective coating against further reaction with air or water, so about a third of all zinc metal produced today is used to galvanize other metals to prevent corrosion.
From sockets to radiators and nails, it is commonly used to make electrical, automotive and hardware equipment. Due to the reduced cost, it is often chosen for larger products that require a larger volume of materials to manufacture.
• Can be galvanized onto other metals
• Universal (can be mixed)
What to choose?
When compared by cost, the price of stainless steel is higher due to the chromium content, and despite the higher cost, it is a durable material that is corrosion resistant. Although some connections may be very strong, overall it is stronger. Zn is cheaper than chromium and therefore its alloys are relatively cheaper in general. However, Zn is a heavy element and when fused with other metals it provides better corrosion resistance, stability, dimensional strength and toughness. Due to the lower casting temperature, it provides much longer die life, which further reduces production costs. When it comes to tight tolerance casting components and thinner wall areas, no other connections compare.
The online store msmlock.ru offers a wide range of handles on the strip and rosette for interior and entrance doors at a low price. The ordering and delivery form will allow you to buy your favorite fittings (locks, closers, hinges) and other products online.
Ultimately, the choice will depend on your needs. In general, due to cost differences, zinc is usually preferred for larger items where aesthetics are less important (outdoor applications), while stainless steel is most often used for smaller items where aesthetics matter (indoor use and decor ).
Source
Properties of zinc alloys
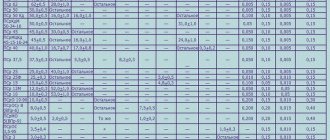
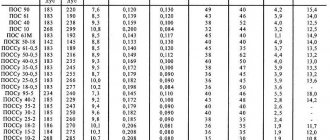
Excellent casting properties of the alloys are noted. Due to their high ductility when hot, metals are used for casting parts with complex shapes, deep cavities, threads and thin wall thickness. They do not stick to the mold because they do not react with the iron. Casting parts have high precision and clean surface. The alloys have excellent mechanical properties: sufficient tensile strength, hardness and are well processed. They can be soldered and welded.
Disadvantages include susceptibility to aging, high density and corrosion. When using zinc alloys, their natural aging process occurs, as a result of which the parts decrease in size. The largest shrinkage occurs in the first 5 weeks, and subsequent shrinkage occurs over a very long period of time. To compensate for the dimensions of the parts, they are subjected to heat treatment - annealing. To reduce corrosion in alloys, the magnesium content is limited to 0.1%. To increase the durability of parts, they are subjected to protective coatings: nickel-plated, chrome-plated, cadmium-plated.
STAINLESS STEEL
It is an alloy of iron, carbon and at least 10.5% chromium, known for its strength and corrosion resistance. It comes in many different grades, which are determined by the degree and combination of elements mixed with iron, carbon and chromium. Modern combinations may contain elements such as nickel, niobium, molybdenum and titanium to improve corrosion resistance, improve strength and ductility to environmental factors found in a variety of climates: tropical, dry, temperate, cold and polar, on land and at sea, and even in the upper layers of the atmosphere and space.
Types of alloys
According to their intended purpose, zinc alloys are divided into:
- Deformable. The basis of these alloys is zinc. Their properties are similar to brass. Ingots are produced using the casting method, and rods, strips, and sheets are made from them.
- Foundries. They have high fluidity. Fills the mold perfectly without sticking to it. High-quality castings of complex configurations are obtained by injection molding.
- Anti-friction. The alloys have a low coefficient of friction and good wearability of the bearing to the shaft journal.
- Solders. They are used for soldering products and have good ductility and strength.
- Typographical. Used for casting hand and machine typefaces. Replace toxic lead alloys. Abrasion resistant.
- Protective. Protects internal and external parts of sea vessels from corrosion. They are used with a special paint coating.
Characteristics and properties of brass
A copper-zinc alloy in which copper is the main component and zinc is the alloying component is called brass. The color of the metal depends on the composition and varies from light yellow tones to reddish shades. Such alloys are characterized by resistance to corrosion and have high strength. They lend themselves well to various processing methods. The fluidity of brass allows parts to be manufactured using the casting method. Using plastic deformation of the alloy, wire, sheets, tapes, and various profiles are produced from it by rolling. The zinc content in the alloy can vary and range from 5 to 45%. In addition, it also includes additional alloying components that are used to improve the properties of brass:
- Nickel. Helps increase corrosion resistance and strength.
- Silicon. Improves anti-friction properties.
- Tin. Affects strength and resistance to salt water.
- Lead. Improves machinability.
- Manganese. Affects strength and corrosion resistance.
When various combinations of alloying components are used, brass with the required qualities and characteristics is obtained. Products made from such alloys are not exposed to environmental influences and have high wear resistance.
TsAM or stainless steel in door fittings
Zinc alloy vs stainless steel
They are common materials used for parts in many applications. The choice of material will depend on the specific applications. The finished product will have its own mechanical and physical properties that determine its durability, strength and overall functionality.
The casting process involves injecting liquid metal into a mold or die under high pressure to achieve a specific shape. This process is ideal for high-volume parts due to its dimensional accuracy, intricate detailing, and ability to create highly complex geometries. The choice of zinc or other alloys will ultimately be determined by factors such as volume, cost, use and size, among other market-driven reasons.
Application of alloys
Without zinc and its alloys, many industries from mechanical engineering to medicine cannot exist.
Application of zinc alloys in various fields and industries:
- mechanical engineering - for the production of gas tanks, trunk lids, carburetor bodies, mufflers, gas pumps, radiators, pumps, accessories;
- foundry - weapon bolts;
- electrical engineering – production of accumulators and batteries;
- printing – for typing texts and printing illustrations;
- processing of metal structures - metallization and galvanizing of various surfaces from destruction and corrosion of metal;
- medicine – antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs, obtaining radionuclides for the diagnosis and treatment of a number of diseases;
- paint production – production of zinc white;
- construction – for roofing, wall cladding, drainpipes, gutters;
- art – coinage, graphics;
- jewelry - personal jewelry, boxes, buttons, zippers, decorative overlays;
- household – for kitchen equipment, cornices.
Zinc casting alloys
The following requirements apply to alloys for injection molding. They have to:
- have excellent fluidity;
- do not react or weld to the mold;
- have a short crystallization interval;
- have strength at high temperatures.
Such alloys are used in the following cases:
- For injection molding of parts with complex configurations and thin walls. This is how brake equipment parts and pumps are produced using the properties of alloys, such as resistance to cracking, fluidity, and low melting point.
- For the production of cast decorative products. After galvanization, a beautiful and durable coating is installed on the surface. It may not be of very high quality if the surface is porous or contains excessive aluminum.
- For the production of antifriction zinc alloys used in mechanical engineering.
- For casting typographic fonts. With changes in technology, the need to manufacture them disappears.
Basic methods of zinc casting
In non-ferrous metallurgy, several technologies for producing castings are used, and this somewhat complicates the work of the technologist in terms of determining how the part will be manufactured. Before making a final choice in favor of one technology or another, you need to understand the following:
Centrifugal casting method
- The chosen casting method must guarantee that the resulting parts will fully meet the requirements of regulatory, technical and working documentation. All parameters included in the part will be observed, and allowances for machining should not exceed the norms defined in the relevant standards.
- The technical process must have appropriate productivity and efficiency.
- The use of the selected process must be based on the operation of existing equipment and fixtures.
Zinc sand casting method
To produce castings from zinc alloys, the following main types of casting are used, and their features must be taken into account. For example, casting in sand or metal molds is the most common and, probably, economical method of obtaining the necessary blanks. But it is necessary to take into account that after casting in sand, additional surface treatment will be required, since its quality leaves much to be desired. When producing small batches of parts, it makes sense to think about die casting. But in this case, the high cost of equipment may become an obstacle.
Centrifugal casting
The result of constant improvement of foundry technologies was the emergence of machines for performing centrifugal casting. The principle of this method of producing castings is simple - the melt is fed into molds rotating around its axis, under the influence of centrifugal force it is “smeared” over the mold and after a predetermined time the finished product will be formed. This technology makes it possible to smelt products without air bubbles.
There are horizontal and vertical machines. They are used to produce large-sized castings. The use of equipment of this class is justified from an economic point of view when organizing mass production.
This technology makes it possible to produce hollow castings without the need to use additional devices, such as rods. The casting obtained using this technology has a dense and fine-grained material structure. However, the equipment to perform work using this technology is quite expensive. In addition, for a number of reasons, in particular, due to the low flexibility of the shape, defects in the form of cracks may appear.
Injection molding
Die casting of zinc alloys is based on the following principle - the melt is fed into the mold under pressure from 7 to 700 MPa.
Its level depends on the composition of the alloy and the characteristics of the future part. Using existing equipment, it is possible to produce parts weighing from several grams to tens of kilograms. Advantages and disadvantages of casting technology Among the many casting technologies used for working with zinc alloys, the following are used:
Chill casting
Guarantees the production of workpieces with high surface quality; as a rule, such parts do not require machining operations. But the mold has a high price due to the high labor intensity of its production.
A high cooling rate leads to a decrease in the fluidity of the melt and this can lead to the appearance of various types of defects. The virtual absence of gas permeability of the mold leads to the fact that the gases generated during the casting process remain in the workpiece. Die casting of zinc alloys makes it possible to produce complex products with minimized wall dimensions. The quality of the resulting product allows us to avoid further machining. This type of casting is distinguished by its level of productivity. However, expensive equipment is required to ensure it. In addition, there are restrictions on the overall dimensions of cast parts.
Automotive industry
The automotive industry is one of the leading areas of mechanical engineering. Research is steadily being carried out here on the use of the latest materials and alloys, which have significant performance and technological properties. These include zinc alloys in accordance with GOST 21437-75.
It includes four grades of alloys, two of which are casting, and the others are pressure-processable. These materials are used to produce car parts (bushings and bearings) with anti-friction properties. Cast zinc alloys GOST 19424-74 and 25140-82 are used for the manufacture of carburetors with complex shapes and gasoline pumps by injection molding, using their high fluidity properties. The disadvantage of alloys is that the parts are practically irreparable.