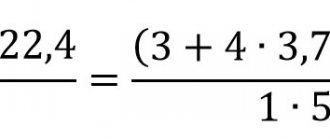Copper has been known to man since ancient times; people learned to mine it and use it to create tools, utensils, and jewelry. The popularity of this metal today is due to its high electrical conductivity. Therefore, it is used in the manufacture of cables, electrical wires, in industry, and electrical engineering.
Slavic jewelry made of copper
In Russia, copper mining is carried out constantly, without stopping, new mines are opened, ore processing technologies are improved.
Geological features of production
Copper is not found in the earth's crust in its pure form; it is one of the components of ore. There are several types of copper-containing minerals:
Chalcozine
- chalcocite, also called copper luster, is a mineral that, in addition to copper, contains sulfur and sometimes silver. Such ore is considered rich because it contains up to 79% pure metal.;
- chalcopyrite is a mineral containing copper, iron and sulfur, it is the most common ore in nature, basically all production is carried out on the basis of the development of chalcopyrite (pyrite) deposits;
- cuprite is the mineral ore with the highest metal content, but it is rare in nature, and discovering a deposit is considered a great success.
Since copper mining has been carried out since ancient times, the deposits have become noticeably depleted. If previously the content of copper ore in the soil was considered to be more than 5%, today mines with a content of 0.5% are being actively developed.
Chalcopyrite
This speaks not only about the depletion of the rock, but also about the high technologies of ore processing and the variety of enrichment methods, as a result of which the maximum metal can be extracted from the ore.
The geography of copper deposits is quite extensive; they are present on all continents. According to experts, 5 billion tons can be mined in all currently explored areas. This is a low figure, but it does not at all indicate the disappearance of the metal.
Secondary processing of copper plays an important role. This metal is easy to melt and can be easily separated from various alloys; therefore, the industry of processing copper products is widely developed.
Repeated smelting is carried out with minor losses, and several times less resources (labor, energy, material) are spent than during extraction.
Copper market in Russia and its main players
The domestic history of copper mining dates back to the 17th century - it was at that time that the first copper smelting deposits were built on the territory of the then Russian Empire. However, they did not work even 10 years, and a real rise in the development of copper production occurred only in the 20th century.
In 2022, Russia extracted 1.145 million tons of copper from the ground and produced a little more than 1 million tons of refined copper (with production of the latter exceeding the million mark for the third year in a row).
There are three truly major players in the domestic market. These are the Ural Mining and Metallurgical and Russian Copper Company. There are also independent enterprises, but the volumes of copper they extract amount to thousands and amount to only a few percent of total Russian production.
Main copper deposits in Russia
How it's done: copper mining
In terms of proven reserves of metal in the bowels of Russia, it ranks 7th, while it has only 3% (20 million tons) of the total volume of copper deposits. In terms of production volumes, Russia is also in seventh place, but accounts for 4% of the global volume.
Copper exports from leading copper mining countries
The largest deposits are concentrated in the Taimyr administrative district, among them the following are actively being developed:
- Norilsk-1;
- Oktyabrskoe;
- Talnakhskoe.
There are also active deposits in the Volga and Ural federal districts:
- Uchalinskoe;
- Sibayskoe;
- Gayskoe;
- Yubileinoe was recently discovered and is currently only being prepared for development;
- Podolskoe - has large deposits of copper ore - is mothballed and is in the state reserve.
The Chita region is also rich in copper; one of the largest deposits not only in Russia, but also in the world is located here - the Udokan deposit. About 15 million tons are mined here annually, but it is currently not being developed at full capacity, the reason for this is the lack of infrastructure.
Copper reserves
There are no good transport links, considerable distance from processing and enrichment plants. In the near future, Metalloinvest, the company that owns the right to develop the Udokan deposit, plans to double production volumes.
There is an economic sense in measures to create a comprehensive infrastructure - the Udokan deposit consists mostly of copper sandstones, which have an almost monometallic composition with minor silver impurities, which greatly simplifies the enrichment process.
Depth of various mines in the country
The Talnakh mine is located in the northwestern part of the Siberian Platform. It is also one of the largest deposits in Russia in terms of volumes of copper ore, the peculiarity of which is the constancy of the composition with a predominance of chalcopyrite.
Copper is extracted from ore, iron and copper sulfides
Mining here is carried out underground, the total length of the mines is 12 km, and the greatest width is recorded at 3.5 km. In parallel with copper, nickel is mined at this deposit.
One of the oldest deposits in Russia, which began to be developed industrially, is Degtyarskoye. It is located on the Ural ridge, in industrial development since 1914, although it was explored back in 1888.
Currently, its development has been suspended due to the low metal content in the ore, however, according to estimates, honey-bearing ore has not yet been mined here. But since the development of this mine is carried out underground, and it is quite expensive, the mines are currently not profitable.
The importance of copper in the world
Features of copper
Copper was one of the first metals that human civilization recognized and began to use. Man invented its production before iron.
Copper is the second most consumed non-ferrous metal in the global economy after aluminum.
This metal got its name from the island of Cyprus.
What does it consist of? Its structure contains many crystals: nickel, zinc, molybdenum, gold, calcium, silver, lead, iron, cobalt and many others.
And its high electrical conductivity has made it a particularly valuable electrical material, from which windings of transformers and generators, power line wires, and internal electrical wiring are made.
Reference. Previously, up to half of all copper produced in the world was spent on electrical wires, but today more affordable aluminum serves these purposes. And copper itself is becoming the most scarce non-ferrous metal.
Copper alloys are also widely used - with zinc (brass), with tin or aluminum (bronze), etc.
Production
Copper ores are mined in 50 countries.
Tab. 1. The largest manufacturers in the world according to the results of 2014-2015.
| A country | 2014 | 2015 | ||
| thousand tons | place | thousand tons | place | |
| The whole world | 22 000 | 19021 | ||
| Chile | 5 750 | 1 | 5 764 | 1 |
| China | 1 694 | 2 | 1 659 | 2 |
| Peru | 1 339 | 3 | 1 654 | 3 |
| USA | 1 391 | 4 | 1 408 | 4 |
| Australia | 969 | 5 | 960 | 5 |
| DR Congo | 915 | 7 | 918 | 6 |
| Russia | 740 | 6 | 741 | 7 |
| Zambia | 693 | 8 | 705 | 8 |
| Canada | 694 | 9 | 690 | 9 |
| Indonesia | 379 | 587 | 10 | |
Source: website people.conomy.ru
The main production capacities of copper mining enterprises are concentrated in South America. It is here that 41.2% of the world's copper ore is mined, 19.8% comes from Asian countries.
The situation in the production of refined copper looks different:
Tab. 2. Comparative characteristics of refined copper production volumes by region of the planet, thousand tons
| Copper ore | Refined copper | |
| The whole world | 19021 | 22211 |
| North America | 2656 | 1883 |
| South America | 7841 | 3307 |
| Europe | 1864 | 3764 |
| Asia | 3759 | 11382 |
| Africa | 1893 | 1388 |
| Oceania | 1008 | 487 |
Source: website people.conomy.ru
According to the results for 2015, production of refined copper is concentrated in the Asian region (51.2%). South America, the leader in copper ore production, accounts for 14.9%. Here it is inferior even to Europe.
Rice. 1. Distribution of continental contributions
Almost 80% of all copper was produced from virgin raw materials, the remaining 20% was produced from copper scrap. Global copper production remains highly consolidated – a third of it (34.8%) in 2015 was accounted for by the top five producers, which includes:
- Codelco (Chile).
- Freeport-McMoRan (USA).
- Glencore (Switzerland).
- BHP Billiton (Australia).
- Southern Copper (Mexico).
For reference. In 2014, Wood Mackenzie (Brook Hunt) published a forecast of global copper production for the period up to 2025.
Wood Mackenzie is a global energy, chemicals, renewables, metals and mining research group with an international reputation for providing comprehensive data, written analysis and advice.
In 2015, the company was acquired by American analytics and analytics company Verisk Analytics (en.wikipedia.org). Tab. 3. Forecast data for 2014-2025
| Year | Thousand tons | Year | Thousand tons |
| 2014 | 24 305 | 2020 | 25 928 |
| 2015 | 25 830 | 2021 | 25 643 |
| 2016 | 26 449 | 2022 | 25 553 |
| 2017 | 26 580 | 2023 | 25 317 |
| 2018 | 26 517 | 2024 | 24 945 |
| 2019 | 26 115 | 2025 | 24 713 |
Source: Wood Mackenzie (Brook Hunt)
According to the company, global production in 2016 was 19.9 million tons, and its production reached 22.5 million.
Reserves
According to data for 2014, the territories of North and South America held almost 60% of all world reserves, more than half of which were recorded in Chile. And on a planetary scale, this country accounts for 34% of the deposits of this non-ferrous metal.
Rice. 2. Copper deposits in the world 2014 Source: website mining-prom.ru
The Russian Federation accounted for 5% of the world's proven copper reserves (after Chile, the USA, Peru and Australia, this is 5th place).
According to geologists, about 5 billion tons of copper ore reserves are located at the bottom of the oceans.
How is the copper ore mining process carried out?
Depending on the depth at which the copper ore deposits are located, the mining process can be carried out in different ways: underground and open.
Copper alloys in various mining locations
Underground involves the construction of mines that go deep underground, and their length sometimes reaches several kilometers. The mines are equipped with elevator cages that deliver workers and equipment underground, and also serve as a lifting mechanism for the mined ore to the surface.
Under the ground, the rock is destroyed by special drilling mechanisms, which are equipped with large cone-shaped spikes; they cut into the soil, destroying it. Then, with the help of buckets, the rock is collected and loaded onto vehicles.
To ensure safe operation underground, intermediate stations are created for miners, and above-ground structures are created - towers that ensure the operation of elevators. After the rock is delivered to the surface, it is sent to processing and processing plants.
Location of copper mines in the world
The open-pit mining method is used when deposits are located deep, up to 400 - 500 meters. First, the top layer of waste rock is removed, then the copper ore is excavated. This is a fairly hard layer and explosive devices are used to facilitate the process.
Drilling rigs place explosives at a certain depth; after the explosion, the destroyed rock is loaded using excavators onto dump trucks and removed from the quarry. Not far from the quarry there is an ore processing station, which is delivered here by dump trucks. Further processing of the rock is carried out in a standard manner, which is also used for ore mined underground.
How copper production is carried out
After copper ore is mined, it is delivered to the processing plant, where at the first stage it is crushed, since sometimes the pieces of rock reach one meter. This happens on powerful crushing machines that can process up to 4 thousand tons of rock per hour.
Simplified copper ore processing scheme
The gyratory installation consists of two cones, one of which is fixed, and has wide plates made of high-strength steel. At the exit from the crusher, fine-grained ore is obtained, up to 150 mm, which is then sent along a conveyor to an ore storage facility or production.
Further enrichment of copper includes two more stages of grinding in huge mills, from there it is sent to flotation machines, which have a working bowl volume of up to 300 m3. Here the rock is mixed with water and a special reagent that promotes the formation of pulp - foam to which the metal sticks, and the waste rock settles.
Under the influence of air flow, bubbles with metal particles are blown out of the liquid and sent to the intermediate hopper, where they burst and the metal settles. Then the composition enters thickeners, where it accumulates and thickens to an almost solid substance (up to 65%), after which it is sent for filtration and to a press plant.
At the end of the enrichment cycle, purified ore is obtained, which has a consistency similar to sand. Further, production is carried out at metallurgical plants. From the prepared ore, which still contains a large percentage of sulfur (up to 50%) and other metals: gold, silver, iron, it is necessary to extract copper and precious metals with minimal losses.
For this, a pyrometallurgical method is used, which involves three stages:
Structure of copper wire rod
- melting for matte:
- matte conversion;
- electrolytic refining.
Production begins with the roasting of ore in furnaces, during which part of the sulfur is oxidized, and part is removed with gases. Matte smelting is carried out at temperatures up to 1300°, resulting in two products - an alloy of iron and copper (matte) and slag.
Afterwards, the matte is sent to envelope installations, where the liquid alloy is blown with compressed air, under this influence ferrous oxide is formed, which interacts with the flux and is removed from the composition. The result is blister copper, the composition of which still includes up to 1.5% impurities (mostly precious metals remain); they can be removed by electrolytic refining.
Production is carried out in special baths where cathodes are placed - thin sheets of pure copper, anodes and sulfuric acid, which acts as an electrolyte. When an electric current is applied, copper particles collect at the cathode, and gold and silver particles settle at the bottom, they are called slurry. The output is the purest metal with a minimum amount of impurities - up to 0.05%.