Micrometric bore gauge (shtikhmas) is a measuring device used to measure the cross-section of the internal parts of various parts. The first modern analogue of this tool was invented in the USA in 1867. It is used in machine shops for repairing industrial equipment, in machine-building enterprises and automobile stations.
Description of the tool and its purpose
A bore gauge today is a high-precision tool that is designed to determine the size of holes, grooves and other internal elements of any product. It is distinguished by high reliability and ease of use. It can be used to measure a variety of parts with low mass. This instrument is also called shtikhmas. The word comes from the German language. Translated, shtihmas is a device or instrument that measures the diameters of holes.
The design of the bore gauge, in its classical sense, provides for measurement using two ball tips. This method is called two-contact. There are also three-point models for more accurate measurements that have automatic alignment. The mechanism is also equipped with a special element, thanks to which the measurement line is centered.
The types of instruments depend on the method by which the measurement is made. There are two options: absolute and relative. Based on this data, the types of bore gauges are divided. There are two main ones: indicator and micrometric devices.
A mechanical or digital element may be used to demonstrate measurements. Models with a screen, as a rule, weigh less and are practically not susceptible to mechanical stress. They also have a wider range of functions. Their memory can store the data of all measurements in the required sequence.
Scope of use
The main task of the bore gauge is to calculate the absolute distance between the walls of the cavity. During application, the strokemass touches two points. For uneven edges and complex configurations, manipulations should be performed several times, using different positions.
The market is filled with popular models from the best manufacturers. However, they are all used for the following purposes:
- determining the degree of wear of the structure from the inside;
- in the manufacture of parts with an internal cavity;
- when checking the actual dimensions declared;
- in case of ovality.
The scope of application of the device for interior work is expanded. A review of reviews shows that without this device the following enterprises cannot function normally:
- For car repairs. We are talking not only about passenger cars, but also about specialized vehicles, where it is quite important to understand how great the degree of wear of a particular part is, and how quickly it should be replaced.
- Mechanical engineering. All units are subject to control, especially those that are constantly in a static state, rotating, or are expected to be in constant motion.
- Metalworking, hole drilling, slot milling.
- Certification and testing of all kinds of devices. For this purpose, the best measuring devices are used, which have been certified and approved for use for important purposes.
Indicative bore gauge and its features
An indicator bore gauge is a device that uses a relative measurement technique. It must first be configured to a specific value, and then determine how much the real indicator differs from the specified one. The indicator bore gauge can measure holes from 6 mm. In this case, the device has a minimum error in the range of 0.015–0.025 mm.
The design of the indicator bore gauge is quite simple. It has only two components. The first is a rod with measuring nozzles, the second is a round indicator head with a scale on which two types of divisions are presented:
- The main scale with a step of 0.001 mm displays the relative deviation of the parameter being measured.
- Small scale. It marks the total number of revolutions of the instrument needle (a full revolution is 1 mm). With its help you can find out the size of the hole in millimeters.
The device is equipped with additional attachments, the use of which allows you to measure various parts in an extended range.
Before using the indicator bore gauge, you need to select a replacement element that will fit in length and attach it to the device. The tool is then inserted at an angle into the hole being measured. Next, light rocking is carried out to set it strictly perpendicular to the axis of the hole.
After completing these steps, the arrow will begin to oscillate. If its stroke is directed to the left, then the diameter of the hole is larger than the established one, if to the right, then it is smaller. To make the calculations, you will need some data. For example, if, when using a 10 mm interchangeable nozzle, the pointer moves 12 divisions to the right, then the final size will be calculated as 10−0.12 = 9.88 mm. When deviating in the other direction, the sign in the example changes to positive.
To ensure that all measurements are carried out correctly, the device should be held only by the special handle. You cannot touch the rod itself, since minimal heating will cause the metal to lengthen by several hundredths. This will give a significant error and lead to erroneous calculations.
Measurement technology
Now let's talk in more detail about how to use this tool. The accuracy of the calculations directly depends on the accuracy of the execution.
Checking the MH type bore gauge
Confirmation of technical characteristics should be carried out:
- during commissioning;
- regularly when used;
- after long-term storage.
The regulatory document responsible for this procedure is GOST 17215-71. According to him, you need to act in stages:
- Evaluate the appearance, markings and completeness of the package.
- Test the parts for their compatibility.
- Using an instrumental microscope, estimate the division value on the scale.
- Check the radius of curvature of the tip and head.
- Using a horizontal optimeter, measure the error.
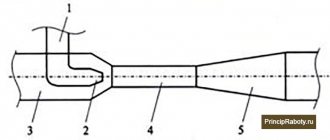
Let's look at the bore gauge in the picture:
How to set up a micrometer and use it
It is necessary to take a setting measure. Using it, set the parameters to zero. To do this, place the head in the hole and turn the drum to the zero mark.
Now you can additionally install extension cords and begin measuring. Insert the tip into the space to be measured (one part is already touching the wall) and rotate the handle until it stops. You can find the most distant points by shaking the device. Record the results.
Checking indicator bore gauges
The stages of external inspection and testing of NI and IM are no different. However, for more precise instructions, please refer to the regulatory document MI 2194-92. These are guidelines that differ for devices with different division values.
How to set up and use the device
The algorithm is the same:
- calibration;
- placing the head inside the hole;
- extending the rods all the way.
The only thing that changes is how to interpret the result. If the arrow goes to the left, then the size is smaller than the reference by the indicated number of divisions. To the right means more.
How to use a micrometer bore gauge
For more accurate checking and measurements, a micrometric gauge is used - what it is was described above. This device shows real size values. The measurement error is very small and amounts to only 0.006 mm. To understand how to use a bore gauge correctly, you need to understand its features.
The micrometric bore gauge consists of the following elements:
- drum with scale;
- head for connecting the drum with extensions and removable nozzles;
- fixing screw;
- extension;
- tip - element for taking measurements.
A micrometric bore gauge is not used to measure the diameter of cylinders. With its help, only internal dimensions are determined. There are several ranges that it can measure (in millimeters):
- 50–75;
- 75–175;
- 75–600;
- 150–1250;
- 860–2500;
- 1520–4000.
The design of this device is similar to a micrometer. It also has a screw and a drum, rigidly connected to each other using a special cap. There is also a spherical tip rod, a safety cap and a locking stopper.
To figure out how to use a bore gauge, you need to know the rules for installing it. The measuring device is installed strictly perpendicular to the axis of the hole. One end of the measuring rod should rest on the edge of the hole, and the other should be moved all the way to the opposite surface. This installation principle is similar for all types of bore gauges.
Characteristics and purpose of the nunometer
Currently, bore gauges look like tubular rods with a rounded tip. It is with the help of the tip that the instrument is able to measure places that are inaccessible to simple measuring instruments.
In this case, the measurement accuracy error is not reduced. The principle of operation of the bore gauge is that the rod is in a movable state. When immersed in the hole being measured, it transmits data to the reading device.
Mechanisms for transmitting readings vary depending on the type of instruments used. Consider a typical micrometer sample.
It includes the following elements:
- Screw.
- Connecting cap.
- Drum mechanism.
- Protective cap.
- Spherical type rod.
- Locking mechanism.
- Set of extension cords.
The structure of other types of devices may be different. All products are manufactured in accordance with GOST standards.
Like any other device, a bore gauge has its pros and cons. The main advantage is the penetrating ability, with which it is possible to make accurate measurements.
There aren’t too many downsides either – here they are:
- Replacing nozzles if the dimensions of the groove being measured change;
- The need to carefully handle the instrument.
How to set up a bore gauge
Setting up a bore gauge is impossible without understanding its operating principle. You should know that it is identical to the operating principle of a micrometer, which allows you to compare the indicators obtained on the two devices. If the micrometer has an error within acceptable limits, then you need to follow the following procedure to set up the bore gauge:
- Select a base rod. It can be of any length and must be mounted on a measuring rod.
- The micrometer is set to the same value as the rod.
- The locking screw must be tightened to secure the value.
- The rod sleeve should be fixed in a vice, and its main part should be placed between the measuring jaws.
- The arrow must be aligned with the zero on the dial by rotating the caliper head.
In this way, you can calibrate the value of the device and adjust it to the data necessary for operation and accurate measurement. This will make it possible to measure with an accuracy of a hundredth of a millimeter. Setting up a bore gauge is a very important process that will affect the quality of work in the future. The same algorithm is used to carry out annual verification of the device.
Preparing for work
Before starting measurements, check that the micrometer head is correctly set to zero according to the installation standard.
The adjustment must be carried out at an ambient temperature within 20 ± 5 ° C. Insert the micrometer head between the measuring jaws of the setting standard, and press the tip rod against one of them. By rocking the top of the micrometer head and rotating the drum, determine the shortest distance. The measuring surfaces of the bore gauge should touch the working surfaces of the gauge with slight friction.
Secure the microscrew with the locking screw and remove the head. The zero division of the drum must exactly coincide with the longitudinal stroke of the stem.
After setting the head to zero, unscrew the tip from the coupling, select the appropriate extensions and connect them to the micrometer head. Screw the tip back in.
How to store the tool after use
Proper storage and operation of the device is necessary to ensure its operation and reliability of use. Since the purpose of the instrument is to make accurate measurements, it is necessary to maintain its integrity and avoid major mechanical influences that could affect the calibration. Failure to follow these rules can cause a lot of inconvenience later.
An important step when using the unit is verification. The interval of such examination is one year. During this period, the mechanism may lose its integrity or the strength of the fixing screw, and the accuracy of the readings largely depends on these factors.
The verification procedure includes a number of necessary and extremely important actions. They must be carried out in compliance with all standards, as well as the correct installation of equipment.
The purpose of the bore gauge is to provide accurate data on the internal diameter of the product being measured. In order for these indicators to continue to correspond to reality, it is important to store the instrument correctly. The storage procedure is carried out in compliance with a number of rules:
- the air temperature in the room should be in the range from 15 to 25 degrees;
- the humidity level should not exceed 80%;
- Before you start measuring something with a bore gauge, the needle on the scale must be set to zero.
Proper storage will help keep the tool tuned for a long time in order to carry out work without a high level of error. Also, such measures will allow the device to always be ready for operation, since the harmful influence of various factors is excluded.
Setting the bore gauge using a micrometer
First of all, the accuracy of the micrometer is checked using a gauge block. If the error is within acceptable limits, then you must act according to the following plan:
- a replacement rod is selected (for example, 10 mm long) and installed on the measuring rod of the bore gauge;
- the micrometer is also set to 10 mm, after which the locking screw is tightened;
- The bore gauge is fixed in a vice through a wooden sleeve on the stem. This ensures his immobility;
- the bore gauge rod is placed between the measuring jaws of the micrometer;
- the deviated hand is aligned with the pointer on the dial by rotating the indicator head.
To measure the diameter of a cylinder, the device is placed inside the hole so that its rod is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the product. The desired position is achieved with light rocking.
If the arrow deviates to the left from zero, then the diameter of the hole being examined is larger than the size of the sample. If to the right, then less.
We take readings: the arrow has deviated to the left by 15 divisions. Let's do the calculation: multiply 15 by the price of one division (0.01 mm) and get 0.15 mm.
Knowing the diameter of the sample (10 mm), we make the final calculation: 10 + 0.15 = 10.15 mm.
When taking readings, it is worth considering that the indicator has two scales:
- large – hundredths of mm;
- small - millimeters.
To measure large holes, additional extension rods are used, included with the bore gauge. More detailed information on how to use the device can be found in the operating instructions.
Assembling and disassembling the tool
To prepare the bore gauge for work, you need to perform certain steps in this order:
- Attach the meter to the fixture rod.
- Screw in the extension rod for final assembly.
This procedure for preparing the device for operation is basic and must be strictly followed. Disassembly is carried out strictly in the reverse order to eliminate the possibility of calibration violation. First you need to unscrew the rod so that the meter becomes independent of further actions, then remove the indicator itself.
If you do not plan to use the device further, you must do the following before storing it:
- First of all, the device must be wiped dry. This should be done as carefully as possible using a soft, lint-free rag.
- After this, all elements of the meter, except the dial scale, must be wiped with aviation gasoline or another substance suitable for this case.
- Packaging is carried out in a special case, which closes securely and eliminates the possibility of movement of parts inside.
Such care will help avoid corrosion on metal elements, eliminate the possibility of damage, and also fully preserve the functionality and configuration of the instrument.
If there is any doubt about the integrity or correct operation of the device, the following procedure must be followed:
- inspect the tool for markings and all components;
- check all elements for correct connection;
- all distances must fully comply with the standards;
- product error indicators must be within acceptable values;
- The device should not have any dents, chips, scratches or other damage that appears during improper use or storage.
Such an inspection will help eliminate incorrect operation and errors in measurements. Incorrect measurements can have fatal consequences in the production of precision machine parts.
What types of devices are there?
All popular models produced differ in functionality, characteristics, material of manufacture, area of use, weight, length, width and other parameters. However, all manufactured products are divided into two main groups:
| Kinds | Description |
| Bore indicator gauges (NI) | The relative method for determining internal parameters is used. In some models, the amount of movement of the movable measuring rod is transmitted to the reporting device through a wedge transmission. There are devices with lever transmission. Used for repairing power plants. Allows you to make control measurements of cylinder diameters. |
| Digital indicator bore gauges (SIC) | A distinctive feature is the presence of an electronic indicator and a digital display for easy reading of indicators. The relative method of measuring internal holes is used. You can set zero at any point, define any measuring system (inches or millimeters). |
It is worth noting that all manufactured equipment from domestic and foreign manufacturers can be manual or stationary.
High precision bore gauges (NI-B) can be found on sale. They are equipped with a measuring head with a reading accuracy of 1 micron. The devices are designed for high-precision measurements of internal grooves using the relative method. The upper limit of measurements is up to 450 mm. You can order products with verification and calibration.
Products are classified according to the shape of the measuring surfaces, and therefore the following designs are distinguished:
- conical;
- lever;
- telescopic;
- ball;
- wedge;
- with side jaws.
To measure micro-holes, it is worth purchasing a collet product. The set consists of a variety of interchangeable heads, which are installed depending on the task assigned to the device.
Maintenance and operation
In order for the device to serve its intended duration - at least 4-5 years - it must be used correctly; Moreover, it needs to be inspected regularly. The set of measures depends on the type of instrument.
Micrometric models deserve close attention - they are verified to ensure compliance with the requirements of GOST 17215-71. This interstate standard sets standards for such parameters as:
- labeling, equipment, appearance;
- drum and rod strokes;
- head radius and error;
- distance from stem to end;
- general tool tolerances, including extensions;
- rigidity (for models whose operating limit exceeds 1250 mm);
- measure parameters at contact points;
- runout in the touch zone;
- the nature of the interaction of all structural elements.
Above, we described how to properly set up a micrometer-type bore gauge, but we did not say what to avoid. For long-term and trouble-free operation, you should avoid over-tightening the extension cords. To prevent the sample from losing its reference parameters, there is no need to unscrew the screws from it or wastefully remove the rods. In the process of directly performing tasks, the tool should be held on those surfaces that do not overheat, and in places of least deflection.
It is also important to periodically inspect indicator models - verification is carried out for compliance with MI 2193-92 and 2194-92. These methods imply:
- thorough external examination;
- conducting trial tests;
- and determination of specific metrological and technical characteristics.
You should know not only how to measure a hole with a bore gauge, but also how to disassemble it. Because all components of the device must be stored separately. There is nothing complicated in this question: first you need to unscrew the rod, then separate the indicator from the rod. Each element, except the dial, must be lubricated and wiped with gasoline (preferably aviation gasoline), and then placed in a packaging box and sent to a dark place with a temperature of +15...25 degrees Celsius.
Rating of products priced up to 90,000 rubles
NI electronic 160-250 0.001 MIC Micro
The products belong to the inexpensive category. Has an increased accuracy rate. Allows you to determine the internal diameter of products using the relative method. First class. You can't help but pay attention to the electronic indicator. It allows you to display the received information on an electronic display. Data tracking is easy and convenient. For additional protection of the housing, a heat-insulating sleeve is used.
There are replaceable nozzles, which allows you to make a measurement range of 160 - 250 divisions. The manufacturer equipped his creation with a centering bridge to make it possible to align the measurement lines with the axial plane of the holes. Device parameters – 215*125*40 mm. Weight – 394 g. Material of manufacture – tool steel. The step size on the scale is 0.001. Device type – electronic. The manufacturer provides a 1-year warranty on its product. The product is sold in a convenient and practical case for storage and transportation.
The sellers are asking 57,650 rubles for the products.
NI electronic 160-250 0.001 MIC Micro
Advantages:
- reliability;
- low error rate;
- practicality;
- functionality;
- ease of use;
- compactness;
- can be ordered in the company’s online store.
Flaws:
- not found.
0.01 CHIZ NM 50-600 134435
Convenient mechanical device with an expanded scope of operation. It is in high demand due to its strength, reliability, and value for money. It goes on sale in a special case, which makes the process of transporting and storing the device convenient and safe. High precision device. During the measurement process, a minimum error is maintained. Used in the construction and industrial sectors. Allows you to measure internal holes in small and large parts. Measurement range – from 50 to 600 mm. Accuracy class - first. The step size is 0.01 mm. The error is at the level of 20 microns. Design parameters – 500*200*50 mm. Weight – 1 kg. The surface is smooth. Color – metallic. Manufacturer's warranty – for 1 year.
The purchase price is 35,348 rubles.
0.01 CHIZ NM 50-600 134435
Advantages:
- minimum error;
- practicality;
- ease of use;
- long service life;
- versatility.
Flaws:
- none.
NM 50-175 0.01 SHAN 136305
The micrometer type bore gauge is very popular due to its ease of use and reliability. The scope of application is expanded. Allows you to determine the internal size of products. It is supplied for sale in a practical and durable case, which makes it possible to store it and transport it to its destination. The set contains extension cords that allow you to expand the functionality of the device. First class. Error – 6 microns. The manufacturer provides a guarantee for its creation for a year.
The average cost is 21,220 rubles.
NM 50-175 0.01 SHAN 136305
Advantages:
- convenient case included;
- wear resistance;
- practicality;
- functionality;
- value for money;
- small measurement error.
Flaws:
- not identified.
GTO NI 18-50 0.001 DBGHP 185001
An indicator device with a division value of 0.001 mm. Purchased for the purpose of carrying out high-precision measurements of internal grooves of parts. There is a two-point contact with the surface under study. The manufacturer has equipped its products with an hour indicator. There is also a centering bridge. Works with structural elements, car parts, machine components. Error – 3.5 microns. Accuracy class - first. Manufacturer's warranty – 1 year.
Purchase price – 13,750 rubles.
GTO NI 18-50 0.001 DBGHP 185001
Advantages:
- low error rate;
- practicality;
- advanced functionality;
- value for money;
- positive reviews.
Flaws:
- not installed.
6-10 mm, 0.01 mm, CHIZ NI 43154
An indicator-type bore gauge is considered a practical and easy-to-use tool. Designed to measure the internal cavities of parts with extreme accuracy. Often found in car service centers and manufacturing plants. The range is insignificant, but the error is minimal and amounts to 0.008 mm. Dimensions – 100*100*600 mm, weight – 3 kg.
The average price is 13,567 rubles.
6-10 mm, 0.01 mm, CHIZ NI 43154
Advantages:
- ease of use;
- wide scope of application;
- practicality;
- minor error;
- acceptable price.
Flaws:
- not found.
NI 18-50 0.01 1 class. accuracy Calibron 71866
The design is intended for precise measurement of internal cavities of parts. The measuring principle is two-point contact. The method used is relative. First class. The holes have a centering bridge. The set contains replaceable rods with which measurements are taken. Measurement range – 18-50 mm. Error – 12 microns. Device type – indicator.
The sellers are asking 13,493 rubles for the products.
NI 18-50 0.01 1 class. accuracy Calibron 71866
Advantages:
- ease of use;
- practicality;
- strength;
- wear resistance;
- long service life.
Flaws:
- not installed.