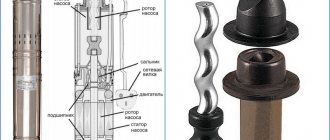
A vane pump is better known as a vane pump, since its working parts have the form of flat or shaped plates - vanes. In 1899, US scientist Robert Blackmer developed the design of a rotary pump with gate valves. It was this device that was the prototype of modern sliding vane pumps with a displaced center of rotation.
In the USSR, such a pump was patented by a group of scientists from the Tatar State Research Institute of Oil Industry in 1974. And in May 2016, Russian inventor Boris Grigoriev filed a patent in 29 countries for an improved design of the internal element of a vane pump. In the new device, the Russian engineer managed to increase the volumetric, hydraulic and mechanical efficiency of the vane pump.
Operating principle of a vane pump
The increased outlet pressure is created by the “vortex effect”. That is, the displacement of the rotor rotation axis relative to the housing axis allows the plates to extend in a place of greater clearance and be pressed against the stator by centrifugal force.
When the pump starts, a vacuum forms in the suction port. The transported mass is sucked into the space between the plates and pushed out through the outlet pipe.
Pumps with a variable displacement axis are used to adjust the volume of pumped liquid.
Material execution
The main components of vane pumps can be made from a wide variety of materials to provide the required corrosion, abrasion and temperature resistance. The following main materials can be distinguished:
| Pump flow part: | Rotors and tappets | Plates |
| Gray cast iron | Carbon graphite | Carbon graphite |
| Ductile iron | PEEK (polyetheretherketone) | |
| Carbon steel | NBR (flexible rotor pumps) | |
| · Stainless steel | EPDM (flexible rotor pumps) |
Advantages
- Compared to screw or gear pumps, the efficiency of vane pumps is much higher.
- The most simplified design is strong and durable. The strength of the mechanism reduces the likelihood of malfunctions to a minimum.
- Vane pumps allow you to pump abrasive and crystallizing liquids: with soft inclusions up to 1 cm, with hard inclusions no more than 500 microns.
- Easy replacement of plates in case of breakdown. Repairing a vane pump does not require the involvement of professional repairmen, which significantly saves money.
- The pump body (sleeve, glass) and plates (blades) are selected for the pumped substance.
- To create a vacuum, a “dry” start is possible.
- Some models provide a reverse mode, which significantly expands the scope of application of vane pumps and makes it possible for production to be multidisciplinary.
- The almost silent operation of the compact equipment does not cause inconvenience to workers. The vibration of vane pumps relative to other devices is approximately 50% lower.
- Economical energy consumption reduces material maintenance costs by approximately 20-30%. As a result, the cost of transported products is reduced.
- Can be used as a dispenser.
- The design of vane pumps allows for the manufacture of working parts from different materials to obtain a certain resistance to chemicals, eliminate sparking, increase wear resistance, use in the food industry, and so on.
It is not recommended to use the vane pump dry for long periods of time. The performance of the device is increased by the electric heating function, a special heat exchange jacket, and Teflon O-rings.
Double or double acting vane hydraulic machines
The main feature of a double-acting vane pump is that its stator is oval in cross section. Moving along the inner surface of such a stator, each rotor gate performs two strokes per shaft revolution. A double-acting vane pump operates according to the following algorithm.
- Temporary working chambers (the transported medium is pumped into them and then displaced into the discharge line) are formed by such elements as the outer surface of the rotor, the oval inner surface of the stator, two adjacent plates and side disks. In this case, temporary working chambers of the smallest volume are created in that place of the internal cavity of the vane pump where the gap between the rotor and the stationary part of the engine is minimal.
- The high tightness of the temporary working chambers is ensured due to the fact that the plates, sliding their end part along the inner surface of the stator, are tightly pressed against it.
- After the plates pass the area with a minimum gap between the rotor and stator, the volume of the temporary working chamber increases. This leads to the fact that the pressure in it sharply decreases, which means that an area of rarefaction of air is created. When passing the section of the inner surface of the stator, where the side disk is located, the slots in which are connected to the suction line, the temporary chamber is filled with the pumped medium.
- When the temporary working chamber, already filled with the pumped liquid, passes the next section with a minimum gap between the rotor and stator, the pressure of the working medium increases in it, which helps to displace the latter into the slot of the second side disk connected to the discharge line.
- Thus, due to the oval shape of the stator cross-section, the entire process described above occurs twice during one revolution of the rotor shaft.
Operating principle of double acting vane pump
The force of pressing the end part of the working plates against the inner surface of the stator as they slide along it is influenced by the pressure of the pumped liquid exerted on the rear surface of such elements. The force with which the plates are pressed against the inner surface of the stator during sliding can be calculated by multiplying the pressure of the fluid acting on the rear surface of such elements by the area of their end part. When pumping liquids with poor lubricating properties under a certain pressure, situations may arise when a thin film of the working medium does not form between the end surface of the plates and the inner walls of the stator. Operation of a vane-type pump under such conditions contributes to intensive wear of its working elements.
If a vane pump is planned to be used for pumping liquid that enters the suction pipe under a pressure exceeding 150 bar, then to solve such problems, select models of pumping devices, the design of which is equipped with double plates. In such cases, the pumped liquid is supplied through an opening in the rear end of the vane pump and enters the space between the paired plates, which allows one to compensate for too much liquid pressure exerted on the working blades.
Application
Vane type pumps are actively used in large and small industries that involve transporting products with a liquid or viscous texture. The popularity of these devices is due to the possibility of completely preserving the working mass: the plate mechanism eliminates the occurrence of losses. The use of vane-type pumps significantly increases the volume of production or processing of suspensions and viscous masses, while being the safest process for operating personnel.
The self-priming effect of vane pumps has found wide application in the chemical, pharmaceutical and oil refining industries, cosmetology and food production.
Materials used in the production of pumping equipment
The body of the vane pump, as well as the main elements of its flow part, are made of gray or ductile cast iron, as well as carbon or stainless steel alloys. The pusher and rotor in a vane pump can be made from:
- polyetheretherketone;
- carbon graphite;
- NBR;
- EPDM.
The equipment model is selected taking into account the requirements for its temperature, abrasive and corrosion resistance. The shaft seal of pumping equipment can be cartridge or end-type. It is also possible to equip the shaft with a magnetic coupling.
Use of vane pumping systems
Vane pumps are used to pump various products:
- Crude oil, bitumen, fuel oil, paraffin, oil sludge, grease and mineral oils.
- Glue, varnishes, putties, paints, latex emulsions, epoxy resins and mastics.
- Acids, solvents, black lye, liquid glass, creosote, caustic soda, caustic soda.
- Grease, glycerin, emulsifiers, liquid soap, ink.
- Honey, mayonnaise, molasses, chocolate, condensed milk, vegetable oil, ketchup, syrups.
And many other liquid and viscous masses.
In the automotive industry, these pumps are used for power steering, boost, afterburning air, large truck power brakes, and automatic transmissions. In diesel passenger cars, the intake vacuum of engines is created by a vane pump.
In household appliances, a similar device saturates soda with carbon dioxide and is used in coffee machines.
In most light aircraft, the gyroscopic devices are driven by this type of pump.
Adjustable type hydraulic machines
In variable-type vane pumps, the position of the stator ring can be changed. Adjustment of the spatial position of the stator relative to the rotor rotating inside it, for which there are three screws in the pump design, is carried out as follows.
- Using the feed limit screw, you can change the eccentric path along which the rotor moves. Thanks to this, the flow level of the vane pump is regulated.
- Using the support position adjustment screw, you can change the spatial position of the stator in the vertical plane. The dynamic characteristics of the pump and the noise level it produces during operation depend on this parameter.
- The maximum pressure adjustment screw allows you to control this parameter by changing the degree of compression of a special spring.
Design of a vane pump with adjustable displacement
The operating principle of a variable-type vane (vane) pump is as follows.
- The pressure of the pumped medium, depending on the value of the fluid resistance in the hydraulic system, acts on the inner walls of the stator, and through them on the adjusting spring. As long as the value of this pressure is less than the resistance force of the spring, the stator ring is in eccentricity with respect to the rotor.
- As the pressure of the working medium increases in the hydraulic system, the degree of its influence on the walls of the stationary part of the engine and the adjusting spring also increases.
- At the moment when the fluid pressure exceeds the counter pressure of the spring, the stator ring will begin to move from eccentricity to a concentric position. In this case, the volume of the temporary working chambers of the vane pump decreases, and, accordingly, the pressure of the liquid that it supplies to the discharge line decreases. As the pressure of the liquid entering the suction pipe increases further, the pressure of the working medium in the discharge line may approach zero (zero stroke of the pump). However, even in this situation, the pump will supply the pumped liquid to the discharge line, the volume of which will be equal to the amount of internal leaks of the device. The amount of fluid pressure in the supply line at which the above-described situation becomes possible is changed by the degree of compression of the control spring.
Operating principle of the pressure regulator
Variable vane pumps with a zero stroke option include a drainage system. Through it, all internal leaks are removed from the high pressure zone of the working chamber of the device. The presence of such a system in the design of a vane pump makes it possible to effectively remove heat from the rubbing elements of the device and also ensure their lubrication.
Fire vane pump device
To improve the technical and operational characteristics of centrifugal pumps, vane pumps are installed in the vacuum systems of fire trucks. Their autonomous operation does not interfere with the design of the vehicle's exhaust system and can be either manually or electrically driven. Devices made from corrosion-resistant materials operate more reliably. Since the working process does not exclude water from entering the cavity, the gates can jam due to the accumulation of rust in the rotor grooves. It is also necessary to carefully monitor the oil lubrication of the rubbing elements, since the oil used during operation is gradually thrown out, mixing with water.
The vacuum plate unit creates the vacuum necessary when filling with water in the suction hoses and cavity of the fire pump, creating a pressure of 16-18 MPa.
Single acting devices
The cross-section of the rotor of vane pumps operating on the single-acting principle is cylindrical. The change in the volume of the temporary working chamber (this is a necessary condition for the effective operation of vane-type pumping equipment) is ensured due to the fact that the rotor, relative to the stationary part of the engine, performs rotational movements along an eccentric trajectory.
The operating principle of single- and double-acting vane pumps, despite the differences in their design, is the same.
Operating principle of a single type vane pump
Hand pump
Manual vane pumps are used to pump small volumes of liquid from one container to another. Most often, manual devices are used to provide drinking or technical water in country houses. A hand pump helps pump water from a well or reservoir using mechanical force for various reasons:
- In the absence of electrical wiring to the water intake point, and, therefore, there is no possibility of using an electric pump.
- A small amount of water is needed and not continuously.
The advantages of hand pumps include their long service life, low cost, independence from the availability of electricity, simple installation and maintenance, and the ability to be used anywhere. However, their use does not provide a constant supply of water and requires physical effort.
Features of repair and replacement of elements
It's no secret that any technology sooner or later begins to fail. At the same time, the breakdown is not always some kind of major malfunction, and repairs can be done with your own hands. In any case, to repair a vane pump you need to have at least a little knowledge of mechanics and repair work.
Pump parts should only be purchased from trusted stores.
Types of repair work:
- Rotor failure. If the rotor wears out for one reason or another, experts recommend repairing it rather than replacing it. Replacing one rotor with another is much more difficult and expensive than repairing it. As a repair, it is necessary to restore the grooves so that their walls become parallel again, the necks and ends must be ground.
- Blades can also wear out from intense work over a long period of time. In this case, they are simply replaced with others. In this case, new blades can be made from a different, more durable material.
- Shakey. If the rotor journals are worn out, they are repaired by chrome plating or grinding.
As a rule, the journals of a rotary pump are repaired together with the ends, which must also be properly ground. Repair work on setting up gate-type equipment is quite labor-intensive and requires a lot of time and at least minimal knowledge in this area. And yet, despite this, minor defects and breakdowns are best corrected through repairs. For example, replace worn bearings or strengthen the oil seal.
In some cases, it is best to seek help from specialists, and in case of major breakdowns, replace the pump parts with new, more stable ones, or purchase a new device.
Design and use of hand pumps
Vane hand pumps are a low-power design consisting of a long pipe with a rotary vane pump mounted on it. Water or other liquid is sucked from a source (barrel, tank or well) by rotating the pump handle and transferred to the consumer through a tap. The mobile vane pump is easy to install and move to a new location. To use it, you only need a hose.
A manual vane pump can also be used to pump various liquids from barrels, for example, motor and transmission oils, diesel fuel and others, to refuel equipment or pour oil into cans.
Design features of vane pumps
The key working body of a vane pump is considered to be a rotor equipped with specific channels, inside of which there are plates (hence the name of the pump - vane). The rotor of the working body is connected to a shaft connected to the engine. In addition to the plates and rotor, the equipment design contains:
- sealing system for the electric motor shaft;
- discharge pipe;
- suction pipe (located on the outside of the working chamber).
How to choose a hand pump?
When choosing a hand pump, you should understand that such a device can pump about 30-40 liters of liquid per minute. It is indispensable in remote places where it is not possible to use automatic pumps. A vane pump is useful for periodically watering vegetable beds in the country. But it is not suitable for long-term use, for example when lifting large amounts of water from a deep well. When purchasing a hand pump, you should pay attention to its appearance: there should be no cracks, chips, or poor-quality seams on the body. A more expensive pump made from time-tested cast iron will last longer. Models made of stainless steel and plastic are popular. The rubber valves will wear out faster. And brass or bronze ones will last many times longer. Piston rings can also be made of cast iron or leather and rubber, which affects the life of the pump and its price.
Thus, the choice of a hand pump is based, first of all, on the expected volume of water consumption or pumped liquid and the feasibility of its use. And also on its other characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages of external gear pumps
Advantages:
- Pumping low-viscosity liquids at fairly high pressures
- Plate wear compensation
- Possibility of pumping solvents
- Ability to work “dry” for short periods of time
- Only one shaft seal
- Ability to create a good vacuum to absorb liquid
Flaws:
- Hard to maintain. Lots of spare parts
- Cannot work at high pressure
- Cannot handle high viscosity liquids
- Not very good resistance to abrasive liquids
Oil-free rotary vane pumps
To create a vacuum in which there are no various foreign impurities and vapors, oil-free rotary vane vacuum pumps are used. There is also no need to constantly monitor the oil level in the pump, which simplifies its maintenance. The plates for such pumps are made of materials that can operate without lubrication, for example, graphite. The housing of vacuum oil-free rotary vane pumps is made of metal, so the graphite blades glide over the surface with a minimum coefficient of friction.
Significant wear of the graphite plates reduces the performance of vacuum pumps. In this case, the pump does not fail; replacing the plates will restore performance.
The disadvantages of oil-free rotary vane pumps include a much shorter service life of the vanes. Typically, service life does not exceed 10,000 hours even from the most reliable manufacturers, while metal vanes (used in oil-based rotary vane pumps) last 50,000 hours or more.
Rotary vane pumps are not intended to create deep vacuum; they are mainly used to quickly create medium vacuum. In addition, they are used as fore-vacuum pumps, providing the necessary degree of vacuum before turning on high vacuum pumps. As the plates wear, graphite powder is formed, which over time covers the internal surfaces of the outlet pipes. In addition, at the points of contact of the plates, the housing wears out faster than with oil analogues.
Photo of CNV single stage oil free pump:
Rotary vane pump 2NVR 5DM
The manufacturer of the two-stage monoblock pump 2NVR 5 DM is Vakuummash LLC. The electric motor installed at the factory has reliable protection against overheating, which prevents its premature failure. Oil rotary vane pumps 2NVR 5 DM are used for pumping gases, steam-gas mixtures, vapors from sealed containers, the volume of which does not exceed 3.5 m3. The pumped-out medium must not contain flammable or explosive mixtures of gases or aggressive chemicals. For normal operation of the pump, VM-6 or VM-1S oil in a volume of 1.2 liters can be used. Depending on the oil used, the maximum residual pressure can be from 1x10-5 (VM-1S) to 1.3x10-5 (VM-6) kPa. Since the pump is sensitive to abrasive particles, a mechanical filter is usually installed at its inlet. In cases where the presence of abrasive particles is excluded, the 2NVR 5 DM vacuum rotary vane pump can be operated without a filter.
Appearance of the vacuum rotary vane pump 2NVR5 DM: