Protect your eyes | 02/23/2016
Welding, as a type of joining metal elements, became widespread a little more than a century ago. However, today it is used in many fields of activity, from electronics production to the construction of giant structures. Since the composition of the metals used is very diverse, many types of equipment have been invented and implemented to obtain reliable welds. The most popular among them are welding machines. Let's look at what types of welding machines there are, the pros and cons of each.
Transformers
The transformer is the most traditional type of electric welding machine. At the same time, it is one of the simplest in design. The main design element of this type of welder is a step-down transformer, which converts the mains voltage to the value required for welding. The current strength is changed using different techniques, the most well-known is the displacement of one winding relative to the second. As the gap between the windings changes, the current changes.
A feature of welding transformers is considered to be alternating current at the output, which leads to noticeable spattering of metal and deterioration in the quality of seams. In order to weld non-ferrous metals and improve the quality of arc combustion, fairly massive and bulky components must be added to the structure of the apparatus. The main element - the transformer - is also not compact and light in weight. When using the device for serious work, specific (for alternating current) electrodes and considerable experience of the welder are required.
The efficiency of the device is quite high, reaching 90%, but part of the energy is spent on heating. Cooling is carried out using fans of different power, since it is necessary to cool a unit weighing several tens and sometimes hundreds of kilograms. The use of this type of welding machines is declining today, but they are still in demand due to their low cost, reliability and durability. Transformers are used for welding low-alloy types of steel .
Types of electricity
Most teachers who provide students with information about electricity talk primarily about direct current (DC).
It is a stream of electrons that follow each other at a certain distance. The most popular analogy from experienced teachers is the comparison of a stream with ants walking in a column and carrying ordinary dry leaves. This idea is quite general, but the basic idea is correct. The circuit resembles a continuous electrical loop that powers a regular flashlight. However, electricity works differently in larger appliances. Wall-mounted outlets provide an alternating current (AC) power source to appliances. In it, electricity switches at a high speed of 50-60 times per second, that is, the frequency of such switchings is 50-60 Hz.
It is not entirely clear to an ordinary person who does not have knowledge in the field of electronics how such a current powers devices if it constantly changes the direction of its movement. However, the answer to this question is simple. For example, you can take a regular wall lamp that runs on AC power. When you plug it into a power outlet, the electrons begin to actively move, change places and change the direction of movement. The whole process happens very quickly, so heat is generated in the wires.
It is this heat that will pass into the lamp, causing it to glow. Alternating current powers devices just as efficiently as direct current, but the electrons in it move in place.
Rectifiers
Welding rectifiers can be considered an improvement on transformer devices. In welds obtained using rectifiers, those defects that are caused by the use of alternating current are practically eliminated. The devices, in addition to the step-down transformer, have a diode block (rectifier), control, starting and protection elements in their design. Alternating current not only changes voltage, but is also converted to direct current. This makes it possible to obtain an even, stable arc. Accordingly, metal spattering is reduced, and the seam is of higher quality. You can work with any electrodes.
The scope of use of the welder is also expanding - you can join not only low-alloy “ferrous” steels, but also non-ferrous metals, stainless steel, cast iron (using appropriate electrodes). Since direct current has polarity, you should not forget about this - when connecting the electrodes, this parameter should be taken into account. Some welding work is purposefully performed with reverse polarity (aluminium welding).
Many manufacturers today are reducing the production of this type of household appliances. If we talk about professional use, they are still used quite widely . Disadvantages include heavy weight, the need for a qualified welder, and a serious voltage drop in the electrical network during the welding process. Advantages: low price, reliability and good seam quality.
How to choose?
Stationary, portable and mobile welding units are selected based on the operating conditions and purposes. The range of devices on the market is very extensive. Experts recommend giving preference to brands from Europe, the USA, Russia and China. You should trust well-known and experienced manufacturers with a good reputation, who honestly indicate its real parameters in the equipment passport.
Before making a purchasing decision, it is important to provide detailed answers to the following questions:
- For what operating conditions is the equipment purchased?
- What are the volumes and quantity of the proposed work?
- What metals do you need the machine to process?
- How important are the parameters of weight, mobility and ergonomics of a tool?
If the device is needed for professional work with different metals and in different conditions, you should give preference to a universal welding unit with a wide range of characteristics. For domestic purposes, there is no point in buying expensive and powerful equipment. An economical AC installation can handle this task quite well.
For operation in cold climates, it is better to purchase equipment with a gasoline engine, since it is easier to start at low temperatures. It is also worth considering that diesel units are safer and more economical, which is important for facilities where the use of flammable substances is possible. When choosing any model, you should definitely pay attention to the availability of components, warranty and service.
Semi-automatic
Semi-automatic welding machines in an environment of inert or active gases, or simply semi-automatic devices, are more complex devices than transformers or rectifiers. However, they are more convenient to use. Often used in car body repairs, they are widely used in everyday life and in private households.
The structure consists of the following components:
- transformer;
- rectifier;
- wire feeding drive;
- gas cylinder;
- sleeves with a burner.
Welding of parts is carried out with a wire melting in an electric arc, which is located in a protective gas environment during the process. The current is most often adjusted in steps; the wire feed speed is also subject to change. The ratio of these parameters establishes the required operating mode .
Various models of semi-automatic machines work:
- only with gas;
- with or without gas (switchable);
- only without gas.
If work is carried out without gas, a special wire (flux-cored) is used. Flux-cored wire differs from ordinary flux-cored wire in that its composition, in addition to metal, includes flux. When the flux components burn, a cloud of protective gas is formed, which prevents oxidation of the weld pool by air. In addition, the active elements of the flux composition give the metal the necessary parameters, and the arc becomes more stable. This does not require a gas cylinder, which is convenient, but the wire itself is significantly more expensive.
When working with different metals, different gases are used - carbon dioxide when welding iron, a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide when working with steel, and argon when welding aluminum. Gas cylinders should be used industrial or branded.
Semi-automatic machines are characterized by high productivity and produce excellent quality welds on various metals. Disadvantages include spattering of metal and high consumption of materials for waste.
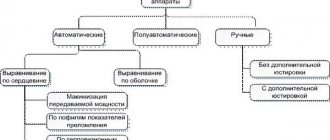
Device classification
There are many models of inverters.
They can be massive and equipped with special batteries. Portable models are available that are small in size and used for various purposes. Devices are also divided according to the power they consume and produce. This parameter is considered the main one when choosing, especially if a high indicator is needed, for example, in production. It is worth noting that even the most powerful inverters are not designed to operate at maximum performance for a long time. Depending on the principle of operation, devices are divided into the following:
- dependent ones that work only from the network;
- autonomous, equipped with a battery;
- voltage and current inverters.
Autonomous models are usually used for short-term operation and do not depend on a current source. Some devices are designed specifically for permanent connection to the network. Sometimes devices are equipped with solar panels.
Each option has its own advantages. For example, autonomous ones are suitable for any device and can help out in a difficult situation. Solar saves electricity, and dependent ones do not need recharging or other conditions to function. At night, the solar battery is inappropriate and will not serve the owner, so such models are rarely chosen.
There are also universal devices that can work online and offline, but not at the same time. The disadvantage of such devices will be their large size, since to ensure operation in two modes it is necessary to equip the unit with additional parts.
Devices that were installed before 1970 used special mercury-arc valves. Modern models are usually solid-state and are considered more efficient and safe.
Inverters
Devices of this type are also called pulsed. Today, welding inverters are considered one of the most common devices due to their light weight and general availability. And if 10 years ago inverters were expensive and not very reliable, now these shortcomings have been eliminated . The use of inverter technology today results in a reduction in the size of the transformer, an increase in the quality properties of the arc, optimization of efficiency, and a reduction in metal spatter during welding.
The welding inverter consists of a power transformer, the purpose of which is to reduce the mains voltage to the required value, a block of electrical circuits and a stabilizer choke, necessary to minimize current ripple.
The supply voltage is supplied to the rectifier in the inverter, at the output of which a circuit block transforms direct current into alternating current with a high frequency. This alternating current, obtained at the output of the power unit, is supplied to a high-frequency welding transformer, which is more compact and lighter than a conventional network converter. The voltage at the output of the welding transformer is rectified again and supplied to the arc.
Principle of operation
The inverter operates on a simple principle, which can be understood by giving a specific example.
A conventional battery operates primitively and produces a constant flow of current that does not change its direction. If you add a switch to this design, which at the output will change the direction of electron movement, then AC will flow to the device. To make it correct, the switch must work properly and operate at least 50 times within a second. About 3,000 changes in the flow of electrons occur per minute. A mechanical inverter works somewhat differently and, using special magnets, also quickly changes the direction of the current. The principle of its operation is reminiscent of a doorbell. When a button is pressed, a person acts on a spring, which sends a signal to change the power and flow of electricity. When released, everything returns to its original position. The device is also equipped with a special controller that performs other functions:
- voltage regulation in the device;
- switching frequency synchronization;
- providing protection against overloads and breakdowns.
Thanks to this, even the mechanical model of the device allows large electrical appliances to operate uninterruptedly.
Argon arc welding machine
This type of welding equipment uses special non-consumable tungsten electrodes; the protection gas is helium or argon..
An argon arc apparatus using a tungsten electrode contains the following components:
- a source that provides direct or alternating welding current;
- regulation device for working with current;
- set of burners for use with different voltages;
- control circuit providing welding cycle coordination and protection;
- stabilizing device for excitation and alignment of the arc.
Units of this type are used if there is a need for high-quality welding of non-ferrous metals.
Features of operation
The welding inverter, despite its popularity, requires careful care. The unit must be used in a well-ventilated area or outdoors at a temperature of 10...25 °C.
- Do not use the equipment in areas with high humidity or high dust concentrations.
- It is better to check the adjusted parameters on metal sheets up to 3 mm.
Branded models are not sold without instructions and technical data sheets; you should not rely on experience. Safety rules for working with a welding unit are written in the passport of a specific model and are constantly changing.
Spot welding machine
Spot welding is one of the types of contact welding of the thermomechanical class. The process itself consists of several moments. To begin with, the parts, folded in the required manner, are placed between the electrodes and compressed with each other, after which they are heated until plasticity is achieved and are deformed together. Welding speed in factory conditions is up to 10 points per second.
The parts are heated using an instantaneous (0.01–0.1 sec.) welding current pulse. This rapid impulse makes it possible to achieve heating of the metal until it melts, which leads to the appearance of a liquid zone common to both parts. After the current stops, the parts are still aligned, pressed against each other until the temperature drops and the molten point solidifies. Compression of parts stops with a time delay to create conditions for better crystallization of the metal.
The advantages of spot welding include cost-effectiveness, reliability and strength of the seam, and the ease of achieving automation. Unfortunately, this type of welding seam is not airtight, which limits the scope of its use. .
Unpretentious autonomous ADD units on a chassis
The designers took the path of simplification and reduction in cost. The single-post installation is mounted on a 2–4-wheeled chassis in a solid frame with a channel strap, covered with a casing to suppress noise and protect it in bad weather. Provides energy to a professional welding machine . It is possible to connect other electrical equipment and tools.
The manufacturer, for the sake of reliability of the equipment, excluded electronics.
Result:
- Operation at 98% humidity is acceptable.
- Operating temperature range –45–+450 C.
The 4-cylinder diesel engine is cooled by air flow, an additional measure to prevent engine damage. Current adjustment is available in coarse stepwise, smooth, remote with a distance of up to 20 m. 3-step control ranges:
- 60–165 A;
- 150–320 A;
- 300–430 A.
The DC generator ensures ignition stability, combustion maintenance, and arc elasticity. Qualitative superiority over collector-type diesel generators has been confirmed.
Operating voltage 36–100 V. Electrode size limited to Ø 6 mm.
The unit is adapted for hooking and transportation by vehicles or tractors over rough terrain. The volume of the fuel tank is sufficient for continuous operation throughout the day. At sub-zero temperatures, the fuel network warms up automatically. In bad weather, the work site is covered with a polypropylene waterproof tent.
Characteristics of ADD welding units on a single-axle trolley:
| Brand | Diesel | Fuel consumption | Current range | Type of cooling | Weight, dimensions |
| ADD-4004P | 37 kW, 1800 rpm | 4.4 kg/h. | 60–450 A | Air | 1.03 t, 1.68x1.93x2.85 m |
| ADD-4001 | 36.8 kW, 1800 rpm | 5.2 l/hour | 45–430 A | Air | 0.82 t, 1.0x1.3x224 m |
Gas cutting and welding machine
Gas welding involves heating the part until it melts with a high temperature flame . In this case, flammable gases are used - hydrogen, natural gas, acetylene. A distinctive property of these gases is their good combustion in air. Most often, acetylene is used in gas welding machines, which is easily obtained using calcium carbide and water. The combustion temperature of this gas is 3200–3400 °C.
Advantages of gas welding and metal cutting:
- Simple technology.
- No access to the electrical network is required, no need to use electric current.
- The equipment used for welding is quite simple.
It should be noted, however, that gas welding will not provide high speed and productivity, because it can only be done manually.
When gas welding, serious attention is paid to preparing parts, regulating the power of the torch, and installing it in the desired position.
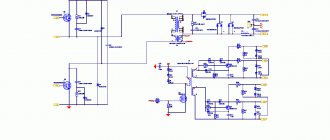
Current control
The inverter welding current is regulated using an electronic feedback controller shown in the diagram. Using the potentiometer located on the front panel of the welding inverter, the required welding current value is selected.
When the potentiometer knob is rotated, a certain reference voltage level is established at the input of logic elements built on operational amplifiers.
The signal coming through the feedback line from the current sensor located at the output of the device is compared by a comparator with the level of the voltage set by the control potentiometer.
If the voltage levels of the master circuit and the current sensor signal do not match, the amplitude of the control pulse supplied to the controller changes.
In this case, the duty cycle of the pulses generated by the controller changes, which causes a change in the switching mode of the transistors and, ultimately, the value of the welding current.
That is, the regulation principle is that the circuit always strives to maintain correspondence between the values of the specified and actual current, which ensures its stability.
The TL494 microcircuit, produced by the American company Texas Instruments, or its analogues is usually used as a controller that generates adjustable pulse-width modulation signals.
The given block diagram shows only the principle of operation and interaction of individual functional blocks. The detailed electrical circuit of each type of inverter may have individual characteristics.