It is difficult to name an industry that does not use metal and products made from it, for the production of which a rolling mill is actively used. Metallurgical enterprises today place quite high demands on equipment. That is why modern industrial machines, in particular rolling mills, differ significantly from the models that were produced earlier.
Rolling mill for the production of corrugated sheets
Purpose
Metal rolling machines are mechanical installations designed to create metal products by deforming raw materials in roll devices. The equipment allows us to produce various types of products:
- Long products. These include rods and strips of various geometric shapes, as well as shaped parts, spring and rhombic.
- Special purpose profile. Metal products in the form of angles, channels, I-beams, as well as combined blanks with a variable cross-section.
- Rolled products in the form of thin sheets up to 4 mm, as well as thick sheets more than 4 mm.
- Pipe profile with connection using welding and seamless joints.
This is interesting: Lathe 1M63 - technical characteristics and design
Pros of a homemade device
Ultimately, everything you need to make such a universal device can be purchased at a low cost at any hardware store, or you can select the necessary components from old, long-forgotten things, as well as select drawings. In any case, the price of such a machine will very quickly pay for itself, since it can produce parts of any complexity with minimal costs for consumables.
Important: renting a rolling machine will cost a tidy sum, which is why you can place ads and make good money from your device.
The work done pays off quite quickly, since you can produce any parts. Here is just a small list of them:
- professional pipes;
- metal guides for profiles for drywall;
- coverings for standing seam roofing;
- elements for metal siding;
- metal sheets of square and rectangular shape;
- additional fastenings for siding;
- wire for electrical wiring.
All these homemade products will be useful to you when building a new house or renovating it. As practice shows, homemade sheet bending machines are extremely in demand, since their design does not require complex manufacturing, but at the same time allows the production of a lot of useful and necessary parts.
Video: DIY rolling machine.
Design and principle of operation
The rolling press consists of three main parts:
- The cage is working. The design of these elements includes rolling rolls, installation plates, a base frame, and wiring.
- Electric motors for transmitting movement to working elements.
- Mechanisms of distribution and transformation of motion. Consists of a spindle, couplings and gears.
The units differ in the number of stands and work roll sizes:
- Machines for thick metal have up to two working compartments with rollers ranging from 3 m to 5.5 m in length. In addition, vertical rollers can be installed, which are used for processing side edges.
- Broadband equipment contains up to 15 stands, rolls have a length of up to 2.5 m.
- Universal rolling presses consist of 5 compartments, and the length of the shafts is up to 1.5 m.
In industry, there are three methods for processing metal raw materials until they acquire the required geometric shape:
- In the first case, a rolling device is installed on the casting unit, and the initial contour of the part is obtained until complete crystallization. The disadvantage of this method is the need to maintain a high temperature until the end of processing, as well as additional precise running-in.
- As a result of rolling through furnaces with temperatures inside the chamber up to 1350 C, the edges are independently welded. At the exit of the equipment, a finished pipe profile is obtained.
- The third method involves manufacturing parts at a workpiece temperature corresponding to the environment. To prevent defects, the units use a large number of rollers that rotate in the opposite direction.
Making a rolling machine with your own hands
For a profile pipe, you will need to make a small machine with your own hands, which differs significantly from industrial installations in size. This can be done in everyday conditions if there is free space for the machine.
It can be noted that a homemade machine can allow you to produce parts of any complexity. With its help, you can quite easily make wire of any diameter, cut sheet metal, which provides for the roofing of any roof, as well as many other parts that are often in demand in everyday life.
First, you will need to select suitable drawings so that you can get a homemade rolling machine. After this, you need to prepare its components, namely:
- a pair of powerful stands made of strong metal;
- a steel rod whose diameter will be at least 5 cm;
- top plate with M10 nuts;
- two gears of the appropriate size;
- gear;
- springs and stops;
- as well as bronze bearings and bushings.
Once you have all the components in stock, you can begin to manufacture a working machine, which will be sufficiently mobile to move:
- Using bolts, a kind of working cage is assembled from racks and a metal plate.
- Two working shafts are mounted to the same racks. They must first be turned from a previously prepared steel rod. They also need to be hardened to obtain improved metal strength.
- The lower shaft is mounted between the racks using prepared bushings and bearings. The upper shaft is mounted on special slides and is a movable element of the machine. The upward movement of the sliders is limited by stops.
- Continuous compression of the two separate shafts is provided by a spring, which keeps them under constant tension. It is attached simultaneously to the plate, the bases and the directly movable upper shaft.
Important: to ensure the operation of such a machine, synchronous rotation of the working shafts is necessary. You can solve this problem using a gear transmission, which transmits torque to a gear mounted on the lower shaft. Thus, using the handle you can start the device into operation.
The installation made in this way is manually driven. It requires continuous rotation to operate. If the manual mechanism stops, then the shafts will accordingly stop rotating. This creates a universal device on which you can change components and thereby change the profile suitability of the machine.
Specifications
Rolling machines have characteristics that distinguish them from analogues:
- the type of profile produced in a particular installation can be pipe, section, as well as thin and thick sheet;
- the range of metal thickness intended for rolling is from 0.4 mm to 200 mm;
- necessary raw materials for rolling;
- performance indicator, the choice of machine before purchase, as well as the preparation of raw materials, depends on this factor;
- number of working cells with rolls for the required profile;
- the diameter of the working shafts for rolling, as well as their useful length;
- rated voltage - 220 V / 380 V;
- the power indicator of the electric motor used is from 2.2 kW and above;
- assembled installation dimensions;
- total weight of all equipment in the complex;
- presence of reversal in the rolling mill.
Rolling machine
Rolled and stamped profiles
In Russia, the following main rolled and stamped profiles are accepted, from which elements of building structures are made.
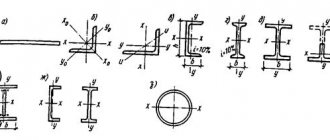
- rolled angular isolateral steel - shelf width from 20 to 200 mm;
- rolled angular unequal steel (Fig. 2, b) - shelf width Bxb = from 30x20 to 200x120 mm;
- I-beams (Fig. 2, c) - profile height H from 100 to 600 mm;
- wide-flange I-beams (Fig. 2, d) - profile height H from 120 to 1000 mm;
- lightweight I-beams - profile height H from 200 to 300 mm;
- channels (Fig. 2, d) - profile height H from 50 to 300 mm;
- lightweight channels - profile height H - 240 mm;
- strip steel - width b from 12 to 200 mm, thickness from 4 to 60 mm;
- square steel - sizes from 8x8 to 200x200 mm;
- rolled round steel - with a diameter from 5.5 to 222 mm;
- rolled universal broadband steel (with rolled edges)—width from 200 to 1050 mm and thickness from 4 to 50 mm;
- rolled thick sheet steel - width from 500 to 2500 mm. and thickness from 4 to 60 mm;
- rolled thin-sheet steel with a width from 600 to 1400 mm and a thickness from 0.9 to 3.75 mm;
- sheet roofing steel (regular and galvanized) - main sheet dimensions 710x1420 mm and 1000x2000 mm, sheet thickness from 0.38 to 0.82 mm;
- corrugated sheet steel - thickness (with reef) from 5 to 10 mm, width from 710 to 1250 mm;
- corrugated sheet steel - thickness from 1 to 1.75 mm;
- rolled and stamped steel of special profiles for metal frames of industrial, public and high-rise buildings;
- hot-rolled steel of periodic profile (Fig. 2, f) for reinforcement of reinforced concrete structures; profile numbers correspond to the diameters of round rods, equal in cross-sectional area (from 12 to 80 mm);
- cold-processed periodic profile steel (flattened) for reinforcement of reinforced concrete structures made of round steel with a diameter of 8 to 28 mm; such steel is produced in two ways: a) by cold rolling a round steel rod between two grooved rolls, and dents are formed on the rod in two parallel planes; b) cold rolling of a round steel rod on a special mill with gear rolls, and dents are formed on the rod in two mutually perpendicular planes (Fig. 2, g). Periodic profile steel has an increased design yield strength of 35 kg/mm2 (compared to δtk=24 kg/mm2 for conventional St. 3), which provides greater savings in reinforcing steel in reinforced concrete; The corrugated surface of this steel ensures reliable adhesion to concrete.
- sheet pile steel (for hydraulic structures): a) flat (Fig. 2, h) - width B = 400 mm; b) trough (Fig. 2, i) - width B=400 mm, height H=80 mm; c) zeta (Fig. 2, j) - width B = 400. H = 320 mm.
- steel pipes for various purposes with a diameter from 5 to 1420 mm
Features of the operation of rolling machines
Purpose
The equipment allows us to produce various types of products:
- Long products. These include rods and strips of various geometric shapes, as well as shaped parts, spring and rhombic.
- Special purpose profile. Metal products in the form of angles, channels, I-beams, as well as combined blanks with a variable cross-section.
- Rolled products in the form of thin sheets up to 4 mm, as well as thick sheets more than 4 mm.
- Pipe profile with connection using welding and seamless joints.
Design and principle of operation
The rolling press consists of three main parts:
- The cage is working. The design of these elements includes rolling rolls, installation plates, a base frame, and wiring.
- Electric motors for transmitting movement to working elements.
- Mechanisms of distribution and transformation of motion. Consists of a spindle, couplings and gears.
The units differ in the number of stands and work roll sizes:
- Machines for thick metal have up to two working compartments with rollers ranging from 3 m to 5.5 m in length. In addition, vertical rollers can be installed, which are used for processing side edges.
- Broadband equipment contains up to 15 stands, rolls have a length of up to 2.5 m.
- Universal rolling presses consist of 5 compartments, and the length of the shafts is up to 1.5 m.
In industry, there are three methods for processing metal raw materials until they acquire the required geometric shape:
- In the first case, a rolling device is installed on the casting unit, and the initial contour of the part is obtained until complete crystallization. The disadvantage of this method is the need to maintain a high temperature until the end of processing, as well as additional precise running-in.
- As a result of rolling through furnaces with temperatures inside the chamber up to 1350 C, the edges are independently welded. At the exit of the equipment, a finished pipe profile is obtained.
- The third method involves manufacturing parts at a workpiece temperature corresponding to the environment. To prevent defects, the units use a large number of rollers that rotate in the opposite direction.
Specifications
Rolling machines have characteristics that distinguish them from analogues:
- the type of profile produced in a particular installation can be pipe, section, as well as thin and thick sheet;
- the range of metal thickness intended for rolling is from 0.4 mm to 200 mm;
- necessary raw materials for rolling;
- performance indicator, the choice of machine before purchase, as well as the preparation of raw materials, depends on this factor;
- number of working cells with rolls for the required profile;
- the diameter of the working shafts for rolling, as well as their useful length;
- rated voltage - 220 V / 380 V;
- the power indicator of the electric motor used is from 2.2 kW and above;
- assembled installation dimensions;
- total weight of all equipment in the complex;
- presence of reversal in the rolling mill.
Varieties
Based on the number of rolls located in the working stand and their placement, rolling machines are divided into the following types:
- double-roll - the design has paired mechanisms for pressing, which can rotate in different directions;
- three-roll - contain three shafts in each stand;
- four-roll - consist of two pairs of working parts;
- multi-roll - have a design of 4 or more rolls, and in universal ones they are used in a vertical position, sometimes they are installed in the spaces between horizontal ones;
- rolls mounted at an angle to the surface of the metal workpiece.
Rolling presses are distinguished by the location of the stands:
- equipment with working mechanisms arranged in one line is called linear;
- in stepped installations, the stands are installed in several lines parallel to the main flow;
- equipment for continuous and semi-continuous rolling; with the help of such machines, industry achieves high productivity.
Depending on the type of product produced during the process of pressing blanks, installations are divided into the following types:
- Crimping equipment. Allows the production of steel ingots weighing up to 25 tons. A piece of square or rectangular cross-section comes out of the working stands.
- Continuous pressing machines for blank material. As a result of the operation of such mechanisms, steel plates are modified into a special profile and sheets.
- Rail and beam machines roll blooms into rails, channels and large beams. In industry, step and sequential mills are used.
- Sectional machines are used to produce metal parts of different grades.
- In the process of manufacturing wire, wire mills are installed in the workshop; they are divided into stepped, semi-continuous and continuous.
- Slabs are processed using a sheet rolling machine. Thick-sheet, wide-strip, and also with winders are used.
- Pipe rolling equipment produces seamless and welded pipes. During the rolling process, two levels of processing are used. Initially, a hollow sleeve is made from a round bar, then a pipe of the required diameter is made from it.
Selection principle
When purchasing equipment, pay attention to the following:
- Productivity of finished products, process automation, reliability and profile quality.
- The use of additional installations to ensure automatic rental.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the rental method include:
- increased productivity;
- wide range of finished products;
- use of software control to automate the process.
Among the negative indicators it is worth noting:
- Using rolling machines requires costs for raw materials and electricity, as well as equipment maintenance.
- After rolling, additional processing is required.
- To press the workpieces should be heated.
Manufacturers and price
Metallurgical enterprises use equipment from foreign and domestic manufacturers. Russian companies are trying not to give in to foreign competitors.
The price of rolling mills depends on the manufacturer. The cost starts from several thousand and reaches 5–6 million rubles. The price is also influenced by productivity, type of finished profile, as well as the number of stands and rolls.
Exploitation
To ensure safe operation of the equipment it is necessary:
- install an automatic control system for the rental process;
- Before starting, check that the installation is working properly;
- moving parts and mechanisms should be protected;
- carry out maintenance of bearing connections and rollers;
- Provide areas exposed to high temperatures with additional ventilation.
Compliance with safety requirements when operating equipment will prevent possible injuries and accidents. As a result of rolling on serviceable machines, the consumer receives high quality material.
Production of rolled products
Long products are produced in the following sequence. The heated ingot is first rolled into blooming, which is a fully mechanized, powerful reversible duostan. Ingots weighing 4-15 tons are fed to blooming. The rolled ingot is cut and blanks (blooms) of square or rectangular cross-section (slabs) are obtained. Blooms are then supplied to billet mills, where billets are rolled for section mills, or directly to large-section and beam-rail mills.
Rail-beam mills roll large-sized rails, beams and channels. Section rolling mills roll: round, square, strip steel, channels and I-beams of medium and small numbers, equal and unequal angles. Wire mills roll round wire rod with a diameter of 10 to 5 mm to produce wire.
In order to produce products with a complex profile during rolling (angles, channels, etc.), cutouts (streams) are made on the working surface of the rolls.
In addition to blooming mills, there are rolling mills - slab mills, which roll slabs (rectangular cross-section blanks) from a flat ingot; The slab is then turned into sheets in sheet rolling mills. The weight of ingots for sheet metal reaches 50 tons (for rolling thick armor plates). In construction, mainly rolled low-carbon steel is used.
Selection principle
When purchasing equipment, pay attention to the following:
- Productivity of finished products, process automation, reliability and profile quality.
- The use of additional installations to ensure automatic rental.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the rental method include:
- increased productivity;
- wide range of finished products;
- use of software control to automate the process.
Among the negative indicators it is worth noting:
- Using rolling machines requires costs for raw materials and electricity, as well as equipment maintenance.
- After rolling, additional processing is required.
- To press the workpieces should be heated.
Improved performance
Manufacturers and price
Metallurgical enterprises use equipment from foreign and domestic manufacturers. Russian companies are trying not to give in to foreign competitors. The price of rolling mills depends on the manufacturer. The cost starts from several thousand and reaches 5–6 million rubles. The price is also influenced by productivity, type of finished profile, as well as the number of stands and rolls.
This is interesting: Surface grinding machines - design and methods of metal grinding
What is this equipment used for?
Rolling and punching machines and other metalworking equipment are most often used to create a specific shape of a metal part. Since this material is used everywhere, it is handled with due responsibility and care.
Rolling machines for metal profiles are ubiquitous, but many people have no idea that they can make such complex equipment themselves. Due to the fact that the price of such equipment is extremely high, we will clearly look at an example of how to make a rolling-notching mechanical machine with your own hands.
A striking example of metal parts, where a rolling machine for profile pipes is used in production, are pipes or battery radiators present in every house or apartment. All these products are made on metalworking equipment, which you can make yourself without any skills or deep knowledge.
Important: if you decide to independently manufacture a rolling die-cutting machine, then for the reliability of subsequent parts produced on it, its assembly should be treated with due care and responsibility.
Basic equipment for rolling production
The main equipment of rolling production is rolling mills and rolls. A rolling mill is a technological complex of sequentially located machines and units designed for plastic deformation of metal in rolls (rolling itself), its further processing, finishing (straightening, trimming edges, cutting into dimensional products, etc.) and transportation.
Rice. 5. Rolling scheme with two rolls
Rolling rolls (Fig. 5) are the main part of the rolling mill: they compress metal 1 and give it the required shape. The rolling roll consists of a barrel 4 (smooth or with grooves), necks 3 located on both sides of the barrel and resting on the roll bearing, clubs 2 intended to connect the roll to the spindle. Roll ends can be flat or cylindrical (splined or keyed)
The rolls are made of bleached cast iron or alloy steel (chrome-nickel and chrome-molybdenum) and carefully ground; steel rollers are heating up. The rolls have a hardness from 150 to 800 HB Brinell. Steel rolls are either cast or forged. Forged rolls are stronger than cast ones. Prestressed composite rolls are used. Currently, small-sized carbide rolls have appeared (for example, from alloys VK6, VK8, etc.). Rolls come in diameters from 3 to 1500 mm and barrel lengths up to 5000 mm.
The necks of the rolling rolls rotate in liners made of textolite, plasticized wood, sliding bearings or roller bearings installed in the stand pads. Textolite liners are lubricated and cooled with water.
Devices that ensure metal deformation in rolls are called main equipment, and equipment for other technological operations is called auxiliary equipment.
Main equipment includes:
- the working cage and its components and parts (rolls, bearings, pressure and balancing devices, axial roll installation devices, roll reinforcement, etc.). The defining characteristics of the working stand are the diameter and length of the roll barrel;
- rolling mill electric motor;
- transmission mechanisms that ensure the transmission of rotation from the engine to the work rolls (spindles, main and main clutches, gearboxes, flywheels, gear cage)
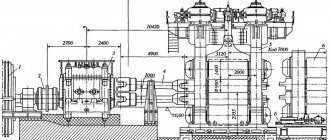
The kinematic diagram of the rolling mill is shown in Fig. 6. In the working stand, a workpiece 2 is rolled between rollers 1 located in pads with bearings. The rotational motion of the rollers is transmitted from the main electric motor 8 through a gearbox 7 with flywheels 6, couplings 5, a gear stand 4 and spindles 3
Rice. 6. Kinematic diagram of a three-roll rolling mill
Rice. 7. Classification of working stands of rolling mills : a - duo; b - trio varietals; c - leaf trio; g - quarto leaf; d - quarto for rolling rolls; e - multi-roll (six-roll); g - multi-roll (twenty-roll); z - universal; and - special
Depending on the design and arrangement of the rolls, the working stands of rolling mills are divided into six groups: duo, trio, quarto, multi-roll, universal and special design. Duo (two-roll) stands are reversible (rolling is carried out in both directions) and non-reversible (in one direction) (Fig. 7).
Trio (three-roll) stands are most often non-reversible. Rolling in such mills is carried out forward between the lower and middle rolls and backwards between the upper and middle.
Quarto (four-roll) stands have four rolls (Fig. 8), located one above the other, of which two work rolls are of smaller diameter and two support rolls are of larger diameter.
Multi-roll stands have five or more rolls.
Rice. 8. Quarto mill for cold rolling of strip : 1 - feed winder drive; 2 — rolled tape; 3 — electric motor for driving the rolls; 4 - gearbox; 5 - spindles; 6 - support rollers; 7 - work rolls; 8 — drum of the receiving winder
Rice. 9. Continuous rail and beam mill (PRC)
Depending on the location of the working stands, rolling mills are divided into single-stand, linear, sequential, semi-continuous and continuous (Fig. 9). Continuous mills are the most advanced. Thanks to automation, rolling speed can reach 60 m/s.
The working stand is the main unit of the rolling mill. Metal is rolled in a stand. It consists (Fig. 10) of two frames 5 with bosses (feet) 2, plates 1 on which the frames rest, installation pipes 9 connecting the frames, covers 3, rolling rolls 10, cushions of the lower 7, middle 6 and upper 4 rolls and bearings for them, a mechanism 8 for installing the rolls in the vertical plane and in the axial direction, and a device 11 for balancing the lower roll. In addition, there are roller fittings (rulers, wires, passes, etc.), devices for lubricating, cooling or heating the rolls.
The supports (cushions) contain sliding liners or rolling bearings for the roll journals. The frames are made in two types - closed and open (with a lid). Closed beds better ensure the accuracy of the rolled profile, but in such a mill it is difficult to replace rolls. But there are designs of open beds with a wedge fastening of the lid (Fig. 1 61), which have high reliability and in terms of rigidity bring the open bed closer to the closed type beds.
Rice. 10. General view of the trio stand of the large-section mill 500
Rice. 11. Wedge fastening of the bed cover
In addition to rolling stands with horizontally located rolls, stands that simultaneously have horizontal and vertical rolls for compressing rolled products from all sides without turning are widely used.
For rolling mills, DC or AC motors (asynchronous and synchronous) are used. Since the speed of high-speed motors usually does not correspond to the number of revolutions of the rolls in rolling stands, gearboxes are installed between the motors and the stands. In rolling stands, the motor torque must be distributed among several rolls. For this purpose, gear stands are used. Torque from the engine to the rolls is transmitted using spindles and couplings.
Gear stands and gearboxes
In cases where each rolling roll is driven by an individual motor (modern blooming, slab and quarto plate mills), no gears are required. All other rolling mills must have gear drives in the gear stands and gearboxes.
The gear cage consists of the main gears, a frame, bearings for the main gears (cushions filled with babbitt, rolling bearings) and a system of nozzles and pipelines that provide abundant lubrication to the rubbing parts.
The main gears have a ring gear, journals (trunnions) and clubs made as one piece from 40, 45 or 40X steel with surface hardened teeth. Gears operate under heavy loads (often dynamic) and high speeds. The number of teeth is taken from z = 18 to z = 29, chevron cutting.
The gear cage frame is a one-piece or two-half box cast from modified cast iron or steel. During the operation of the gear stands, special attention is paid to continuously supplying a sufficient amount of lubricant to the teeth and journals of the main gears at a pressure of 0.2. . . 0.5 MPa.
Gearboxes between the gear stand and the electric motor are used if their installation and operating costs justify the difference in the cost and operating costs of low-speed and high-speed motors. Depending on the gear ratio, gearboxes used in rolling mills are single-, double-, and sometimes and three-stage.
The connecting devices that transmit torque from the engine through the gearbox and gear cage to the rolls are represented by couplings and spindles of various designs.
The drive gear of the gear cage is connected to the driven shaft of the gearbox or to the motor shaft (if there is no gearbox) through a coupling, which is usually called the main one. The most common are gear couplings, as well as elastic or elastic couplings.
The rolls of two adjacent stands of a linear mill, as well as the main gears and work rolls, under conditions of slight movement in the vertical plane, are connected to each other by club-type couplings and spindles, which allows the spindle to operate with some misalignment (1...2°). When there are significant movements of the rolls in the vertical plane, when the spindle axis makes a significant angle with the horizontal plane, articulated spindles with rolling bearings are used to drive the rolls, arranged on the principle of a Hooke's joint, which can transmit rolling torque to the rolls from the gear stand when the spindles are misaligned up to 10 12 °
Since spindles have a significant weight with a length of tens of meters, they are balanced using weights or springs.
Place and purpose of the rolling shop at a metallurgical plant
A modern metallurgical plant with a full metallurgical cycle combines three main industries: blast furnace, steelmaking and rolling. The latter usually includes several independent workshops that produce various products according to the range.
Cast iron produced in blast furnaces is processed in converters, open-hearth or electric furnaces into steel. The supply of liquid iron, which ensures uninterrupted operation of steelmaking shops, is contained in heated storage facilities (mixers).
The ingots obtained in the steelmaking shops enter the stripper department, where they are removed from the molds and sent to the rolling shops.
The technological process for the production of rolled products consists of two stages: rolling the ingot into a semi-product and rolling the semi-product into a finished product.
In Fig. 42 shows a plan for the location of the main workshops of a metallurgical plant with a full cycle.