Tell ! Tin food solder - does it have a brand, number? (in stores they shrug their shoulders) nok71964, 01 July 12, 10:45
When bending the rod, crackling and creaking is felt. buddy, Oct 25 12, 03:26
I used to look for a way to make a tin plague, because they sell flux already with gray powder mixed with it, it’s good to tin a copper pipe from the inside or a copper dimrot, so it’s good to make the powder and mix it with the flux, warm the pipe and it tins itself, a very good thing, we have in Ireland this is a problem, so only the plague will save you) I was looking on eBay for something like this mixture, it costs a lot of money and there is nothing there Claw, 31 Oct. 12, 02:43
make a copper plague, because flux is sold already with gray powder mixed, it is good for tinning a copper pipe from the inside or a copper dimrot, Claw, 31 Oct. 12, 02:43
decompose the tin into gray powder, I meant. Claw, 31 Oct. 12, 19:36
Last ed. 31 Oct. 12, 20:07 from aleksej-serikov
So what about the solder that contains copper – does it also crumble below -12 into a plague? or more durable? aleh, 25 Jan. 13, 00:44
Has anyone used solder paste like this? REMS Cu paste 3. 250 g. Soft paste made from a mixture of S-Sn97Cu3 according to DIN EN 29453 and flux. Soft soldering of copper pipes with copper, brass fittings and tin-zinc bronze fittings, for plumbing and heating installations up to 110°C.
Does not contain lead, harmless to health and the environment. There is no additional addition of flux, it is already contained in the paste. No melting of pipes or fittings, excellent soldering, strong connections.
As I understand it, spread it, heat it up and you're done?
Last ed. 07 March 13, 01:41 from kostiya
Has anyone used solder paste like this? REMS Cu paste 3. 250 g. Soft paste made from a mixture of S-Sn97Cu3 according to DIN EN 29453 and flux. Soft soldering of copper pipes with copper, brass fittings and tin-zinc bronze fittings, for plumbing and heating installations up to 110°C.
Does not contain lead, harmless to health and the environment. There is no additional addition of flux, it is already contained in the paste. No melting of pipes or fittings, excellent soldering, strong connections.
As I understand it, spread it, heat it up and you're done?
I don't know about this one. I myself use VIEGA Lotpaste No. 3 (250g). I recommend.
Solder for soldering copper pipes is a special alloy or pure metal that fills the free space between the pipes being soldered. To obtain a strong connection, it is necessary not only to choose the right solder, but also to use it correctly during the work.
Read also: How to remove a magneto from a partner chainsaw
Special alloy for soldering copper pipes
Foods Rich in Copper
Macro- and microelements in full are contained in seafood. Seafood also contains large amounts of copper.
Squid, fish, shrimp, mussels and edible algae, when regularly present in the diet, can provide the body with a sufficient supply of this element.
Copper is also present in plants and “regular” animal foods. It accumulates in plant products mainly because copper microfertilizers are used to improve the yield of many crops.
Therefore, the mineral is present in vegetables, fruits, and cereals. They contain copper along with molybdenum, and this increases their value as sources of microelements, because these two minerals “work in pairs” in the body.
Some plants “purposefully” accumulate copper. Thus, ginseng, known for its numerous beneficial effects, is distinguished by its high content.
Raw egg yolks also contain high dosages of copper, but due to their specific taste and the risk of salmonella infection, raw eggs should not be eaten.
Liver, fermented milk products, and meat are rich in copper from animal sources.
Type of substance
Additive E 519 is included in the group of food stabilizers.
In nature, the substance is found in the minerals chalcanthite and butite. It is an inorganic binary compound, a copper salt of sulfuric acid.
For industrial needs, the product is obtained by dissolving copper in heated sulfuric acid while simultaneously blowing with air.
The second method is oxidative roasting followed by dissolving copper oxide in sulfuric acid. The product is purified by recrystallization in boiling distilled water, followed by cooling and separation of the precipitate using a filter.
Absorption of copper from food
The body absorbs about a tenth of copper from food. Despite this, it is usually absorbed in sufficient quantities in the intestines, and additional copper is not required. Absorption occurs better if the element enters the body together with molybdenum; in pairs they work much more efficiently than individually, since they are integrated into the same biochemical reactions when they participate in the exchange of protein and sulfur. However, it is not necessary to worry about the supply of molybdenum; most products containing copper already include molybdenum in their composition.
Cereal phytins bind copper in the intestines. If there is an excess of dietary fiber in the diet (this happens when deliberately consuming large doses of bran), copper molecules can also bind and be excreted from the body.
Formula, equation, properties of copper sulfate
The copper salt of sulfuric acid has the following chemical formula:
CuSO4
At temperatures above 650 °C, thermal decomposition of the compound begins:
CuSO4 →CuO + SO2 + O2↑
This produces oxygen gas, copper oxide (2) and sulfur dioxide.
A qualitative reaction to copper sulfate is interaction with alkalis:
CuSO4 + 2NaOH → Cu(OH)2↓+ Na2SO4
During the reaction, a blue precipitate is formed - copper hydroxide (2), as well as a soluble sodium salt of sulfuric acid. Adding barium chloride to a copper sulfate solution is also a way to identify the compound:
CuSO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 ↓+ CuCl2
A white precipitate formed by barium sulfate is clearly visible, indicating the presence of sulfate ions in the solution.
Copper sulfate is hydrolyzable and can react with simple and complex substances. The compound interacts with alkalis, as well as with other salts, and has pronounced redox properties.
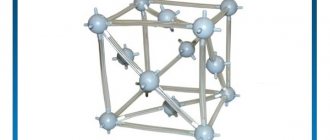
Copper sulfate molecule
Biological role of copper
Functions of copper in the human body:
• Together with molybdenum, it participates in protein metabolism • Together with iron, it carries out hematopoiesis; in case of iron deficiency, for some time it partially replaces it in the formation of hemoglobin and red blood cells • Takes part in energy production - the formation and transformation of ATP molecules • Is part of a huge number of enzymes , especially those involved in tissue respiration and neutralization of toxins • Promotes normal functioning of the nervous system • Improves the production of the fibrous framework of organs and tissues, including the skin. This is done by stimulating the formation of collagen and elastin • Plays a huge role in supporting liver function • Takes part in the production of a number of hormone-like substances and hormones • Reduces the risk of stomach ulcers • Participates in the formation of skin and hair pigment • Strengthens the immune system • Increases insulin activity • Copper compounds have bactericidal effect and work as antiseptics.
Reactions with copper sulfate, compounds
Copper sulfate hydrolyzes well, forming an electrolytic solution with an acidic environment:
CuSO4 → Cu 2+ + SO42-
This produces a fairly strong electrolyte. Electrolysis proceeds with the release of free oxygen, copper and sulfuric acid:
2CuSO4 + 2H2O →2Cu + 2H2SO4 + O2
The compound interacts with metals:
CuSO4 + Zn→ZnSO4 +Cu
A substitution reaction is characteristic, during which pure copper precipitates.
Copper sulfate is characterized by interactions between ion exchange and various precipitation. Most often, copper sulfate reacts in this way with other salts:
3CuSO4 + 2Na3PO4 – Cu3(PO4)2 ↓+3Na2SO4
As a result, greenish crystals of copper orthophosphate fall out. Sometimes the exchange reaction occurs with a change in oxidation states, then we are talking about redox reactions:
2CuSO4 + 4NaI → 2CuI + I2 + 2Na2SO4
Cedi sulfate reacts with sodium iodide, free iodine is released.
Copper sulfate can be reduced with hydrogen when heated:
CuSO4 + H2 → Cu + H2SO4
It often forms complex salts, such as ammonia:
CuSO4 + 4NH4 → [Cu(NH3)4]SO4
The reaction produces a bright purple solution and tetraamine copper sulfate is formed.
Signs of copper deficiency
Humans are much less sensitive to copper deficiency than plants or farm animals. However, a situation with an element deficiency may arise. In rare cases, people experience symptoms of copper deficiency: premature graying, hair loss, anemia, liver problems, digestive disorders, fatigue, decreased mood, skin rashes, etc. It usually takes a long time to identify their cause, because copper deficiency is rare, and its symptoms are similar to other diseases.
There is evidence that with a long-term lack of copper in the body, the walls of blood vessels become less durable, which can lead to hemorrhages and even the formation of aneurysms - protrusions of the walls of blood vessels that can become damaged and rupture. Copper deficiency also accelerates the aging process in the body.
Characteristics and properties of fluxes
The properties and composition of the solder must be completely suitable for the metals with which it will be soldered. Also, the solder intended for soldering pipes must be at a lower temperature than the metal so that it does not get damaged. Therefore, there are two types into which materials are divided:
- Low-temperature solders have a low melting point, which does not reach 450 degrees Celsius. In this case, the load on the adhesions should not be too high. The metal and its physical properties remain unchanged.
- High temperature solders provide greater strength and quality, but their melting point can be above 800 degrees Celsius.
Choice and its features
The higher the melting point, the more it affects the metal from which the pipes are made. Therefore, it is worth knowing what load will be placed on the pipes and choosing the appropriate solder. If the load is expected to be light, then you can choose soft, low-melting solder. If the pipes are intended for the food industry, then it is necessary to choose a solder that is non-toxic and does not cause harm to human health.
Important! When choosing solder for copper pipes, you need to know the melting point and composition of the material for which it is intended!
Signs of Excess Copper
Excess copper in the body is now rare, but in the past this phenomenon was par for the course. The fact is that in the past, people often used copper utensils. When cooking and storing food in such containers, copper particles passed into the food, and its excessive amounts can have a toxic effect.
With an overdose of copper, disorders such as hair loss, sleep disorders, seizures, mental problems, endocrine disorders, jaundice and much more are possible.
There is also a rare disease called Wilson-Konovalov disease. This is a storage disease - a disorder in which a defect in enzyme function causes copper to accumulate in the body. Symptoms include severe disorders of the liver and nervous system.
The use of copper in the food industry and its bactericidal properties
Research conducted in 2006 at the Center for Applied Microbiology showed that the use of copper and brass utensils reduces the risk of the proliferation of pathogenic microflora in food products, better than stainless steel. Various stainless steel containers are widely used in the food industry as it is non-corrosive and can easily withstand the use of chemical cleaning agents to remove harmful pathogens.
Escherichia cli O 157 is one of the most serious foodborne pathogens in the world, causing health problems ranging from diarrhea to hemorrhagic colitis. Researchers say that cattle are the main carriers of E. coli O157, so dairy products, processed beef and meat are at risk.
At cold temperatures typical for food storage, the study found that 10% of bacteria were still alive on stainless steel tiles after 34 days, while bacteria were completely killed on brass tiles within 12 days and on copper tiles in just 14 hours.
This research prompted the International Copper Association to commission CAMR to conduct further research into the germicidal properties of copper, brass and stainless steel surfaces under a variety of conditions encountered in the food industry. For example, in the acidic environment found in fruit juice processing, E. coli O157 was found to survive for 45 minutes on copper.
For comparison, in stainless steel containers, the death of bacteria occurred within 2 days. And in environments containing animal feces with anaerobic bacteria E. coli O157, copper and brass elements showed excellent bactericidal properties.
All these studies led to the use of copper containers in the food industry for storing and transporting food. Dishes and containers do not always consist entirely of copper; most often the inner surface is sputtered. The introduction of copper equipment into food processing plants has led to a reduction in outbreaks of E. coli O157.
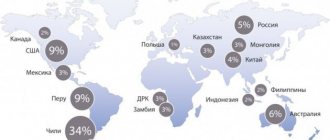
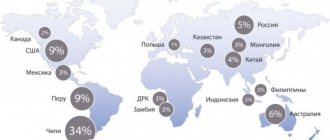
In Russia and the CIS countries, stainless steel is still widely used in the food industry. And the price of copper per kg, which is about 250 rubles depending on the brand, is more interesting as non-ferrous scrap. Although processing and its further use in the food industry may become a more profitable undertaking for both private and public enterprises.
Product Names
Generally accepted standards indicate the official name copper sulfate. Internationally, the name Cupric Sulphate is accepted.
In addition to the food industry, E519 is used in pharmaceuticals, photography, agriculture, and the textile industry.
In the countries of the European Union, the food additive is named according to the encrypted code - E519 (sometimes indicated with a dash between the letter and numbers).
Other names are also known among industrialists or chemical industry workers. The most popular are copper sulfate, crystalline hydrate, divalent copper sulfate, individual names in German and French.
Daily requirement of copper
For a healthy person, the daily intake of the element is up to 2.5 mg. If the need arises, the dosage is increased. If necessary, vitamin complexes and medications are prescribed. The course of treatment is carried out as prescribed by the attending physician.
The need for Cuprum for women increases during breastfeeding and pregnancy - up to 3 mg. If a woman does not receive a sufficient amount of the element per day, the risk of developing pathologies in the fetus increases.
Dosage in children:
- from birth to 2 years – 1 mg;
- 2-7 years – 1.5 mg;
- 7-18 years old – 2 mg.