Today, many citizens have a car. Since a vehicle is a rather complex mechanism, many different breakdowns happen to it. One of them is the imbalance of wheels and tires. For this reason, a balancing machine is a very important piece of equipment. The quality of balancing tires and wheels directly depends on the accuracy with which the machine copes with its task. The machine can help with the following:
- facilitates the work of workers, since balancing is carried out with a special device;
- increases the post's throughput level.
General operating principle
How does a balancing machine work? In general, the principle of its operation is as follows:
- To start working, you need to install the wheel on a special working shaft of the machine.
- Using special cones, you need to center the wheel and install it more accurately.
- Then, either manually or automatically, the wheel accelerates to the required speed.
- The balancing machine has a special measuring device that reads the parameters of the movement of the wheel on the shaft. After that, it transfers them to the device processor for processing.
- The process processes the data, generates a report about the malfunction or serviceability of the wheel, after which the report is transmitted to the display.
Operating principle of a conventional balancing machine
The wheel is mounted on a balancing machine and centered using cones. The measuring device reads the necessary information as the wheel spins. The information received is processed using the program and data on the condition of the wheel and recommendations for adjusting the weight and position of the weights are displayed on the balancing stand monitor.
All balancing stands are designed in such a way that they divide the wheel exactly in half in a vertical plane, thus balancing occurs in two planes. But if the wheel does not sit perfectly perpendicular to the shaft, the wheel balancer will divide the wheel unevenly and require the operator to place the balancing weight in the wrong place. The larger and heavier the wheels, the more noticeable the impact of errors in securing the wheels on the machine on the quality of balancing.
How parameters are measured
Next, you should pay attention to how the balancing machine evaluates the wheel by measuring its parameters. To do this, the object is conditionally divided into two planes - horizontal and vertical. Thanks to this, the tire is also conditionally divided into 4 equal parts.
The accuracy of mounting the wheel on the shaft of the balancing machine plays a decisive role in determining its parameters. Ideally, all 4 parts should be equal to each other. If you violate the perpendicularity of the installation of the wheel on the shaft, then its division into parts will also be disrupted, which means that the data collection will initially occur with an error.
Balancing is not just weights. How to properly balance a wheel without ruining anything
To be honest, when I asked my friend a tire fitter about balancing, I expected to get something very standard in response, but with some details that I didn’t know about before. But everything went wrong in life, and in response messages in the messenger I received a total of just over an hour of voice messages. Maybe a little less than an hour, if you remove the unprintable vocabulary (the reason for which I will give below), but still a lot. And I decided that there would be two materials. One is just about balancing (which, it turns out, I knew only superficially), the second is about how, based on some signs, to distinguish a normal tire mechanic from a crooked ghoul and extortionist of money.
Why is balancing needed?
Balancing is necessary to preserve three things: money, security and comfort. Money means taking care of the chassis. There is no mechanism in nature that would benefit from extra vibration. There are enough parts in the chassis that do not like unnecessary rhythmic impacts, even if they are not very strong. These include wheel bearings, silent blocks, and ball joints. In addition, the tire itself wears out quickly. So balancing is a clear manifestation of care for these elements, and therefore for the means to replace them prematurely.
As for security, everything is also simple. Remember what happens to a phone that just lies on the table. Nothing happens to him. But if you call it, it will start crawling on the table in vibrate mode. It just doesn't have enough grip on the table surface. The situation with an unbalanced wheel is the same: it bounces along the road, there is no question of a uniform contact patch, and the grip deteriorates rapidly. It smacks of latent suicide, although many don’t even think about it.
And last but not least – comfort. Here, too, everything is clear: shaking and the steering wheel jumping in your hands is very annoying. You have to be too calm a person not to pay attention to this. True, the lack of balancing is not felt on all cars, so if there is no shaking, this does not mean that everything is in order with the wheels. A shaking steering wheel is already an extreme degree of disregard for balancing, and it is better not to lead to this situation.
What's a motor, what's a wheel?
The question arises: when should balancing be done? Is it really before the steering wheel starts to shake? Strange, but yes. There are several situations in which balancing is necessary.
The first is assembling a new wheel. Each newly assembled wheel needs to be balanced. It is obvious. The second situation is related to seasonal “re-shoeing”. If the wheels were stored assembled, they also need to be checked for balance. It happens that balancing is not required, but more often it still has to be done.
This is where the obvious situations end and not so obvious, but no less vital ones begin.
Oddly enough, very often a wheel with a new tire has to be balanced twice. The first time is during wheel assembly, the second time is after running in. The fact is that during storage of the tire it may lose its round shape. A slightly “squared” tire is placed on a rim and balanced, but over time the tire returns to its shape. Sometimes the balancing is maintained after this, sometimes it is not. Therefore, it is recommended to check the wheel with a new tire for balancing again; the recommended mileage is 1000 kilometers.
Now let's move on to the run. It turns out that the wheels need to be checked every maintenance. For some reason they don’t think about this, but it’s better to check the balancing at the same time as maintenance. Changed the oil - check the wheels. And 10 thousand kilometers is not so little if the car has to drive on broken Russian roads.
The fifth reason to go for balancing is precisely those very broken roads. More precisely, pits. It is very advisable to follow the rule: if you fly into a hole, go for balancing. The driver himself may forget about this hole the next day, but the wheel remembers it for a long time. It happens that the balancing does not change, but it doesn’t hurt to check the wheel. If only for the reason that, for example, it is difficult to bend a cast disk from the outside, but from the inside it’s like two fingers on the asphalt. And this moment also needs to be controlled.
In general, it's better to be safe than sorry. There is no such thing as too much attention.
Just out of interest: is it possible to not balance the wheels at all? We do not consider the situation with innate idiocy. And then there is only one option left to tighten the balancing bolt: drive at a speed of no more than 40 km/h. It is believed that at this speed balancing is not necessary.
What and how?
Now let's move on to the most interesting part: how balancing is done and what is often done wrong.
Captain Obvious tells us: the wheels are balanced on a balancing machine. The cost of the machine can be different: you can buy dead junk for 10 thousand rubles, or you can snatch a top-end Hofmann for 1.4 million. But in general, many people don’t like to save money on a balancing machine: the client doesn’t really care how or what they used to put the tire on the rim, and he will easily notice a balancing error. Therefore, it happens that balancing machines are installed at the top level, and the rest of the equipment is simpler.
Theoretically, a wheel can be balanced normally on a cheap machine. Not ideal, but okay. It all depends on the degree of crookedness of the master. Too crooked and on a machine with automatic measurement of parameters it can cause trouble.
Pay attention to how the master will center the wheel on the machine. By the way he does this, you can estimate the radius of curvature of his hands. There are three ways in total. The first is the simplest and most undesirable. In this case, the cone, which fits into the central hole of the disk, is installed outside the disk. That is, the wheel is hung on the machine shaft, then the cone is put on, then pressed with a nut. For alloy wheels, this is the most undesirable method of centering. The fact is that on the outside this disk is simply cast, but on the inside it is milled. And the inside of the central hole is noticeably more accurate than the outside. Therefore, it is better to install the cast disk differently: the cone should fix the inner part. In this case, the sequence of arrangement on the machine will be as follows: a cone is put on the shaft, then a wheel, and then it is pressed against the faceplate with a plate. By the way, for stamping, both methods will be normal: with the accuracy of making a stamp “plus or minus a tram stop”, the side of application of the cone does not matter at all.
What determines which method the master will choose? Only from the master himself. Any machine allows you to center the wheel in both ways. But the first one requires fewer body movements, and the lazy person will choose this one. You can also lose some parts, without which the second method cannot be applied. This also happens, and this is a sign of a very mediocre tavern.
There is another way of centering - using a flange adapter. This method was invented by the Haweka company (where, in fact, modern balancing was invented). The method is based on the fact that the wheel is centered on the hub not by a central hole, as many people think, but by conical (or spherical) nuts or bolts. Here, first a cone is put on the machine shaft, then a wheel, and then a flange adapter, which centers the wheel with mounting holes. In this case, the centering is perfect: the wheel sits exactly the same as on the hub. But this method has a small drawback: it is labor-intensive, takes more time, and balancing with an adapter costs 30 percent more than balancing using the first two methods.
And finally, the most fantastic method. It is not a cone that is placed on the shaft, but a bushing that matches the diameter of the central hole of the disk. The disk itself is clamped not by a cone, but by a flange adapter. This is the most accurate and complex method. They say it is used in a parallel Universe by sober and clean-shaven tire fitters wearing white gloves. In our life, this, alas, does not happen.
Consumables for balancing are primarily weights. They are stuffed (spring) and self-adhesive (adhesive). Which ones are better? Both have their advantages and disadvantages.
Padded weights are attached closer to the edge of the rim and are more accurate. And since they are attached mechanically, they stay on the rim better. Such weights are good where strength is needed, not aesthetics. For example, on SUVs. Padded cargo also has disadvantages. First of all, they are not very beautiful. Secondly, the spring of such a load fits between the disk and the tire, and if the disk is old, air will leak in this place. However, if tires with rims bleed along the spring, they will soon begin to bleed everywhere. This is a disk problem (its corrosion), not a weight problem.
Self-adhesive adhesive weights also do not fall off the disc, although it is easier to tear them off if desired. And sometimes the Chinese ones fall off on their own, it happens. But they do not spoil the appearance of the disc.
What if he cheats?
I’ll tell you next time how to distinguish a normal master from a fake one. It's very interesting, but very long. For now, you’ll just have to see how a specialist will balance the wheels and how a low-skilled fraudster will do it (for simplicity, let’s just call him a “ghoul”).
A good specialist will never balance a dirty wheel. Firstly, the weight of the wheel, not the dirt, is important for balancing; secondly, it’s easier to wipe a clean wheel with solvent before gluing the weight; thirdly, it’s just more pleasant to work with. If a tire shop doesn’t wash wheels, it’s better not to balance anything there.
You need to balance a straight wheel. The ghoul does not know this and does not check the geometry of the disk and the tire itself before balancing. A good master will check them, and if it turns out that the disk is crooked, he will first offer to straighten it. And if the new tire is crooked, return it to the store. Also, a good specialist will first check the disk on the machine, and only then the wheel assembly, so as not to once again torment the tire during installation. This is especially true for low profile tires.
The ghoul removes the tape from the old weights from the disk with a knife. Usually - along with paint. A good specialist can use a special plastic spatula or an attachment on a drill (a circle for removing stickers).
The ghoul will jump around the machine for a very long time. Most likely, the reason for his dancing is an uncalibrated machine. A normal technician, using a well-maintained and working machine, balances a tire in about a minute.
Before installing the wheel on the hub, a specialist will check the adjacent surfaces. There can't be any dirt there. By the way, a small note to those who like to paint the brake drums on their VAZs: the paint falls off the drum (yes, this “high-temperature” one too), and the wheel begins to wobble. With such wheels you can only go for a Darwin Award.
The ghoul, of course, will not check anything: he will remove the wheel from the machine and screw it to the dirty hub. And he will also tighten the nuts (or bolts) with a wrench with a wild torque. And since the wheel is centered precisely with the nuts, what will happen to the balancing after such an installation is a mystery. A normal master uses a warm lamp torque wrench for broaching.
And lastly: a good specialist will balance everything that has a central hole (and sometimes even does not, as on some Peugeots and Citroens). The phrase “the wheel isn’t balanced” is only uttered by a ghoul. By the way, there were cases when, for fun, they balanced an old bucket and a stool. The humor is, of course, specific, but that’s what it is.
And the words “rubber, sixteenth radius, balloon, slope and nipple” belong to the vocabulary of ghouls. But, as agreed, we’ll talk about this next time.
Survey
How long have you had your wheels balanced?
Your voice
Total votes:
Types of devices
Today there are three main types of balancing machines.
- Machines for working with passenger car wheels.
- Machines for working with truck wheels.
- Universal machines. Can be used to evaluate wheels of both cars and trucks.
The main difference between these types of devices lies in the two main characteristics of the balancing machine - load capacity and diameter. It is also worth noting that the load capacity directly depends on the tire diameter.
The classification of units is also carried out according to the control method. In this case we are talking about automatic or manual devices. In the case of automatic machines, it will read all the data about the wheel independently. Setting up a manual balancing machine means that all initial data must be loaded manually by the operator. Naturally, the difference in service time on an automatic and manual machine is very different and the automatic machine works much faster. This is due to the fact that the system itself will read the geometry and other parameters of the tire. As for the technologies used by the machine to measure parameters, a variety of methods are used, including laser technologies.
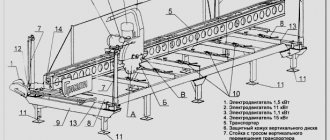
Main design elements
The machines currently in use consist of 4 main elements:
- electric motor as a driving device;
- balancing device;
- device for measuring parameters;
- correction device.
The rotation of the wheel on the shaft occurs due to the efforts of an electric motor. The oldest and most primitive machines used the operator's manual efforts as a drive. To balance a wheel, it must be placed on the shaft, after which it is centered using special cones. Very often, balancing machine errors are associated with wear of these cones. Because of this defect, the error of the entire device greatly increases.
Balancing machine for tire fitting and service stations
Balancing machines refer to equipment whose purpose is to identify areas and the degree of imbalance of the rotating parts of the car (shafts, wheels, electric motor rotors). Wheel balancing (and other parts of the car) is performed in a car repair shop or service station. Its purpose: to determine and eliminate the uneven distribution of wheel mass relative to its center. As a result of lack of balancing (when the car is moving), vibrations occur, as well as premature wear of tires, rims and suspension. In addition, the driver and passengers will feel extremely uncomfortable in the car (precisely because of such rattling noises).
Unit malfunctions
How to calibrate a balancing machine? How to reduce the error? These and other questions will inevitably arise after long-term operation of the machine, since over time its individual parts become unusable. Conventionally, all breakdowns of such units are divided into two groups - mechanical breakdown and breakdown of electrical components.
In the latter case, most often the problem is associated with the failure of one of any sensors. As for mechanical breakdowns, they usually occur due to shocks, falls or any other external influences on the equipment. Typically, you should start looking in the machine after the following signs appear:
- several inspection cycles are required to obtain a correctly balanced wheel instead of one;
- The parameters of the tested disks are determined incorrectly.
Calibrating the machine, which was mentioned earlier, is necessary in order to determine the type of failure. Once the cause is found, the faulty part is usually simply replaced with a new one. This is due to the fact that repairing a broken part is much more difficult than buying a new one, which makes repairing the machine impractical. In addition, even if you repair any element, it is most likely that it will fail again in the near future.
Working with the machine
Operating instructions for the balancing machine are included with each model separately. However, in general it can be represented as follows.
In order to start working with such a unit, you should fix the disk. This is usually done with a single nut and cone. After this, you should definitely check the reliability of the fastening, since the speed during the check may be quite high and the object may fall off. After this, the device can be put into operation, the disk or tire will spin up, and the indicators will be measured and recorded for further display. After this stage is completed, you can begin to compare the obtained data with the reference ones. The difference between them can be no more than 2 and 1.5 degrees. In this case, the error of the first indicator is considered horizontal, the second - radial.
After the initial measurements, all weights should be removed and another measuring step should be carried out. It is important to note that the disc will always stop at the heaviest point downwards. When carrying out measurements, this information must be taken into account. After stopping, the disk is rotated 90 degrees and a weight is installed on this opposite side.
It is worth saying that if the wheel has turned 45 degrees and does not spin any further, then the machine has been calibrated successfully.
Equipment supports
In order to make accurate measurements, the machine must be stable. Depending on the supports of this device, there are two main types:
- The supports can be soft. In this case, the unit is used to test the unbalanced wheel through the amplitude and frequency of movement of these supports. One of the important characteristics for a machine is the accuracy with which it makes these measurements. Therefore, for each element there are separate types of machines with soft supports.
- Rigid supports involve measuring pressure and rotor phase. Such devices are considered universal and can be used for various types of parts. For example, a balancing machine for cardan shafts also has rigid supports.
Balancing methods
Using the advice of experienced drivers, you can carry out balancing yourself the old fashioned way without using a special machine. This will take more time than a service technician would spend, but it will help save money.
If desired, wheel balancing can be done independently in a garage.
To perform the procedure yourself, you will need the following equipment and materials:
- jack;
- balancing weights;
- chalk or marker;
- a set of keys.
Interesting! To balance wheels on cast or forged wheels, it is advisable to purchase self-adhesive weights. But in winter, such weights can come unstuck due to temperature changes.
Balancing weights are required for balancing
Without removing the wheel
The self-balancing process consists of the following steps:
- Preparatory. The wheels are cleaned of dirt and stones stuck in the tires, the caps are removed, the pressure in the tire is reduced, and old weights are removed. The jack is installed on one side of the vehicle, freeing 2 wheels. Check the free rotation of the wheels. If the wheel is difficult to spin, you need to undo the cotter pin and loosen the hub nut.
- Determination of an easy point. The wheel is turned counterclockwise and waited for it to stop. Mark the top point. Then turn the wheels clockwise and mark the top point again. The midpoint between the two marks is the light point.
- Installation of weights. Using a hammer, weights weighing from 10 to 45 grams are placed on the found point, starting with the light ones. After this, they spin the wheel and wait for it to stop. The weights should be at the bottom. If it turns out wrong, the light weights are removed and heavier ones are added. It is not recommended to use more than 60 grams of weight on one wheel.
- Static balancing. As soon as the weights are at the bottom after stopping, they begin to move them apart in different directions. The wheel begins to rotate and the weights move apart. The goal of the process is to ensure that the wheel stops in a different position each time. Once this starts to happen, the weight is distributed evenly, that is, static balance is achieved.
The procedure is carried out in this sequence with each wheel. To check the correctness of the balancing, you need to drive the car at least ten kilometers at a speed of more than 90 km/h. If you don’t feel any jolts or tapping while moving, it means everything was done correctly. If the procedure is performed incorrectly, specific shocks to the steering wheel appear.
For your own confidence, at the first self-performed balancing, you can undergo diagnostics at a service station. If the specialists confirm that everything was done correctly, in the future you can carry out the procedure yourself.
Important! Self-balancing in the garage is only permissible if there is a static imbalance. Eliminating dynamic imbalance requires the use of equipment. Experts recommend contacting a service center if your car has worn tires and old bent wheels. Without special equipment, it is impossible to balance such wheels yourself.
At a homemade stand
You can make the balancing process easier by making a homemade stand in the garage. In this case, you do not have to remove the brake pads from the wheel and loosen the step nut.
A homemade stand simplifies the process of wheel balancing
The stand is mounted from an old hub with a working bearing. The hub is installed on the frame so that the wheel rotates freely and the entire structure is firmly held on the surface. It is convenient to use vertical metal posts as a frame, between which the wheel is attached. Further balancing actions coincide with the previous method of performing the procedure.
On the machine
Even an experienced motorist in a garage carries out balancing “by eye”. Therefore, there can be no complete confidence in the correctness of the process. In specialized workshops, balancing is performed on computer-controlled machines.
Modern service stations are equipped with CNC balancing machines
The machine consists of a cone-shaped support for mounting a wheel, a rotating electric motor and sensors. The wheel rotates when performing tire mounting, and at the same time the computer detects vibration and pressure. Sensor readings help to accurately calculate the weight and location of weights.
The workshops are equipped with two types of machines:
- Manual - in which the master measures the wheel with a ruler and manually enters the data.
- Automatic - information is read by sensors and displayed on the monitor in digital or graphical form.
Based on the type of supports used, machines are divided into:
- Soft, measuring wheel parameters, taking into account the vibrations of the supports.
- Rigid, measuring pressure and rotor phase.
Interesting! On rigid machines you can test various parts, but the quality and accuracy of measurements is reduced for this reason.
Most modern services are equipped with automatic balancing machines. The master puts the wheel on the shaft, tightens it with bolts and unscrews it. Sensors determine the points of axial runout. The computer determines the intensity of the push and calculates the mass of the load that must be attached to the calculated point. The computer will also inform you if the wheel cannot be balanced.
Balancing with granules
One of the newest methods of wheel balancing is the use of special granules instead of weights. The essence of the technique is to pour special granules into the tire, which slide while driving in the internal space. This free movement eliminates imbalance when driving at speed.
Modern wheel balancing techniques involve the use of microbeads
The advantage of this method is that the granules are poured once, and they perform their intended function throughout the life of the tire. The disadvantage of this balancing method is the high cost of the granules. Therefore, balancing in this way has not gained popularity at present.
Video: DIY wheel balancing
Characteristics
For each machine, the characteristics will be individual, but their set is all the same. You can consider the most important parameters based on the B-500 AE&T brand equipment.
- One of the important parameters is entering information. In this case it is manual.
- The next important characteristic is the diameter of the disk, which can be checked. For this unit, the diameter is in the range of 10-24.
- The maximum wheel weight is 65 kg.
- Since machines are also used for balancing wheels, their diameter also plays an important role. In this case, the maximum value is 960 mm.
- Another characteristic that is not decisive, but quite important, is the time required to carry out measurements. In this case it is 8 seconds.
- Power consumption is 200 W. In this case, the unit is connected to a regular network of 220 V and 50 Hz.
- The rotation speed of the disc or tire is 200 rpm.
Detailed description of parameters
You should start by manually entering parameters. This is very important, as it increases preparation time and also requires special training for the operator. Automatic devices do not have this disadvantage. As for the diameter of the disk, this does not mean the diameter of the wheel in general. The 10-24 range allows you to balance rims on cars, SUVs and small trucks.
Next, it is worth noting the maximum weight. This characteristic often goes unnoticed, and many people believe that weight is not regulated. However, installing an object with a weight exceeding the maximum usually leads to a rapid decrease in the life of the unit, which will lead to its rapid failure. As for the measurement time, as mentioned, the parameter is not too important. But it’s still worth paying attention to, for example, if there is a lot of workload. That is, for large-scale workshops this is an important characteristic.
How often to carry out
There are no clear and specific recommendations for all cars on the frequency of balancing. It all depends on the operating conditions of the vehicle, the condition of the wheels, and other factors. Experts recommend balancing:
- While changing tires. In reputable service stations, the procedure is included in the price of the car.
- If the wheel hits an object or falls into a hole. Such situations lead to disc damage and wheel imbalance.
- After 15,000 km. During the season, few car enthusiasts accumulate such a number of kilometers, so a standard car only needs balancing when changing tires.
- Every 8,000 km for lovers of an aggressive driving style.
- Before traveling over 1500 km.