Outer and inner diameter
Most often, this design parameter is measured in inches, which are easily converted into centimeters (the value is multiplied by 2.54). First of all, you need to decide what needs to be measured: the inner diameter of the pipe or the outer diameter. Products used for water and gas supply are usually measured by internal diameter. This is due to the fact that this indicator determines the throughput of the structure.
The outer diameter can have different values depending on the wall thickness (the mechanical strength of the entire product depends on it). According to GOST 355–52, each subsequent pipe diameter differs from the previous one in better throughput (by 50%). The permeability of a structure is often called the conditional (nominal) diameter. In this case, the indicator usually differs from the internal diameter (by 1-10 mm). This important parameter is considered the main characteristic of the product, which is taken into account during the design and installation process.
If the product is not available
When it is impossible to take direct measurements of the pipe for some reason, you can use the copying method.
- For this purpose, attach a ruler or a small object to the pipe, the linear parameters of which are known in advance. For example, a matchbox whose length is 5 cm.
- Next, take a photo of this area.
- Make further calculations and measurements using the photo.
- To do this, you need to measure the visible thickness (in mm) of the pipe in the picture.
- Then convert the data you received into the actual dimensions of the product, taking into account the scale of the photograph.
Many home craftsmen are interested in how to measure the diameter of a pipe. After all, when troubleshooting problems in a water supply or drainage network, you often have to replace pipes with new ones or repair old ones.
This is required not only for the listed systems, but also when installing a gas system or chimney. Professional craftsmen know well how to select assortment sizes for a water supply system, or any other system.
When repairing a water supply or sewer system, it is necessary to accurately determine the diameter of the line.
Before measuring the size of the assortment, you should take into account that the technological features of laying and carrying out calculations when working with steel and plastic lines are different.
For this reason, it is necessary to first gain an understanding of the standard sizes of pipe-rolling materials for pipelines, and only then measure them. Without this knowledge.
Rolled steel pipes are primarily determined by their internal volume, measured in inches. In accordance with these units, you can find the names “inch” and “half-inch” pipe materials. One inch is equal to 25.4 mm, and half of it is correspondingly defined as 12.7 mm.
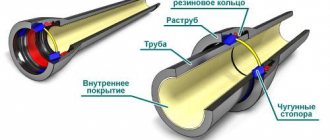
Plumbing fixtures are in no hurry to measure the outer diameter. Often installation can be done without it. It is necessary to measure this value in cases where it is necessary to measure a pipeline fastened with joints on a threaded connection.
Usually it is cut on the outer part
tubular product, and its value depends on the dimensions of the wall of the tubular product. During these actions, you should remember that if you measure pipes with different internal volume indicators, the wall size will be different.
To make it easier to measure and calculate the amount of materials needed for a pipeline, you can use a special thread system to indicate the external volume of pipe products. These values differ from the usual indicator, which can be measured in mm.
To correctly determine the size of pipe products in millimeters or find out their dimensions in inches, you need to take into account the following information.
For example, if the diameter of the metric thread knurling is designated M16, then the tubular product has an outer volume of 16 mm. In the version with pipe threads, all this is different. In inches these calculations are slightly different.
The outside diameter of a half-inch product does not reach 21 millimeters, and its thread knurling is the same in size. And this product gets its name “half-inch” because of the volume inside. In inches this value is denoted - ½. To make it easier to convert inches to mm, it is recommended to use special tables.
We measure with a caliper
Using this high-precision instrument, parameters of various structures are measured. How to measure the diameter of a pipe with a caliper? To do this, you need to spread its jaws, insert the product into them and bring them together so that they are pressed against the surface. When closing, the jaws must be parallel to the cross-sectional plane of the pipe, otherwise the measurement will be incorrect. The internal diameter is also measured with a caliper. On its reverse side there are jaws that are placed inside the structure and moved apart until they abut the walls.
Sometimes it is necessary to measure the diameter of an installed pipe that is too large. In this case, you can measure the chord with a tool and calculate the diameter mathematically. We spread its lips to the maximum distance and apply it to the pipe. The resulting indicator is the length of the chord. To calculate, you will also need to measure the height of the device’s jaws. The diameter is calculated using the formula:
D = (2L/4H)+H.
If the jaws are too long, then you can place some part (a block, etc.). Then the height will be calculated using the formula:
H = H1-H2.
What are calculations for?
Bernoulli's law, known to many since school, says that the speed of fluid flow in a pipe depends on pressure and diameter. Accordingly, if the diameter of the pipe is small, the pressure will be too high, which can lead to pipe rupture. And if the pressure is lowered, the speed of movement of the liquid will also drop, and as a result, the pressure with which water flows from the taps.
Today, several types of pipes are used to create a water supply system:
- Metal (from alloys of copper, cast iron, steel).
- Plastic (made from thermoplastic polymers - polyethylene, PVC, polypropylene).
- Composite, or reinforced (in them layers of polymer and metal mutually reinforce each other).
The strength characteristics of these materials differ significantly, and therefore the parameters of the pipes used to create a water supply system differ from each other.
The weight also differs. Therefore, taking a pipe “with a reserve” may also not be justified: it will cost more, weigh more, make installation more difficult and require more reliable brackets. However, the gain in throughput may not justify all these shortcomings. Therefore, in order for pipes to be optimally suited to the plumbing system, it is necessary to calculate the outer and inner diameter, length and thickness of the pipe walls. To find out how to choose the right plastic pipes for sewerage: selection, dimensions, read this article.
We measure with a ruler and tape measure
If the cross section is visible on the pipe, then the diameter can be measured with a regular ruler. We apply it to the cut area so that the scale runs exactly in the center. We take the distance between the required points (for the internal or external diameter). The distance between the extreme points will be the outer diameter. If you need an internal size, you can find out the wall thickness and subtract it from the resulting figure.
Everything is clear with a ruler, but how to measure the diameter of a pipe with a tape measure? This tool is suitable for solid and large structures that are difficult to reach. We wrap the product so that the tape with the scale fits tightly, and find the place where it intersects. The resulting figure is the circumference. To get the diameter, divide it by Pi (3.14).
Pipe measurements using improvised means
Most often, the well-known caliper is used to measure the diameter of a pipe.
But you may not have it, or if you do have it, it may not be possible to measure a large pipe diameter with it. In this case, the simplest set of tools and knowledge is used: a flexible ruler (similar to the type of measuring tape used in sewing); tape measure; school knowledge of the number Pi (it is equal to 3.14). With such a set of tools you can measure the diameter of not only a pipe, but and any other round object - a rod, column or garden bed. We only need to make one measurement - determine the circumference of the pipe using a tape measure or flexible ruler. To do this, a measuring tape or tape measure is placed on the surface of the pipe in its widest part. The resulting circumference value should be divided by 3.14.
For more precise dimensions, the value used is 3.1416. It should be noted that imported supplies of pipes are accompanied by documentation that already indicates the values of pipe diameters in inches. To convert these values to centimeters, they are multiplied by 2.54. Similarly, to convert centimeters back to inches, multiply by 0.398.
Copy method
If you don’t have any tools at hand, but have a camera, then you can use the copying method. How to correctly measure the diameter of a pipe? To do this: - take an object with known dimensions (for example, a brick);
— place it on the pipe, along its length or next to the cut; — we photograph this area so that we can evaluate the difference in size; — we carry out calculations based on photographs; — using the data obtained, we estimate the actual dimensions (it is important to take into account the scale).
How to calculate weight
When purchasing a steel pipe, it is very important to determine its weight in advance. After all, many transportation and installation issues depend on this parameter. Several methods are used to determine the weight of a pipe.
You can most accurately determine the weight of 1 linear meter of pipe, armed with the table given in GOST. However, this method requires certain technical skills and the ability to use documentation.
For an approximate calculation (such accuracy is usually sufficient), you can apply the rule: Weight = (Diameter - Wall thickness) * Wall thickness * 0.025. The last number is the coefficient that is used to calculate the weight of round pipes. For a square section, the coefficient is 0.0316, for a rectangular section - 0.0158.
Many pipe manufacturers offer pipe calculators based on formulas. These are special forms on the manufacturers’ websites on the Internet. You need to enter the pipe parameters in the windows, and the program itself will determine the weight.
We measure with a micrometer
High-precision measurements (up to 0.01) of the pipe can be made using a micrometer. It should be noted that they are convenient for measuring small products. The tool is a bracket equipped with a support heel and a stem with a high-precision thread (for screwing in a microscrew). On the stem you can see a scale with millimeters and their hundredths. This equipment allows you to obtain more accurate indicators.
How to measure the diameter of a pipe with a micrometer? We place the structure between the end of the screw and the heel. We begin to rotate the ratchet handle until it clicks three times. First, we look at the lower scale of the stem, showing the number of whole millimeters. We check for the presence of the risk, which is on the right. If it is not visible, we take readings from the drum. If there is a risk, add 0.5 mm to the resulting number. Measurements on the drum are determined relative to the line on the stem between the scales.
Laser sensors
Modern laser sensors have been created to take dimensions from pipes (and not only). Their advantages: lack of contact with the surface, the ability to use on different structures (hot, sticky), durability and speed of obtaining results. How to measure the diameter of a pipe with such sensors? There are several measurement methods.
With laser triangulation, the beam from the sensor creates a spot on the surface of the structure. Behind the laser is a camera scanner that sees it from different angles. Using these indicators, the digital processor calculates the distance between the sensor and the product.
We measure the diameter using the shading method. In this case, the sensor serves as an emitter and a receiver, but they are located in different housings. Inside it, the laser beam is reflected from a rotating mirror, bends around the measurement area and creates a virtual strip of light. Inside the device, a moving beam passes through a special diode, which measures the duration of shading (corresponds to the size of the object).
Another option is the principle of light section. The sensor is equipped with a laser, camera and electronic circuitry. The laser creates a line perpendicular to the product, and the camera is positioned at a certain angle to it. Any curvature causes the laser line to deform, which is what pushes the sensors away when calculating dimensions.
It was described above how to measure the diameter of a pipe. But it is important to know that some structures have curvature (maximum 1.5 mm per 1 m of length). In this case we talk about their ovality. This parameter is determined by the formula: the difference between the large and small diameters is divided by the nominal one. Allowable ovality: no more than 1% for pipes with a wall up to 20 mm, no more than 0.8% - with a wall more than 20 mm. This parameter is very important because it affects the performance characteristics of the structure.
Monitoring pipe parameters in production conditions
Production control of pipe parameters
The outer diameter of water or sewer pipes in large production conditions is controlled and checked using a more complicated formula: D = L: 3.14 - 2∆p - 0.2 mm.
In this formula, in addition to the already known values, the symbols ∆p mean the thickness of the tape measure in mm, which you use to measure the diameter, and “0.2 mm” from the formula are the permissible deviations that take into account the fit of the tape measure to the pipe. The permissible deviation value for pipes with a cross-section of 200 mm is ±1.5 mm.
When measuring large diameter pipes, permissible deviations are measured as percentages. Example, for products ranging in size from 820 to 1020 mm, permissible deviation = 0.7%. For such measurements, an ultrasound-based measuring system is used.
In large production conditions, the wall thickness of pipes is measured with a caliper with a scale division of 0.01 mm. The permissible deviation from the nominal thickness towards reduction should not exceed 5%.
The values of pipe curvature are also subject to control, which should not be higher than 1.5 mm per linear meter of pipe length. The total curvature of products in relation to its length should not be more than 0.15%. The ovality of the pipe ends is determined by the ratio of the difference between the largest and smallest diameters to the nominal diameter of the pipe.
The value of this parameter should not exceed 1% for pipes with a wall thickness of up to 20 mm and not higher than 0.8% for walls above 20 mm.
The ovality of the pipe can be determined by measuring the diameter of the pipe end using an indicator clamp or bore gauge in two mutually perpendicular planes.
Simple school knowledge and careful use of simple tools will significantly simplify your task - how to measure the diameter of a pipe using improvised means.