To accurately distinguish brass from copper at home, it is enough to know the composition and some characteristics of these materials.
Copper is a pure metal, and its alloy with zinc is called brass. Due to their different compositions, these materials have several important differences:
- Color . Copper has a reddish tint, while brass is yellow.
- Weight . Copper is slightly heavier than brass.
- Hardness _ Copper is softer, brass is harder.
- Density _ For copper it is 8920 kg/m3, for brass it is from 8300 to 8700 kg/m3.
It should be noted right away that it is not possible to recognize at home that what we have in front of us is a metal or its alloy using a magnet. Both materials are not attracted to them.
However, there are several ways to distinguish copper from brass without resorting to spectral analysis in the laboratory. All of them are described below - from the simplest to the most complex.
Briefly about the element
Pure copper (Cu) is a golden-pink metal with high ductility, thermal and electrical conductivity. Chemical inertness in an ordinary non-aggressive environment is ensured by a thin oxide film, which gives the metal an intense reddish tint.
The main difference between copper and other metals is color.
. In fact, there are not so many colored metals: only gold, cesium and osmium are similar in appearance, and all elements included in the group of non-ferrous metals (iron, tin, lead, aluminum, zinc, magnesium and nickel) have a gray color with varying intensity of shine.
An absolute guarantee of the chemical composition of any material can be obtained only through spectral analysis. The equipment for carrying it out is very expensive, and even many expert laboratories can only dream of it. However, there are many ways to distinguish copper at home.
with a high degree of probability.
Characteristics and features
Copper appears as a golden-pink metal, which when exposed to air acquires an oxide coating of a yellowish-red hue. Just like gold, cesium and osmium, it is characterized by individual coloration. There are some other features of the metal:
- It has a high degree of electrical conductivity (in second place after silver), especially when used in its pure form. The admixture of other metals or any substances in the composition reduces its conductivity.
- The metal is strong and durable, therefore it is widely used in the production of pipes and roofing materials.
- The attractive color and shine of copper made it possible to use it for making dishes, various decorative items, objects and interior decorations.
- An important feature of copper is the oxidation process. When interacting with a humid environment, the metal acquires a unique coating. Thanks to the patina layer, the metal is protected from corrosion and various damages. This property of copper is often used by artists and sculptors. By artificially exposing the metal to moisture, an unusual color of the product is obtained. An example is the Statue of Liberty in the USA. Over the years, a patina began to form on it, and the monument acquired a green tint. Now Americans call their symbol “Green Lady.”
- It is highly energy efficient. The good thermal conductivity of the metal allows for significant energy savings. If the heating system is equipped with insulated copper pipes, heat loss is reduced many times. Conversely, in cooling systems, the metal maintains the set temperature.
- This is an essential trace element involved in many processes of the human body: hematopoiesis, sugar and cholesterol metabolism, promotes the absorption of iron, improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system and brain.
Many foods are rich in this metal. The daily dose required for the normal functioning of the body is from 1.5 to 3 mg per day. It must be borne in mind that an insufficient amount has a detrimental effect on the human body.
PROPERTIES
Copper is a golden-pink ductile metal; in air it quickly becomes covered with an oxide film, which gives it a characteristic intense yellowish-red hue. Thin films of copper have a greenish-blue color when exposed to light.
Along with osmium, cesium and gold, copper is one of the four metals that have a distinct coloration that is different from the gray or silver of other metals. This color tint is explained by the presence of electronic transitions between the filled third and half-empty fourth atomic orbitals: the energy difference between them corresponds to the wavelength of orange light. The same mechanism is responsible for the characteristic color of gold.
Copper has high thermal and electrical conductivity (it ranks second in electrical conductivity among metals after silver). Specific electrical conductivity at 20 °C: 55.5-58 MS/m. Copper has a relatively large temperature coefficient of resistance: 0.4%/°C and is weakly dependent on temperature over a wide temperature range. Copper is diamagnetic.
There are a number of copper alloys: brass - with zinc, bronze - with tin and other elements, cupronickel - with nickel and others.
RESERVES AND PRODUCTION
The average copper content in the earth's crust (clarke) is (4.7-5.5) 10−3% (by mass). In sea and river water the copper content is much lower: 3·10−7% and 10−7% (by weight), respectively. Most copper ore is mined by open pit mining. The copper content in the ore ranges from 0.3 to 1.0%. World reserves in 2000 were, according to experts, 954 million tons, of which 687 million tons were proven reserves; Russia accounted for 3.2% of total and 3.1% of confirmed world reserves. Thus, at the current rate of consumption, copper reserves will last approximately 60 years. Copper is obtained from copper ores and minerals. The main methods for obtaining copper are pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy and electrolysis. The pyrometallurgical method involves obtaining copper from sulfide ores, for example, chalcopyrite CuFeS2. The hydrometallurgical method involves dissolving copper minerals in dilute sulfuric acid or ammonia solution; From the resulting solutions, copper is replaced by metallic iron.
APPLICATION
Due to its low resistivity, copper is widely used in electrical engineering for the manufacture of power cables, wires or other conductors, for example, in printed circuit wiring. Copper wires, in turn, are also used in the windings of energy-saving electric drives and power transformers. Another useful quality of copper is its high thermal conductivity. This allows it to be used in various heat removal devices and heat exchangers, which include well-known radiators for cooling, air conditioning and heating. Alloys using copper are widely used in various fields of technology, the most widespread of which are the above-mentioned bronze and brass. Both alloys are general names for a whole family of materials, which in addition to tin and zinc may include nickel, bismuth and other metals. In jewelry, alloys of copper and gold are often used to increase the resistance of products to deformation and abrasion, since pure gold is a very soft metal and is not resistant to these mechanical influences. The predicted new mass use of copper promises to be its use as bactericidal surfaces in medical institutions to reduce intra-hospital bacterial transfer: doors, handles, water stop valves, railings, bed rails, table tops - all surfaces touched by the human hand.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Mineral color | copper-red, fading to black or green in air |
| Stroke color | copper red |
| Transparency | opaque |
| Shine | metal |
| Cleavage | No |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 2,5-3 |
| Strength | malleable |
| Kink | jagged |
| Density (measured) | 8.94 - 8.95 g/cm3 |
| Radioactivity (GRapi) | 0 |
| Magnetism | diamagnetic |
OPTICAL PROPERTIES
| Color in reflected light | pinkish white |
| Pleochroism | does not pleochroate |
| Luminescence in ultraviolet radiation | not fluorescent |
CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC PROPERTIES
| Point group | m3m (4/m 3 2/m) - hexoctahedral |
| Space group | Fm3m (F4/m 3 2/m) |
| singonia | cubic |
| Cell Options | a = 3.615Å |
| Morphology | cubes, dodecahedrons and tetrahexahedrons; rarely octahedra and complex combinations; thread-like, tree-like |
| Twinning | {111} twins according to the spinel law |
Benefits of Copper
- High anti-corrosion properties;
- Aesthetically attractive appearance;
- High thermal conductivity;
- Good indicators of flexibility and ductility while maintaining strength;
- Low level resistance.
Flaws
High price. The main (conditional) disadvantage of copper can be considered the rather high cost of the material.
Other cases of fire and acid testing
Exposure to flame is used not only to identify metal relative to aluminum. For these purposes, a gas stove, lighter or fire is sufficient. Heating copper leads to the formation of its oxide, which affects the color change. The surface of the metal gradually becomes dull until it acquires a completely dark shade.
Nitric acid is another identifier for copper at home. It is also important to be careful here. It's better to just drip the liquid onto the metal. Pure copper at the point of contact will turn blue-green.
Video - how to distinguish aluminum from copper:
Biological value for humans
Copper belongs to the category of vital elements, and the body of an adult contains about 100 grams of this metal. A reassessment of the toxicity of this substance was carried out in 2003 by the World Health Organization. Studies have found that copper is not a cause of diseases of the digestive tract, and does not provoke the development of Wilson-Konovalov disease (hepatocerebral dystrophy affecting the liver and brain), as previously thought. Scientists have concluded that a lack of copper is more harmful to human health than its excess.
The bactericidal properties of copper have been known for a long time, and recent studies in this area have confirmed the effectiveness of the metal in the prevention of swine flu and infection by Staphylococcus aureus. In experiments, it was found that 99% of pathogenic bacteria die on a copper surface within 2 hours. Therefore, copper and its alloys are widely used for water disinfection. In Europe, door handles, locks, hinges and railings are made from this metal, which are installed in medical institutions and public places.
Sources
- https://vseprokamni.ru/metal/kak-vyglyadit-med.html
- https://cuprum-metall.ru/informatsiya/med/
- https://othodynet.ru/othody/med-tsvet-osobennosti-dobychi-harakteristika-metalla
- https://mineralpro.ru/minerals/copper/
- https://metalik-msk.ru/kak-otlichit-med-ot-latuni.html
- https://met-all.org/cvetmet-splavy/med/osnovnoj-tsvet-i-ottenki-medi.html
- https://ocvete.ru/raznye-cveta/mednyj-cvet.html
- https://xlom.ru/vidy-metalloloma/uchimsya-opredelyat-med-i-otlichat-ee-ot-drugix-metallov-i-splavov
- https://instanko.ru/drugoe/kak-opredelit-med.html
- https://rcycle.net/metally/cvetnye/kak-opredelit-latun-ili-med-ih-osnovnye-otlichiya
- https://cu-prum.ru/med.html
[collapse]
DIFFERENCE IN HARDNESS
For this method of comparing copper and brass , suitable objects are suitable for bending and making dents:
- Copper, as a purer material, has greater ductility and the ability to deform without violating its integrity;
- Brass, which is an alloy of copper and reinforcing additives, has low ductility and higher strength and brittleness compared to copper, and therefore, if you try to deform, it will have greater resistance and may burst.
A LITTLE ABOUT BRASS
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. The percentage of zinc can vary from 5 to 45%. In some cases, the percentage of zinc content may slightly exceed 45%. The zinc in brass is intended to improve the quality of the metal, while significantly reducing its cost compared to the original material - copper.
Brass is divided into two main groups in its composition:
- Two-component. They consist of two components - copper and zinc. Moreover, the latter is the main binding component and usually makes up from 30 to 50%. Two-component brass containing up to 97 percent copper is called red. Their second name is “tompak”. Brass with a copper percentage not exceeding 35 is called yellow;
- Multicomponent. Alloys containing several alloy additives. The most commonly used amplifiers are manganese, tin, nickel, lead and silicon.
The marking of a brass alloy directly depends on the type and percentage of components. Thus, two-component brass is marked with alphabetic and numerical designations, where L denotes the material, and subsequent numbers indicate the percentage of copper content. Multi-component alloys have more complex markings, but the essence remains the same as simple brass.
Basic properties of brass
- Ease of processing under pressure;
- Good anti-corrosion resistance;
- High temperatures, aggressive environments, and exposure to sulfur dioxide increase the risk of corrosion;
- When temperatures drop, ductility increases, but strength does not decrease;
- When exposed to temperatures from 200 to 600 degrees, fragility increases significantly;
- Good anti-friction qualities;
- Good ability to weld with other metals.
Application areas of brass alloy
- Manufacturing of bushings and other transition parts;
- Production of components for motor units;
- Plumbing equipment and accessories;
- Decoration elements of various directions;
- Shipbuilding;
- Army needs.
Advantages of brass
When comparing brass with copper, there are common properties and characteristics:
- Ease of processing and polishing;
- Aesthetic appearance;
- Loyalty of tombak when welding with other metals;
- High anti-friction properties.
And yet: how to distinguish copper from brass ? There are many indicators by which you can see how copper differs from brass, such as the difference in temperature, color, hardness, etc...
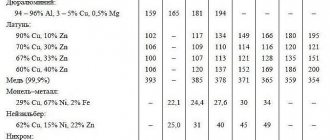
DIFFERENCE OF COPPER AND BRASS IN SPECIFIC GRAVITY AND DENSITY
The brass alloy has a lower density compared to copper, and therefore the specific gravity will be less than that of copper. Determining which is heavier: copper or brass, if we are talking about a small volume, without using scales will be quite problematic.
Determining the type of material using a scale
- Determine density. This characteristic has fixed values and corresponds to 8.96 g/cm3 for copper and 8.73 g/cm3 for brass;
- Selection of necessary equipment. Such equipment will be: spring scales, tape measure, calculator and a cylindrical container with water;
- Determination of mass by weighing;
- Mass is converted to gram unit of measurement;
- Calculation of volume in cubic centimeters. For samples of the correct shape, it is necessary to measure the length, width and height, and multiply the values. For objects of irregular shape, the calculation is carried out by immersion in liquid and calculating the displaced volume;
- Calculation of density based on the data obtained. For this action, mass and volume are converted into the required dimensions and divided among themselves.
The results obtained are compared with standard indicators and become determining what kind of material the sample is.
Use of chemical reagents
The use of any reagents is a fairly effective, but destructive way to determine the type of copper alloy . It is carried out in several stages:
- it is necessary to remove chips from the surface of the sample or separate a small piece of thickness;
- prepare a solution of nitric acid (HNO3) in a 1:1 ratio with water;
- place the prepared shavings in the reagent;
- Heat the container with the acid solution to boiling temperature and maintain it until the chips are completely dissolved.
- The presence of brass will leave the solution clear without changing color .
- Bronze produces a white precipitate as a result of the reaction of tin with acid.
How to distinguish copper by eye
Visual examination of a non-ferrous metal or alloy is not the most effective method for identifying copper. It is sufficient to distinguish copper from aluminum, nickel and zinc.
The natural color of copper is red-pink, without distortion it is easy to determine in natural light. This is important to consider because artificial light can give the metal a yellowish-green tone.
During visual examination, it is necessary to remove the oxide from the metal. This is easy to do by treating the surface of the product with a file or cutting it.
It is difficult to distinguish copper from bronze and brass, as well as from copper-plated aluminum. At receiving points, copper is valued more expensive than bronze, aluminum and brass. For this reason, it is necessary to be able to accurately identify this non-ferrous metal in various ways.
Copper Applications
Due to their valuable qualities, copper and copper alloys are used in the electrical and electrical engineering industries, in radio electronics and instrument making. There are alloys of copper with metals such as zinc, tin, aluminum, nickel, titanium, silver, and gold. Less commonly used are alloys with non-metals: phosphorus, sulfur, oxygen. There are two groups of copper alloys: brass (alloys with zinc) and bronze (alloys with other elements).
Copper is highly environmentally friendly, which allows its use in the construction of residential buildings. For example, a copper roof, due to its anti-corrosion properties, can last more than a hundred years without special care or painting.
Copper in alloys with gold is used in jewelry. This alloy increases the strength of the product, increases resistance to deformation and abrasion.
Copper compounds are characterized by high biological activity. In plants, copper takes part in the synthesis of chlorophyll. Therefore, it can be seen in the composition of mineral fertilizers. A lack of copper in the human body can cause deterioration in blood composition. It is found in many food products. For example, this metal is found in milk. However, it is important to remember that excess copper compounds can cause poisoning. This is why you should not cook food in copper cookware. During boiling, large amounts of copper can leach into food. If the dishes inside are covered with a layer of tin, then there is no danger of poisoning.
Iodine test
You can check the authenticity of the metal using an iodine solution purchased at a pharmacy. A drop of iodine is applied to the surface and left for several seconds. Iodine will not harm noble metals - gold, platinum, silver. If the color of a drop of iodine does not change, and after removing it with a napkin, no traces or stains remain, this indicates the authenticity of the metal. If darkening is visible at the place of the drop, then this is a low-quality alloy or an outright fake.
Iodine testing of gold
Exposure to high temperatures
Heating to 600˚C allows you to determine the type of copper alloy. The alloying impurities included in its composition react to high temperatures in different ways. Bronze simply heats up, and if you try to bend its sample, it will most likely break. In brass, zinc oxidation when heated causes a white coating to appear on the surface. The metal becomes more ductile and does not break when deformed.
To carry out such a test, you need a fairly powerful gas burner, since the flame of a gas stove, much less a lighter, will not be enough.
How to distinguish copper from aluminum
Naturally, metals are easy to distinguish by color. The situation becomes more complicated when it is necessary to determine what the cable cores are made of. Tinned copper takes on a silvery tint, while copper-plated aluminum takes on a yellow tint. The result is that it is extremely difficult to distinguish metals from each other by color.
Tinned copper in cables
The best option is to measure the resistance. For a copper twisted pair cable about 100 meters long, the parameter value reaches 4–8 ohms. The resistance of a similar aluminum cable is significantly higher: 12 – 20 Ohms. This method is good because there is no mechanical impact on the metal.
The second method is bending/extension of the vein. The aluminum conductor will break quickly. The next option is a flame test. The melting point of aluminum is 600 °C, that of copper is much higher.
How to determine copper wire or aluminum
Advantages of copper cable. Why do many people prefer cables with copper filling?
Copper cable has better conductivity compared to aluminum. With the same cross-sectional area of the cable core, copper can withstand loads significantly greater than aluminum.
For example, with a cross-sectional area of 10 mm2, an aluminum conductor can withstand an electric current of up to 50A, and a copper conductor of the same cross-section can withstand a current of up to 70A.
That is, if it is necessary to replace an aluminum cable along a ready-made main line and the thickness of the cable is limited, and the expected load has increased, then laying a copper cable instead of aluminum will allow, with the same cable dimensions, to increase the permissible load.
Copper cable has better conductivity compared to aluminum. With the same cross-sectional area of the cable core, copper can withstand loads significantly greater than aluminum.
For example, with a cross-sectional area of 10 mm2, an aluminum conductor can withstand an electric current of up to 50A, and a copper conductor of the same cross-section can withstand a current of up to 70A.
That is, if it is necessary to replace an aluminum cable along a ready-made main line and the thickness of the cable is limited, and the expected load has increased, then laying a copper cable instead of aluminum will allow, with the same cable dimensions, to increase the permissible load.
Copper cable has greater chemical resistance compared to aluminum. Copper is a noble (inert) metal and does not react chemically with most substances. And aluminum is exposed to chemical attack, as a result of which it is destroyed.
Copper cable has greater mechanical strength compared to aluminum. This can be observed at the connection points of aluminum cables in home wiring. In the area of the terminals, the aluminum core is always very crushed and often destroyed, which never happens with a copper core.
Advantages of aluminum cable.
Aluminum cable is suitable for temporary wiring. Due to its low cost (low cost is at least three times cheaper than a copper cable), you can save a lot on this type of cable.
First of all, it is, of course, lightweight. This is an indisputable advantage: it is more convenient to roll out a coil or coil with a lightweight cable, and when it comes to installing power lines, then lightness becomes the most valuable quality.
But in addition to the advantages, there are also disadvantages of aluminum cable.
Aluminum as a conductor, compared to copper, has a higher electrical resistivity - 0.0271 Ohm x sq. mm/m versus 0.0175 Ohm x sq. Mmm. The difference is almost double!
It is the high resistivity that negates the advantage of aluminum being lightweight. It turns out that in order to ensure the same conductivity, we will have to take a much more powerful, and therefore heavier, aluminum conductor than if we used copper.
Everyone knows very well that aluminum is a corrosion-resistant metal. But from the chemistry course we know that this is not entirely true. Aluminum itself oxidizes in air very quickly. But the resulting thin film of oxide protects it from further chemical destruction.
But the protective film already has slightly different properties than the metal itself. In particular, it is no longer such a good conductor. This means that increased contact resistance may form at the point of electrical contact with the aluminum oxide film. And this leads to heating of the contact, which in turn leads to an even greater increase in electrical resistance.
This is such a vicious circle. The result is melted contacts, an open circuit or unreliable power supply.
You have to look for the problematic contact, tighten it, or change the clamps, and aluminum subjected to prolonged heating, which already does not have much ductility, can break off from any careless movement. Then a cable replacement will be required, which is not always technologically possible.
However, the use of a particular cable also depends on the purpose for which it is used. Each electrical appliance has its own power, which will directly determine the cross-section of the cable, and therefore its filling.
In the cable abbreviation, to denote an aluminum core, the letter A is at the beginning. That is, A is added to the already familiar rulers, and the result is AVVG, AVVGng, AVVGng(A)-LS, AVBbShv, AVBShv, respectively.
If you have decided on the type of cable that is right for you, be sure to check the quality of the product before making a purchase. A cable made of any metal must be stored in appropriate conditions and have all the necessary technical documentation.
Advantages of aluminum wiring
The fact that aluminum, not being a standard for electrical wiring, is preferable in its quality in residential buildings is due precisely to its advantages over other metals.
Distinguish copper from brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. Not surprisingly, visually they are very similar. The more zinc in the alloy, the lighter the brass. So copper is definitely redder. In addition, brass is a harder metal; it is difficult to bend without additional heat treatment (casting). So we try to bend it or check for a tooth.
Brass is also lighter. Electrodes for the plug of any electrical household appliance are made of brass. So at home there is always something to compare with.
Determination by color
The easiest way to determine whether a product is copper or brass is by its color. For accuracy, it is recommended to thoroughly clean the metal surface from dirt and oxide film. As mentioned earlier, copper has a reddish tint, sometimes brownish or pink.
If the product under study has a yellowish color, reminiscent of gold, then this is most likely brass. And the more pronounced the yellowness, the greater the proportion of zinc in the alloy.
You can determine the metal by color by comparison with a known product. In everyday life, as a copper sample, you can use an electrical wire, cleared of insulation and protective varnish. Brass can be seen on the plugs of electrical appliances - their pins are made from this alloy.
How to distinguish copper from brass and bronze
Both brass and bronze are derivatives of copper. In the first case, it is an alloy with zinc, in the second - with tin, and with a small content of these components, it is very difficult to identify the metal by color.
You can distinguish copper from another metal chemically:
- in the area exposed to nitric acid (one drop is enough), the copper surface will acquire a characteristic blue-green tint;
- copper elements do not change color when in contact with hydrochloric acid (the reagent can only clean them of patina), and a white coating (zinc chloride) appears on the surface of brass under such influence;
- in a saline solution heated to 50 °C (200 g of salt per 1 liter of water), copper changes color after 15-20 minutes, and bronze is immune to such effects.
Copper is softer than brass and bronze, but bending comparisons may not be entirely accurate due to differences in product parameters. A reliable way to check is to remove chips. Pure copper - soft, ductile and pliable - is curled into a curl, and brass shavings remain in the form of a straight, needle-like strip.
When manually pressing on a copper surface with a metal object, a dent remains, but bronze can withstand such loads without visible consequences.
Determination using chemistry
This method is one of the simplest and most accessible, and at the same time quite accurate. To determine the composition of the metal, you will need a solution of hydrochloric acid. Such liquids are often used to clean contacts when soldering in radio electronics. Accordingly, acid can be bought at any radio store. And it's inexpensive.
Without going into details and without resorting to chemical formulas, the essence of the test is as follows. A few drops of acid must be applied to the surface of the metal being tested. If it is copper, then it will simply be cleaned and acquire its natural reddish or pinkish tint. If we have brass in front of us, then a chemical reaction will take place on its surface with the release of a white substance - zinc oxide.
For those familiar with electrical engineering
Very often, copper cores from electrical cables are sold as scrap non-ferrous metals, and there are often cases when copper-coated aluminum is used in the production of electrical products. This material has a significantly lower density, but due to its irregular geometric shape, determining the volume to calculate the density is quite difficult. In this case, copper can be determined by electrical resistance (of course, if you have the appropriate instruments - a voltmeter, ammeter, rheostat). We measure the cross-section and length of the core, take instrument readings, and Ohm’s law will help you. Resistivity is a fairly accurate characteristic by which any metal can be identified with a high degree of reliability.
Determining the authenticity of copper using improvised means
Copper is a widespread metal, because man was one of the first to master it.
Due to its ductility, malleability and high strength, copper has long been used to make weapons, kitchen utensils, jewelry, coins and art objects. Today, since it is also the best conductor of heat and electricity, it is most often used in the production of electrical products. In nature, it can be found both in nuggets and in the form of compounds. In order to correctly determine the authenticity of copper at home, it is important to remember that its properties are greatly influenced by the content of any impurities. In its pure form, it has a number of characteristic features; you just need to figure out how it differs from other metals.