19.03.2020
- What is a CNC Router
- Features of the design and device of a CNC milling machine
- Working principle of CNC milling machine
- Types of CNC milling machines
- Cantilever type machining centers
- Non-cantilever equipment
- Setting up a CNC milling machine
Advanced equipment for complex processing of metals, polymers, and wood deserves close attention. Therefore, we will comprehensively consider the configuration options and capabilities of a Russian-made CNC milling machine, and also analyze its types and general setup principles. We offer practically useful information for understanding how one model differs from another and for what tasks to use one or another of them, as well as for making the right choice and commissioning.
Separately, we note the demand: today ME650, ME850, GQ600 from the Izhevsk company Sarmat (and their analogues from domestic and foreign brands) are widely used in advanced industrial enterprises. Moreover, they are actively used even in conjunction with 3D printers, which makes it possible to produce parts and components of the most complex shapes.
What is a CNC Router
This is a device also used for processing and creating workpieces by cutting, but with computer numerical control (the abbreviation CNC is common in English-speaking countries). All commands are preset, executed and controlled electronically - the operator does not need to do anything manually.
This solution allows you to:
- increase labor productivity;
- eliminate errors caused by human factors.
As a result, operation is simplified and accuracy, and therefore the overall quality of parts and components, is improved.
Each modern model (like the already mentioned GQ600 or ME650) is a processing center, and multifunctional - turning, engraving, and so on.
Features of the design and device of a CNC milling machine
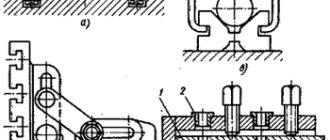
- All mechanisms and functional units are fixed to the frame (1).
- The movement of the work table (2), where workpieces and auxiliary devices are fixed using T-shaped grooves, is carried out both back and forth (transversely) and left and right (longitudinally) - the vectors are set by guides (3).
- The spindle (4) clamps the cutter (cutting tool) and ensures its rotation, and the quality of processing directly depends on its vibration resistance and rigidity. It, in turn, is located on a column (5) capable of moving up and down.
- The door (6) opens and closes access to the area for performing planned operations.
- Protective covers (7) protect the operator from pressurized coolant (cooling lubricant) and chips.
- All cutting tools are located in a drum-type magazine (8), and the desired one is selected and installed in the spindle automatically - by a special device, in accordance with a given program.
- The bracket-mounted control stand/control panel (9) can be positioned to suit your needs.
Machine characteristics
The characteristics of such machines directly depend on the characteristics of the spindle, the speed of movement and the size of the table. Spindle speed is the range of rotation speed of its head. Drive power is the rated power of the air turbine, electric motor or piston motor that drives the spindle.
The number of cutters that the tool magazine supports is also an important criterion, as it gives the machine a certain versatility. On simple machines, only one tool can be operated at a time.
Motion options for milling machines include:
- number of axles;
- maximum movement along the X axis;
- maximum movement along the Y axis;
- maximum movement along the Z axis.
As for the size of the table, its length is measured parallel to the main axis of movement. The width of the table is measured perpendicular to the main axis of movement.
Working principle of CNC milling machine
In computer-aided design systems (AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Compass-3D, etc.) and a graphic editor (Corel Draw, AutoCAD or other similar) an accurate vector image of the workpiece is built. Then, using CAM or CAD/CAM systems (HSMWorks, Inventor HSM, Creo Parametric, etc.) it is converted into G-code of the control program and then loaded into the equipment’s RAM, where it is processed by software and translated into G-codes, which control servomotors or, in cheaper devices, stepper motors. microstepping motors.
There is another modern approach to developing control programs for CNC. For example, at Siemens it is possible directly on the device without a CAM system. This is due to the availability of special software ShopTurn, ShopMill, in which you can easily define part elements and process them. In the same way, other systems have this opportunity, for example, Fanuc, Heidenhain, etc.
Next, the software and UP control the operation of servos or stepper motors.
The latter, according to a given algorithm, move the work table with the part and/or the spindle along three coordinate axes, forming a motion trajectory. A cutting tool fixed in a collet - conical, cylindrical, end, end or other shape, solid, welded or assembled - cuts, drills, removes, engraves material. It is made of a much denser metal than the workpiece itself, so CNC milling is efficient. Productivity is also facilitated by the high rotation speed of the mechanical part of the equipment. Accuracy is ensured by automatic electronics.
All the operator needs to do is enter the appropriate program from the remote control, and then visually monitor the correctness of its execution by looking at the panel. In the event that a technological operation does not go according to plan or an emergency occurs, all that remains is to shut down.
Modern models offer their users a whole system of solutions that improve safety and production quality, but do not require outstanding knowledge and skills from operating personnel - learning to operate any of them is relatively simple.
CNC classification
The following software is used to control the operation of the machine:
- Positional - working parts move to points with specific coordinates. They differ in the accuracy of stopping at a given point.
- Contour rectangular (collinear) - moving elements move in a straight line. The speed is determined by the specified cutting modes, in turn for each coordinate axis. Making curved surfaces is not possible.
- Contour (continuous) - elements move in space along a predefined path, shape and end points. Volumetric parts of complex configuration are created.
- Adaptive (self-adjusting) - the work process automatically adjusts to speed, cutting force, and feed. The motor and feed drive automatically protected It is distinguished by high-quality processing and increased reliability.
Contour and adaptive controls are based on 4 and 5 coordinate systems, providing a complex trajectory of movement of moving elements. Processing is carried out along at least 2 axes simultaneously.
Conversion of a 3-axis machine into a 4- or 5-axis machine occurs by installing an additional rotary surface. At the same time, the work area is reduced.
Types of CNC milling machines
Their classification is quite extensive and is based on a number of key parameters, but in the most general case they are divided into:
- Cantilever - the workpiece is fixed to a moving part (gantry). In this case, the spindle is in the same position during operation of the equipment.
- Non-console - they can move both of the above-mentioned elements, with the table in two directions and the tool holder in different directions.
Based on the type of programs used, there are:
- positional – the coordinates of the end points are clearly recorded;
- contour – the trajectory of the processing is already specified;
- combined - combine the features of the two previous options;
- multi-circuit – the widest possible range of functions.
According to the tasks they solve, they are classified into:
- CNC drilling and milling machines – used to create technological holes;
- boring – used to expand seats to the required diameters;
- turning – designed for rough and finishing turning of conical, cylindrical, shaped surfaces, trimming ends, and so on;
- Widely universal - they can perform all of the above, including due to the presence of an additional spindle head that can function both simultaneously with the main one and separately.
Any of the subtypes of this equipment can be either desktop or installed on an individual base. In addition, there is a classification according to the material being processed, and each type here deserves a more detailed consideration.
Gantry and mini CNC milling machines for metal
Some of the most popular in modern industry (in particular, in instrument and mechanical engineering). They are used to drill, bore, and countersink parts made of steel, cast iron, and alloys.
Their main feature is the increased strength of the cutting tool, because it must be much stronger than the surface on which it acts.
Capable of supporting all 4 program options. By design, they can be either with a console (with a table moving both parallel and perpendicular to the spindle axis) and without it. They maintain high rotation speeds, and with their use it is quite possible to achieve optimal processing accuracy.
There is a fairly important division by size. So, a small desktop CNC milling machine for metal can be installed in a small workshop, in a private workshop, or even at home. Its main advantage is its compactness - it is in demand when a small area does not allow the operation of more powerful equipment. Although its productivity is sufficient for the production of small-scale batches.
Widely universal centers are a different matter: they are large and therefore are usually intended for large plants and factories. They cost more, take up more space, but choosing them is completely justified. To two spindle heads (the first is the main one, the second is an additional one, mounted on a trunk, retractable and rotatable at any angle), you can add another one, an overhead one. This solution will make it possible to simultaneously carry out several technological operations at once, for example, to simultaneously carry out both countersinking and boring. Productivity increases 2-3 times, the equipment quickly pays for itself.
Models of CNC milling machines for wood blanks
With their help:
- perform contour cutting;
- grooves are applied;
- carry out a selection of folds;
- cut out curved surfaces;
- create large and thin forms;
- achieve excellent cross-planing quality.
At relatively high rotation speeds, both hard wood (ash, oak, poplar, acacia, beech) and soft wood are precisely processed, and delicately - without scuffing, fluffiness, or tearing out fibers. Therefore, they have found the widest application in furniture factories and in workshops for the production of patterned frames, carved door frames, souvenirs, and decorative elements.
Milling and engraving group
Such equipment is designed for applying arbitrarily complex relief inscriptions, drawings, images on the surface of various materials: not only metal or stone, but also wood, plastic, glass and even ivory.
The design is quite standard: in the mechanical part, either a table or a portal can be movable, the part is fixed either rigidly or automatically, with pneumatic clamps; in the electronic part, there is also nothing fundamentally new - a microprocessor controls the accuracy of the move. The key difference is the shape of the cutting head, as well as the hardness of the tool.
If we name the most frequently carried out milling work on CNC machines, an example would be engraving on furniture, on car bodies and vehicles in general, on jewelry. The equipment is convenient and easy to use, it is distinguished by functionality, productivity, reliability, and high quality of the final result, which determines the breadth of its modern application.
Cantilever type machining centers
The main feature of their design is a moving load-bearing part (portal, bed) with the spindle fixed in one position. Due to this structure, they are distinguished by relatively high rigidity, which contributes to the accuracy of technological operations. The most popular are divided into several subtypes, each of which deserves consideration.
Offers wide versatility
These include drilling, turning, and CNC milling and boring machines - several models in one, capable of performing all types of processing of metals, alloys, plastics, wood and other materials. They are especially in demand in mass and large-scale production, as they can boast of multitasking. They have two spindle heads at once (the second is on a retractable trunk, so it’s not a problem to place it at any angle), plus another overhead. This design solution allows you to quickly produce and/or prepare parts of the most complex shapes - according to the principle “one tool removes excess material, the other at the same time bores the hole.”
Examples of such equipment include:
- JET JMD-939GH;
- NGF-110-Sh4+VGF;
- SF-676 (675).
The universal CNC milling machine, which belongs to a slightly different category, deserves special attention. Unlike models with broad functionality (it is important not to confuse them), it is in demand in small-scale and individual production, often installed in small workshops and workshops. Allows you to prepare all surfaces, corners and grooves of light workpieces - spirals, die models, etc. All its elements are located on the frame; the mandrel with the cutting tool is supported by a trunk with pendants. Its console moves up and down, the table on the slide moves left and right (in accordance with the spindle axis), which ensures high speed of problem solving.
Popular examples include:
- XN6336C;
- Optimum MF1 Vario;
- PROMA FVV-30.
Horizontal type
In terms of scope, principle of operation and design, it is similar to a universal one: all the main components of a CNC milling machine are located on the guide, and the feed box and tool magazine are located on the portal. The key difference is that there is no rotating device. Therefore, the table of such models can move either only perpendicular to the spindle, or only parallel. Therefore, to perform operations involving division or screw movement, additional devices are required.
They remain in demand when preparing shaped and screw surfaces, grooves and corners - using cylindrical and disk, end and end, angular cutting heads.
The list of equipment in demand today:
- 6P80G;
- NGF-110-Sh4;
- 6M82GB (based on 6M82G).
Vertical type
This could be a CNC coordinate milling machine, the accuracy of its programs is combined with wide capabilities. Manufacturability is achieved, among other things, due to the location of the spindle, which allows some displacement along the axis and a slight horizontal rotation.
Another feature is a mandrel in the form of a Morse cone (if you follow the Soviet standard) or ISO-40 (for foreign brands) for installing an end cutting tool.
Bottom line
Professional tools include controls that include or support CAM (computer-aided manufacturing) and CAD (computer-aided design) software.
The tools are configured for both semi-automatic and automatic operations: milling, engraving and drilling. Rotating tables allow you to move the workpiece along several axes.
Vertical milling is the most common - it is simpler. If there is a need to remove a lot of material or maximum accuracy is not needed, horizontal milling is used.
Suppliers will help you set up accurate equipment calibration. Some tools come with a user interface or application that mirrors the virtual workspace.
To prevent overheating or damage to milling equipment during prolonged operation, some have a spindle cooling system.
Non-cantilever equipment
The fundamental difference is that in this case both the table and the spindle head can move, independently of each other. This makes it faster and easier to prepare workpieces of non-standard sizes, large dimensions, and large masses. It is divided into two subspecies.
CNC Vertical Milling Machine
It is used for cutting and turning gears, frames, corners, grooves and similar parts made of steel, cast iron, non-ferrous metals, alloys. Since this model does not have a console, the table with all the functional units moves directly along the frame guides, and this is with a spindle with vertical adjustment movement (which, together with the sleeve, can be moved slightly along the axis).
The advantage of this design is extreme rigidity, which improves the accuracy of technological operations.
The following models continue to be considered classically popular:
- 6Р12П;
- Craton WMM-2.55;
- 6Р13.
Horizontal CNC Milling Machine
Its configuration is similar to the previous type, with the difference that its spindle head is located horizontally. This solution allows the table to move in three directions, perpendicular to each other (along the guides of the frame and stand), but without changing the angle of inclination.
In practice, it makes sense to designate them for the preparation of large-sized parts, since, due to their rigidity, the accuracy of technological operations is maintained even at high shaft rotation speeds. They are convenient because they can be additionally equipped with a vice, dividing head and other devices to expand the range of tasks they can solve. They are produced by many brands, including the Swiss JET and the German Optimum Maschinen GmbH and Heinbohr.
Requirements for control systems
Industrial and desktop CNC routers must meet certain requirements. They must work with common modeling programs (DeskProto, VCarve Pro, ArtCAM, Mach3 and others). Control should be clear and accessible to the technician working on the device. There must be a mechanical adjustment of the device when the computer fails.
Master working on a machine
Setting up a CNC milling machine
This is a whole system of actions that must be performed and involve manually turning on mechanisms and software, checking their interaction, using buttons, switches and toggle switches on the control panel. It is carried out in 8 steps - let's look at them in order.
Acquisition (receipt) of tools and other technological equipment
It is carried out in accordance with the printout of the program (the ESTD map GOST 3 1404 74, if you are guided by non-foreign standards). Thus, all involved cutting heads must be equipped with auxiliary devices (if the latter are provided at all) before the start of technological operations. Then they will be completely ready for installation in a tapered spindle hole, which will allow you to determine whether correction is needed even before starting work - time savings are obvious.
Comparison of tool radii (diameters) and lengths with their calculated values
The stage of setting up a CNC milling machine, the correct execution of which determines the dimensional accuracy of the final workpiece. It is necessary to measure 2 parameters:
- The radius of the cutter (taking into account radial runout) is determined using the BV-2013 device. You should install its shank into the spindle, fix it and begin to slowly move the horizontal carriage. As soon as it touches the tool at the extreme (largest) point, you have found the desired value.
- Reach length - use the flywheel to gradually and slowly move the other carriage, the vertical one. When the end of the cutting edge begins to contact the pin, you will obtain the desired characteristic.
Then all that remains is to compare and, if the real numbers do not coincide with the standard ones, go to the next step (if they are equal, just skip it).
Determining correction values associated with tool sizes, recording them by type and number of correctors
Each discrepancy should be recorded in the documentation, and then corrected by selecting exactly the appropriate parameters. To speed things up, you can use optical rather than mechanical devices for comparison - they are more sensitive.
Charging the reader
You need to place it under the technological console, and then implement one of two methods:
- Reels - a long punched paper tape will go from the first to the second, and then, at the end of the program, will be rewound to its original position by a special mechanism.
- Endless tape - it is glued together at the ends, placed between the leading drums, enters the guide tray, and then onto the reading head, and as a result is scrolled as many times as necessary.
Orientation and installation of fixtures and workpieces according to the coordinates of the origin point (IP)
Place the surfaces of the part in the correct position relative to zero (origin) and the axes of movement of the cutting edge.
Installation of tools
If there are several of them and the change is carried out manually, fix the first one in the spindle before the start of the technological operation, and mount each subsequent one during pauses specially designed for this. If the automation is working, it is enough to pay attention to the display and replace the heads immediately when the corresponding number is displayed.
Entering correction
If deviations of the actual dimensions from the calculated ones are detected, the CNC milling machine is re-programmed. The punched paper tape is rewritten with amendments - a different number of impulses - providing changes in:
- geometry – reach length, diameter, radius;
- operating mode – shaft rotation speed, feed speed.
Adjustments are made before the start of the technological operation, at the initial reference point, on the remote control manually, recording the corresponding code, which indicates all preparatory functions.
Experienced automatic part processing (several workpieces with multi-position processing)
It is carried out to check the correctness of the specified program. If the dimensions obtained during this procedure differ from the calculated ones, you will have to make the edits again, resetting the previous correction to zero and entering new updated values.
You can request drawings and control diagrams for CNC milling machines from their manufacturers. For example, the Sarmat company, which produces such multifunctional equipment, is open to customers, and its managers are always happy to provide detailed advice on all issues of choosing models for the needs of a particular enterprise.
Selection principles
There are a variety of CNC metal milling machines. To avoid mistakes when choosing, you cannot completely trust beautiful advertising. It is necessary to pay attention to a number of features:
- Understand the categories of professional and amateur equipment.
- Consider the dimensions of the device depending on the free space in the room.
- Explore additional features and functionality of the equipment.
- Find out in advance what kind of power is needed for the operation of moving elements.
- Take into account the material from which the frame and fastening elements are made.
The motor power is selected depending on the materials being processed. For hard wood and metal, a powerful electric motor is required. High cost is not an indicator of quality.