[Plasma cutting] allows you to cut metal, but not with a cutter - this unit has a plasma jet.
The essence of how a plasma cutter works is this: an electric arc is formed between the nozzle, electrode or material being cut.
Gas comes out of the nozzle, it is converted into plasma after exposure to electricity.
The metal is cut by plasma, the temperature of which can reach 30 thousand degrees.
The article discusses in detail the technology of plasma cutting of metal, the principle of its operation and some nuances.
What equipment is used?
Typically two types of equipment are used:
- Transformer. Can cut metal up to 40 mm thick.
- Inverter. The efficiency is higher than that of transformer devices, however, it is impossible to cut a workpiece whose thickness is more than 30 mm.
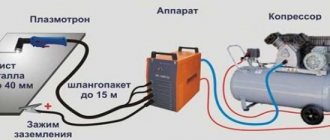
The operating principle of these mechanisms is the same. They consist of a compressor, a power source and a plasma torch.
When choosing a tool, you need to study the markings of the device. Some devices are designed for cutting only. Other equipment allows arc welding. There are universal devices on sale, but they are inferior in quality to specialized devices.
The location of the compressor may change. In some models this element is built-in. These models have low power. A model with a built-in compressor is used in garages and small workshops. For industrial production, it is necessary to use devices with an external compressor.
Pros and cons of a plasma cutter
When choosing a device for effectively working with metal, home craftsmen will have to make a difficult choice and decide what to give preference to - a plasma cutter for metal or a conventional gas torch. The undeniable advantages that a plasma cutter has are known:
- high performance and power;
- high-quality material processing;
- versatility;
- safety;
- environmental friendliness.
The disadvantages of plasma cutters are:
- high cost of the unit;
- limitation of material thickness;
- inability to operate two machines at the same time.
Operating principle of a plasma cutter
The operating principle of plasma metal cutting depends on the equipment used. Before you start cutting metal sheets and workpieces, you need to study the design of the plasma torch:
- The main part is the power source. This could be a transformer or an inverter. The first option has a bulky design and low efficiency. However, the transformer allows cutting thick workpieces. The inverter has many advantages. This is a high efficiency indicator, stable operation, small dimensions.
- The plasma torch is the working part. This is a tool that consists of several parts. These include the electrode, cap, cooler and nozzle.
- Compressor - supplies a stream of air that will heat up during operation. If there is no compressor, the plasmatron may stop working.
Hoses and wires are used to connect key parts of the device.
The principle of operation of a plasma cutter is that a stream of heated ionized air is created using the equipment. The air itself ceases to be a dielectric and begins to conduct current. After turning on the device, an arc is formed, with the help of which the metal workpiece is cut. At the moment of contact between the plasma and the surface of the material being processed, it is exposed to a temperature of 30,000 degrees.
Plasma cutter - characteristics
You need to know the main technical characteristics of metal cutting devices in order to understand the types of models and understand how they differ. Information about the parameters of plasma cutting devices should contain:
- Current strength
is the main indicator that affects the thickness of the metal that the tool can work with and the speed of operation of the device. You can calculate the required current value yourself if you multiply the thickness of the alloy in millimeters by 4, for example, for plasma cutting of a metal sheet 20 mm thick you need a cutter with a power of 80 A. - The duration of switching on
is measured in %; for example, we can say that the operation of a plasma cutter with 60% duty cycle characteristics should be 6 minutes, and the next 4 minutes. the unit must rest. Professional models of plasma cutters have a duty cycle of 80%, home inexpensive devices - about 50%. - The type of power supply for the unit
varies. There are models of machines on sale that require a two- or three-phase network; 380 V is required for professional three-phase models. Conventional devices operating at home 220 V parameters are more convenient to use.
Types of plasma cutting
There are several types of manual plasma cutting:
- Use of shielding gas flow. It protects the cutting site from environmental factors. This results in a better quality cut.
- Plasma cutter using water. The liquid cools the surface being processed and the plasmatron itself. In addition, water protects the cut site from the effects of environmental factors during heating. Water prevents the molten metal from emitting harmful fumes.
- Simple. The classic way to use a plasma torch. Electric current and air flow are used for cutting. Not suitable for cutting thick metal sheets and alloy steels.
When cutting workpieces, an arc can be used, which is formed between two electrodes.
Manual plasma cutting
Types of plasma cutters
A huge assortment of cutter models is presented in professional electrical goods stores. Hand-held plasma cutters differ from each other in many ways. Which type of unit to choose - portable or stationary, programmable or manual - depends on the specific needs of the owner. Plasma cutters are divided into the following types:
- by type of energy consumption
- transformer and inverter models; - by type of contact
– non-contact and contact; - by type of work
- manual and CNC.
Technology
When carrying out work, you should adhere to the following metal plasma cutting technology:
- The nozzle, from which a stream of air will burst out, is located at the edge of the metal sheet.
- The wizard starts the device using the power button. The initial arc is turned on, which gradually turns into a cutting arc.
- The burner is tilted at 90 degrees. Cutting is done slowly and carefully.
- The master must control the appearance of splashes of molten metal. If they do not appear, it means that the metal workpiece could not be cut through.
- Do not touch the nozzle or point it towards other objects immediately after turning it off, as hot air will continue to flow from it for some time.
If you cannot cut through a metal sheet, you need to change the angle of inclination, slow down the pace of work, or increase the voltage.
Plasma cutting technology
Processing of non-ferrous alloys
When processing non-ferrous metals, various cutting methods are used, taking into account the density of the material, its type and other technical indicators. To cut non-ferrous metals, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Cutting aluminum - for material up to 7 cm thick, compressed air can be used. Its use is impractical when the material density is low. High-quality cutting of aluminum sheets up to 2 cm is achieved using pure nitrogen, and with a thickness of 7-10 cm using hydrogen and nitrogen. Plasma cutting of aluminum with a thickness of more than 10 cm is carried out using a mixture of hydrogen and argon. The same composition is recommended to be used for thick-walled high-alloy steel and copper.
- Cutting stainless steels - the use of compressed air is not recommended for the work; taking into account the thickness of the material, pure nitrogen or mixtures with argon can be used. It should be taken into account that stainless steel is quite sensitive to alternating current, which can lead to changes in its structure and faster decommissioning. Stainless steel cutting is carried out using an installation that uses the principle of indirect action.
Advantages
Plasma cutters for metal are often used on construction sites and in private workshops. The demand is explained by the advantages of the plasma cutter:
- Using a plasmatron you can process different types of metals and alloys.
- There is no need to prepare the work surface. High quality processing can be achieved without cleaning the metal from rust and paint.
- By carefully and slowly moving the cutter along the surface being processed, a highly accurate cut is obtained. No scale or sagging remains.
- Even if the metal sheet is not very thick, it will not be damaged due to strong heating. This is due to the characteristics of the equipment used.
- Using a plasma cutter you can make smooth, shaped cuts.
During operation of the plasma torch, virtually no harmful substances are released, which makes the processing process safe for health.
Plasma cutting of metals is a technological process using a special tool that allows you to cut metal sheets. The choice of plasma torch depends on what materials will be processed. If the device is not selected correctly, the plasma arc will not be able to cut the metal workpiece.
What metals can be cut?
Using plasma technology, almost any metal can be processed:
- Cutting and cutting of sheet metal from steel, titanium, non-ferrous metals (copper, aluminum, etc.) and their alloys (including bronze, brass, etc.).
- Cutting steel of different thicknesses and workpiece shapes. Processing of carbon and alloy steels of almost all grades is provided, incl. high alloy stainless steels. Plasmatrons can be used to cut strips (narrow long steel strips) and cut rolled steel.
- Cutting cast iron. Plasma ensures deep cutting, which makes the method more effective compared to other technologies.
- Cutting and processing of pipes of different diameters. Special pipe cutters with centralizers are used. In addition to cutting, you can process the surface of pipes, chamfer, clean welds, and process edges.
- Formation and processing of holes.
- Shaped cutting of metal blanks. Special equipment even allows for artistic carving and production of parts of complex shapes.
Important! Various equipment is used to carry out operations, including CNC machines.
How does a plasma torch work?
The devices use a plasma jet as a cutting tool.
Metal cutting process:
- From the electrical power source, current is supplied through the cable to the burner, where an electric arc is formed between the anode and cathode.
- The compressor supplies gas flows, which are directed by swirlers to the electric arc.
- When flows pass through the arc, the gas is ionized and heated to a high temperature (up to 30 thousand degrees).
- The gas turns into a plasma jet.
- When exposed to heated air escaping under high pressure, the metal is cut.
Plasma torch circuit
Types of cutting systems
Systems differ depending on the type of plasma gas provided by the technology.
Conventional systems use ambient air as gas. The current strength in this process ranges from 12-20 thousand A/in². The shape of the plasma flow depends on the nozzle opening. Such systems are used for both manual and mechanized cutting. Deviations in the dimensions of the cut part are allowed.
High frequency (high current density) systems are used for plasma cutting with increased precision. Purified air, oxygen, and mixtures of hydrogen and nitrogen are used as plasma gas. Plasmatrons and consumables of a more complex design are used in the technological process. The current strength for high-frequency separation is 40-50 thousand A/in². The main goal is to achieve increased accuracy when focusing the arc and obtain high quality cutting.