Protecting metal from the occurrence and development of corrosion is a very pressing issue, the solution of which can significantly extend the service life of metal products, as well as make their operation more reliable. The most common method to provide such protection is galvanizing, which involves applying a coating to the surface of the metal, the chemical composition of which can contain up to 95% zinc. Galvanizing of metal can be performed using various technologies, each of which is used in certain situations and has both advantages and disadvantages.
Galvanizing is the most widespread among other anodic protective coatings of metals.
Working principle of galvanizing
The rust protection method is based on the chemical oxidation process. Most metals in air react with oxygen, as a result the surface is covered with a film, which begins to play a protective role. The exception to this series is iron and its alloys; they form a film of loose composition, which does not protect, but, on the contrary, promotes further oxidation of the material and its destruction. Zinc is used to protect steel and other iron-based metal materials. It forms a galvanic couple with Fe, and due to its greater activity, it begins to oxidize first, forming a film that serves as surface protection.
The thickness of the film varies depending on the technology; it can be thin - from 6 microns or dense - up to 1.5 mm.
Why is a layer of zinc applied to steel?
It is well known that products made of steel are very susceptible to corrosion processes, especially when used in conditions of high humidity. Meanwhile, if you galvanize a steel part, you can provide it with reliable protection against corrosion. This is explained by the fact that the zinc coating forms a galvanic couple with the base metal, in which zinc has a greater degree of electronegative charge than steel.
In such a galvanic couple, when its components are exposed to aggressive environmental factors, it is the zinc that is exposed to corrosion, and chemical reactions of steel are practically eliminated. Thus, corrosion protection of the steel will be ensured until the zinc coating is completely destroyed. At the same time, in those areas of the steel product where the zinc coating is destroyed for some reason, zinc hydroxide is formed under the influence of oxygen and moisture, which also has good protective properties.
Advantages of applying zinc before painting
Galvanizing steel products allows them to provide not only barrier, but also electrochemical protection. Galvanizing of metal can be carried out using different technologies, for the implementation of which various equipment is used. Using certain types of such technologies, you can perform galvanizing at home and still achieve excellent results.
Areas of application of galvanized structures
- Construction work of various profiles: road, bridge, construction of buildings and structures.
- Oil production and oil refining.
- Gas production and gas processing industry.
- Energy sphere.
- Connection.
- Automotive industry.
- Agriculture and other areas.
The method is applicable for structures that are operated under different conditions
- Supports of high-voltage transmission lines.
- Supporting metal structures of bridges and pipelines.
- Various equipment.
- Valves and locks of hydraulic systems.
- Frames of houses and fences.
- Piles supporting various types of floors.
- Stair steps and flights.
- Pipes of various systems, including ventilation.
- Ship hulls.
- Monuments and architectural structures.
General information and purpose
Steel products are susceptible to corrosion, especially when used in conditions of high humidity. The galvanized steel part is reliably protected from corrosion. The coating together with the metal forms a galvanic couple, where zinc has a higher degree of electronegative charge compared to steel. Accordingly, zinc undergoes corrosion, and steel reacts practically without any reaction. The anti-corrosion protection of the metal will last until the zinc coating is destroyed.
There are several galvanizing technologies. Some technologies allow do-it-yourself galvanizing with obtaining an acceptable result.
Galvanizing production processes
Several galvanizing methods are used in metallurgical and chemical production.
- Galvanic galvanizing
- Hot galvanizing of metal
- Cold galvanizing method.
- Diffuse galvanizing method.
- Shoping.
- Gas-dynamic method.
- Duplex processing methods
A phosphating method can be used, which, in addition to the main method, provides additional protection to the surfaces of metal objects and parts. Most often used for non-ferrous metals.
The widespread use of galvanizing is associated with the coating’s resistance to aggressive environments, temperature changes, and high anti-corrosion properties.
Galvanic galvanizing
Electroplating is an electrochemical method of coating metal structures with zinc. It is carried out in large containers with zinc-containing electrolyte. The complexity of this method lies in the effect of two processes on the metal at once: electrical physical influence and chemical method.
In the galvanic method, an active process of adhesion of elements of metal material and zinc occurs. Adhesion involves the adhesion of dissimilar substances at the intermolecular level.
Electrogalvanic production technology
Metal products, structures or parts are immersed in electrolytic baths equipped with an anode - a zinc plate, from which, with the help of an electrolyte - zinc sulfate and zinc chloride, the anions of this metal pass to the surface, covering it with a uniform layer.
The galvanizing process is influenced by the composition of the electrolyte and the temperature maintained in the containers. Coloring additives and shine-forming components are added to the solution. This is done to give objects a decorative appearance.
Electrolytes used in the production process are:
- Acidic and slightly acidic: sulfates, borofluorides, chlorides.
- Ammonia: alkalis and neutral solutions.
- Cyanide and zincate: alkaline electrolytes with cyanide and sodium zincate in sodium hydroxide solution.
Before carrying out work, it is necessary to prepare metal products: cleaning and degreasing surfaces, fluxing - applying a film to prevent oxidation.
Characteristics of zinc electroplating: the surface is distinguished by such properties as ductility, continuity on parts that must work under conditions of cyclic deformation. For example, steel springs.
Hot galvanizing of metal structures
The hot-dip galvanizing method is usually used for ferrous metals, primarily steel. This is the most common method of covering surfaces with zinc film.
The technology boils down to lowering parts or structures into a bath of molten zinc. The temperature is maintained at 460 degrees. C. The process takes place under the influence of oxygen from the atmosphere, it reacts with the metal to form ZnO - zinc oxide, which combines with carbon dioxide CO2. As a result, zinc carbonate is formed - ZnCO3. It has a characteristic matte gray shade.
Before lowering into the bath, a stage of cleaning, degreasing and etching the surface of the parts is necessary.
After being in the bath, the products are centrifuged to remove excess metal. To remove sagging, threaded areas on large parts are ground; small parts, such as fasteners, are not subjected to such treatment.
As a result, products with an increased service life, resistant to aggressive environments, do not require additional coating with a paint layer.
Negative characteristics include unevenness of the surface with high consumption of zinc, and the dimensions of the products are limited by the dimensions of the container. Production is considered harmful. Further processing becomes more difficult, the parts are poorly connected by welding.
Features of the hot galvanizing process
- The technological process is simple.
- High productivity is noted, it passes quickly.
- Highly trained employees are not required.
- The equipment is quite simple.
- The zinc layer has a thickness of 30 to 100 microns.
Compared to galvanic methods, hot-dip galvanizing is a more expensive method, but also more effective.
Cold galvanizing of metal
The method consists of applying zinc-rich paints, compositions and primers to the surface. Not the entire surface of the product is covered, but the designated areas.
It is widely used for processing individual structures and large areas.
Positive aspects of cold galvanizing
- You can process products and surfaces of any size, there are no restrictions on area and shape.
- There is no need to carry out preliminary dismantling work in order to immerse it in a container for electrolysis or hot-dip galvanizing.
- The process is characterized by productivity.
- Temperature range: from minus 20 degrees. From to positive 40 gr. WITH.
- The zinc layer after the cold method allows welding; it does not destroy the zinc surface. After welding, the seam can be covered with an additional protective layer.
- The structure of the coating is flexible and reliable.
- Zinc silicate paint has adhesion characteristics that are compatible with metal and finishing paints.
- The method is quite simple and does not require special professional training.
- Can be used to repair parts and areas that have previously undergone a galvanizing process.
- A convenient way to apply a touch-up layer under varnish or chemical-resistant paint for double protection. This is a combined coating method.
- You can process the entire structure without disassembling it into individual components.
- Economical way.
The composition for cold galvanizing contains highly dispersed zinc powder - up to 95%. Before carrying out work, it is necessary to prepare the surface and strictly comply with the technological requirements of the work.
In the production process, a necessary stage is quality control to ensure the absence of defects in the zinc layer. At the end of the process, the coated products are allowed to “rest” for several days to harden the layer.
The resulting coating is waterproof, electrically conductive, and fireproof.
Thermal diffusion galvanizing method
The diffusion method was called “Sherardization” after the inventor, a specialist from Great Britain, Sherard.
Thermal-diffusion coating is an anodic coating, covering ferrous metals with a dense film of zinc. The name is associated with the process of diffusion of metals, zinc and iron. It takes place in passivation solutions, which are necessary to provide protection from exposure to atmospheric oxygen.
Thermal diffusion coating is similar to the galvanic method, but surpasses it in anti-corrosion characteristics.
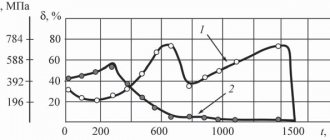
Products processed by thermal diffusion are characterized by a uniform surface coating from 30 to 80 microns. For small areas of parts, subject to precise production, thicknesses from 5 to 150 microns can be achieved. When structures with complex surfaces are processed, the variation in coating thickness is large - up to 80 microns.
The technology consists of saturating the area of parts and structures with zinc in a powder medium.
Zinc-containing fine powder is diluted with absorbents such as charcoal. The temperature is maintained at 400-500 degrees. C. Temperature conditions are different for different types of products, the characteristics of steel that are fixed in its grade, and production requirements.
A hermetically sealed container in which surfaces are enriched with zinc is a prerequisite for the technology. After the main process, finishing is carried out on products that will be used in conditions of high humidity, sea or other salt water, during periods of condensation and drying.
Features of thermal diffusion coatings
- The technological process of processing at low temperatures, in addition to anti-corrosion properties, gives the metal increased ductility.
- Treated products are resistant to abrasive wear, which is formed as a result of cutting, deforming, and scratching effects. Occurs during processing and transportation.
- The coating accurately reproduces the relief of the structure.
- Increased hardness distinguishes the processed products; the property of fragility does not arise.
- Zinc coating can be applied to pre-assembled units.
- Preparation of the thermal diffusion galvanizing process does not require complex operations.
Shoping
Metal shopping refers to metallization, or spraying processing. For work, a special apparatus is used, which is sometimes called a pistol. Molten zinc is sprayed onto the surface under compressed air pressure. The method owes its name to the inventor G. Schoop.
The metallization method is applicable for large structures, as well as for the restoration of worn parts made of steel of various grades. The zinc layer applied by shopping forms a stable film, which acts as a primer for applying the paint layer.
Gas-dynamic galvanizing
The gas-dynamic method is galvanizing using the kinetics of finely dispersed metal in a gas stream, carried out by a supersonic flow.
The starting material is zinc powder with ceramic or metal particles. It is accelerated by a jet of gas from a high-temperature nozzle and welded to the surface towards which the flow is directed. Additional material - metal and ceramic - increases the density and reduces the porosity of the surface.
The equipment for the gas-dynamic method is a portable heater for compressed air, which is equipped with a supersonic nozzle. This is a kind of atomizer. Gas at t 500-600 gr. C draws in the powder and directs it to the surface.
Advantages of the method
- Processing of products and parts of any size.
- The adhesion of the composition is higher than that of any paint and varnish layer – 40-100 N/mm2.
- The thickness of the layer can be different; the layer can be thickened in areas of increased risk of corrosion.
- The porosity of the zinc layer is less than 1%.
Combined – duplex processing methods
Duplex coatings involve a combination of zinc material with polymer or paint.
The combination of the electrochemical effect of zinc protection with the waterproofing effect of the paint layer creates a double protective effect.
Characteristics of duplex systems
- Provides galvanic or cathodic protection and at the same time barrier protection.
- It is as easy to apply as a paint coating.
- A special type of zinc is used in production - atomized.
- Increases resistance to mechanical damage
- It does not require complex preparation of the source material for the coating process - it is enough to treat it with a solvent.
- Can be applied over hot-dip galvanized and metallized surfaces.
- Non-toxic and environmentally friendly.
Metal galvanization
In principle, the technology in all methods is the same: a thin layer of zinc is applied to the metal surface and it is covered with a film, protecting it from mechanical damage. It is zinc that protects the metal surface from all loads and damage, and galvanizing the metal:
- a very inexpensive procedure;
- safe for any properties (including mechanical) of manufactured parts;
- It is possible to set different thicknesses.
Zinc is the most accessible metal that provides electrochemical protection for iron. Therefore, galvanizing is often used in the following areas: construction, mechanical engineering and others. Wear resistance is the main component of this procedure. It is this that determines the durability of the metal. For example, if a zinc-coated metal is exposed to atmospheric components, it deteriorates slowly, forming a thin layer of a protective film. It is this that protects the deepest layers from corrosion, it prolongs life and is wear-resistant compared to other products. Typically, the following alloys are suitable for galvanizing: copper, aluminum, cast iron, steel and others.
Do-it-yourself metal galvanizing
Most galvanizing methods are production methods that require industrial equipment and special metal processing.
Some of them are available to craftsmen in workshops. Most often they talk about “garage galvanizing,” since they are the ones who need to restore car parts and components.
The most accessible method is cold galvanizing.
There is a possibility of galvanic processing of parts. It allows you to form patterns and decorative elements on the surface of products.
DIY galvanizing
To work with this method, an electrolyte is required. This can be zinc chloride (ZnCl), hydrochloric acid (HCl), zinc sulfate (ZnSo4). Formulations require maximum care; chemical components have a tendency to explode or enter into unexpected reactions.
The zinc composition involves the extraction of zinc from salt batteries, galvanized metal objects, Soviet-made fuses, or purchase at the auto or radio market.
How to work:
- The bathroom can be a plastic or glass container.
- The anode is a zinc plate with a positive charge supplied.
- The workpiece plays the role of a cathode. It must be prepared - cleaned, degreased, activated. It is located equidistant from the anode.
- Power source - battery, power supply. The precaution is to avoid active boiling. If the process is smooth, long-term galvanization will provide a thick protective layer of zinc.
How to perform the procedure at home
Galvanizing at home is carried out mainly by the electrochemical method or using cold galvanizing technology, which is explained by the simplicity of these methods. To perform galvanizing yourself using the electrochemical method, you must carefully prepare the surface of the workpiece. Such preparation consists of cleaning and degreasing, as well as acid etching and subsequent rinsing with water.
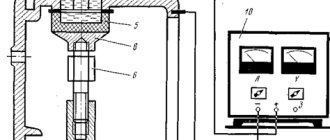
Diagram of a galvanic installation for self-galvanizing
Your own device for performing galvanic galvanizing can be made from a direct current source that produces a voltage of about 6–12 V with a current strength of 2–6 A, a container made of dielectric material and a device with which the electrode and the workpiece will be fixed. The electrolyte in this case can be a solution of any salt containing zinc. You can prepare such a solution from battery electrolyte by placing zinc in it for a while and waiting for the dissolution reaction to complete. The resulting composition should be filtered before use for galvanizing.
When performing galvanizing with your own hands, you should keep in mind that the following factors influence the thickness and quality of the coating formed:
- current density per unit area of the workpiece;
- temperature of the electrolytic solution used;
- density of the electrolyte used;
- geometric parameters and complexity of the shape of the processed product.
When is galvanized metal used?
We are constantly in contact with galvanized metal. It is used in decorative items: buckles, key rings, buttons, stationery, etc.
Products with zinc protection are used in various areas of industry, construction, landscaping and everyday life. They are used in metal structures, for arranging roofs, fences, decking, fencing, and in other areas. Galvanized metal products are used everywhere in urban infrastructure.
Due to their low price and increased resistance to corrosion, such materials are in demand in shipbuilding, machine tool building, mechanical engineering and other industries.
Galvanizing is used on pipes for protection and durability. Galvanized pipes are widely used in the plumbing industry. Since they are constantly in contact with water, it is necessary to create good conditions so that they do not begin to rust and deteriorate. People need clean water, free from rust and foreign impurities.
Hot
Coating products in this way is popular in many countries. Its main positive properties are high quality and long service life. Therefore, this method has become one of the best. There are also a number of negative properties. First of all, the method is not environmentally friendly, since many chemicals are used at the preparation and galvanizing stage. In addition, there is a significant difficulty in hot working. It is necessary to maintain the temperature of zinc in the range from 500 to 5000ºС. Maintaining this level of heating requires a lot of electricity. Hot galvanizing metal at home is a rather complex process.
Technologically, the process is divided into two stages. This is the preparation and galvanizing of metal. At the first stage, they prepare the metal product. Its surface must be degreased and cleared of debris. After this, etching, washing and drying occurs.
These operations are prescribed in regulatory documentation.
To coat a part with zinc, you need to immerse it in a special bath. It contains a special solution that prevents corrosion. Methods for fixing metal during hot-dip galvanizing can be different. They depend on the type and shape of the product. This technology is used in many industries. For example, for the production of galvanized wire, pipes, etc.
After applying the hot method to them, the products have a long service life, that is, they are reliably protected from corrosion. The only difficulty is the baths. To process large parts, it is necessary to find a bath of appropriate volumes, which is quite difficult. This feature affects costs. Where is hot galvanizing of metal performed? Kursk, Moscow, Chelyabinsk, Yaroslavl - this is just a small list of cities where various companies offer this service. Often they work with large volumes.
How does it rust?
As mentioned earlier, products are affected by moisture, as well as oxygen and aggressive substances.
Their molecules enter the deep structure of the metal, which leads to the appearance of rust. As a result, holes appear on the surface. This process can take a long time. To slow down the oxidation process, use a zinc solution.