Laser cutting technology
The treatment is carried out with an ultra-fine high-energy beam. When it hits the surface, it evaporates particles of the substance, forming a thin and even cutting seam. In this case, the workpiece itself does not heat up, since the cutting beam moves quite quickly along the cutting line.
Advantages and disadvantages of technology
Advantages of this technology:
- there are no workpiece fasteners;
- there is no dust and noise, saving time on cleaning;
- the ability to cut out fine details and patterns;
- speed of processing;
- jeweler's precision;
- can be used at home.
The main disadvantage is the need for special equipment. Of course, it is quite expensive, but it pays for itself in high productivity and quality of work.
How the process works
The sequence of actions when working on laser equipment is the same as on any CNC. You can easily master this on your own. For a fully configured machine, with special software installed on a PC, the process of cutting plywood is quite simple:
- Based on a drawing or sketch, we perform digital drawing in special computer design programs (CorelDRAW, AutoCAD, etc.).
- We set the parameters: head movement speed, emitter power, focal length, lens blowing force.
- We place the workpiece on the work table.
- Let's launch and observe.
Possible problems
- The leaf may not cut through completely. This happens when there is not enough emitter power or the mode is set incorrectly. An undercut can also appear due to material defects: moisture, curvature, floating thickness, knots.
- The appearance of carbon deposits on the surface of the seam. It occurs mainly from insufficient airflow through the lens, incorrect ratio of laser speed and power.
- “Torches” and “shootings”. “Flares” are persistent sources of fire on the reverse side of a sheet during through cutting. The edges become charred along the cut line. “Shooting” is the reflection of the cutting beam from the workbench, which also leads to burning of the back side.
Dark carbon deposits then have to be cleaned off manually. Additional effort, time and money are wasted.
DIY laser for cutting wood and plywood: myth or reality?
A simple laser cutter can be made from available materials, but it will not cope with wood and thick sheets of plywood. To create an entire machine, you will need to purchase expensive parts:
- stepper motors or electric motors from the printer to move the device along its axes;
- transistors and boards for motor control;
- DC-DC regulator;
- cooler for emitter;
- electronic board with a digital display for displaying information;
- controllers;
- laser with a power of at least 30 W;
- Limit switches;
- timing belts and pulleys;
- frame;
- computer and USB cable for communication with the cutter controller;
- boards for making the working frame of the apparatus;
- metal rods with a diameter of 10 mm.
In addition, you will need bearings, bolts, ties, screws, etc. The laser cutting machine is a shuttle type device. Its moving elements and guides serve to move the working head along two axes and regulate the cutting depth. Stepper motors that move the laser head are mounted on fixed parts of the frame frame and connected to moving parts via toothed belts.
To perform engraving on plywood and wood, a special program is loaded onto the PC, transmitting commands to the controller. It regulates the movement of the carriage with the laser, adjusting the movements of the working head to the selected pattern. Professional software allows you to apply images of any complexity to plywood with the high precision inherent in laser cutting technology.
Thus, with proper preparation and the availability of the necessary parts, you can independently assemble a medium-power laser machine capable of cutting thin sheets of wood or plywood.
How to choose plywood
This composite consists of layers of wood veneer glued together with a special substance (resin or varnish). Depending on the type of glue, there are the following types:
- FC – based on urea resin, used indoors;
- FSF – phenolic resin, waterproof, for outdoor use;
- FB – impregnated with bakelite varnish, for use in aggressive and humid environments.
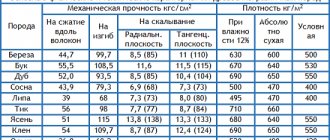
It's better to choose FC. Urea resin is the least heat-resistant. It cuts easier and faster and burns less. Therefore, it is possible to cut sheets of greater thickness.
Waterproof types (FSF, FB) are denser and more difficult to cut through. For example, to cut 4 mm FSF, the same mode is used as for 12 mm FSF.
Material made from deresined coniferous veneer is easier to process. Its density is low, and therefore it cuts through easily. Hardwood veneer is much denser, which slows down the process. The optimal thickness of the workpiece is 4-6 mm. Thick (more than 6 mm) requires more effort and burns more often. For high-quality work, plywood must be:
- well dried
- flat,
- without knots,
- not covered with paintwork!
Processed materials [ edit | edit code]
Any steel of any condition, aluminum and its alloys, and other non-ferrous metals are suitable for laser cutting. Typically used sheets of the following metals:
- Steel from 0.2 mm to 30 mm
- Stainless steel from 0.2 mm to 40 mm
- Aluminum alloys from 0.2 mm to 25 mm
- Brass from 0.2 mm to 12.5 mm
- Copper from 0.2 mm to 16 mm
Different types of lasers are used for different materials.
Metals with low thermal conductivity are best processed, since in them the laser energy is concentrated in a smaller volume of metal, and vice versa, when laser cutting metals with high thermal conductivity, burr can form.
Many non-metals, such as wood, can also be processed.
How to choose the right machine
Still, the main question remains the choice of equipment. Convenience, quality of work, and productivity depend on it. And many problems simply will not arise. When choosing, it is important to consider reliability, accuracy, and ease of use. You need to select for specific tasks, so as not to overpay for unnecessary options, but also not to miss out on everything you need. Basics:
- emitter power,
- working field size.
Which laser tube to choose
This element is a glass tube filled with carbon dioxide CO2. When voltage is applied, it induces radiation.
For plywood, it is selected at the rate of 10 W per 1 mm of thickness. So, for example, if you are going to cut a thickness of 10 mm, you need a tube of at least 100 W. But the optimal mode of operation of the cutting element is 80% of the maximum.
Working field size
Selected according to the scale you plan to carry out. For example, for the production of small elements or products, a machine with a working field of 500x300 mm may be suitable. For larger tasks (furniture, billboards) - 1200x900, 1600x1000 or even 2000x3000 mm.
Equipment selection examples
For example, for the production of small icons on a stand made of thin plywood, a table-top machine Elixmate NG 0503 M, with a 50 W tube and a field of 500x300, is quite suitable. And if you are working on built-in furniture, decorating shop windows or cafe halls, then the powerful Rabbit Flat Bed 1220, with a 100-130 W tube and a working field size of 1200x2000 mm, is suitable.
These brands have proven themselves well and offer a wide selection of CO2 CNC machines for any task.
Process [edit | edit code]
For laser cutting of metals, technological installations based on solid-state, fiber lasers and gas CO2 lasers operating in both continuous and pulse-periodic radiation modes are used. The industrial use of gas laser cutting is increasing every year, but this process cannot completely replace traditional methods of separating metals. Compared to many of the installations used in production, the cost of laser cutting equipment is still quite high, although recently there has been a tendency towards its reduction. In this regard, the laser cutting process becomes effective only if there is a justified and reasonable choice of the area of application, when the use of traditional methods is labor-intensive or completely impossible.
How to avoid carbon deposits
This problem most often appears when there are not enough machine resources. Or the settings are not selected correctly:
- head speed,
- beam power,
- beam focusing,
- air supply for blowing the lens.
Important! These parameters are interrelated. If you change at least one of them, you need to select the corresponding others.
Speed setting
This parameter is selected experimentally, taking into account:
- density and thickness of the workpiece,
- radiation power.
The thicker the sheet, the slower the process occurs. Water-resistant types of material also slow down processing. The higher the energy of the beam, the faster it cuts. This means that the speed must be chosen so that the beam has time to cut through, but does not char.
Beam power
It is selected so that the machine cuts, but does not burn. If the emitter allows, this parameter is selected for the maximum speed of head movement. Important! The strength of the light flux depends on the condition of the laser tube. It has a limited resource. Over time, it sits down and the radiation weakens.
Focusing
The radiation from the tube is redirected using a prism to a lens, which focuses it onto the working surface. For the process to proceed cleanly and quickly, the beam must be well focused on the surface of the workpiece and be as thin as possible. This is achieved by adjusting the focal length. Focusing also depends on the state of the focusing lens:
- temperature regime,
- cleanliness of the lens surface.
Blowing the lens
Cooling is carried out by air flow. If the airflow on the lens stops or becomes weaker, it will begin to heat up. The laser spot area becomes wider. Soot appears. For thick sheets, airflow of 1.5-2 atmospheres is used. This ensures a bright and clean cut surface.
What can a 2.1 W laser do?
A 2.1 W laser is relatively low power for a laser. It is enough for effective cutting of paper, cardboard, plywood, dark acrylic up to 1–1.5 mm thick. Although this laser is more optimal for engraving, cutting is still possible at a relatively good speed. Cardboard and paper show virtually no charring at cutting speeds of 200–300 in the CNCC LaserAxe software.
Of course, the color of the material and the structure itself play a significant role. When we talk about efficient cutting, we mean a clean, uncharred cut. Again, I would like to remind you that many Chinese lasers do not have the declared power and very much do not correspond to the declared parameters.
Recommendations for choosing milling equipment
- Check with managers for information about the model. In particular, information about what materials the machine works with. All our equipment undergoes triple quality control. And this process is recorded on video, which you can ask managers before purchasing the machine.
- Attend a demonstration. This can be done for free before purchasing any equipment. You can bring your workpiece to the demonstration, see how the machine works on it and ask questions about its operation.
- Check the package. When you have decided on the choice of machine, be sure to check the equipment components. There must be a software control unit for the machine, cords with connectors of the appropriate configuration and disks with software. All this and more can be done during commissioning, which is carried out in our service center by qualified engineers.
Milling machine Wattsan 0609 MINI Wattsan 0609 MINI is easy to use: a minimum number of settings and an intuitive interface. Details HERE.
Energy consumption[ edit | edit code]
The efficiency of industrial lasers can vary from 5% to 15%. Energy consumption and efficiency will depend on the laser's power output, its operating parameters, and how well the laser is suited to the specific job. When determining the feasibility of using a particular type of laser, both the cost of the laser together with the equipment that serves it, and the cost of maintaining and servicing the laser are taken into account. In the 10s of the 21st century, the operating costs of a fiber laser were about half of the operating costs of a carbon dioxide laser.
Read also: DIY soldering iron sponge
The amount of required power required for cutting depends on the type of material, its thickness, processing environment, processing speed.
- What a 2.1 W laser can do
- 3.5W laser cutting
- 5.6 W laser with short throw lens
- 8W Ultra Power Laser Cutting
- Basic nuances of laser cutting
Many people believe that cutting can only be done with powerful CO2 and fiber optic lasers. Actually this is not true. Diode lasers with a power of 2 W or more can already cut many materials. So, let's start from the very beginning.