No wonder there is an expression “cast iron is the bread of industry.” The first time this was said was at the beginning of the 20th century. Over the past century, many varieties have appeared, and the quality of processing has improved markedly. Today this material is widely used for the production of a wide variety of things, due to its high level of wear resistance. But over time, even such a durable metal begins to lose its qualities. Then welding using argon gas comes into play.
Previously, to achieve a high-quality seam for long-term use of products, it took a lot of effort, and the work was very hard. Today, the process is still difficult to implement, but now it has become available to home craftsmen.
Features of the technology of welded cast iron products
The connection of cast iron products is carried out in the same way as in the case of other metals. In this case, the structure of the weld itself is identical to the base material. Welding technology necessarily includes preheating followed by leisurely cooling.
When the cast iron parts being welded are in the preheating stage, the structure of the metal changes, which leads to the precipitation of graphite. The result of this is an increase in the plastic properties of the material. If welding is performed using a graphite electrode, this avoids metal impurities getting into the seam. In addition to it, special cast iron plates are used, as well as flux-cored wire.
At the end of TIG welding, the joined workpieces must be cooled. The difficulty of the whole procedure is to prevent a sharp drop in temperature - everything should take place gradually. Moreover, if you simply leave the parts at room temperature, it is not always possible to achieve the desired effect. It is for this reason that various insulating materials are used. They cover the workpieces and leave them to cool for some time. Or you can simply fill them completely with sand, which is used by many home craftsmen.
Cold procedure
In industrial conditions, the technique of cold welding of cast iron is actively used, which does not require preheating. There are several varieties, but three types are often used, based on the electrode materials:
- steel;
- non-ferrous metals;
- low carbon steel.
This variety is good because it significantly simplifies the production of cast iron products, immediately eliminating two stages. Accordingly, the cost will be lower. In addition, preheating requires the use of special equipment.
Connecting cast iron workpieces with argon using the cold method has one feature - the process must be carried out with a low current. This will prevent mixing of all elements in the welded joint. In addition, residual stress is removed from the metal, which usually destroys the weld. In addition, the gaseous environment acts as a certain protective barrier. The likelihood of cast iron becoming brittle is minimized.
Features of the material
Cast iron contains iron, carbon in an amount of at least 2.14% and impurities. The material has high hardness, but low malleability and ductility, which makes it brittle. Additional substances include:
- silicon;
- manganese;
- sulfur;
- phosphorus;
- additional additives.
The following substances are used as metals for alloying:
- chromium;
- nickel;
- vanadium;
- aluminum.
The metal has a density under normal conditions of 7200 kg/m3; it is used in the foundry industry in the manufacture of machine beds, as well as large parts. Melting of cast iron occurs at a temperature of 1200°C, while the carbon in the composition does not have time to penetrate into the depth of the material, but is located mainly on the surface. This effect makes the metal brittle.
Types of cast iron
The material is classified into the following types:
- White cast iron. In this form, carbon has the state of cementite, while on the cut there is a white tint and shine characteristic of metals. This type of cast iron is wear-resistant, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant. Used for smelting into steel.
- Gray cast iron contains carbon in the form of flake graphite. When cut, it has a gray tint, without obvious shine. Used in the manufacture of parts with compression loads.
- Malleable iron is a white type after heat treatment, causing the graphite in the composition to take the form of flakes. These conditions make the material plastic and viscous. Used in the manufacture of parts with complex configurations.
- The high-strength type contains carbon in a spherical form, while the metal base is not subject to rupture in the structure. It is used in mechanical engineering for the manufacture of critical high-strength parts.
Weldability of cast iron and other properties
When joining parts of cast iron by welding, some difficulties arise due to its characteristics. When a critical temperature is reached, metal flow may occur, causing it to flow out of the weld. The combustion of graphite and gas formation leads to the appearance of cracks in the metal, as well as to a poor-quality weld with pores. Such phenomena make cast iron a difficult material to weld.
Preparatory stage
This procedure requires more careful and careful attention than when joining other metals. This is due to the qualities of cast iron itself - it is prone to destruction and cracking.
During preparation, the following operations are performed:
- The edges of the parts to be joined should be thoroughly cleaned of contaminants - dirt, rust, slag.
- Existing cracks are sawed off, otherwise it will close only at the top, and a weak structure will remain deep in the metal.
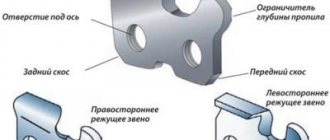
- The edges are cut along the entire length of the seam with bevels at an angle of 45°, and sharp edges are rounded. This measure ensures uniform heating.
- The products are placed on graphite pads, which avoid leakage of molten metal, and the products themselves will not be deformed.
If there are minor oil contaminants, they are removed with an organic solvent or burned out using a gas burner.
Useful tips
Even following the above plan exactly does not guarantee that you will get the expected effect. Below are some recommendations from experienced welders:
- when processing material at home, any method of preheating the part is allowed;
- the maximum length of short seams should not exceed 30 mm;
- blows with a hammer to relieve stress should be performed gently and carefully to avoid cracking of the part.
The high quality of the resulting joint is the main reason for the popularity of argon welding of cast iron products. With proper experience, the process proceeds quickly, and when purchasing nickel filler rods instead of bronze or aluminum, the quality is high. The difficulties associated with the physical and chemical characteristics of cast iron are eliminated when welding is performed in an argon environment. However, this is achievable only if a number of conditions are met.
Did we miss any nuances when welding cast iron? In the comments to the article, you can share your opinion on this topic.
Materials and equipment used
To connect cast iron workpieces, you will need both appropriate materials and the main tool of the procedure - special equipment. Without all this, the work simply cannot be completed.
Filler material
This is a necessary paraphernalia for welding cast iron with argon, which you simply cannot do without, and therefore the choice of additives is of paramount importance. Cast iron rods are widely used. Moreover, those that do not have an external coating.
The most popular brands of additives for joining cast iron products in an argon environment are:
- “A” – corresponds to hot welding.
- “B” - indicates that it belongs to hot TIG welding using local heating of workpieces.
- “NCH-1” is a designation for connecting thin cast iron products using semi-hot welding.
- “NCH-2” – applicable to semi-hot welding of cast iron products with thick walls.
- “BCh, KhCh” – for a weld with high wear resistance.
It is also permissible to use nickel additives for argon TIG welding. The table below shows the brands of this type of filler material, listing their properties and composition.
| Brand | Mechanical properties | Chemical composition | ||
| Yield strength, Pa | Tensile strength, MPa | Elongation, % | ||
| OK TIGROD 19.82 | 800 | 500 | 35 | C |
| OK TIGROD 19.85 | 700 | 425 | 44 | C -67.0 |
| OK TIGROD 19.92 | 500 | 300 | 27 | C-0.02, Mn-0.4, Cu-0.1, Ti-3.0, Al-0.1, Ni ->93.0 |
The diameter of the filler rod is selected based on the thickness of the cast iron products - it should be half the size of the walls.
Equipment
An argon arc apparatus is used to weld cast iron products in a gas environment. This type of equipment includes two welding modes:
- electric;
- gas.
As a result, the permanent connection acquires the necessary quality for further long-term operation. At the same time, you can find a variety of automatic or semi-automatic models on sale.
A semi-automatic machine using an inverter produces a high-quality seam. However, before work, the workpieces must be preheated to a temperature of at least 300 °C. Next, all that remains is to make the necessary settings - set the current strength, additive feed rate and current. The operating instructions for the equipment contain information regarding the voltage that is provided for a particular case.
When using automatic devices, preference is given to powder additives. A person’s participation in the welding process is limited to installing the apparatus at the welded joint, and he can do the rest on his own.
Additive for welding cast iron with argon - Metalworker's Handbook
Cast iron is an alloy of iron and carbon. It has different properties, depending on its composition. carbon in the alloy ranges from 2 to 6%. It makes cast iron a durable material that is difficult to deform, forge, and weld.
It’s not for nothing that cast iron is considered one of the most difficult to weld. Without preliminary preparation of the part, it is impossible to reliably weld the seams of this alloy without defects. Therefore, it is important to choose the right welding machine and solder.
And, of course, only compliance with welding technology will allow you to make a truly high-quality seam.
Welding cast iron with argon
What is cast iron? It is an alloy of iron and carbon, in which the latter can be presented in the form of graphite or cementite (Fe3C). If graphite is used in production, the result is gray cast iron, which is easy to process and weld.
If there is cementite, then the result is white cast iron, which cannot be cooked. It just won't work. The welding process itself can be performed using almost any technology.
In this article we will be interested in welding cast iron with argon using a non-consumable tungsten electrode (TIG).
But before you start to deal with it, it is necessary to say that there are three main directions of welding.
- The welded cast iron parts are connected to each other using a cast iron seam.
- The same thing, only the seam will be made of low-alloy steel.
- And the last one is a seam made of non-ferrous metals.
That is, it turns out that argon welding of cast iron (TIG) can be carried out using filler elements of different compositions.
But it must be added that the argon technology for welding cast iron itself necessarily includes preheating of the workpieces. Although additives are increasingly appearing with which you can cook cast iron without heating.
Depending on the temperature to which the cast iron parts will be heated, the types of cast iron welding also depend. There are also three of them.
- Hot welding, when the workpieces are heated to 600C.
- Semi-hot – up to 400C.
- Cold – they don’t heat up at all.
Welding procedure for cast iron
To obtain a high-quality weld, you must strictly adhere to a certain technology:
- First of all, prepare the products to be connected.
- Set the welding mode.
- Arm yourself with a torch with your right hand, and take the filler wire with your left.
- Gas from the burner should be supplied 20 seconds before the start of the process.
- A distance of 2 mm should be maintained between the seam and the electrode.
- Turn on the device - voltage is immediately applied to the electrode, which causes an electric arc to occur.
- Argon is supplied to the area of the welded joint. The additive will begin to melt and, in liquid form, will begin to fill the void between the products being joined.
- After forming the weld, you need to allow the workpieces to cool.
Only by adhering to technology, as well as observing safety precautions, can you obtain a high-quality welded joint that will last a long time. And thanks to argon, the seam will not become covered with cracks and pores.
For clarity, you can find suitable videos on the Internet where you can see that someone is doing a good job. For example, here you can see how a process is performed using argon.
Important Tips
When performing welding work in an argon environment, you should not discount a number of points:
- Half of the entire procedure is preparation, and the quality of the welded joint depends on it.
- The cast iron products to be joined must be preheated using any available means.
- The seam should be done in short sections of 25-30 mm.
- Smooth feed of filler wire will avoid spatter.
- During welding, the torch must be constantly moved without holding it in place. Otherwise, the metal will overheat, which will lead to strong evaporation of carbon. Weldability will deteriorate, and the hardness will not be throughout the entire seam, but within local limits.
- It is optimal to carry out welding in the lower position, which will prevent leakage of molten metal from the weld.
Sometimes even a high-quality seam may exhibit residual stress. This has a negative impact on the durability of the workpieces. You can remove it by tapping the already cooled seam with a hammer along its entire length.
Additive for welding cast iron with argon
Welding cast iron is a difficult process and requires certain skills and the use of special technologies. Anyone who has faced such a task knows how difficult it can be to achieve high quality welds and to make its physical characteristics exactly the same as those of the base material of the product.
In many cases, the seam either “hardens” (that is, it becomes too strong, which complicates further processing of the part), or pores and cracks appear in it, leading to its rapid destruction.
Welding cast iron with argon, which is recognized as one of the most reliable ways to obtain a weld of the required quality, helps to avoid such consequences.
Features of cast iron welding technology with argon
The use of a technology such as welding cast iron with argon allows us to obtain a weld whose material characteristics are absolutely identical to the main material of the parts or as close as possible to it. In order to achieve this result, the process includes the stage of gradual heating of the welded zone and its subsequent cooling.
Heating the part allows you to change the structure of cast iron - as a result of this procedure, graphite is released on its surface, and the plastic properties of the material increase.
And in order to prevent foreign metals from getting into the weld, graphite electrodes or rods are used during the welding process.
In addition, special cast iron plates or flux-cored wire can be used for this type of welding.
After the welding process is completed, the resulting product must be cooled. In this case, a sharp decrease in temperature (for example, using water for cooling) is unacceptable - the process must be gradual.
Even simply leaving the part at room temperature does not always help achieve the desired effect. Therefore, in many cases, cooling of the part occurs using special insulating materials that cover the product, or sand, which is used to fill the resulting welded part.
This welding method is most often used at home.
As for industrial welding of cast iron with argon, cold welding of cast iron has also become widespread here - that is, welding cast iron parts without preheating them. Currently, there are more than a dozen options for such welding, but three of them are most often used:
- welding using steel electrodes;
- welding using electrodes made of non-ferrous metals;
- welding, the process of which involves small-diameter electrodes containing a minimum percentage of carbon.
The use of cold welding makes it possible to simplify (and therefore reduce the cost) the entire procedure for manufacturing a product by removing two stages from it at once.
In addition, proper heating of the part to the required temperature requires the involvement of special equipment in the process.
Welding cast iron using argon has one more feature: it should be carried out at low welding currents - this minimizes the possibility that the elements making up the weld pool will mix.
Also, a low current helps relieve residual stress in the metal, which can subsequently lead to failure of the weld. Protecting the weld pool with argon during both hot and cold welding of cast iron allows one to cope with such a “minus” of cast iron as its fragility.
The main points of welding cast iron with argon at home
Welding a cast iron product under the protection of argon allows you to protect the entire welding zone from exposure to air, and therefore from the appearance of oxides on it.
As is known, argon is heavier than air, and during the welding process it reliably envelops the cast iron product, preventing not only oxygen, but also other gases from reaching it, which can cause bubbles to appear in the weld pool, which subsequently transform into pores in the weld and reduce its quality is exponential.
When welding cast iron with argon at home, it is important to follow some basic rules:
- Before starting welding, the surface of the cast iron part must be thoroughly cleaned of any contaminants - this will ensure that there are no foreign substances in the weld.
- It is better to use preheating of the part - at home you can use various available equipment for this. Also remember that the part should cool gradually.
- The entire welding process must take place at low current levels.
- Welding is carried out in short sections - the maximum length of one “segment” should be approximately 2.5 cm.
And one more piece of advice from professionals: even when welding at low currents, residual stress remains in the product material, which can negatively affect the durability of the weld. To relieve this stress, you can tap the weld seam lightly with a hammer.
Welding cast iron semi-automatically
I'm sure many people have a semi-automatic welding machine. Often such people wonder how to weld cast iron semi-automatically and is it even possible to do this? First of all, you need to know that cast iron is an alloy of iron and carbon. carbon in cast iron is at least 2.14% . By the way, carbon is also present in steel.
It is noteworthy that pure metal practically does not exist in nature, therefore steel, no matter how pure it is, contains a percentage of carbon. It is no more than 2.14%.
Welding cast iron in an argon environment
Cast iron does not exist in nature. Cast iron is an alloy developed by humans. Given that cast iron contains a lot of carbon, it is reasonable to conclude that it will be brittle. Despite the fact that it is a strong metal, it is also fragile.
https://www..com/watch?v=c5pR7qBoDXY
Many people who have worked as welders for many years believe that welding cast iron with a semi-automatic machine is unrealistic. However, such people are mistaken, because it is possible to weld cast iron using semi-automatic welding.
To do this, you need to use a special flux-cored wire, which allows you to quickly and efficiently weld the cast iron product you need. This wire is called PP-ANCh-3 .
It is best used with heating, because heating promotes the highest quality of welding.
Also, when welding, non-oxidizing and fluoride fluxes are used. This welding gives you the opportunity to obtain high-quality seams as quickly as possible and at low cost. Today, this welding wire has a great sales success due to its high quality, because many professional welders use only the best welding equipment.
As you can see, welding cast iron using semi-automatic welding is a simple process, however, when welding cast iron products you need to be careful and never allow the metal to overheat, because cast iron can develop a crack, and in the future, perhaps even split. Therefore, you need to be careful not to damage your product.
In addition to the fact that you can ruin the product, you can also simply waste time trying to do something after the metal has been severely overheated.
How better it is to just be a little more careful and avoid many problems.
However, if you do experience overheating of the metal, you need to protect it from even a drop of water, that is, under no circumstances should you allow the metal to cool suddenly.
The process of argon arc welding of cast iron
The application of this technology is aimed at obtaining a seam that is identical in its physical and mechanical characteristics to the base material.
Hot welding
To achieve the result, the temperature regime of the work is important.
Uniform heating of the area where the future seam will be applied, and a gradual decrease in temperature upon completion of laying the seam are two key conditions for high-quality work.
The ductility of high-carbon alloys, unlike steels, is much lower. Therefore, when the temperature changes, defects associated with the destruction of the integrity of the metal near the welding site are very likely.
- Preheating the element promotes the release of graphite and improves the plasticity of the metal base. The additional use of graphite electrodes, rods, flux-cored wire or cast iron plates of the same grade helps to guarantee the homogeneity of the chemical composition of the welded joint.
- After completing the welding process, the technology for obtaining a high-quality joint does not end. Now we need to achieve uniform cooling at low speeds. Unlike stainless steels, which are watered, cast iron will not tolerate this technique. It has been proven by practice that even uniform cooling at ambient temperature cannot always give the expected result. In this case, the use of exothermic mixtures and coating materials to insulate the surface is justified. At home or in the absence of special materials, they can be replaced with dry sifted sand.
Cold welding
To increase the profitability of production and reduce losses of working time on an industrial scale, it is customary to use cold welding of cast iron with argon. There is no preliminary stage of heating the parts.
Key points and recommendations for argon arc welding of cast iron at home
The method for obtaining a high-quality seam was made possible thanks to the use of inert gas for this procedure. The absence of oxides and their harmful effects on the processes in the molten bath, improved quality and mechanical characteristics under dynamic loads, the absence of pores and bubbles are obtained thanks to argon.
The burner uses the principle of 38% greater mass of argon compared to ambient air. Consequently, the welding site is reliably protected by a “falling” cloud of this gas. It is absolutely not worth saving on argon consumption when welding capricious cast iron.
It is advisable to adhere to the recommended gas flow rates from the reference literature.
Interesting information.
To understand the variety of uses of argon arc welding, you need to know that there are many designations for it: RAD (manual argon arc welding), AMA (automatic argon arc welding), AADP (automatic argon arc welding with a consumable electrode). The international marking of the non-consumable tungsten electrode welding method is designated as TIG/GTAW. Welding cast iron with argon is the most common method for connecting and repairing it.
Basic rules of application:
- The cleanliness of the surface of the welded elements will ensure uniformity and homogeneity of the seam, will help to avoid the appearance of unpredictable phases with uncertain properties and influence on the characteristics of the seam.
- If possible and economically feasible, it is better to use hot welding. Preheating and gradual cooling of the elements being joined can reduce the lack of skill and dexterity when working with an iron-carbon alloy.
- Minimize welding current. This will help to avoid unpredictable thermophysical processes in the thickness of the element subject to the connection.
- The optimal length of the seam applied at a time should not exceed 25 millimeters. If a longer length is required, the cascade welding technique is used.
The stresses that arose in the seam during reference work can be relieved by using a hammer and tapping it along the line of the welding joint.
Welding cast iron with argon - technology
capable of solving many problems for equipment designers and repairmen.
Cold welding of cast iron - without preheating
With cold welding technology (without heating), it is very important to have good control of the welding arc and make welds as short as possible. The best option is for the seams to be no more than 25 mm long. It is also very important that they cool gradually.
Arc welding processes for cast iron
· Manual arc welding with electrodes
Argon arc welding
Semi-automatic welding
Manual arc welding of cast iron with coated electrodes
There are four types of electrodes that can be used for manual arc welding of cast iron: cast iron electrodes, copper-base electrodes, nickel-base electrodes and steel electrodes. There are reasons and characteristics for using each of these types of electrodes: machinability, strength and ductility of the seam after welding.
When welding with cast iron electrodes, it is necessary to heat the part to a temperature ranging from 120 °C to 425 °C, depending on the size of the part. Typically, cast iron electrodes have a diameter of 6 to 15 mm, and they require a welding current of 200 to 600 Amps. It is better to use small diameter electrodes and relatively low welding currents.
There are two types of copper-based electrodes: tin alloy electrodes (ECuSn) and aluminum alloy electrodes (ECuAl). Electrodes made of tin alloy are used to perform soldering to obtain seams with good ductility. Aluminum electrodes are used to obtain a stronger weld.
There are three types of nickel-based electrodes. The first type (ENiFe-CI) contains about 50% nickel, the second (ENiCI) contains about 85% nickel and the type (ENiCu) contains nickel and copper. The use of these electrodes gives approximately the same results. These electrodes can be used for welding without heating, but heating up to 40 °C is recommended.
Steel electrodes (E-St) are not recommended for welding cast iron if the weld seam will subsequently be machined. This type of electrode should only be used for minor repairs.
Semi-automatic MIG MAG welding technology
The MIG MAG process can also be used to weld cast iron. Several types of welding wire can be used in this process, including:
1. Steel wire (E70S-3) using a gas mixture of 80% Ar + 20% CO2.
2. Nickel wire (ENiCu-B) using 100% argon for protection.
3. Silicon bronze wire (ECuZn-C) using 100% argon (50% argon +50% helium).
Semi-automatic MIG MAG welding technology is similar to other processes. Since low currents are required, the diameter of the welding wire should be correspondingly minimal.
Features of argon arc TIG welding of cast iron
Argon gas (TIG) welding of cast iron is possible, but the process is very complex. Cast iron contains a large amount of carbon, ranging from 2% to as much as 6%.
This carbon content, as discussed above, makes cast iron very brittle and very difficult to weld.
When welding cast iron, adherence to technology and careful temperature control are required to ensure the quality of the weld and prevent the formation of cracks.
When welding with argon, nickel filler rods are used. They are the most preferred and popular for TIG welding of cast iron. Aluminum-bronze rods are also used as an additive, which are much cheaper. But their use is not recommended if the part will subsequently be exposed to heat.
As with any other process, when welding with argon it is necessary to comply with a number of requirements:
· the surface of the welding site must be thoroughly cleaned of dust and rust
· the part must be preheated before welding with argon to prevent the possibility of cracks
· welding should be carried out at low currents in short sections of the weld to control temperature and prevent cracking
· each welding seam must be tapped with a hammer to remove residual stresses
· after welding is completed, it is necessary that the product cools slowly and gradually
conclusions
Welding cast iron is a rather complex process; cold or hot welding, electrodes, argon or semi-automatic welding are used. If you use the right technology and take into account the features mentioned above, you can achieve optimal results. And, therefore, excellent welding quality.
Weldability Characteristics of Cast Iron
Cast iron is not the most favorable material for welding, so it is common to use additional technologies. Important properties of the metal include:
- Lack of plasticity. This suggests that during operation, overvoltage of individual parts of the parts may occur, especially at the junction. Therefore, damage in the form of cracks can sometimes form, but they will manifest themselves only a few hours after welding.
- Cools down quickly. This feature entails the so-called “whitening” effect. This means that a white layer of metal will form on the surface, which is not favorable for further processing.
- Fragility. One of the properties that creates a lot of problems when welding individual sections.
- The amount of carbon required is reduced by exposure to high temperatures. During operation, the carbon begins to burn out, causing pores to appear both inside and outside the seam.
Weldability of cast iron and other properties
Welding cast iron with argon involves taking into account all the properties of this metal. It has a number of specific features that you should know so as not to cause harm. After all, the weldability of cast iron is not at the highest level and the use of all additional technologies helps to avoid problems. Among the important properties it is worth noting:
- High metal cooling rate. This property leads to a “whitening” effect. At this time, a layer of white cast iron appears on the surface of the material, which subsequently cannot be processed.
- The metal has low plastic properties. This leads to overvoltage in certain areas, especially in welding areas. Because of this, cracks form at the seam site, which may not appear immediately, but several hours after cooling.
- Reducing the amount of carbon from temperature effects. When carbon burns out, CO oxide appears, which contributes to the appearance of pores inside the seam and on its surface.
- The brittleness of the material also poses many problems when welding individual parts.
Welding technology
In principle, you need to cook cast iron using argon arc technology in the same way as other metals. No deviations or technological nuances. It is important to correctly configure the welding machine, which should produce a current of 40-80 amperes. The spread of values is quite large, because in this range it is possible to weld parts of different thicknesses. The optimal indicator is achieved experimentally, in which the metal does not crack during welding.
The welding process itself can be carried out in two directions: the torch moves in front of the filler rod or vice versa. This does not affect the quality of the seam. If two thick workpieces are welded, then, firstly, an X-shaped edge is made, and secondly, the seam itself is welded on both sides.
There are several points that you need to pay attention to when welding cast iron with TIG welding.
- You can immerse the welding filler rod into the weld pool after it has heated up well.
- It is better if the additive is not removed from the welding zone during the entire process. But this is not critical, because after filling the bath with molten metal, it has to be evenly distributed throughout the entire gap, forming a weld. It is at this time that the filler element will only interfere there. But this takes a fraction of a second, so the rod does not have time to cool down.
- Welding with a non-consumable electrode in argon must be carried out continuously. As much as possible. If for some reason the process was temporarily suspended, a new seam must be applied to the edge of the old one, which has already cooled down.
- Keeping the burner flame in one place for a long time is not allowed. In the process of strong heating of cast iron, carbon begins to evaporate from it, which leads to bleaching of the metal. It becomes strong and hard, that is, its welding characteristics are reduced.
- It is best if welding cast iron in an argon protective layer is carried out in the lower position. Thus, the molten metal will not flow out of the weld pool under the influence of its weight and under the influence of the pressure of the shielding gas itself.
- If two large and thick cast iron pieces are welded, then the gap between them will be quite large. Therefore, surfacing is carried out in several layers. In this case, it is necessary to periodically stir the contents of the weld pool with the end of the filler rod so that pores do not form inside the molten metal. It is in this way that gases dissolved in the metal are removed.
Sequencing
Welding cast iron products with argon is a popular method to reduce the risk of parts cracking after joining.
The work is performed using a tungsten electrode, which minimizes the amount of slag in the process. Argon welding of cast iron is especially in demand in auto repair when processing parts consisting of the material in question.
In addition to the non-consumable tungsten electrode, nickel filler rods are used. They are less often replaced with bronze or aluminum, usually due to the low cost of the latter. If the part obtained by welding is subject to thermal effects, the use of bronze or aluminum is strictly prohibited!
Mandatory process requirements:
- preliminary cleaning of the surface;
- heating the workpieces to reduce the risk of cracks;
- low current values;
- the seam is applied in short sections;
- each seam is tapped with a hammer to remove residual stresses;
- At the end of the welding process, the resulting part cools down naturally, slowly and gradually.
Filler materials have a length of 60-70 cm and a diameter of 6-15 mm. Why is welding cast iron with argon considered the best way to process the material? The reason is obvious - the gas protects the weld pool from air penetration and slag does not form inside it (contrary to the tendency of cast iron to this process).
When everything necessary is prepared, they begin to work. Below is a brief description of the sequence of actions:
- the user turns on the device;
- the filler material is supplied to the surface (welding area) at an angle of 20-30 degrees;
- the distance between the torch nozzle and the part to be welded should be from 3 to 10 mm;
- perform several short seams instead of one long and continuous one;
- each new seam is tapped with a hammer;
- after forming the seam, allow the parts to cool under natural conditions;
- if necessary, remove deposits (welding spatter) and treat the joint with sandpaper, an angle grinder, or a metal brush.
Tungsten has a very high melting point, so it is not in danger of melting or being exposed to extreme temperatures for long periods of time.
Methods
Welding cast iron with argon can be carried out in several ways. Since all this is carried out in the same protective environment, the main difference is which tool will need to be used. Here, infusible electrodes and filler wire are distinguished, which can have a different composition, depending on the purpose for which the seam is created.
Using a non-fusible tungsten electrode is not as convenient as using a fusible filler material and cannot carry out the welding process if there is a gap between the parts. Welding, in this case, should occur only at the joint. But this method allows you to create a weld pool of sufficient temperature to weld the required depth of metal.
Tungsten electrodes for cast iron
Other types and methods of welding metal with argon involve the use of filler wire. It can fill gaps and weld at an angle, make ceiling and vertical seams.
Technology of welding cast iron with argon
Choosing a method
The most common option is using filler wire. It is more expensive because it requires spending money on consumables. At the same time, this is a more universal method that can be used in almost any position. If it is necessary to reduce the cost of the welding process, then cheaper wire can be used if the composition of the cast iron allows. For thick layers of metal, this method is not always convenient.
Welding with a non-consumable electrode is used when it is possible to create a large pool, which is feasible with a high metal thickness. Tungsten does not melt during welding, so you can use the same tool over and over again. But here it is necessary to use additional flux to improve weldability, as well as to enrich the metal with carbon.