Bronze products are widely used among amateur craftsmen who make various objects of art, weapons and accessories, jewelry, etc.
The lack of a production base is not an obstacle to the work; the main problem is the lack of information about the properties, melting point of bronze and processing modes of copper alloys. Most amateurs do not know that bronze casting is also done at home; the main thing is to follow the technology and provide the necessary conditions for the process to proceed.
Necessary equipment
As in most non-ferrous metallurgy enterprises, the equipment used to produce bronze depends on many factors: the raw materials used, the characteristics of the smelting, the composition of the finished bronze, the financial capabilities of the enterprises, and so on. Smelting is still a very delicate and highly probable process, and two identical plants can use completely different technologies.
For smelting, a device and furnace power are selected that would ensure the fastest possible melting of copper and other components. There are several options for this.
- Electric furnaces - arc and induction . The latter can be with or without a steel core. Recently, induction crucible furnaces have become more common. In this case, it is easier to prepare the device for a new melt, and the waste in such furnaces does not exceed 0.5–1%.
- Electric arc furnaces with indirect heating - the arc is formed between horizontal graphite electrodes. During melting, the furnace rocks at an ever-increasing angle as the temperature rises. In this way, local overheating of the melt can be avoided.
For casting copper alloy, various types of gating systems are used. Their design is determined by the composition of the alloy, the size and configuration of the casting, and so on.
- The most common device refers to expanding systems with siphon - bottom, and top side inlet. This design is universal and allows you to obtain parts of both simple and complex configurations.
- To obtain blanks with simple configurations, rain or top gating systems are used.
- If castings are produced from alloys that do not form high-strength oxide films, then devices without complex slag traps are used. Otherwise, such a device is necessary.
- If you need to obtain small-sized workpieces, you can use systems with bottom supply.
Next, bronze producers in Russia are considered.
Brass grades and applications
The brand of brass and its scope of application depend on the composition. For example, tombak, which belongs to the class of wrought brasses, which contains more than 95% copper, can easily combine with steel, forming a bimetal with it. This compound is used in the manufacture of insignia and various objects of art and interior design - figurines, frames, candlesticks .
LO grade brass is used for the manufacture of condenser tubes used in various heating equipment, for example, gas boilers, autoclaves, and bellows.
The LS brand is used to create parts for watch mechanisms, adapters and connecting bushings. Printing matrices are also made from it.
LMC - is found in old Soviet coins with denominations up to 5 kopecks, fittings, nuts and bolts, and its subtype with the prefix “A” is found in parts of river and sea vessels.
Brass, marked LA or LZhM (and its subtypes), is also used for the construction of sea ships and aircraft, various electrical machines and bearings. Very common in parts for various chemical equipment.
This is interesting: How and what to clean copper oxide from at home: the most effective methods
Casting technology
- Pieces of raw material are placed in a crucible and heated in an oven to the desired temperature (50-100˚ Celsius above the pouring temperature) and held for 4-5 minutes. Overheating is undesirable, since some alloy components can burn at high temperatures. Before pouring, the melt is stirred several times with a stick. Melting is carried out under a layer of flux. It isolates the metal from the air and prevents oxidation.
- The crucible with liquid metal is removed from the furnace using a hook and tongs. Be sure to use a spoon to remove the slag from the surface of the melt.
- Using a thin continuous stream, the material is carefully poured into the tooling cavity through a special hole (sprue).
- When the metal has cooled, the hardened product is removed. Sometimes the melting mold is opened and the part is knocked out or the equipment is destroyed if it is disposable.
If the part has complex geometry or is very small, the melt may not squeeze out all the air from the cavity, and defects may appear on the part. In this case, centrifugal casting is used. The equipment is installed in a rotating centrifuge. Under the action of centrifugal force, the liquid metal is evenly distributed throughout the mold cavity. The centrifuge drive can be manual or electric.
Preparing the form
Before work, the mold is warmed up. The oven is heated to 500-600˚C, the equipment is placed there and the temperature in the oven is increased to 900˚C. Calcinate for 2-5 hours. The time depends on the size of the mold. Then it is taken out and cooled to 500-600˚C. After this, the metal can be cast.
Safety rules at work
Any work with products heated to high temperatures must be accompanied by strict compliance with labor safety standards.
This is the only way to prevent accidents and injuries. The person working with the stove must have protective clothing. This should be a heat-resistant apron that covers the entire front part of the body, thick leather gloves and boots with large soles. There should be no shirts or pants made of synthetic materials under protective clothing. Such products ignite very quickly and do not extinguish well. Give preference to items made from cotton or wool.
If you're wondering where you can get these safety gear, don't worry. Most likely, the same place where you will find crucible tongs and other equipment for melting metals. You can also buy safety glasses, a face mask or a respirator with a special filter there. These devices will help protect your face, eyes and lungs from the harmful effects of waste fumes emanating from molten metal.
How to make a casting mold
The mold is made using molding sand and a mold. The mixture consists of sand (75%), clay (20%) and coal dust (5%). The components are thoroughly mixed until smooth.
The flask consists of two shallow boxes stacked on top of each other. One, the bottom one, has a bottom and is filled with molding sand to the very top. The second box does not have a bottom, but is equipped with two crossbars.
Mold making process:
Casting mold and its elements
- the model, previously coated with a thin layer of talc or graphite powder, is pressed halfway into the molding sand of the lower drawer;
- then the top box is installed and filled with the mixture, compacted so that the model is completely and tightly covered with it;
- for pouring, one or more holes are made - sprues;
- the form is cut along the junction line of the boxes and divided in half;
- the model is removed, and the boxes are connected again, the voids from the model are connected and form a cavity that has the required shape.
At the end of the process, the form must be dried a little and can be used for its intended purpose.
Step-by-step instruction
In artisanal conditions, small bronze items are mainly made, for example, decorative elements. a room specially adapted for these purposes , as well as special equipment . In some cases, it is necessary to resort to finishing the casting to the desired state by editing at home , such as removing excess molten material by hand, grinding and polishing the product.
Before you start melting metal, you need to prepare the room and acquire the necessary tools and equipment . The main requirement for the room is the presence of good exhaust ventilation, as well as a floor made of non-combustible materials such as concrete, cement or brick. When making small products, these requirements are quite easy to comply with, otherwise you will have to use the garage.
In order to smelt bronze at home, you need to purchase a special muffle furnace with the ability to regulate the temperature, but you can get by with a simple forge, the fuel for which will be charcoal.
Preparing tools
A novice foundry worker should purchase or make the following tools.
- A refractory crucible made of a refractory material (such as cast iron or steel) is a special vessel with a spout into which pieces of metal to be melted are placed.
- Devices for removing the crucible from the furnace that minimize the risk of getting burned are special hooks and tongs.
- A mold for pouring molten metal, which is made using a flask and a model.
- The flask itself is two boxes that hold a casting mold filled with molding sand.
- A welder's suit or simply a very thick apron and mittens, the purpose of which is to protect a person from flying sparks and splashes of molten metal.
Once you are convinced that all of the above is present, you can proceed directly to melting bronze.
- Preheat the oven by setting the temperature using the regulator. The temperature depends on the chemical composition of the bronze, as we discussed above. For example, for aluminum bronze this temperature will be 1040-1084 degrees Celsius.
- Next, be sure to warm up the mold , this is done so that the molten metal does not freeze when it enters a cold container. The mold is placed in the oven when it warms up to a temperature of 600 degrees, after which the thermostat is set to 900 degrees. When the temperature inside the oven rises to 900 degrees, leave the mold to warm up for 3-4 hours, after which it is carefully removed using special devices and cooled to 500 degrees Celsius.
- Place a crucible with pieces of bronze intended for melting inside a furnace heated to the desired melting temperature and bring it until the metal is completely melted. After this, leave the crucible to overheat for another 5 minutes to achieve better metal fluidity and better casting quality.
- Remove the crucible from the furnace or forge using hooks and tongs and begin pouring it into the mold.
Let's look at how to properly make a mold to obtain a high-quality product. In foundries, such a mold is made using a flask into which a mixture consisting of clay, sand and coal powder is poured. The flask consists of two halves, each of which is a box into which the molding sand will be poured.
- First, take the first box and begin to fill it with the mixture, filling it halfway, and place the model inside the box.
- Next, they continue to pour bulk material until the box is filled to the very top. During work, it is necessary to constantly level and compact the molding mixture.
- Place a second box on top and continue pouring a mixture of clay, sand and coal powder.
- In the second box it is necessary to provide sprues - holes for pouring molten bronze into the mold.
- When both boxes are filled to the top, separate them using a sharp object. One half of the model is in one box, the other half is in another.
- Carefully take out the model, connect both boxes again - the resulting void inside is the mold for filling.
Pouring into a mold
The molten metal is poured in a thin stream from the crucible into the mold , making sure that the stream flows continuously. If the part being cast has a complex shape, you need to use a special centrifuge , which, using centrifugal force, will help the melt to be correctly distributed inside the mold, completely filling it.
How to make high-quality castings
To obtain high-quality bronze casting, subsequent machining of the casting will be required. It is necessary to sequentially perform the operations of separating the sprues, removing flash, mechanical grinding and polishing of the product. It is impossible to immediately obtain a high-quality finished casting at home, so you need to prepare for finishing procedures.
Art bronze casting technology in pictures
Comparative characteristics and differences between metals
In the metallurgical industry, there are clear criteria for distinguishing between bronze and brass. However, if a person is not associated with this field of activity, he will not be able to determine by eye what material is in front of him. Combining copper with tin or zinc produces alloys that have different properties and are used in specific areas.
Bronze and brass have different properties and belong to completely different categories. The first alloy can be tin or tin-free, while the second can be two- or multi-component.
Bronze alloy consists of tin to which lead may be added. The color of the metal will depend on the percentage of one element or another. The main additive element in brass is zinc.
Bronze is resistant to chemical and aggressive compounds. In addition, its negative reaction to salty sea water made it possible to use the alloy in shipbuilding and navigation. Brass cannot boast of this, so to give it improved qualities, additional elements must be introduced into the alloy. In addition, bronze has better strength and anti-friction characteristics than brass. This allows you to significantly expand the scope of application of the alloy.
The high zinc content in brass gives the alloy a variety of colors from pink-red to golden yellow. This is what makes it similar to noble gold.
What does brass look like?
The silvery-white color of bronze is achieved by adding more than 35% Sn to its composition. An alloy containing at least 85% copper is brownish-red in color. Since compounds with high levels of impurities are rare, it can be argued that basically brass is a metal of golden yellow color, and bronze is closer to red, sometimes dark brown. The same colors of brass and bronze will appear on the broken objects. This allows you to easily distinguish brass products from bronze ones.
From a metal such as brass, not only decorative elements are made, such as furniture fittings or artistic objects for interior decoration, but also main parts used in various industrial fields.
Bronze and brass have a lower melting point than pure copper. This makes it possible to make various products from them for home use. Artistic casting made of bronze and brass looks very beautiful. However, for this you need to have the appropriate equipment and know the technology and rules for performing such a procedure.
Preparing for bronze casting at home
To melt bronze at home, you must have the appropriate equipment and devices. The process occurs at high temperatures, with the release of smoke and other combustion products, so it is best to work in a garage or workshop; it is not recommended to perform all actions in an apartment.
Melting furnace used at home - device
Melting bronze compositions requires a high temperature, in the range of 900–1200°, so it is impossible to do without a muffle furnace or forge. It will be necessary to equip high-quality exhaust ventilation; the floor covering must meet all fire safety requirements. It is necessary to prepare a container for melting (experts recommend making the melt in a cast iron container with an elongated spout for casting precision, which is called a crucible).
To remove the hot crucible from the furnace and grab the hot castings, you will need pliers (tongs) and a hook. Be sure to take care of protection from sparks or splashes of molten metal and prepare an apron and mittens from dense and durable material (ideally, you can use a welder’s suit).
You will need to make a casting mold, and you will need charcoal for the forge.
Is it possible to cast bronze at home?
The good news is that this metal can be melted not only in industrial conditions, but also at home. True, “home” is a relative concept. You won't be able to pour in your kitchen. You need at least a separate room with good ventilation. This is for small things, such as small art castings. For large parts you will need a garage or hangar.
Bronze has low shrinkage - less than 1%, and is used to make precision castings. But in any case, it will not be possible to achieve industrial quality casting. And most importantly, you need to follow safety precautions and fire safety! They will be discussed at the end of the article.
Bronze scrap is used as a raw material; you can melt down plumbing parts with your own hands. The industry produces metal in ingots.
Melting points
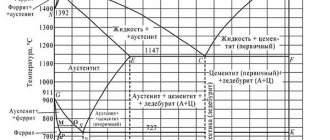
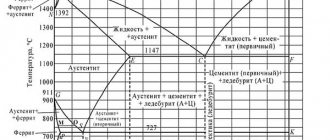
The melting point of bronze directly depends on the filling of the alloy with chemical elements. After all, refractory elements can act as alloying components. Thus, the maximum temperature for casting bronze is 1350 °C.
Marking of alloying elements added to copper alloys:
- aluminum (A);
- beryllium (B);
- iron (F);
- silicon (K);
- manganese (Mc);
- nickel (N);
- lead (C);
- selenium (O);
- titanium (T);
- zinc (Z).
To divide bronze alloys, two definitions are used: tin-bearing and tin-free bronzes. The melting point of a material suitable for casting, depending on its chemical composition, is given in the table.
| Alloy, designation | Temperature for casting, °C |
| BrOF4-0.25 | 1300 |
| BrOTs4-3 | 1250 |
| BrOTsS4-4-4 | 1200 |
| BrAZH9-4 | 1200 |
| BrA9Mts2L | 1150 |
| BrA10Zh8L | 1190 |
| BrA11Zh6N6 | 1185 |
| BrAZhS7-1.5-1.5 | 1150 |
| BrS3O | 975 |
| BrA5 | 1200 |
| BrKN1-3 | 1050 |
| BrBNT1.7 | 1050 |
| BrAMts10-2 | 1150 |
| BrKMts3-1 | 1150 |
| BrMts5 | 1150 |
| BrB2 | 1100 |
| BrSN60-2.5 | 1100 |
This is not a complete list of cast bronze alloys.
If bronze smelting is done at home, then special attention should be paid to the melting point of the alloy. Tin bronzes do not need to overcome the thousand-degree threshold. They need 900°C - 950°C. Tin-free alloys already require 950 °C - 1100 °C.
Parts produced from bronze by centrifugal casting
When smelting bronze parts, it is worth considering their high viscosity. Therefore, for high-quality casting, they should be heated above the melting point by about 100 degrees. Bronzes have minimal shrinkage, which does not exceed 1.5%. This characteristic is an advantage over brass and makes it possible to obtain shaped castings.
For comparison, you can look at the melting point of brass. There are two categories of brass: two-component and multi-component brass. The two component alloys contain zinc in addition to copper. Its amount affects the melting point, which is in the range 880°C - 965°C.
For multi-component temperature conditions increase to 895 °C - 1070 °C due to the introduction of alloying components with a high melting point.
Main characteristics of bronze alloys
Bronze is the collective name for copper alloys with various alloying additives. There are many such additives that can be used:
Classification of bronze alloys
- Tin.
- Aluminum.
- Lead.
- Beryllium.
- Silicon.
All types of bronze contain small amounts of zinc, lead or phosphorus. At the same time, alloys of copper with zinc (as a full-fledged component) do not belong to bronze and are classified as brass. A separate group are alloys of copper and nickel (constantan, cupronickel, copel, nickel silver).
Bronzes are divided into:
Copper alloys - characteristics
- tin. They are alloys of copper and tin in one ratio or another;
- tin-free. Instead of tin, other materials are present (beryllium, aluminum, etc.).
Tin types are the most common. Widely known bell bronze (80% copper and 20% tin). The disadvantage of tin bronze is its fragility.
Tin-free compounds have a lot of specific qualities that are successfully used to perform various tasks.
Common types of tin-free bronze are:
- Beryllium bronze. Has high strength, superior to high-quality steel.
- Silicon-zinc. It is resistant to friction and has high fluidity in the molten state, which is facilitated by the addition of silicon.
- Lead. Demonstrates high resistance to corrosion.
- Aluminum. It is resistant to corrosion and has high friction capabilities.
Alloying additives of alloys in bronze
How to properly pour metal into a mold
If molten metal is poured into large casting molds, then its own weight is quite enough to displace all the accumulated air from them. If casting is performed in small molds, then it is almost impossible to displace air from all the internal cavities of such structures due to the mass of molten metal. In order to obtain high-quality castings in such cases, it is necessary to use special technological techniques.
Casting molds are placed in special centrifuges, powered by manual or electric drive. During rotation, centrifugal forces are created that evenly distribute the molten metal throughout all the internal cavities of the molds. This technology is effective only if the metal is still in a liquid and not a solidified state.
Homemade centrifuge for casting small parts
After the casting process is completed and the metal has cooled, the casting is removed using simple mechanical devices. It should be borne in mind that the surface of products freshly removed from the molds is not of high quality, so they must be subjected to various types of mechanical processing.
Characteristics of brass
The manufacture of products from this alloy is achieved primarily through casting . Therefore, it is very important to know at what temperature brass melts. This greatly depends on its chemical composition, and more specifically, on the zinc content in it, because the more of this metal, the less heat is required to melt it. If brass contains a significant amount of bismuth or lead impurities, this has a very negative effect on its flow, complicating the processing of products. Therefore, its melting point ranges from 880-950 degrees Celsius.
When making brass products, it is very important to cover them with a protective layer. For this you can use regular varnish. Despite its resistance to corrosion, it is very susceptible to oxidation in the open air. Many exposed parts or furnishings need to be cleaned regularly to prevent them from discoloring. But this is easy to do, because brass polishes very well .
Technical characteristics of the alloy
In addition to its melting point, brass has several other important characteristics due to which it is so widely used in various fields. Here are some of them:
- Specific electrical resistance is in the range of 0.07−0.08 microohms per meter.
- Density is about 8.3−8.7 tons per cubic meter.
- Heat capacity is 0.377 kilojoules per kilogram Kelvin.
Depending on the composition, brass is:
- Double - an alloy containing only copper and zinc.
- Multicomponent - containing a large number of other metals and impurities.
Pouring metal
In order to melt the material you will need:
- Melting muffle furnace, preferably with a heating regulator. For large castings you need a forge. Sometimes the material is melted with an autogen, a blowtorch, a gas or gasoline burner.
- Crucible - a steel, cast iron or fireclay (fireclay) container for melting, preferably with a spout.
- Tongs and a hook for removing the hot crucible from the furnace and other manipulations.
- Casting shape. How to prepare it for work is described below.
- Flux. Needed to protect the alloy from oxidation by air. Charcoal, borax.
- Fuel for the forge, for example, is the same charcoal.
- Ceramic or birch stick for stirring the melt.
Copper in forensics
M. poisonings are accidental and occur in industry, agriculture, and everyday life, when drugs containing M. can enter the body through the respiratory tract and orally. The lethal dose of M. sulfate is 10 g. At the autopsy of a person who died from poisoning with copper-containing substances, and histol, the study diagnoses phenomena of irritation of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity (sometimes its bluish color), stomach and intestines, especially the colon; severe dystrophy of the liver, myocardium, kidneys; purulent bronchitis, small focal pneumonia.
Judiciary-chem. M.'s detection in internal organs is based on its isolation from the mineralizate in the form of M.'s diethyldithiocarbamate, transfer of M. again into the aqueous phase of salt, and then determination of M. ions using qualitative color reactions. Quantitative determination is made by complexometric titration, and in small quantities - by colorimetric determination of diethyldithiocarbamate M. Sensitivity of methods for detecting M. in forensic chemistry. definitions - 0.4 mg per 100 g of organ tissue. When quantitatively determining M. in internal organs, its natural content in the tissue of these organs should be taken into account.
Bibliography:
Biological role of copper, ed. V. V. Kovalsky, M., 1970; Katsnelson B. A. et al. On the influence of copper-containing compounds in quartz dust on the development of experimental silicosis in rats, Gig. labor and prof. zabolev., No. 3, p. 30, 1969; Lutsenko L. A., Kochetkova T. A. and Titova I. N. The significance of low concentrations for the experimental assessment and standardization of ore dusts with fibrogenic and toxic effects, in the book: Gig. labor in the mining industry, ed. A. P. Shitskova, p. 69, M., 1978; Mashkovsky M.D. Medicines, part 2, p. 355, M., 1977; Molecules and cells, trans. from English, ed. G. M. Frank, V. 4, p. 136, M., 1969; Radiation Safety Standards (NRB-76), M., 1978; Pauling L. and PolingSH Chemistry, trans. from English, p. 31 and others, M., 1978; Shvaykova M.D. Toxicological chemistry, p. 318, M., 1975; H o 1 tz man NA Menkes' kinky hair syndrome, a genetic disease involving copper, Fed. Proc., v. 35, p. 2276, 1976; Lede-r e g S. M., Hollander JM a. P e r- 1 man I. Table of isotopes, NY ao, 1967; Menkes JH ao A sex-linked recessive disorder with retardation of growth, pecular hair, and focal cerebral and cerebellar degeneration, Pediatrics, v. 29, p. 764, 1962; Radioactive Isotope in Klinik und Forschung, hrsg. v. K. Fellinger u. H. Vetter, Bd 9, Miinchen—B., 1970; Trace elements in human health and disease, ed. by AS, Prasad, v. 1, NY, 1976.
Production of high quality castings
It is possible to obtain products of higher quality than by casting into the ground. For this purpose, lost wax casting is used.
The equipment is made of gypsum. It is disposable and destructible. To make a mold, you need a model of the product made of wax, paraffin or other fusible material. This material should be lighter than water. The following will explain why this is important.
A wax model is also made by casting into plaster casting. Models of complex configuration are made from several parts. And plaster equipment for the model is made according to the original product or its model, similar to equipment made from sand. The result is a chain: original product - plaster mold for wax model - model - plaster mold for metal - finished product.
When the tooling for the product is ready, a wax model is melted from it by immersing the mold in hot water or simply heating it. The melted wax flows out of the cavity through the same hole into which the metal will then be poured. That is why the material of the model must be lighter than water - so that when smelted in water it rises to the surface.
You can familiarize yourself with the process by following the instructions in the video provided.
Areas of use of bronze
The use of this alloy is determined by its basic characteristics. Quite often, various additional components are added to bronze, which characteristically change and complement its features.
As for the tin subtype of the alloy, it has been used since ancient times. Various bronze products were especially popular - jewelry, figurines, household items, etc.
To increase the alloy's resistance to corrosion, nickel, zinc, phosphorus and other similar elements are added to it. Most often, this material is used to make all kinds of tools for navigation.
Aluminum and silicon-zinc types are used, as a rule, to create objects of art.
Features of the casting process
The bronze melting process occurs in the following sequence:
- Bronze scrap is crushed and placed in a crucible.
- The crucible is placed in a muffle furnace, which is recommended to be heated in advance.
- The molten metal must be overheated, for which it is kept in the oven for 5 minutes longer than necessary. This makes the melt more fluid.
- Using a hook and tongs, the crucible is removed from the oven and immediately poured into the prepared mold.
The mold should be prepared by thoroughly calcining it in the oven. If this is not done, the metal will immediately cool down and become hard when casting begins, without filling the entire mold.
Centrifugal casting
The form is prepared in the following order:
- The oven heats up to 600°.
- The mold is placed in the oven and heated to the desired temperature.
- The heating of the oven is increased to 900° and the mold is maintained in such conditions for about 3–4 hours.
It should be taken into account that the melting temperature of bronze of a given grade should be lower than the heating value of the furnace. The melt must be heated to a higher temperature to obtain maximum fluidity (bronze has a high viscosity in the liquid state), as well as to obtain a certain temperature reserve for high-quality production of the casting.
Processing temperature and technical properties of tin bronzes
Special Moments
For casting various thin metal products, preference should be given to brass, since it melts much more easily than bronze. As for equipment, it is better to choose crucibles made of ceramics and clay, since they are more suitable for working with this alloy.
Regarding the remelting of ancient bronze, it should be said that during this procedure one must be especially careful, since it may contain arsenic.
You should also consider the amount of impurities that bronze has. The melting point of the material may vary significantly depending on this. For a tin alloy, the readings are in the range of 900-950 degrees, while for tin-free alloys you need about 950-1080.
Bronze is an alloy of copper with the addition of various non-ferrous metals. This material is durable, hard and resistant to corrosion. In the past, bronze was used to make various tools, jewelry, weapons and sculptures, and nowadays other metals are added to this alloy to obtain special characteristics. Due to this, aluminum bronze is used in the manufacture of various parts of pipelines and aircraft, silicon bronze is used in navigation, and phosphorus bronze is used for various springs and parts of electrical equipment.
Pouring bronze into a mold
Pouring bronze melt into a casting mold
Pouring the melt in itself is not difficult - the metal is poured in a thin, even stream until the mold is completely filled.
Difficulties may arise if there are no air channels into which air can escape. If the outlets are clogged, air pockets will not allow the melt to completely occupy the entire mold, and the casting will be damaged. The problem can be solved by using a centrifuge, which distributes the metal inside the mold and helps it overcome the resistance of air pockets.
The main thing about copper
In the periodic table this material is called Cuprum. It is assigned atomic number 29. It is a plastic material that can be easily processed in hard form by grinding and carving equipment. Good voltage conductivity allows copper to be actively used in electrical and industrial equipment.
In the earth's crust, the material occurs in the form of sulfide ore. Frequently encountered deposits are found in South America, Kazakhstan, and Russia. This is copper pyrite and copper luster. They form at average temperatures, like thin geothermal layers. Pure nuggets are also found that do not require slag separation, but require melting to add other metals, since copper is usually not used in its pure form.
The metal has a reddish-yellow tint due to the oxide film that immediately covers the surface upon interaction with oxygen. The oxide not only gives a beautiful color, but also promotes higher anti-corrosion properties. The material without an oxide film has a light yellow color.
Pure copper melts when it reaches 1080 degrees. This relatively low figure allows you to work with metal both in production conditions and at home. Other physical properties of the material are as follows:
- The density of copper in its pure form is 8.94 x 103 kg/m2.
- The metal is also distinguished by good electrical conductivity, which at an average temperature of 20 degrees is 55.5 S.
- Copper transfers heat well, and this figure is 390 J/kg.
- The release of carbon when a liquid material boils starts at 2595 degrees.
- Electrical resistance (specific) in the temperature range from 20 to 100 degrees - 1.78 x 10 Ohm/m.
Marking
The marking principle is as follows:
- They write the letters Br (meaning “bronze”).
- Write letters denoting alloying elements:
- Write numbers indicating the percentage of each element. For wrought bronzes, the numbers are written at the end of the markings in the same order as the letters. For foundries, a number is written after each alloying component. For example:
BrOF10-1 – deformable bronze. Tin is approximately 10%, phosphorus is 1%, the rest is copper. Or:
BrA10Zh3 – cast bronze, where aluminum is 10%, iron is 3%, the rest is copper.
There may be other impurities, but their number is insignificant.
Types of alloys
Bronze contains copper and alloying additives (beryllium, lead, aluminum, silicon and tin). All its alloys also contain components such as zinc, phosphorus, etc. In addition to bronze, the modern industrial industry is engaged in the production of other alloys from copper - constantan, copel, nickel silver, cupronickel, brass, etc.
The amount and type of alloying components in a bronze alloy determines its chemical and physical characteristics, as well as the color of the material.
Brands of bronze alloys, the melting point of which lies in the range from 930 to 1140 degrees Celsius, have their own markings. , bronze-based alloys
- Tinless;
- Tin.
People learned to combine tin with copper to produce bronze a long time ago. Tin makes the material stronger and also reduces its melting temperature. A striking example of this type of alloy is bell bronze. It contains twenty percent tin and eighty percent copper. However, products made on the basis of bell bronze are characterized by high fragility.
Tin-free bronzes, as the name suggests, do not contain tin. Such alloys today are classified into separate categories of bronzes:
Beryllium is the strongest and has many characteristics superior to steel;- Silicon-zinc - have increased resistance to abrasion (the advantage of such bronzes of this group is that when molten they have high fluidity);
- Based on aluminum and copper, they have high anti-corrosion protection and excellent anti-friction properties.
Currently, the most common bronzes are those containing tin. For the purposes of marking the material, regardless of the composition, the designation “Br” is used, after which the additives used and their content in the material are indicated. For example, you can decipher the bronze “BR OTSSNZ-7−4−2-. This tin alloy contains tin, zinc, lead and nickel. The numbers indicate their percentage in bronze. The composition of any brand of bronze may contain other elements having the following designations:
- A - aluminum alloys;
- B - beryllium-based alloys;
- F - ordinary iron;
- K - silicon element;
- Mts - ordinary manganese;
- F - phosphorus.
Main stages
Bronze casting involves a technological process that requires the use of special equipment and compliance with certain production stages:
- First of all, a drawing of the future workpiece is prepared.
- A connection to the gating system model is created. This is done by soldering or gluing.
- An injection mold is made from refractory mixtures.
- The form is freed from the model composition. To do this, it is heated with steam or lowered into a container with hot water.
- Using a centrifugal machine, molten bronze is poured into a mold.
- The future workpiece is allowed to cool on its own.
For further processing of the bronze part, the mold is broken. The workpiece is washed using chemical compounds.
How to improve the quality of a product?
In fact, it is impossible to obtain a truly high-quality item at home without fine-tuning.
It is also possible to improve the quality and appearance by making the mold using a low-melting material . To do this, we first make a plaster cast of the model from which our part will be made; this cast must consist of two parts that are fastened to each other. Paraffin or wax melted in boiling water is poured into the resulting cavity, and after it hardens, the gypsum shell is removed.
Next, the resulting low-melting model is placed in a special casting mass, forming holes for draining paraffin and pouring molten bronze. After this, the casting mass is placed in boiling water, the paraffin melts, and it is easily poured out of the mold.
The resulting casting mold is smoother and produces higher-quality products than a mold made using the conventional method.
The following video shows the process of smelting bronze at home.
Foundry models
Artistic casting of bronze and brass involves obtaining the smoothest possible surface, so fairly hard materials are used to recreate the model:
- wood;
- gypsum;
- Ivory.
To obtain the smoothest possible surface, it is subjected to elimination of porosity by puttying, priming and varnishing. Casting models are made detachable; one-piece - suitable for casting products of simple shapes; special for parts with a rather complex configuration.
Average copper consumption and status.
Typical diets meet or exceed the RDA for copper. The amount of copper consumed in the average human diet ranges from 800 to 1000 mcg per day for children aged 2 to 19 years. In adults 20 years of age and older, the average daily intake of dietary copper is 1,400 mcg for men and 1,100 mcg for women. Total intake of dietary supplements ranges from 900 to 1100 mcg/day for children and from 1400 to 1700 mcg/day for adults over 20 years of age.
According to an analysis of data from the 2009–2012 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 6–15% of adults aged 19 years and older who do not take a copper supplement have a copper intake below the EAR.
Casting at home
Experienced metallurgy masters practice bronze casting at home. To carry out this process you need to purchase:
- bugle;
- forceps;
- charcoal or coal;
- crucible in which metal will be melted.
A gas burner is often used as a heating element for melting a bronze alloy. This is due to the fact that bronze can be melted at a low temperature. This way you can save on the purchase of an induction furnace.
Casting at home
Creating a casting mold
Casting bronze at home requires the correct production of casting molds. The molding mixture should consist of a mixture of sandstone, coal dust, and clay. Stages of mold making:
- The molding mixture is poured into a wooden box called a flask. It is compacted from above with weak blows.
- Next, a model of the future workpiece is immersed in the molding mixture.
- On top there is another box (flask). The molding mixture is poured into it. It's being compacted.
- Next, the master divides the form into lower and upper halves.
How to properly pour molten bronze into a casting mold
Bronze casting at home requires special preparation of casting molds. It is necessary to remove air from them in order to obtain durable castings without defects. The molds must be spun in an electrically driven centrifuge. After this, the molten metal can be poured.
How to get better quality castings
The casting quality can be improved. You need to use another modified technology. In this case, wax is used. It is used to make molds into which the castings will be poured. You can use paraffin. To make such a model, you need to use a ready-made mold that is heated in boiling water. Bronze casting has been known for many hundreds of years. Using this technological process, decorative elements, fences, lamps and sculptures are made. The composition of bronze includes various components that affect the characteristics of the alloy. There are different types of making bronze castings, which involve different technological processes.
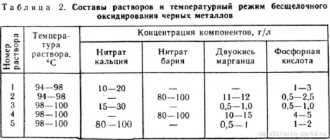
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS WHEN MELTING BRASS
During the process of smelting brass at home , or in industrial enterprises, precautions must be taken.
- The molds are removed using tongs with long handles.
- Work clothes should be made of non-flammable or flame-retardant fabrics and cover the maximum area.
- The face must be protected with a one-piece mask, or goggles and a visor.
- The casting process is carried out under the condition of ensuring high-quality ventilation.
- Surrounding surfaces must be insulated using non-flammable coatings. The most popular and affordable option for such coating is asbestos.
- All manipulations with the molten alloy are carried out over previously prepared sand.
- The presence of moisture is not permissible due to the risk of splashing of molten material.
The melting time of the alloy directly depends on its composition, and the final result depends on compliance with all necessary conditions. Upon completion of the process and complete cooling of the workpiece, it is given the proper appearance. This is achieved by cleaning and polishing.
Determination through chemical experiments
The reaction with concentrated nitric acid is indicative: if the latter is dropped onto the surface of a copper product, a green-blue color will occur.
A qualitative reaction to copper is dissolution in hydrochloric acid followed by exposure to ammonia. If a copper sample is left in an HCl solution until completely or partially dissolved, and then ordinary pharmaceutical ammonia is dropped into it, the solution will turn intensely blue.
Important: working with chemicals requires precautions. Independent experiments should be carried out in a well-ventilated area using personal protective equipment (rubber gloves, apron, goggles)