Copper pipes are often used to organize plumbing systems. In addition, such elements are often used when decorating residential premises in the steampunk style. Regardless of the purpose of using such elements, copper pipes must be somehow connected to each other. The easiest way to do this is with copper-phosphorus solder. In this case, the joint will be neat and airtight. After the seams harden, the structure will be as strong as a solid pipe. However, before you start soldering with copper-phosphorus solder, it is worth knowing some of the characteristics of the material you are going to work with.
Useful information about copper
The soft metal alloy began to be used in ancient times for minting coins.
Today this material has become a little less popular, but heating and plumbing systems made from copper pipes are still the most durable, reliable and durable. Installation of such lines is carried out using soldering. During the work process, metal elements are connected to solder - a specially selected material, the melting point of which should be lower than that of the workpiece.
The soldering process itself is simple. The main thing is to choose the right connecting material. In our case, this is copper-phosphorus solder. It is also worth deciding on the soldering method. There are several of them.
The soldering process itself is simple. The main thing is to choose the right connecting material. In our case, this is copper-phosphorus solder. It is also worth deciding on the soldering method. There are several of them.
Copper-phosphorus type of solder
Three-component copper-phosphorus type solders with a silver percentage of up to 15% are used when exposed to high temperatures, mainly in refrigeration production when using gas.
We recommend: Brass thick-walled bronze pipe: GOST 1208 90
Special Features
Copper-phosphorus type tinoli have a low melting point. This type of material is significantly fluid when working with metal products of various compositions with copper content. The positive aspect of this case is that there is no need to use flux when working with such solder, since phosphorus is already in it. The resulting seams when soldering in this way are reliable and of high quality. Such strong connections are required when using installations in the refrigeration industry. Refrigeration units operate with connections that are subject to slight vibration influences. At the same time, the high silver content in the solder makes the material quite ductile. In the process of soldering reinforcing parts, non-heat-resistant parts should be cooled to prevent overheating. When connecting metal parts, it is necessary to use a blowing agent such as dry nitrogen through a special installation. This must be done to prevent the formation of scale on the equipment. Substances of copper-phosphorus composition are not used when working with steel parts, due to the appearance of a crumbly film of phosphites on the created seam.
The types of copper-phosphorus solders are as follows:
- Type 102 . Three-component material of copper-phosphorus type with a percentage of silver within 2%. This alloy is quite inexpensive and has average spreading properties. It seems possible to use it when installing refrigeration equipment when connecting parts that are not affected by vibration force. In this case, you need to purchase a soldering iron or gas torch;
- Type 105 . Three-component material of copper-phosphorus type with a percentage of silver within 5%. This material has plasticity and slow spreading, making it possible to fill large gaps. It is important to note that by joining copper parts in this way, the resulting solder seam will be able to withstand slight vibration and minor shocks. It is recommended to use for connecting copper products, as well as alloys with it in refrigeration systems;
- Type 115 . Three-component material of copper-phosphorus type with a percentage of silver within 15%. As a result of the high percentage of silver, the product has a high degree of ductility. This method is recommended for attaching copper parts and alloys with it. The resulting seam after soldering is able to withstand moderate shocks and vibration phenomena during changing thermal conditions. This method is popularly used when connecting refrigeration systems that use special gas.
We recommend: Types of pipe cutters for copper pipes: overview of companies, characteristics, price category
Methods
There are two ways to independently connect a copper pipe line:
- Low temperature. This method is the simplest and most commonly used at home. In this case, soft solder is used from tin, lead or alloys of these metals with the addition of some silver. During low-temperature processing, the melting point of copper-phosphorus solder is no more than 450 degrees.
- High temperature (solid). Such soldering is quite difficult and expensive to organize at home, since in this case the melting temperature of the material should be from 600 to 900 degrees.
There are two main methods of soldering copper blanks:
- High temperature. Silver or copper based refractory solder creates a rigid and durable connection. The seam is called solid and can withstand mechanical and temperature loads. To prevent annealing from leading to a deterioration in the strength of the main parts, the finished soldering should be cooled exclusively naturally, without blowing with cold air or immersing it in liquid.
- Low temperature. This type of soldering is called soft soldering. Solders are prepared on the basis of metals with low melting points. The low temperature avoids annealing and there is no reduction in the strength of the pipes. The method forms seams with a width of 7 to 50 mm, on pipes from 6 to 100 mm in diameter.
Soft connections cannot be used when installing gas pipelines.
For soldering you will need:
- flux for surface treatment of the workpiece;
- solder corresponding to the selected soldering method;
- device for chamfering the end of a pipe;
- wire brush and brush for cleaning workpieces;
- pipe expander;
- measuring instrument: tape measure, measuring gauge, square, spirit level;
- burner.
A portable propane torch makes it possible to heat a joint in a few seconds. In places where the use of an open flame is unacceptable, the joints are heated with an electric soldering iron with replaceable clamps and electrodes for different pipe diameters
Silver solder.
Another common type of composition used for soldering copper is silver solder. As a rule, it is a combination of silver with copper and zinc. This composition can be used for soldering almost any metal. Its only drawback is that silver is too expensive. Therefore, silver solders are used only in cases where the economic feasibility of their use has been proven - for example, when particularly high demands are placed on the connecting seam.
Silver-based solders have no competitors in terms of wettability and spreading. They are also highly resistant to corrosion processes and can withstand shock loads and vibration.
The marking of such compositions contains the letters PSr (silver solders) and a number indicating the silver content in the substance. The more silver included in the composition, the higher the characteristics it has, but it is also more expensive. In practice, one of the most commonly used compositions is PSr-45, which contains 45% silver, as well as 30% copper and 25% zinc. This solder is capable of forming a connection with the highest quality and performance characteristics, therefore it is used for soldering in the most critical places of the product.
Note! In addition to copper and zinc, silver solder may also contain cadmium, which lowers the melting point of the substance to 250 degrees. But when using such solder, special precautions must be observed, since when it melts, cadmium vapors that are harmful to humans are released into the air.
Silver solders are most often produced in the form of rods or strips, the diameter of which is 2–3 mm. When soldering using silver compounds, a flux (most often borax) is used.
Copper pipes have gained popularity due to their high strength and easy machinability. They are installed in pipelines supplying gas and water, heating systems, air conditioners and refrigerators.
Copper does not oxidize in air, does not emit toxic substances, and helps destroy microorganisms. Many other products are made from copper, including wires, taps, door fittings, and jewelry. Soldering is used to repair or manufacture parts.
What tools will you need?
To properly connect the highway, you must immediately prepare the following tools:
- Pipe cutter Without it, it will not be possible to cut the highway elements evenly. Using a pipe cutter you can make a perfect cut.
- Bevel remover. This tool is necessary for rounding and cleaning the edge of the cut pipe in order to ensure high-quality joining of parts.
- Pipe expander. If you plan to use couplings and fittings during the work, then thanks to this tool you can quickly expand a part of the pipe to the desired size.
- Brushes and brushes. After soldering, the pipes must be cleaned of oxide formations.
- Reflector. It is attached to the burner nozzle in order to direct the flame to a specific area. If you do not install the reflector, there is a risk of damaging surrounding objects.
- Gas-burner. With its help, copper-phosphorus solder is heated.
It’s worth talking about the last working tool in a little more detail.
Gas-burner
To ensure that the pipeline is properly welded, care must be taken to select the appropriate torch. The devices are:
- With disposable cylinders (household).
- With a stationary cylinder.
- Acetyl-oxygen.
The latter type is optimal for connecting copper pipes. This is exactly the kind of burner you need to buy.
The devices also differ in the strength of solder heating. The higher the heating temperature, the more powerful the device is needed. Respectively:
- For soft solder, a cheaper and less powerful torch is suitable. Therefore, you can safely purchase a semi-professional tool with a hot air gun. This burner is capable of reaching temperatures up to 650 degrees. The main advantage of such a tool is the ability to regulate the intensity of the flame. Thus, you can select the optimal melting temperature.
- For hard soldering you will need a professional tool, the cost of which will be several times higher. Therefore, there is no point in spending money on it, but if you really want it, then why not.
Before soldering pipes with copper-phosphorus solder, you need to purchase a material that will act as a binding component. Solder also comes in two types:
- Solid. This solder is made in the form of long rods. The composition of solid-type connecting materials Cu94 P6 and Cu92 P6 Ag2 includes a 6% addition of phosphorus, so the maximum permissible melting point is 750 degrees. Other types of solders do not contain substances that reduce the possible temperature treatment, so they can be heated up to 900 degrees. Carbide materials are most often used to connect gas supply, air conditioning and hot water supply pipes, as well as for the installation of pipelines operating at high pressure.
- Soft. Solder of this type is produced in the form of a thin wire, the diameter of which rarely exceeds 3 mm. Soft material is more suitable for use at home, when organizing water supply networks.
Additionally, it is recommended to purchase flux for copper-phosphorus solders. This paste-like substance, sold in cans, is necessary to quickly and effectively clean pipe joints. Flux removes oxide well from seams, due to which the characteristics of solder are significantly improved. In addition, this component enhances the adhesion of the solder and the copper surface.
The paste is available for soft and hard solder. Therefore, it is necessary to choose flux based on the chosen method of connecting pipes.
In addition to solder, torch and other tools, it is also recommended to prepare fittings. They will be needed if you have to make turns in the water main. These elements are inexpensive.
Silver solders
Such silver “tools” with a high percentage of silver up to 55% are used in high-temperature processes in the food industry using refrigeration equipment.
Specifics of silver tinoles
Low melting point and relatively good wetting of the material during soldering are the main advantages of silver solders. This material fills the gaps between the joined parts quite well, creating tight and vacuum seams. Such soldered seams are required for the installation and manufacture of refrigeration units. This tinol has a lower spreading temperature compared to other solder materials. This option allows the use of this solder during the processing of reinforcement parts of the system.
The types of silver tinoli are as follows:
- Type 1530 . A four-component substance with a percentage of silver within 30%. Quite inexpensive, has average spreading over the surface being finished, and fills gaps quite well. Used in various installed systems except food equipment due to the presence of harmful cadmium;
- Type 530Sn . Four-component material with a percentage of silver up to 30%. It has a high melting temperature, which is achieved using a gas burner. This creates an excellent solder seam no matter how the part is positioned. It's worth noting that it's not all positives;
- Type 538Sn . Four-component material with a silver percentage of up to 38%.
What properties does copper-phosphorus solder have, where is it used.
The basis of copper-phosphorus solder is copper, to which phosphorus is added as an additive. This solder perfectly connects copper parts without requiring a very high heating temperature of the product, since it melts at a temperature of 700–850 degrees. The exact melting point depends on the specific solder formula.
For example, a compound that contains copper and phosphorus in a ratio of 91%. 9%, melts at 800 degrees. And if the solder composition, in addition to copper and phosphorus, also includes tin and a small zinc content (ratio 89.5 (copper). 6 (phosphorus). 4 (tin). 0.5 (zinc)%), then melting begins at a temperature of 690 degrees C.
The most common brands of copper-phosphorus solder are PMF-7, PMF-9 and PMFOTsr-6-4-0.03. In the labeling of a compound, the number following the abbreviation indicating the composition indicates the percentage of phosphorus. PMFOTsr brand solder also includes tin and zirconium, which is indicated in its name with the letters O and Tsr, as well as numbers that indicate the amount of these additives (4 and 0.03%).
Copper-zinc solder for soldering copper.
For high-temperature soldering of copper and alloys based on it, copper-zinc solder is used, which has the following main characteristics:
- high thermal conductivity;
- excellent electrical conductivity;
- plasticity;
- corrosion resistance;
- strength.
Solder can exhibit all these properties in different ways - it all depends on the specific amount of zinc included in its composition. For example, the more zinc, the lower the temperature at which the composition begins to melt.
The main brands of this type of solder are PMC-36, PMC-42, PMC-48 and PMC-54. The letters in the product labeling indicate its composition (copper-zinc solder), and the numbers indicate the copper content in it.
In appearance, this type of solder is grain-like and is divided into different classes based on particle size:
- class A – grains 0.2–3 mm in size;
- class B – grains 3–5 mm in size.
The scope of application of such solders depends on their brand. For different metal compositions, a different substance is selected:
- PMC-36 is suitable for soldering brass, which contains from 60 to 68 percent pure copper;
- PMC-48 is used to connect parts containing more than 68% pure copper;
- PMC-54 is used for working with bronze parts; it can also be used for soldering steel workpieces.
It is worth noting that solders, which contain exclusively copper and zinc, also have a significant drawback - the seam obtained with their help is not highly reliable. This is especially pronounced when the connection is subjected to shock loads, is strained when the product is bent, or is exposed to vibration. The reason for this is the evaporation of zinc during the solidification of the solder joint. In order to avoid weld destruction, alloying additives are added to copper-zinc solders to increase the strength and performance of the joint. As a rule, such additives are tin and silicon. The inclusion of tin in the composition makes it possible to further reduce the melting point of the solder while simultaneously increasing its fluidity. And silicon does not allow zinc to evaporate during the soldering process, and also protects it from oxidation. In addition, the solder may also contain lead.
Note! The presence of lead in the composition is indicated by a lighter shade of solder. When choosing such a substance, you should be aware of the toxicity of lead. Therefore, it is prohibited to use it when soldering some pipelines - for example, drinking water pipes.
Soft soldering
Low-temperature soldering is suitable for installing a heating or water supply network if the temperature of the coolant does not exceed 130 degrees and the diameter of the copper pipes is no more than 10 cm.
To perform soldering you need:
- Clean the surfaces to be joined.
- Apply flux to them.
- Insert elements into each other.
- Heat the connection area with a burner to 200-250 degrees.
- Apply solder to the very edges of the parts.
- Constantly moving the burner, heat the connection for 15-20 seconds.
- When the flux darkens, you need to place a little more solder on the soldering area. As soon as the material is on the hot surface, it will immediately begin to melt and fill the space between the pipe and the socket.
Brazing
This method of connecting pipes is necessary if the operating temperature of the pipeline exceeds 110 degrees. In this case, soldering is performed using the gas-flame method and the working material is annealed.
When using solid material, there is no need to treat surfaces with flux.
To make a connection you must:
- Assemble and warm up the docking unit.
- Inject hard solder into the area where the socket and pipe connect to each other.
- Soften the material using a gas torch. It is necessary to ensure that the product does not overheat, so it is recommended to constantly move the burner.
- When the primary adhesion of the main line elements occurs, rotate the pipe and wind the molten solder onto the adjacent section.
This soldering method is more complicated than the previous one, but it has several advantages:
- The seams are stronger and more reliable.
- It becomes possible to slightly reduce the width of the joint, making the seam look neater.
In addition, this method is applicable when installing systems that operate at fairly high temperatures.
Soldering brass with copper-phosphorus solder is carried out using the same technologies.
Currently, there is such a method of joining metals as the use of hard solder, which is excellent for creating capillary and slot soldering, connecting copper pipes for water supply, installing gas pipelines and refrigeration equipment. This method allows you to form a reliable and high-quality connection while working with the attached materials.
High temperature
Completely different possibilities for operating pipelines appear after hard soldering. Hot, almost boiling water can be in pipelines under a pressure of 16 atm.
Liquid solutions with a temperature of 65 ℃ can be pumped into systems at a pressure of 25 atm. Warm water, heated to 30 ℃, can, if necessary, remain in pipelines under a pressure of 40 atm.
With phosphorus
Copper-phosphorus (copper-phosphorus) solder is ideal for hard soldering. It contains only 6% phosphorus. The rest is copper.
A very small amount of phosphorus significantly lowers the melting point of copper, making the process energy-efficient.
Phosphorus solder provides a strong connection and does not require the use of fluxes. Due to the high concentration of copper, the solder has almost the same coefficient of expansion as the pipe material. This makes the job much easier.
Solder based on copper (92%) with phosphorus (6%) and silver (2%) is popular. When melted, it functions not only as solder, but also as a flux.
To repair refrigeration equipment, mixers, powerful electrical machines, and air conditioners, copper-based solder is used with the addition of approximately 6% phosphorus, 4% tin, and about 0.95% zirconium.
This alloy must be immersed at the moment of maximum possible heating of the parts. A rod of solder with zirconium is introduced into the working area until it begins to completely spread.
Phosphorus-containing alloys cannot be used for soldering non-ferrous metals with a nickel concentration of more than 10%, aluminum bronze, cast iron, and steel alloys.
If you plan to solder copper products with bronze or brass, as well as high-temperature connections between bronze and brass, it will be impossible to do without a special flux. You should purchase a ready-made composition, specifying the range of its possible uses.
With zinc and silver
A ductile, durable connection is formed using copper-zinc solder, consisting of 30% zinc, 26% copper and 44% silver.
It has a relatively high cost and is used for soldering copper food products. The absolutely harmless composition forms a compound with high thermal conductivity that is not subject to corrosion.
Basic mistakes
During the work process, some people do not take into account defects on the surfaces of the elements being joined. Very often they appear after cutting pipes. If you leave these defects unattended, the seam will not be as reliable as it should be.
The flux must be applied evenly, without gaps. If it is not present in any section, the pipeline may begin to rust quite quickly.
If the pipe overheats too much, the flux paste will simply burn. This is also not very good.
During work, it is easy to get serious burns (not only from the burner flame, but also from contact with chemically active substances), so before starting soldering you must wear protective gloves, glasses and clothing.
Why do you need a tiny pocket on jeans? Everyone knows that there is a tiny pocket on jeans, but few have thought about why it might be needed. Interestingly, it was originally a place for storage.
Top 10 Broke Stars It turns out that sometimes even the biggest fame ends in failure, as is the case with these celebrities.
How to look younger: the best haircuts for those over 30, 40, 50, 60 Girls in their 20s don’t worry about the shape and length of their hair. It seems that youth is created for experiments with appearance and daring curls. However, already last.
Surprise: Husbands Want Their Wives to Do These 17 Things More Often If you want your relationship to be happier, you should do the things on this simple list more often.
9 Famous Women Who Have Fallen in Love with Women Showing interest in people other than the opposite sex is not unusual. You are unlikely to be able to surprise or shock anyone if you admit it.
11 Weird Signs That You're Good in Bed Do you also want to believe that you please your romantic partner in bed? At least you don't want to blush and apologize.
Beginner shareholders often make mistakes. The most typical of them are:
- Uncorrected surface defects after cutting: scoring, chips, out-of-roundness. Soldering over defects weakens the connection, reducing its durability and tightness.
- Poor quality degreasing.
- Narrowing of the installation gap. A narrow solder joint will also be unreliable.
- Underheating of workpieces. Cold parts will not be able to melt the solder with their heat and ensure its flow into the mounting gap. Cold solder joints can fall apart with a simple touch.
- Lack of flux paste. The part of the seam surface that is not covered with flux is not cleaned of the oxide film and is not soldered.
- Burnt joint. In this case, the flux burns out, the oxide film is not completely destroyed, and scale appears on the surface. Solder strength is significantly reduced.
- An attempt to test the strength of a hot joint. Leads to deformation of the solder layer in the mounting gap and its detachment from the parts.
Neglecting safety requirements is also a common mistake. High temperatures, harmful fumes, and chemically active fluxes require the use of personal protective equipment. These include:
- protective glasses;
- shoes, clothing and headwear made of non-flammable fabric;
- thick split leather gloves
- respirator.
There should be no flammable materials near the soldering area; it should be well ventilated. You cannot solder in the top position.
Correctly selected soldering composition allows you to obtain reliable and durable solder joints. It is equally important to use the appropriate flux and strictly adhere to the requirements of soldering technology and safety precautions.
How to choose?
If you want to purchase a copper-phosphorus filler material for soldering, then first of all you need to decide on its specific chemical composition. Basically, the choice is made between two broad groups, which differ from each other in the presence of silver in the composition.
Options with silver allow you to achieve higher strength for the final result of the connection than models without it. Also, models with silver should be used if the product operates at negative air temperatures. To do this, you need to purchase solder with a silver content of at least fifteen percent.
There is a rule that states that the thinner the metal, the lower the melting point of the filler material should be. In addition, the low melting point significantly increases the ability of the material to spread evenly over the working surface. It is worth noting that some models have fluxes of the same name; when used together, it is possible to achieve a high quality connection.
When soldering copper pipes, two main types are used:
- soft, with a melting point of up to 425°C;
- solid, with a temperature range of 460-560°C.
The use of silver-containing alloys is recommended as solders. They provide high quality connections, but are expensive. Copper-phosphorus compounds are more accessible and suitable for soldering less critical connections.
Copper-phosphorus
The melting point of copper-phosphorus solder is low. Copper solder allows you to do without flux compounds. The phosphorus contained in the composition will protect the work area from exposure to atmospheric oxygen.
The suture material, formed on the basis of copper-phosphorus solder, is very durable and resistant to vibration. Therefore, phosphorous compounds are widely used when soldering heat exchanger components.
Why do solders sometimes use copper solder when soldering steel parts, but copper cannot be soldered with steel solder? The reason is the difference in the melting temperatures of steel and copper. The copper blanks will already melt, but the steel will still heat up.
At the same time, copper-phosphorus solder is sensitive to overheating, so measures must be taken to cool the joint. The product is produced in the form of a rod. Copper soldering tape is also available. Copper-zinc low-temperature solders are also used for soldering.
Silver
Pure silver composition is not suitable for soldering copper products. They mainly use silver with the addition of iron, bismuth and other elements.
Silver-based copper solder has high wettability towards workpieces and penetrates perfectly into the narrowest gaps between them. The connections do not corrode and withstand large static and periodic dynamic loads.
Ag content
The chemical composition of solders for soldering copper and silver workpieces is described in GOST 19738-74. They are designated by the letters PSR XX, where the numbers determine the percentage of silver
Compositions with a high percentage of silver (50-72) have high electrical and thermal conductivity. They are used in electrical engineering and electronics.
Alloys with a medium percentage are cheaper and are used for soldering joints that are not subject to temperature stress.
Features of tinoles
A characteristic feature of silver-containing compounds is their low operating temperature. High fluidity allows the melt to penetrate into gaps and pores and create high-quality seams.
Brazing
Brazing alloys are used for joints of larger diameter tubes and pipelines. In this case, a paste-like flux, a gas burner for heating and the necessary auxiliary equipment and tools are used.
Low temperature
Low-temperature solders melt at temperatures up to 450°C. The low temperature avoids annealing of the base material of the pipe and preserves its physical and chemical properties. Solders are prepared on the basis of tin or zinc alloys. Lead is also used as a component.
High temperature
High-temperature solder for soldering copper is prepared on the basis of silver or copper, which has a high melting point. At temperatures above 450°C, the workpieces are annealed, leading to a decrease in their strength.
Physicochemical characteristics
Copper-phosphorus solder TsP 6, like other brands, gets its properties thanks to a unique composition that is developed for certain procedures. Based on the presence of certain chemical elements, as well as their ratio, the material is obtained close to the properties of copper, bronze or brass with which the work is being done, but at the same time it has a lower melting point, which allows the properties of the base metal to be preserved. In general, almost all grades have increased wettability, which improves contact with the workpiece. This is what gives excellent performance for copper compounds. In addition, they have a high degree of penetration, forming strong molecular bonds. Some of the brands have a rather dangerous melting point of more than 800 degrees. This may affect the properties of the metal, but creates a strong joint that can rival manual arc welding. Almost all solders have anti-corrosion properties. Copper-phosphorus solder with flux is often found, which is considered one of the best options for copper.
Copper-phosphorus solder CPU 6
Technical characteristics of popular brands
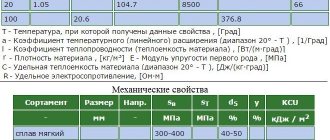
| Solder grade | Content of elements in the chemical composition, % | Melting temperature, Degrees Celsius | Spreading temperature Degrees Celsius | ||
| Silver | Copper | Phosphorus | |||
| PMF102 | 2 | 91,3 | 6,7 | 645 | 820 |
| PMF105 | 5 | 88,5 | 6,5 | 630 | 780 |
| PMF115 | 15 | 80,2 | 4,8 | 650 | 800 |
Features of choice
First of all, you should decide on the composition. There are ordinary materials that contain only two elements, copper and phosphorus, as the name implies, as well as copper-phosphorus solders with silver. It is immediately worth noting that silver gives greater strength to the seam. It also increases frost resistance, therefore, if the connection will be operated at low temperatures, then you should choose brands with a relatively high content of this element, one of the highest levels of which is 15%. But here another dependence is observed, since the more silver in the composition, the less plasticity the final compound has. Thus, if the material will be subject to slight bending or will expand and contract, then it is better to give preference to those brands in which the minimum content of this element, for example, 2%, or is completely absent. Before soldering copper-phosphorus solder, you should familiarize yourself with its composition.
For thin-walled pipes and workpieces with a small thickness, you should select solders whose melting temperature will be as low as possible. After all, the higher it is, the greater the likelihood that the base metal will deform or change its properties after annealing, which will worsen the quality of the connection. Low temperature also increases spreadability, which is also important for a high-quality connection, although even high-temperature solders with phosphorus have good performance in this parameter. For some brands, fluxes of the same name are produced, which should help cope with the more complex conditions of soldering bronze and brass, therefore, when choosing solders for these procedures, you should pay attention to the availability of a suitable flux.
What properties does copper-phosphorus solder have, where is it used.
Properties depend on the chemical composition of the alloy. Thus, low-temperature ones have less strength, but do not reduce the strength and elastic characteristics of the material of the parts.
High-temperature ones, on the contrary, create high-strength joints that can withstand static and dynamic loads. But when using them, great care is required so as not to burn or weaken the base material.
The melting point of high-temperature compositions lies in the range of 645-815 ° C. The seam can withstand tensile loads up to 250 MPa. The operating temperature of the compound, depending on the composition, is 150-250°C. In addition to copper itself, such solders allow you to join brass, red bronze, cast iron, steel and nickel. They also solder aluminum. In addition, they are used to connect copper and stainless steel parts.
How to select solder?
When soldering copper products, both soft and hard types of solders are used. When using soft solder to connect copper pipes, it is necessary to reach a temperature within 4250C. When soldering using hard solder, the operating temperature for soldering should be up to 460-5600C. In these cases, a gas burner is used. The tinol option is determined depending on the percentage of copper and other elements in the alloy. If the alloy contains an element such as silver, the tinol is considered silver. You should know that as the percentage of silver in the tinol composition increases, its melting point decreases and the flow around the soldering area and wettability improves. The quality of joining copper pipes can be increased by using copper-phosphorus type solders, but at the same time their melting temperature will increase and wettability will decrease compared to silver tinols. When soldering copper parts using copper-phosphorus type solder, there is no need to use flux. In the usual connection of copper products with each other, as well as copper with bronze elements, flux is necessarily used. The microgap when using silver tinols should be in the range of 0-0.15 mm, and in the case of using copper-phosphorus type solders - 0.025-0.15 mm.
Technology
To cut pipe blanks, pipe cutters with manual or electric drive are used. To ensure an even cut, after each revolution the pressure-regulating flywheel should be tightened by a third of the stroke. The edge should be treated with a chamfer remover and cleaned with a brush. If the connection is butt, one of the pipes should be expanded. Next, the surfaces are degreased and the quality of their mating is checked.
Flux paste is applied to the inner surface with a brush built into the lid of the jar. It should be completely covered with flux, but at the same time no excess should accumulate on it.