11/12/2021 Author: VT-METALL
From this material you will learn:
- Description of metal etching technology
- Applications of metal etching
- Types of metal etching
- Basic metal etchant solutions
- Features of printed circuit board etching
- Methods and subtleties of artistic metal etching
- DIY instructions for electrochemical etching of metal
- Safety precautions when etching metal
Metal etching is a technology that people have been working with for thousands of years. Thanks to it, in ancient times they processed weapons, all kinds of utensils, objects of ritual ceremonies, and beautiful jewelry. Today, etching comes to the rescue both in industry and at home. If you are a craftsman who likes to do everything with your own hands, then first you need to familiarize yourself with the basics and rules of this procedure, otherwise you can only harm yourself: working with corrosive acids is a very dangerous business.
Our article will help you understand etching technology. You will find out what types it comes in and what solutions are used. We will also share instructions on how to carry out this operation yourself and a safety reminder so that you do not endanger your health in any way.
Description of metal etching technology
This technology involves removing part of the surface layer of a product through a chemical reaction.
When talking about what metal etching is, you need to understand: with the help of solutions of acids, salts and alkalis, products are cleaned of scale, traces of corrosion, and oxides. This approach is also necessary for additional preparation of metal parts for joining and coating, since it provides better adhesion of elements, or the base and the protective layer. It is worth mentioning that the most common is chemical etching of metal, in which the workpiece is immersed in a bath of chemical reagents.
Before starting etching, areas of the surface that should remain unchanged are protected with a special compound. After which the workpiece is exposed to an acidic environment or is dipped into an electrolyte. The thicker the layer of metal that needs to be removed, the longer the processing takes. Sometimes they resort to multilayer etching, in which work is carried out in several stages.
The essence of the method
The effect of acidic environments on the metal is of key importance in the process. The interaction of an aggressive environment with metal is called etching. This is a chemical process to apply a pattern to a knife. The area that is not intended for etching is covered with a protective layer.
It must be neutral to the etching substance. The depth of etching depends on the time of exposure to the blade. The experience of our ancestors revealed several effective methods. In this article we will try to consider all known methods.
Applications of metal etching
Today, the metal etching method is actively used in industry, namely it allows:
- remove oxide film from parts made of different types of steel: carbon, low-alloy and high-alloy, as well as titanium, aluminum;
- improve the adhesion of metal and, for example, galvanic protective coating;
- prepare the steel product for hot galvanizing;
- perform macroanalysis of stainless steels to identify the formation of intergranular corrosion;
- clean small parts, including those used in wristwatch mechanisms;
- apply copper conductive traces in electronics to a semiconductor chip or printed circuit board;
- quickly remove oxides from hot rolled metal and parts after heat treatment;
- reduce the thickness of aluminum sheets in order to reduce the weight of the aircraft in the aircraft industry;
- apply images according to the required stencil on metal products.
Primer or bitumen varnish
Primer GF 021, XB 062 or bitumen varnish is used. First, the entire product to be etched is coated with the substance. Next, use a thin pen or marker to transfer the contours of the drawing. A needle should be made from thin wire or a rod of soft alloys, sharpening the end of the wire.
Etching using a primer
Those areas of the image that must be etched are scratched down to the metal. Care should be taken to ensure that the primer does not chip.
Types of metal etching
1. Method of chemical etching of metals.
Using this approach, the surfaces of metal parts are freed from traces of corrosion, scale, and oxide films. The method allows you to process:
- aluminum;
- titanium and its alloys;
- stainless and heat-resistant steels;
- black metals.
This technology involves the use of sulfuric acid or nitric and hydrochloric acid for etching metal. The workpieces are immersed for some time in a bath with an acidic or alkaline solution, molten salt - the duration of exposure starts from a minute and ends with two hours. This interval is selected in accordance with a number of characteristics.
The cleaning method is based on the fact that the interaction of acid and metal is accompanied by the release of hydrogen. In more detail, the acid, through small surface defects, gets under the oxide film, where it comes into contact with the workpiece itself. This results in the formation of gas, which tears off the oxide film, leaving a clean surface of the product.
However, acid dissolves not only oxides, but also the metal itself, so this process is prevented in production by using corrosion inhibitors.
Basic metal etchant solutions
1. Carbon steels are treated with an 8–20% solution of sulfuric acid or a 10–20% solution of hydrochloric acid. To avoid further fragility of the material and reduce the likelihood of over-etching, corrosion inhibitors are added to the composition, such as KS, ChM, UNIKOL.
2. Stainless or heat-resistant steel is pickled with a mixture of 12% hydrochloric, 12% sulfuric, 1% nitric acid. If necessary, processing is carried out in stages. Then, using 20% hydrochloric acid, the scale is loosened, after which the product is dipped in a 20–40% nitric acid solution to remove surface contaminants.
3. From stainless steel, a thick layer of scale formed during the production process is removed with a 75–85% solution of caustic soda in combination with 20–25% sodium nitrate. Next, the oxides are removed by etching the metal with 15–20% nitric acid.
4. Aluminum and its alloys are cleaned from the oxide film located on the surface of the workpiece using alkaline or acidic solutions. Most often, 10–20% alkali is used, all exposure occurs at a temperature of +50…+80 °C for at least two minutes. Sometimes sodium chloride and sodium fluoride are added to the alkali to achieve more uniform etching.
5. Titanium and alloys based on it are purified in several stages after heat treatment. First of all, it is necessary to loosen the scale in concentrated caustic soda, then it is removed in a solution of sulfuric, nitric or hydrofluoric acid. At the final stage, the remaining pickling sludge is disposed of using hydrochloric or nitric acid with a small addition of hydrofluoric acid.
6. Copper and its alloys are treated with hydrogen peroxide, chromic acid and a number of salts, such as:
- copper chloride;
- ferric chloride;
- ammonium persulfate.
Degreasing in organic solvents.
Organic solvents have low surface tension (20-30 MH/M), wet the surface being treated well and easily penetrate hard-to-reach areas.
Processing is carried out in various ways - immersion, jet under pressure of 0.03 to 0.1 MPa, processing, in the vapor phase and a combined method.
- Alcohols: methyl alcohol, cyclohexanol, ethylene glycol;
- Esters: ethylcellosol, ethyl acetate, butyl acetate;
- Ketones: acetone, cyclohexanone;
- Aromatic hydrocarbons: beznol, toluene, xylene, solvent;
- Petroleum solvents: gasoline, kerosene, white spirit, petroleum ether;
- Chlorinated hydrocarbons: methylene chloride, carbon tetrachloride, dichloroethane, trichlorethylene, trichloroethane, tetrachlorethylene;
- Fluorinated solvents: 1,2,2-trifluorotrichloroethane - freon 113, tetrafluorodibromomethane - freon 114 BB.
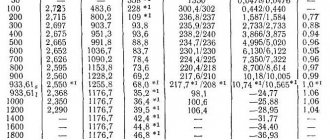
The effectiveness of removing grease stains with the most popular solvents decreases in the following order:
| Type of solvent | E, kg/(m2*h) |
| Freon 113 | 4,450 |
| Trichlorethylene | 3,100 |
| Xylene | 2,200 |
| Tetrachlorethylene | 1,70 |
| Petrol | 1,30 |
| White Spirit | 0,90 |
| Kerosene | 0,650 |
Based on the table, fluorine- and chlorine-containing hydrocarbons are increasingly used, and above all: freon 113 and trichlorethylene. Another advantage of freon 113 and trichlorethylene is fire and explosion safety. The fire hazard of solvents is characterized by flash point, self-ignition temperature of the vapor-air mixture and ignition temperature limits.
Chlorinated hydrocarbons are non-flammable, relatively stable and stable, but are toxic and require strict adherence to safety regulations. These substances have a high dissolving ability in relation to oils and lubricants of plant, animal and mineral origin.
2.1 Degreasing in solvent-emulsifying agents.
If for some reason cleaning must be done at a low temperature (up to 50°C) or the contaminants are poorly soluble, RES (solvent-emulsifying agents) are used.
RES are increasingly used in industry. Degreasing is carried out first only in RES or in a mixture of ES with other solvents; Next, the treated parts are immersed in water or an aqueous solution of SMS. The solvent and remaining contaminants are emulsified and go into solution, ensuring the cleaning of the surface of the products.
AM-15 and “Rhythm” products are commercially produced by industry. These products must be used in sealed installations - submersible machines, following special instructions and safety rules.
RES solutions, in comparison with SMS under identical processing conditions, are 5–15 times more efficient and consume 3–6 times less thermal energy.
Features of printed circuit board etching
As a basis for the board, a blank is taken in the form of a sheet of textolite covered with copper foil - it can be on one or both sides. The task is to form conductive copper traces according to the drawing. To do this, a protective varnish is applied to future tracks, and all other metal is removed.
Metal etching at home is carried out using the following methods:
- Ferric chloride. It is sold at a chemical supply store, or you can make the reagent yourself from hydrochloric acid and iron filings. To etch metal with ferric chloride, you need to wait until the metal particles dissolve and mix the resulting composition well.
- Nitric acid.
- An aqueous solution of sulfuric acid combined with hydrogen peroxide in tablets.
- Copper sulfate mixed with hot water, sodium chloride. The method of etching metal with copper sulfate is considered the safest, but requires a significant amount of time. To prevent processing from taking several hours, it is necessary to maintain the temperature of the composition at least +40 °C throughout the entire reaction.
- Electrolytic method. To etch metal by electrolysis, you need a dielectric capacitance, for example, a cuvette for developing photographs. It is filled with a solution of table salt, into which the board and copper foil are immersed. The latter is designed to play the role of a cathode in this process.
When etching is complete, the board is washed with a soda solution to neutralize the acid.
Glossy paper
In addition to glossy paper (you can buy it at art supply stores, or you can simply cut a sheet out of a magazine), you will need a laser printer, an imaging application, and an iron. The image of the drawing should be mirrored and printed in full size. The image is applied to the surface and ironed several times. After the workpiece has cooled, the paper is washed off with warm water, and the toner remains on the surface of the part. The back and side surfaces that are not subject to etching must be protected with varnish or plasticine.
Glossy etching paper
The main advantage of the method is that the smallest details of the image can be accurately transferred.
The main disadvantage is that you can only work in this way with flat or cylindrical workpieces. The method is very popular in the manufacture of printed circuit boards.
Methods and subtleties of artistic metal etching
Artistic metal etching refers to the application of a relief pattern or three-dimensional image to a steel product. This approach is most often used when working with high-hardness steels that are difficult to process with engraving tools.
This way you can decorate any weapon, forged, cast objects. Craftsmen who manufacture designer hunting and household knives rarely do their work without etching the metal. The most popular in this area are hunting scenes, Arabic script, runes, and geometric patterns. Often, etching is supplemented with bluing, due to which the image acquires a bluish, yellowish or black tint.
Artistic processing by etching a design on metal can be performed in the following professional ways: a composition that reacts with the mordant is applied to the surface of the sketch, or the image is left free, closing all the gaps. Next, acid is used, and in the first case the pattern will have little relief, while in the second the relief will be greatly deepened.
It is customary to divide artistic etching methods into galvanic and chemical. The first is considered less harmful and more effective. It is important that it does not involve the release of toxic gases from the electrolyte solution, which is inevitable during chemical processing.
During chemical etching, an acid-resistant varnish is applied to the surface of the product, in accordance with the planned image. Next, the object is immersed in an etching bath for the required period of time, where the reagent corrodes the unprotected metal, creating an in-depth pattern.
DIY instructions for electrochemical etching of metal
Electrochemical etching of metal is often used by home craftsmen, because this method allows you to transfer any design. To do this you need to go through the following steps:
Prepare the surface of the product
- remove foreign inclusions, traces of corrosion, scale, dirt from the metal;
- wipe it with a rag and degrease it with solvent.
Next they move on to polishing. Sometimes it is not possible to achieve mirror smoothness - then the surface is sanded with sandpaper strictly in one direction.
To create an inscription or drawing on a metal plate, you need to prepare:
- container made of glass or plastic;
- table salt;
- metal plate;
- 5–12 V power supply;
- connecting wires.
1. Cut a rectangular fragment from the metal plate, on which the inscription will soon appear. In any hardware store you can easily find a plate 1-2 mm thick. For example, a cheap steel eyelet will do.
2. Sand the workpiece - use coarse sandpaper for this, and then move on to fine sandpaper. The result should be a shiny surface with many small scratches. Do not forget about sanding the edges and edges of the plate. Next, the metal is degreased with alcohol, a solvent, or washed with hot water and soap, after which it is forbidden to touch the surfaces with greasy hands.
3. Print the design on a laser printer and transfer it to the workpiece using laser-iron technology. Remember that the sketch is printed as a mirror image. If you don't have a laser printer, nail polish or a permanent marker will work for drawing. As a result, the painted area will remain unchanged, but the exposed metal will be etched away.
4. Take a non-metallic container, pour water, add salt. When etching metal in a saline solution, the concentration of the latter affects the speed of work: the more salt, the faster you will achieve the desired result. However, you need to understand that excessive speed is dangerous for the protective layer of varnish or toner, which is why the drawing will turn out to be of poor quality. Therefore, it is recommended to prepare a mixture of a glass of water and a tablespoon of salt.
An anode, the role of which is played by the workpiece itself, and a cathode are fixed in the container. Any piece of metal is used as the latter, but the larger its area, the faster the etching will be completed.
The plus from the power source must be connected to the workpiece, and the minus to the solution. To achieve uniform etching of the metal, it is better to install several negative contacts on all sides of the piece of plate being processed.
A computer power supply, namely its 12 V line, is suitable as a current source. Remember that the etching speed depends on the voltage. Or you can use a mobile charger - its output is 5 V, which is quite enough for the planned procedure. A voltage above 12 V can cause the process to proceed too quickly, causing the protective layer of varnish to fall off and the metal etching solution to reach an unacceptable temperature.
So, when the wires are connected, you can turn on the power supply. Bubbles that immediately come from the cathode are a sign that the process has started. If the bubbles are coming from the workpiece, there was a mistake in choosing the polarity.
Within a few minutes of processing, foam of an unpleasant yellow-green hue will appear on the surface of the solution. And 30–40 minutes after the start of etching, you need to turn off the power and remove the plate from the solution. Do not be afraid of a dark coating on the surface of the metal; it is normal.
5. Remove plaque, wipe off the toner or varnish that acted as a stencil for etching on the metal, and re-sand the metal if necessary. Plaque can be easily washed off with a stream of water; to remove nail polish or toner, you will need acetone or nail polish remover. After these procedures, it is clearly noticeable that the letters are in relief, and the etched surface has become matte.
Chemical degreasing.
Removal of contaminants from the surface usually occurs in 2 ways: emulsification (for the liquid phase) and dispersion (for the solid phase). In all cases, contaminants are transferred to the cleaning solution. The amount of contaminants that a solution can “contain” is called capacity.
Chemical degreasing consists of 4 stages:
1) Wetting the surface of parts, penetration of contaminants into cracks and pores of the film. Wetting (as a phenomenon) is the spreading of a drop of cleaning solution over the surface being treated. It is determined by the contact angle (Θ) - the angle formed by the tangent to the surface of a spreading drop with a solid surface. If Θ <90°, then the surface is wetted (hydrophilic), otherwise it is not (hydrophobic). A clean metal surface is always well wetted.
2) Reducing the connection of pollution particles with each other and with the surface. Subsequently, the particles break off and go into solution. At the same time, saponification of fats and oils can occur.
3) Envelopment of contaminant particles in the solution with detergent molecules. preventing particles from coarsening and settling on the surface to be washed.
4) Stabilization of suspended contaminant particles in solution. Preventing their re-deposition on parts. Stabilization increases when foam forms in the solution, i.e. systems in which the medium is liquid and the dispersed phase is gas.
Foaming ability of synthetic detergents:
| Detergent | Concentration, g\l | Foaming according to Ross-Miles, mm, per 200 ml of solution at temperature, oC | Foam stability, mm at 80°C and duration, min | |||
| 25 | 80 | 0 | 1 | 3 | ||
| Km-1 | 20 | 220 | 45 | — | — | — |
| Labomid -101 | 20 | 140 | 6 | — | — | — |
| Labomid-203 | 30 | 300 | 93 | 83 | 60 | 54 |
| MS5 | 30 | 180 | 50 | 50 | 23 | 11 |
| MS-8 | 30 | 320 | 300 | 300 | 200 | 190 |
| Siliron U-64 | 20 | — | 13 | — | — | — |
Excessive foam formation can create difficulties when using cleaning solutions in mechanized and automated installations. The introduction of synthetic detergents or defoamers (PMS-200, KE-10-12, etc.) into solutions reduces foaming, but at the same time their cleaning ability decreases.
The properties of the chemical degreasing solution are:
- Surface tension;
- Surface activity;
- Contaminant container.
The composition of a chemical degreasing solution most often includes:
- Alkaline agent;
- Phosphates;
- Silicates;
- Surfactants (surfactants).
There are also acidic degreasing solutions, but they are used less frequently.
Properties of inorganic components of degreasing solutions:
| Component | Density, kg\m3 | Melting point, oC | Alkalinity indicator of a 1% solution | |
| pH | Active Na2O content | |||
| Sodium metaslncate | 2614 | 1089 | 12,5 | 0,29 |
| Sodium carbonate | 2540 | 851 | 11,4 | 0,58 |
| Trisodium phosphate | 1620 | 73,4 | 12,0 | 0,16 |
| Sodium tripolyphosphate | 2500 | 820 | 9,7 | — |
| Liquid glass | 1400-1500 | — | 11,3 | 0,18 |
| Caustic soda (caustic) | 2130 | 320 | 13,5 | 0,78 |
Let's consider the effect of each component of the alkaline solution in more detail.
3.1 The role of an alkaline agent in chemical degreasing.
Typically, this role is played by sodium hydroxide, less often - sodium carbonate (for “softer” compositions).
The alkalinity of the degreasing solution affects:
- its ability to saponify fats;
- neutralize acidic components of contaminants;
- reduce contact stress;
- reduce water hardness.
Alkalinity can be general or active. The cleaning effect depends on the latter (solution pH).
The effect of a solution on certain contaminants depends on the pH:
- for asphalt-resinous contaminants, the pH should be 11.8-13.6;
- for oils - 10.8-11.5.
On the other hand, it is important that the degreasing solution is not aggressive to the parts being processed. For this purpose, the pH must be maintained:
- for zinc and aluminum 9-10;
- for tin <11;
- for brass <12-12.5;
- for steel <14.
In order to reduce the aggressiveness of the solution, corrosion inhibitors can be added to it.
The saponification reaction (alkaline hydrolysis) of fats is one of the main defatting reactions that occurs with the participation of alkaline agents. Its diagram is presented below:
The intermediate product of the reaction is fatty acids, which then form salts.
Heating enhances the effect of the alkaline agent.
3.2 The role of phosphates in chemical degreasing.
The effect of phosphates is as follows:
- Stabilization of pH as the solution is used. The importance of pH was mentioned above.
- Binding of hardness salts (Ca, Mg) into complexes and water softening. At the same time, the solubility of carbonates and calcium soaps increases. Polyphosphates have a particularly strong effect.
- Stabilization of contaminants in solution. This is facilitated by the suspending and peptizing effect. Tripolyphosphates are three times more effective than phosphates.
- Improving the washability of the solution. Phosphates not only rinse off well themselves, but also improve the rinsability of alkaline agents.
Excess carbonates can inhibit the action of phosphates.
The amount of tripolyphosphate required to soften water:
| Rigidity, hail | Mass fraction of sodium tripolyphosphate,% (at t oC) | Rigidity, hail | Mass fraction of sodium tripolyphosphate,% (at t oC) | ||||
| 16-18 | 60 | 82 | 16-18 | 60 | 82 | ||
| 3 | 0,05 | 0,05 | 0,05 | 18 | 0,30 | 0,27 | 0,21 |
| 6 | 0,11 | 0,11 | 0,09 | 24 | 0,39 | 0,33 | 0,27 |
| 12 | 0,20 | 0,18 | 0,15 | 30 | 0,50 | 0,48 | 0,33 |
3.3 The role of silicates in chemical degreasing.
Sodium silicate (sodium metasilicate, liquid glass) is a substance of variable composition mNaO*nSiO2 with a different ratio (modulus) m:n. This ratio is usually from 1:2 to 1:4.
The pH of the sodium silicate solution is:
- 11.8 for 1%;
- 12.6 for 5%.
The introduction of sodium silicate into the cleaning solution leads to the following consequences:
- Reducing the aggressiveness of the solution
- Increasing its emulsifying effect
- Formation of a thin film on the treated surface that protects the part from corrosion during interoperational movement or storage. However, this film impairs the adhesion of subsequent coatings.
3.4 The role of surfactants (surfactants) in chemical degreasing.
What is a surfactant? To answer this question, we need to start by looking at surface tension and surface activity.
Let's consider several layers of liquid molecules, the outer one of which borders on air. These phenomena occur when the forces of attraction between the molecules of the outer layer and the molecules of the lower layers are not balanced by the attraction of air molecules.
Therefore, the molecules of the outer layer tend to be drawn into the liquid, as a result of which the surface of the liquid tends to decrease.
- Surface tension forces
are forces that tend to contract the surface. They are measured by the work that must be expended to increase the surface of a liquid by 1 cm2. - Surface free energy
is the product of surface tension and surface area. - Surface activity
is the ability of substances to reduce free surface energy.
Surfactants are substances that reduce the surface tension of a solution. In the cleaning solution they provide wetting of contaminated surfaces.
Surfactants are divided into:
- Cationic;
- Anionic;
- Nonionic.
Synthetic surfactants have a lower critical concentration of micelle formation, i.e. surfactant concentration at which the maximum cleaning effect is achieved.
• To cationic surfactants
include salts of primary, secondary and tertiary amines, quaternary ammonium bases and other compounds.
Cationic surfactants are rarely used, because their effectiveness in defatting is low. • Anionic surfactants
include soaps of carboxylic acids, alkyl sulfonic acids, alkyl sulfates, alkylaryl sulfonates, for example, sulfonol NP-1, sulfonol NP-Z, DS-.
Anionic surfactants dissociate in an aqueous environment to form negatively charged organic ions. • Nonionic surfactants
(unlike anionic ones) do not have a hydrophilic salt-forming group and do not dissociate in aqueous solutions. They are stable in alkaline, acidic and neutral environments. Examples: polyethylene glycol ether (OP-7, OP-10, OP-20, OP-ZO), syntanol (DS-Yu, DT-7).
Particular attention should be paid to the need to use biologically soft surfactants, i.e. harmless to bacterial flora. Biologically harsh surfactants lead to pollution of natural water bodies. These include HP-l, OP-7, OP-10, Petrov’s contact, alphapol 8, alphapol 9, alkyl sulfonate, chloric sulfonol.
Safety precautions when etching metal
During all the work described above, the following rules must be followed:
- The room must be provided with good ventilation; it is advisable to have a fume hood.
- The master must use personal protective equipment: rubber gloves, an apron, thick overalls, a respirator, a protective face shield.
- It is prohibited to place jars with acids and alkalis on high shelves and cabinets.
- Acid is poured into water, and not vice versa.
- To work with acid, you must prepare a soda solution in advance; when using alkali, a weak vinegar solution. These compounds are used to treat the skin after contact with the etching mixture.
- Before using the galvanic method of metal etching, it is necessary to check the electrical equipment used for the absence of mechanical damage and ensure the integrity of the insulation.
- There should be a working fire extinguisher nearby.
When the metal etching composition gets on the skin, it is necessary to immediately wash it with the above solutions to neutralize the effect. If acid or alkali splashes on clothing, remove the equipment immediately. If the etching solution gets on the mucous membranes, it is important to seek medical help as soon as possible. You need to understand that delay threatens the health and even life of the master.
So, now you know much more about metal etching and its varieties. Let our article help you become an even more competent and skillful specialist in the field of processing metal products. Follow the above rules and create beautiful and functional things!
Why should you contact us?
We treat all clients with respect and carry out tasks of any size equally scrupulously.
Our production facilities allow us to process various materials:
- non-ferrous metals;
- cast iron;
- stainless steel.
When completing an order, our specialists use all known methods of metal machining. Modern equipment of the latest generation makes it possible to achieve maximum compliance with the original drawings.
In order to bring the workpiece closer to the sketch submitted by the customer, our specialists use universal equipment designed for jewelry sharpening of tools for particularly complex operations. In our production workshops, metal becomes a plastic material from which any workpiece can be made.
The advantage of contacting our specialists is their compliance with GOST and all technological standards. Strict quality control is carried out at every stage of work, so we guarantee our customers a conscientiously completed product.
Thanks to the experience of our craftsmen, the output is an exemplary product that meets the most demanding requirements. At the same time, we start from a strong material base and focus on innovative technological developments.
We work with customers from all regions of Russia. If you want to place an order for metalworking, our managers are ready to listen to all the conditions. If necessary, the client is provided with free specialized consultation.