Aluminum conducts current and is one of the best conductors in existence. It is used to make conductive busbars, cable lugs and sleeves, cable for overhead power lines, self-supporting insulated wire (self-supporting insulated wire) and wires of smaller cross-section (for domestic or industrial needs), coaxial television cable.
Types of aluminum electrical cable Source ru.prom.st
Other properties
Today, aluminum is produced almost twice as much as copper. And in comparison with all mined metals, it is second only to steel. This confirms that every year the electrical industry is increasing its use. This is explained by a number of reasons, which we will consider further.
Electrical performance of aluminum
According to the International Annealed Copper Standard (IACS), the latter is rated as 100% conductive. According to the above information, aluminum conducts electricity at only 61% equivalent to the generally accepted standard.
Thus, an equal percentage will only be achieved with larger cross sections. Since copper is significantly heavier than aluminum, such an “increased” conductor in mass will still be lighter than copper.
Comparative density of aluminum and copper Source aluminum-guide.com
This fact has been proven through complex mathematical calculations, the result of which shows that 1 kg. aluminum provides equal conduction speed to that of 2 kg. copper Therefore, if certain technical conditions for the size of conductors do not require this, copper is replaced with aluminum.
Healthy! If for use in home wiring the weight of an electric wire does not have a special role, then when used on overhead power lines (overhead power lines), the weight of the current-carrying conductors has a significant effect. Therefore, take the one that is lighter, that is, aluminum.
Strength index
Provided the cross-section is the same, copper conductors are stronger than aluminum conductors. Although, this figure can be easily increased by alloying or thermomechanical treatment, or by increasing the cross-section.
The table shows that aluminum is 2 times weaker in tensile strength Source aluminum-guide.com
The values given in the table show that aluminum conducts current, but is inferior to copper in terms of “break strength”. However, it is able to withstand its own weight and does not overload the overhead power line supports as much as copper.
In addition, extruding aluminum involves obtaining cross-sections of complex shapes, which cannot be obtained from steel. Based on such objective reasons, new elements can be designed in such a way that they will be the most effective in comparison with acceptable analogues from other materials.
What is the resistivity of steel
Steel is a metal alloy of iron with carbon and other elements. It contains at least 45% iron, the carbon content ranges from 0.02% to 2.14%. Depending on the exact composition, steel is used in construction, mechanical engineering and instrument making, as well as in many areas, for example, in transport, the national economy, and in the production of household appliances.
Steel wires have low conductivity
The conductivity of steel is only 7.7 million S/m, the resistivity is 0.13 μOhm/m, that is, it is quite high. Steel conducts electricity poorly and is not used in the production of cables. However, you can often find an outer galvanized steel braid that protects the wires from mechanical stretching. Such protection is needed if the cable runs under a road or on unstable ground, if there is a risk of sharply pulling the wire.
PNSV is also made from steel - a heating wire with a steel core and vinyl insulation. It is placed inside the structure before concrete is poured and is subsequently used for electrical heating of the finished block. The cable practically does not conduct electricity.
PNSV wire is produced from steel
Advantages and disadvantages of aluminum wiring
The widespread use of aluminum wiring was practiced in old buildings. The main criterion in those days was easy availability and low cost of metal. The possibility of a lack of cable cross-section was not considered in those days due to the lack of electrical household appliances in the apartments of average citizens.
Types of SIP cable for connecting a cottage Source yandex.net
Positive factors
The low weight of aluminum wire makes it popular when installing high-voltage power lines. This condition has already been stated earlier, so let’s consider a number of other aspects:
- Relatively low price of metal and products made from it. This factor plays a role when laying long lines. For example, to fully electrify a country house, more than 1,000 m of wire may be needed.
- Resistance to chemical oxidation. This condition is relevant given that the cores are hidden by plastic insulation.
- Durability of areas without insulation. As mentioned earlier, a protective film is formed on the surface of aluminum, which prevents the occurrence of oxidative processes.
High-voltage line with a voltage of 35 kV Source cdn.pixabay.com
Information about the thermal conductivity index
The process of heat transfer in the body of any substance occurs between the atomic and molecular bonds of the material, in which the temperature regime is uneven. Any substance heats up gradually, transferring heat energy from area to area. This heat transfer depends on the state of the substance. Heat conductivity depends on: 1. The state of aggregation of the substance, 2. The heating rate. 3. Density indicator. 4. Melting points. The heat conductivity coefficient is the amount of heat passing through a unit area of a material in a certain period of time when temperatures change.
What does heat conductivity depend on? Aluminum has a crystal structure - a cube. At a temperature of 200C, specific gravity = 2.7 g/cm3. The melting temperature is from +657 to +660.2 0C. If aluminum is of high purity, then the metal begins to melt at +1800 to 2060 0C. The specific heat capacity during the heating period increases, and the coefficients of expansion and thermal conductivity also increase. The thermal conductivity of aluminum, compared to other metals, is considered high.
Aluminum reacts with oxygen to form an oxide film on the surface. The latter protects the metal from further oxidation. Aluminum alloys have unique properties: 1. When aluminum melts, the hydrogen present in it dissolves, which leads to the formation of pores in the metal. If the composition contains impurities of calcium, potassium or sodium, it also leads to porosity. 2. The structure of the material becomes homogeneous upon cooling if the alloy contains additives of iron, vanadium, nickel or zirconium. 3. Aluminum alloys remain inert to some chemical elements. The presence of substances such as sulfur and its derivatives precipitate, forming slag, and do not affect the change in structure and properties of the alloys. 4. Under the influence of nitrogen, phosphorus or carbon, the properties of the material do not change.
The strength of aluminum in its pure form is low, so casting technology is used extremely rarely for the production of finished products. As a rule, these are cast ingots, manufactured for further rolling and forging.
Copper and aluminum
The need to replace a section of electrical wiring may arise under various circumstances (damage, installation of an additional branch, other reasons). In this situation, “copper to copper” or “copper to aluminum” is connected. Contacts made of different metals require special attention, and the reason lies in the following:
- They differ in different resistivities. Even a tightly screwed contact will weaken over time due to aluminum's tendency to thermal expansion.
- Copper also has an oxide protective film. However, it differs from aluminum in different resistances, as a result of which this is reflected in an increase in the contact temperature.
Safe contact of copper and aluminum Source mosoblzhilservis.rf
Important! Connections under load can become a source of sparks, which negatively affects the conductor capacity and can cause a fire.
Methods for connecting aluminum and copper wires Source uk-parkovaya.ru
Connecting copper and aluminum wires is acceptable. However, to do this you must adhere to the following methods:
- Pre-tin the copper with a soldering iron and solder.
- Treat the contact with a special anti-oxidation lubricant.
- Use special metal devices (adapters): “Nut”; Made of 3 parallel plates, in which a current-carrying core is laid between the outer ones; Self-clamping or screw terminal blocks; Crimping; Bolted connection; Spring terminals.
Connection of SIP and aluminum cable Source www.volt-m.ru
Thermal conductivity of aluminum alloys
Products made from aluminum alloys are divided by type of technological cycle: 1. Foundry. Produce cast products. 2. Deformable. The shape is given under pressure (pressing, forging, stamping). Aluminum products used in construction are made from a high-strength alloy. List of standard indicators, taking into account which alloys are characterized: 1. Thermal conductivity. 2. Transition from one state of aggregation to another. 3. The presence of alloying additives that affect product quality and durability (strength).
Information on thermal conductivity is indicated in reference literature, but the main evaluation criteria will be: 1. Density. 2. Thermal conductivity. 3. Linear expansion (coefficient). 4. Temperature at which strength changes. 5. Corrosion resistance. 6. Electrical resistivity.
After the analysis, it is easy to establish the coefficient of dependence of thermal conductivity on the temperature of the metal.
Which aluminum alloys have greater thermal conductivity? If aluminum products contain copper, zinc, magnesium or silicon, then the percentage of thermal conductivity in them increases noticeably compared to aluminum in its pure form.
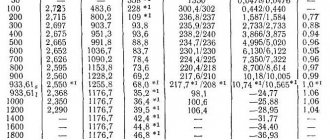
Thermal conductivity table:
Heat conductivity increases with increasing temperature. Alloy AD1 has greater thermal conductivity. Used for the production of profiles, stampings, ingots and other similar products.
Highest thermal conductivity of aluminum alloys
under normal conditions, it is observed in aluminum alloy AD1 - thermal conductivity at 20 0C is equal to 210 W/(m•deg).
Lowest thermal conductivity of aluminum alloys
recorded in casting alloys AK4, AL1, AL8.