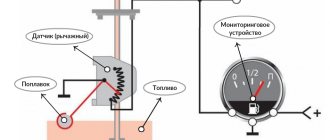
All devices that measure pressure are classified according to several criteria:
By type of pressure measured: pressure gauges, vacuum gauges, pressure and vacuum gauges, pressure gauges, micromanometers, draft gauges, draft pressure gauges, barometers, differential pressure gauges.
Pressure gauges are devices used to measure excess or absolute pressure (pressure difference). The “zero” of the excess pressure gauge is at the level of atmospheric air pressure.
Vacuum gauges are used to measure the pressure of rarefied gases.
A pressure and vacuum gauge allows you to determine excess pressure and rarefaction of a gas.
Pressure meters measure a small excess pressure (no more than 40 kPa), and draft meters measure a small vacuum pressure.
Differential pressure gauges determine the pressure difference at two points.
Micromanometers are differential pressure gauges for determining small pressure differences.
Barometers determine atmospheric air pressure.
According to the principle of operation: liquid, deformation (spring, bellows, membrane), deadweight, electrical and other devices.
Liquid pressure gauges consist of communicating vessels, the pressure is determined by one or several levels. With deformation pressure gauges, pressure is determined by the deformation or elastic force of the deforming element - spring, membrane, bellows. In deadweight piston pressure gauges, the desired pressure value is determined by balancing the mass of the weights and the piston. Electric pressure gauges operate on primary pressure transducers.
Purpose: general technical for measuring pressure in technological processes and reference for verification.
By accuracy class: from 0.4 to 4.0. This indicator characterizes the measurement error of the device.
According to the characteristics of the measured medium: general technical, corrosion-resistant, vibration-resistant, special, oxygen, gas.
Special pressure gauges are used for viscous and crystallizing substances, as well as substances that contain solid particles.
In addition to the above, pressure measuring instruments differ in the limit (range) of measurements, the degree of protection from water (eight degrees), the type of protection from external objects (six degrees), the degree of resistance to vibration, the degree of resistance to humidity and temperature (11 groups ).
Pressure gauges and pressure-vacuum gauges are designed to withstand short-term overload.
The dial of the device is marked with scale markings, units of pressure measurement, minus sign for vacuum pressure, mounting position of the device, accuracy class, name/designation of the medium, State Register sign, trademark of the manufacturer.
See examples of the use of electrical contact pressure gauges in electrical circuits here: Automation of pumps and pumping stations
In many technological processes, pressure is one of the main parameters that determine their progress. These include: pressure in autoclaves and steaming chambers, air pressure in process pipelines, etc.
Determination of pressure value
Pressure
is a quantity characterizing the action of a force per unit surface.
When determining the pressure value, it is customary to distinguish between absolute, atmospheric, excess and vacuum pressure.
Absolute pressure (p a )
- this is the pressure inside any system under which a gas, vapor or liquid is located, measured from absolute zero.
Atmospheric pressure (p in )
created by the mass of the air column of the earth's atmosphere. It has a variable value, depending on the altitude of the area above sea level, geographic latitude and meteorological conditions.
Overpressure
is determined by the difference between absolute pressure (pa) and atmospheric pressure (pv):
Read also: How to connect a reverse starter
Vacuum (vacuum)
is a state of gas in which its pressure is less than atmospheric. Quantitatively, vacuum pressure is determined by the difference between atmospheric pressure and absolute pressure inside the vacuum system:
When measuring pressure in moving media, the concept of pressure refers to static and dynamic pressure.
Static pressure ( pst )
– this is pressure depending on the potential energy reserve of a gas or liquid medium; determined by static pressure. It can be excess or vacuum, in a particular case it can be equal to atmospheric.
Dynamic pressure ( pd )
– this is the pressure caused by the speed of the gas or liquid flow.
Total pressure (p p )
moving medium consists of static (рst) and dynamic (рд) pressures:
Pressure measuring apparatus
Every person, when visiting a therapist, is faced with a planned measurement of intravascular values. If hypertension or hypotension is detected, you will need to regularly monitor intravascular parameters, possibly hospitalization, to find out all the features of the disease. It is also worth purchasing a device for measuring a person’s blood pressure, which allows you to find out the condition of blood vessels in a comfortable environment, and be able to prevent severe attacks.
At the initial appointment with a specialist, the patient is given the first measurement of arterial parameters, using a mechanical, semi-automatic or automatic device for measuring blood pressure - a tonometer.
Considering that restoration of intravascular tension can take years, the patient will need to purchase his own blood pressure measuring device in order to determine the cause of poor health in time and take medications.
A tonometer is a modern medical device used for non-invasive measurement of blood pressure (the device causes pain and does not violate the integrity of the skin during examination).
Thanks to this equipment, you can control blood pressure painlessly, quickly and without the help of medical personnel, and avoid complications that can lead to hypotension or hypertension.
Devices for measuring blood pressure non-invasively are divided into several types, this greatly simplifies their operation. Today, semi-automatic and automatic blood pressure monitoring devices are in demand, but the mechanical one is also not inferior to its improved counterpart. Let's consider all the features and advantages of pressure measuring devices: which one is better? It is important to decide how to choose a device that performs high-performance blood pressure measurement.
Pressure gauge: design of a device for measuring pressure, its types and features
Very often in life, and especially in production, you have to deal with such a measuring device as a pressure gauge.
A pressure gauge is a device for measuring excess pressure. Due to the fact that this value can be different, the devices also have varieties. There are many areas of application for these devices. They can be used in the metallurgical industry, in any mechanical transport, housing and communal services, agriculture, automotive industry and other industries.
Depending on the purposes for which the devices are used, they are divided into different types. The most common are spring pressure gauges. They have their advantages:
- Measuring quantities over a wide range.
- Good technical characteristics.
- Reliability.
- Simplicity of the device.
In a spring pressure gauge, the sensing element is a hollow, curved tube inside. It can have a cross-section in the form of an oval or an ellipsoid. This tube deforms under pressure . It is sealed on one side, and on the other there is a fitting with which the value in the medium is measured. The end of the tube, which is sealed, is connected to the transmission mechanism.
The design of the device is as follows:
- Frame.
- Instrument arrows.
- Gears.
- Axis.
- Leash.
- Gear sector.
A special spring is installed between the teeth of the sector and the gear, which is necessary in order to eliminate backlash.
The measuring scale is presented in Bars or Pascals. The arrow shows the excess pressure of the medium in which the measurement is being taken.
The principle of operation is very simple. The pressure from the medium being measured enters the tube. Under its influence, the tube tries to level out, since the area of the outer and inner surfaces has different sizes.
The free end of the tube moves, and the arrow rotates at a certain angle thanks to a transmission mechanism. The measured value and the tube deformation are in a linear relationship.
That is why the value that the arrow shows is the pressure of a certain environment.
Types of pressure measurement systems
There are many different pressure gauges for measuring low and high pressure. But their technical characteristics are different. The main distinguishing parameter is the accuracy class. The pressure gauge will show more accurately if the value is lower. The most accurate are digital devices.
According to their purpose, pressure gauges are of the following types:
- Self-recording. They contain a mechanism that allows you to draw a graph of the device’s operation on paper.
- Railway. Used in railway transport.
- Ship's. Used on sea and river vessels.
- Reference. They have a high accuracy class. That is why they are used for testing, adjusting and checking other pressure measuring instruments.
- Special. Used to measure the value of various gases. Depending on what gas they are intended for, they have different body colors and marking letters: for measuring flammable gases - red, for non-flammable gases - black, yellow ammonia (A), white acetylene (Ac), blue oxygen (K).
- Electric contact. They have an electrical alarm that allows you to regulate the measured environment. These devices are divided into two types: based on an electrical contact attachment and with microswitches.
- General technical. Designed to measure pressure in various environments. They can measure excess and vacuum pressures.
Based on the principle of operation, the following types are distinguished:
- Piezoelectric. Based on the piezoelectric effect. A charge appears in a quartz crystal under mechanical action.
- Deformation. They are based on the deformation of the sensitive element (membrane, bellows, spring, etc.), which, when deformed, acts on the pointer.
- Liquid. Their basis is a tube filled with liquid. They can be of two types: with one or two tubes. Devices with two tubes are used to compare pressure in different environments.
- Piston. They consist of a cylinder with a piston inserted inside.
Liquid measurement systems
The value in these pressure gauges is measured by balancing the weight of the liquid column. A measure of pressure is the level of fluid in communicating vessels. These devices can measure values in the range of 10−105 Pa. They have found their application in laboratory conditions.
Essentially, it is a U-shaped tube containing a liquid with a higher specific gravity compared to the liquid in which the hydrostatic pressure is directly measured. This liquid is most often mercury.
This category includes working and general technical devices such as TV-510, TM-510. This category is the most in demand. They are used to measure the pressure of non-aggressive and non-crystallizing gases and vapors. Accuracy class of these devices: 1, 1.5, 2.5. They have found their application in production processes, in the transport of liquids, in water supply systems and in boiler rooms.
Electrical contact devices
This category includes pressure and vacuum gauges and vacuum gauges. They are intended for measuring the volume of gases and liquids, which are neutral in relation to brass and steel. Their design is the same as that of spring ones.
The only difference is in the large geometric dimensions. Due to the design of the contact groups, the body of the electrical contact device is large. This device can influence the pressure in a controlled environment by opening/closing contacts.
Thanks to the electrical contact mechanism used, this device can be used in an alarm system.
Reference meters
This device is intended for testing pressure gauges that measure values in laboratory conditions. Their main purpose is to check the serviceability of these working pressure gauges. A distinctive feature is a very high accuracy class. It is achieved thanks to design features and gearing in the transmission mechanism.
Special devices
These devices are used in various industrial sectors to measure the pressure of gases such as acetylene, oxygen, hydrogen, ammonia and others.
Basically, pressure can be measured with a special pressure gauge for only one type of gas. Each device indicates the gas for which it is intended.
The device is also colored to match the gas for which it can be used. The initial letter of gas is also written.
There are also vibration-resistant special pressure gauges that are capable of operating under strong vibrations and high pulsating environmental pressure. If you use a regular pressure gauge in such conditions, it will quickly break, since the transmission mechanism will fail. The main criterion for such devices is corrosion-resistant steel housing and tightness.
Ammonia systems must be corrosion resistant. Copper alloys are not allowed in the manufacture of acetylene measuring mechanisms.
This is due to the fact that upon contact with acetylene there is a risk of formation of acetylene explosive copper. Oxygen mechanisms must be fat-free.
This is due to the fact that in some cases even minor contact of pure oxygen and a contaminated mechanism can cause an explosion.
Recording devices
A distinctive feature of such devices is that they are able to record the measured pressure on a diagram, which will allow you to see changes at a certain time. They have found their application in industry with non-aggressive means and energy.
Ship and railway
Marine pressure gauges are designed to measure the vacuum pressure of liquids (water, diesel fuel, oil), steam and gas. Their distinctive features are high moisture protection, resistance to vibration and climatic influences. They are used in river and sea transport.
Railway gauges, unlike conventional pressure gauges, do not display pressure, but convert it into a signal of another type (pneumatic, digital, etc.). Various methods are used for these purposes.
Such converters are actively used in automation systems and process control. But despite their purpose, they are actively used in the nuclear energy, chemical and oil production industries.
Instruments for measuring pressure are divided into the following types:
- Thrust and pressure gauges are pressure and vacuum gauges that have extreme measurement limits of no higher than 40 kPa.
- Traction gauges are a vacuum gauge that has a measurement limit of (-40) kPa.
- A pressure gauge is a pressure gauge of low excess pressure (+40) kPa.
- Pressure and vacuum gauges are devices that are capable of measuring both vacuum and excess pressure in the range of 60–240,000 kPa.
- A vacuum gauge is a device that measures vacuum (pressure that is below atmospheric pressure).
- A pressure gauge is a device that is capable of measuring excess pressure, that is, the difference between absolute pressure and barometric pressure. Its limits range from 0.06 to 1000 MPa.
Most imported and domestic pressure gauges are manufactured according to all generally accepted standards. It is for this reason that it is possible to replace one brand with another.
When choosing a device, you must rely on the following indicators:
- The location of the fitting is axial or radial.
- The diameter of the fitting thread.
- Instrument accuracy class.
- Case diameter.
- Limit of measured values.
Types of digital pressure gauges:
- Pressure gauges for measuring absolute pressure - used to monitor compliance of the parameters of the measured object with the specified technical requirements. For more comfortable operation, the devices are equipped with a built-in warning system when the specified values are exceeded.
- Pressure gauges for measuring differential pressure are universal instruments with which you can measure all the necessary parameters of various systems. Based on the conditions and tasks, it is possible to connect suitable measuring probes to such a pressure gauge.
Pressure gauges are also classified according to accuracy class:
- 0.5-1 – used for general industrial purposes, for example, to control pressure in an oil pipeline.
- 0.1-0.5 – intended for laboratory research, higher accuracy guarantees higher quality research.
- 0.05-0.1 – standard instruments intended for checking and calibrating other pressure gauges.
Digital instruments have a number of advantages over analog pressure gauges, namely the presence of a digital display, the ability to save and transfer the obtained measurement results to a PC, select measurement units and add new ones. By design, electronic pressure gauges can have replaceable or built-in probes.
Hydrostatic pressure transducers (hydrostatic level gauges)
These converters are a type of excess pressure sensors, when the latter are used to measure the hydrostatic level of liquids. The transducer actually measures the pressure of the liquid column above it. For use in water utilities and water treatment systems, the range of KIP-Service LLC includes submersible hydrostatic level sensors Hydrobar manufactured by KLAY-INSTRUMENTS BV.
As mentioned above, the SI unit of pressure is “Pascal” (Pa).
In practice, other units of measurement are widely used in industry, besides “Pa” the most common are “bar” (bar), “m.v.s.” (meter of water column) and “kgf/cm²” (kilogram-force per square centimeter), as well as derivatives of these units: “mbar” (millibar), “kPa” (kilopascal), “MPa” (megapascal). Conversion table for popular pressure units
| Units | Pa | kPa | MPa | kgf/cm² | mmHg. | mm water column | bar |
| 1 Pa | 1 | 10–3 | 10–6 | 10.197 16 x 10–6 | 0,007 500 62 | 0,101 971 6 | 0,000 01 |
| 1 kPa | 1 000 | 1 | 10–3 | 0,010 197 16 | 7,500 62 | 101,971 6 | 0,01 |
| 1 MPa | 1 000 000 | 1 000 | 1 | 10,197 16 | 7 500,62 | 101 971,6 | 10 |
| 1 kgf/m2 | 9,806 65 | 9.806 65 x 10–3 | 9.806 65 x 10–6 | 0,000 1 | 0,073 555 9 | 1 | 98.066 5 x 10–6 |
| 1 kgf/cm2 | 98 066,5 | 98,066 5 | 0,098 066 5 | 1 | 735,559 | 10 000 | 0,980 665 |
| 1 mmHg (at 0 °C) | 133,322 4 | 0,133 322 4 | 0,000 133 322 4 | 0,001 359 51 | 1 | 13,595 1 | 0,001 332 24 |
| 1 mm water column (at 0 °C) | 9,806 65 | 9.807 750 x 10–3 | 9.806 65 x 10–6 | 0,000 1 | 0,073 555 9 | 1 | 98.066 5 x 10–6 |
| 1 bar | 100 000 | 100 | 0,1 | 1,019 716 | 750,062 | 10 197,16 | 1 |
Automatic devices
The automatic device that measures blood pressure in humans is easy to use, so even a child can use it. This tonometer comes with instructions explaining how to determine blood pressure. Also, some tonometers have an adapter for changing the power supply and a special table that tells you how to find out whether intravascular tension has left the normal limits.
The measuring functions of such a device complement the capabilities of semi-automatic devices, so it is the most accurate and best among all similar devices. This device has cuffs for measuring blood pressure and an electric monitor that allows you to measure blood pressure by pressing just one button.
This type of tonometer is divided into several varieties:
It doesn’t matter how pressure is measured, namely, what automatic device. The goal of each of them sounds the same - to provide the most accurate results. Any automatic electronic device that measures pressure on its own inflates a cuff to measure air pressure. It is located on the shoulder, finger or wrist (depending on the choice of medical equipment designed to record intravascular parameters). Next, the device lowers the cuff and shows the patient the finished result.
Each of these tonometers has an adapter for connecting to an electrical outlet, so by purchasing these pressure meters, you can use them both on a trip, at home, and at a resort.
Semi-automatic devices
A semi-automatic blood pressure meter is a simplified equipment that allows you to measure the pressure of any person, regardless of education and mental development. Semi-automatic devices are sold in pharmacies at a reasonable price. To use this device you will need:
- Put on the measurement cuff, slightly above the elbow (closer to the shoulder), and secure it.
- Then press the button on the equipment.
- Inflate the air pressure cuff manually using a bulb.
As a result, measuring a person’s blood pressure becomes much easier, because a semi-automatic blood pressure meter deflates the cuff itself and shows ready-made results.
The downside to this blood pressure monitor is that it requires batteries or an electrical connection (depending on the manufacturer and model of blood pressure monitor you choose). Batteries require ongoing financial costs, but otherwise the device will not function, then such intravascular voltage control becomes expensive to use. When purchasing a tonometer that requires a network connection, measuring a person’s blood pressure outside the home will become impossible.
However, some blood pressure measuring devices have a special adapter for the tonometer, which allows you to switch the power from the battery to the mains, and vice versa.
Thanks to this device, you can measure pressure anywhere.
Recommendations for intravascular measurement technology
It doesn’t matter at all whether your blood pressure is measured with a mechanical or automatic tonometer, or what the device for measuring a person’s blood pressure is called: shoulder, finger or wrist. It will be necessary to measure intravascular tension correctly, otherwise even the best devices will show an erroneous result.
- The test is carried out on an empty bladder, because the desire to visit the bathroom provokes intravascular tension.
- Whatever device you use, a sitting position will be required. You need to lean your elbows on the back of the chair and not cross your legs, but place them firmly on the floor.
- Devices for measuring a person’s blood pressure, namely cuffs, are put on the bare arm so that clothing does not create additional compression.
To protect yourself from the progression of intravascular diseases, you should consult with a specialist and find out how blood pressure is measured in your case.
This reduces the risk of complications such as heart attack, stroke and hypertensive crisis. The patient should regularly monitor his own intravascular condition to ensure a competent approach to therapeutic therapy and the return of blood vessels to normal.
Application of differential pressure gauges
Differential pressure is the difference in pressure between set values. Therefore, a differential pressure gauge has two connectors, can measure relative pressure, and the resulting measurement results can be both positive and negative, i.e. show excess or low pressure.
Because of this, it is important to apply the correct pressure to the appropriate connector - the positive connector has excess pressure, and the negative connector has underpressure. This will help obtain more accurate measurement results. If you take measurements in dusty and polluted air, it is better to use a pitot tube. The difference between dynamic and static pressure can be used to determine the air speed in the ventilation duct.
Mechanical apparatus
A mechanical device for measuring blood pressure bears this name, because it allows you to measure pressure, regardless of external factors. The main thing is that the person is able to inflate the cuff and evaluate the result. This equipment consists of a blood pressure cuff, a pressure gauge (to measure the air pressure inside the cuff) and a bulb.
A mechanical device for non-invasive blood pressure measurement (also called a sphygmomanometer) is used as follows:
- Cuffs for measuring blood pressure are placed on the arm, as high as possible to the shoulder and secured with special Velcro.
- A phonendoscope, similar to a therapeutic device designed to listen to the chest, is placed on the ears. Its other end is placed on the inside of the elbow bend and pressed lightly.
- Next, the arm cuff is inflated using a bulb. Only after this the results and assessment of blood pressure are summed up.
Gauge pressure converters
Figure 1 — General industrial pressure sensor PTE5000
These converters measure the pressure created by any medium relative to atmospheric pressure. This type of pressure transducers is the most common and is used in almost all industries: housing and communal services, energy, water treatment, water purification, heating, air conditioning and ventilation systems, food industry, chemistry, etc.
To measure excess pressure of water, steam, neutral liquids and gases, KIP-Service LLC offers a pressure sensor for general industrial use PTE5000. These sensors are widely used by Russian enterprises to measure water pressure in boiler automation systems, water supply and sewerage systems, housing and communal services and other systems where the low cost of equipment is in the foreground.
Design of pressure transducers
Figure 4 - Design diagram of pressure transducers
The figure below shows the general design diagram of pressure transducers. Depending on the type of sensor, device manufacturer and application features, the design may vary. This diagram is intended to familiarize you with the main elements of a typical pressure transmitter.
- Cable entry: This part of the pressure transmitter is used to seal the electrical cable into the sensor. As a rule, a gland type PG9 is used, but other connection options are also available (for example PG16, M20x1.5).
- Terminals: Terminals are required to physically connect the electrical wires to the sensor. Today, the vast majority of pressure transducers use a 2-wire connection circuit with an output signal of 4...20 mA.
- Power / spark protection board: This board distributes electrical energy between the electronic components of the sensor. For explosion-proof converters, this board implements the spark protection function. Inexpensive pressure sensors (for example, PTE5000) usually have a combined power supply and conversion board.
- Electronics housing: The part of the pressure sensor that houses the power supply and conversion board. For low-price converters (WIKA, BD Sensors), the electronics housing and the sensor housing itself are one unit. The presence of a separate housing for electronics is typical only for high-quality pressure transducers (for example, KLAY-INSTRUMETNS, EMERSON, VALCOM, YOKOGAWA).
- Converter Board: This is one of the most important parts of pressure transducers. This board converts the signal from the primary sensor into a unified electrical signal in terms of current or voltage.
- Sensor body: The main mechanical part that represents the actual body of the transducer.
- Wires and Atmospheric Tube: Wires are typically a cable harness that connects the sensor leads to the converter board. An atmospheric tube is used in gauge and vacuum pressure sensors to communicate the sensitive element (pressure sensor) with atmospheric pressure.
- Process connection: This part of the pressure transducers is used to physically connect the sensor to the process (pipeline, tank, apparatus). The most common connection is a threaded pressure gauge connection G1/2″ according to DIN 16288 and M20x1.5 thread. Connections G1/4″, G1″, and flange connections are also widely available. In the food industry, special sanitary connections are common, for example milk nut DIN 11851, DRD flange, Tri-clamp clamps. The assortment of KIP-Service LLC includes special pressure transducers for use in the food (dairy, brewing) industry. These are devices manufactured by KLAY-INSTRUMENTS BV - pressure sensors of the 8000-SAN series and intelligent pressure sensors of the 2000-SAN series, which fully meet all the requirements of the food industry in terms of hygiene, measurement accuracy and temperature conditions.
Figure 5 - Process connections - Pressure sensor (primary transducer): The pressure sensor is one of the key elements of any pressure transducer. This element directly converts the pressure acting on it into an electrical signal, which is then unified on the conversion board. Today, there are several ways to convert pressure into an electrical signal. Inductive, capacitive and strain-resistive conversion methods are used in industry. The most common is strain-resistive. This method is based on the phenomenon of the strain effect in metals and semiconductors. Strain gauges connected in a bridge circuit (Wheatstone bridge) change their resistance under pressure, which leads to imbalance of the bridge. The unbalance depends directly on the degree of deformation of the resistors and, therefore, on the applied pressure.
Figure 6 - Wheatstone Bridge
There are 4 main types of sensors on the market, based on the strain-resistive conversion method, which are used by all existing manufacturers of pressure transducers. Let's look at each type separately.
Where to buy air flow pressure meters
You can leave a request or buy differential pressure gauges from our managers by calling, filling out a form on the website or writing by email. We can provide advice on equipment maintenance or select an analogue that meets your requirements. In addition, we provide product warranty service. The SOYUZ-PRIBOR company is the official distributor and dealer of a number of brands and has been operating for more than 25 years! Delivery is carried out throughout Russia.