A bolted connection can rightfully be called the most common type of fastener. But even the highest quality carvings become unusable over time. The way out of this situation may be to contact a mechanic or cut the thread yourself.
In both cases, this will require a set of dies or dies - hand tools for cutting external threads. With their help, you can quickly restore worn-out hardware or obtain a replacement part for an existing stud or bolt.
Design
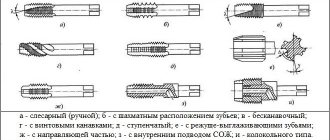
The first feature that distinguishes one lehr from another is the design of the body. In accordance with this, they distinguish:
- Round dies. The body is a solid ring through which the workpiece passes. Thanks to high rigidity, a high-quality thread with a good thread profile is obtained.
- Sliding dies, consisting of two parts, are designed to produce threaded surfaces of various diameters.
- Split - the range of thread diameters is 0.1-0.3 mm. Therefore, it is advisable to use them for imprecise threads.
All about dies
A die or die is a device used to cut external threads of various types. It is represented by a small nut on which there is an edge and a chip outlet. The threaded device can have thread pitch sizes from eight to ten.
Thread pitch is the distance between adjacent threaded threads.
The working area of dies is iron pipes and rods. Threads come in conical and cylindrical shapes. To obtain a high-quality thread, you need to cut in one pass. The die has a cutting edge. To make cylindrical threads, dies with two parts of the working area are used - calibrating and cutting. The calibrating part forms the final diameter and thread profile.
Classification of dies
Ledgers are divided into: tubular, square, round and hexagonal.
They are also divided by structure:
- solid;
- sliding (prismatic);
- cut.
The round lecher is the most widely used. It is threaded in one pass, and not in several, like sliding ones. These dies can cut threads at different pitches. They can also be used to cut pipe and inch threads. The working part of round dies is not subjected to grinding. The outside diameter will depend on the size of the chip guards and the size of thread required.
Thread direction
The thread can be right-handed (threads are cut clockwise) or left-handed (counterclockwise). Dies are also distinguished:
- Rights. Used for thread cutting on bolts, axles, screws.
- Left. They are used relatively less frequently in specific automotive elements, rotational mechanisms, and where right-hand threads will unwind. In the photo of the dies you can see the markings with the Latin letters “LH”.
How to cut threads using a groove
Before you start actually cutting the thread, you should chamfer the end of the workpiece at an angle of 45 degrees. This will make it easier to roll the first turns due to the ability to position the die so that its axis is strictly parallel to the axis of the workpiece. Then you should do the following:
- the workpiece is secured in a bench vice. In this case, it is necessary to control that its axis is oriented strictly vertically;
- the tool and workpiece are lubricated with technical oil;
- the die is applied to the end of the rod strictly horizontally;
- then several initial rotations of this tool are made;
- if in the first circles a clear distortion is noticed, you should remove the bench, tap the bar being processed and start working again;
- rotation of the tool at the beginning of the cutting procedure should be accompanied by uniform pressure on the handles of the die holder;
- Having created the first few turns, you should check the horizontality of the handle and the knob. To do this you need to use a level. If the tool is oriented correctly in space, thread cutting continues along the entire length of the workpiece;
- Having made one or two turns to remove the chips, you need to turn the blade in the opposite direction half a turn;
- when approximately the middle of the piece of workpiece on which the thread is cut is reached, the pressing force can be weakened due to the start of the self-tightening process;
- Having completed the cutting, the tool should simply be returned to its original position along the thread made and removed from the workpiece.
Checking the correctness of the work performed is carried out using special templates, calipers, or by screwing on a nut of the appropriate size.
Profile
According to the profile, there are metric, pipe inch dies, and trapezoidal threading tools. Each variety has its own characteristics:
Metric. As the name suggests, they cut metric threads. They are designated by the letter “M”, followed by a number indicating the thread diameter in millimeters. The standards provide for sizes up to 68 mm, each corresponding to a small or large step. Dimensions, designation examples, acceptance rules for such dies according to GOST 9740.
Read here: Set of ratchet sockets - how to choose a convenient universal professional set
Pipe cylindrical. Visually easy to identify by the letter “G” on the body. This type of thread is measured using the English inch unit, which is 25.4 mm.
So, the designation G 1/2” means that we have a half-inch pipe thread. They are widely used for pipes of heating equipment and water supply systems. Size range from G 1/8” to G 2”.
Pipe conical. In order not to confuse them with other varieties, they are marked with the symbol “K”. They are used when it is necessary to obtain a conical threaded surface - in critical connections operating under pressure or machine components.
Trapezoidal. The cross-section of the threads is an equilateral trapezoid. They are common in power pairs that convert rotation into translational motion. The simplest example is the lead screw and nut of a machine and bench vice.
The design of the die, its difference from the die
A thread cutting die is a nut with axial holes that form the cutting edges, as well as chip holes for removing the generated chips during operation. The working part is, as a rule, an internal cone with 8-10 turns, of which 2-3 turns are the intake part. They can have a solid, sliding or split design. Split and sliding dies have the ability to change the diameter of the thread being cut.
The die material is alloy steel 9ХС, ХВСГВ. High-speed steels are widely used - R18, R6M5K8, R5M5 and others, as well as hard alloys. The steel grade, along with the designation and degree of accuracy, is indicated on the die body (with the exception of 9ХС steel).
The question often arises - what is a lerka and what is its difference from a die. Previously, there was a division - dies were called set-up, adjustable tools for preparing large-diameter threads. Ledgers are solid plates with holes and grooves, usually of small diameter. Now both types of tools are most often called dies.
Die holders
To cut a thread, one tool is not enough. You will also need an auxiliary device for clamping and holding the die body - a die holder.
One device is designed for several standard sizes at once - for small, medium and large threads. The die is installed inside the holder and secured with a screw.
Quality of the tools used
On sale you can find dies made from a wide variety of alloys. The following metals can be used in manufacturing:
- High-speed steel 9ХС and ХСС, Р6М5. Today it is found on sale more often than other steels. This is due to its exceptional performance and relatively low cost. Less commonly used is P18 steel, which was common at the time of the existence of the USSR.
- The quality of a tool largely depends on the precision of its production. If the shape accuracy is poor, or there are defects on the surface, then this indicates poor quality of the tool.
Read also: U13a steel for a knife
The cost of a tool can depend on a fairly large number of factors. As a rule, instruments from foreign manufacturers are much more expensive than domestic ones.
Material
For manufacturing, high-speed steels R6M5 and R18 are used. They are optimal in terms of price-quality ratio, have a long service life and cope well with household tasks and minor repairs.
For production conditions, tools with carbide cutting edges are more suitable. With their help you can obtain threads on high-alloy steel.
Tips for choosing a tool
The cutting die can last for a long period. In its manufacture, as a rule, tool steel is used, which is characterized by high wear resistance.
The tool is selected according to the following parameters:
- Outer diameter of the workpiece.
- Accuracy class.
- Pitch and other thread parameters.
- According to the type of material being processed.
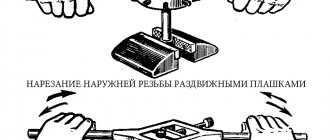
Die threading
Cutting threads using a die
The highest quality and most accurate cutting, as a rule, is carried out when using the split version. The design is characterized by the presence of a locking ring. In addition, there are simply a huge number of different sets on sale, which are represented by products with different diameters and parameters. All the necessary information can be determined by deciphering the markings. All designations, as a rule, are applied to the body of the product.
By design, the following types of dies are distinguished:
- Prismatic or square. These are two identical sliding halves of a square or prismatic cross-section, secured in a frame-shaped clamp with handles. The components have prismatic grooves. Most often, oblique gripping devices with a rectangular window are used - a total of 6 tool numbers. The holder rotates in the working direction in the same way as the tap. The driver or die may have special guide rings, which makes it possible to obtain a more even surface without defects (for example, distortions, burrs, nicks);
- Round dies can be split or solid (or otherwise called dies). The first option is used to obtain more accurate threads. Structurally, the split lehr has a small slot on the side surface. This allows you to easily adjust the processed diameter within 0.1-1.25 mm;
- Solid. Structurally, it is a solid hardened nut, in which the threads are cut in the form of through longitudinal grooves. They also form the cutting contour and serve to remove chips. Thread cutting is carried out in one pass. Despite the fact that the tool has sufficient rigidity, it wears out quickly. This type of dies is used to produce the following types of threads (parameters according to GOST 2173-51):
- metric – with a diameter of up to 52 mm;
- inch – from ¼ to 2″;
- metric fine up to 135 mm. and up to 125 mm. – only five size groups.
Read also: How to distinguish tin from lead
Features of working with dies
Dies can be made of different types and sizes. The parameters are determined by the mark located directly on the device.
The material from which the die is made must be checked. If you do not do this, then inconsistency with the capabilities of the thread-cutting tool can damage either the pipe or the die itself.
The marking (alphanumeric combination) also determines compliance with the pipe diameter, as well as the designation of the thread type.
To obtain better cutting, the die is treated with an emulsion solution (in cases where cutting is done on soft steel or brass), drying oil (for hard steels), and kerosene (for working with aluminum tools).
Conical (inch) tools
These are the same devices as in the previous case. Only on the pipe they make not a cylindrical thread, but a conical one. The body is marked in the form of the letter “K”.
All such products, like the taps themselves, are made from three types of steel:
- R6M5;
- 9ХС;
- CSU.
These types of steel are the most commonly used today. But a species like P18 is quite rare, but it was very common during the Soviet era.
It should be noted right away that all old products that have the USSR quality mark on their body are of better quality than modern ones.
Conical dies
What is a die and what is it used for?
A die is a common tool used for cutting external threads and calibrating them. These devices are used to produce pipes, rods, bolts, studs, as well as other parts and products.
Read also: What is an operating system for?
Photo #1: Die
Die design
The design of the die resembles a large round nut. There is a hole with cutting edges in the center. It has coils (8–10 pcs.). They differ in sharpness of sharpening.