Branch
(syn.
elbow
;
angle
) - a product, fitting, designed to change the direction of liquid (gas) flow in a pipeline.
Made from cast iron, steel, plastic and so on.
A large selection of plumbing fixtures of various types from the company is presented on the website of the AquaCenter store chain. You can study the product catalog in more detail here.
Types of steel bends [edit | edit code]
- Steeply curved solid-drawn ones
are made of carbon and low-alloy steel with bending angles of 45, 60, 90 and 180° from pipes by stamping or drawing along a horn-shaped core. They are used for pipelines for various purposes, including those under the control of regulatory authorities (with the index “P” on the marking) at operating pressures up to 160 atm at temperatures from −70 to +450 °C. Manufactured according to GOST 17375-2001 (3D type with a bend radius of approximately 1.5 DN; versions 1 and 2) and according to GOST 30753-2001 (2D type with a bend radius of approximately 1 DN; versions 1 and 2). Version 1 is made on the basis of foreign standards (DIN) and is produced in Russia mainly with diameters from 21.3 mm to 48.3 mm. Execution 2 is the most frequently used. Although GOST standards stipulate all standard sizes, in Russia, according to GOST 17375-01, bends are manufactured with a diameter from 32 mm to 426 mm. If you need a bend with a similar geometry with a diameter above 426, then usually (based on operating conditions) stamped-welded bends (OKSh) or welded sectional bends (OSS) are used, and according to GOST 30753-01, bends with a diameter of 530, 630, 720 and 820 mm are manufactured. Also, steeply curved bends are manufactured according to OST 34.10.699-97 (for thermal power plants and the nuclear industry from ferrous steels), according to OST 34.10.418-90 (for thermal power plants and the nuclear industry from stainless steels), as well as according to various specifications with geometry in accordance with GOST 17375 -01 made of stainless steel. - Stamp-welded steeply curved ones
are manufactured for main and industrial pipelines with diameters from 219 to 1420 mm for a working pressure of up to 100 atmospheres for oil and gas industry facilities. Manufactured according to TU 102-488-95, bending radius - 1 and 1.5 DN. There are also a number of other specifications. - Welded sections
are manufactured according to OST 34.10.752-97 (with a bend radius of 1 DN and 1.5 DN) from carbon and low-alloy steels for heating networks and thermal power plants at an angle of 15, 30, 60 and 90° degrees for a working pressure of up to 25 atm at operating temperature up to 200 °C; according to various standard schemes (in particular TS-583, developed on the basis of OST 34.10.752-97) with a diameter from 108 to 1620 mm; according to OST 36-21-77 with diameters from 500 to 1420 mm; according to OST 36-42-81 with diameters from 14 to 426 mm (with a bend radius of 1.5 DN) from carbon steels intended for the construction of pipelines designed for pressures up to 25 atm with a temperature range of −30 to +300 °C at chemical enterprises , petrochemical, metallurgical, food, light and other industries. Also, welded sectional bends can be manufactured according to TU 102-488-95, TU 51-29-81, OST 36-21-77, etc.
Key Features
The products are characterized by high performance characteristics. Among their advantages is resistance to the effects of almost all unfavorable external factors of any origin: biological, atmospheric, chemical, man-made. In addition, the list of product advantages includes:
- the ability to smoothly rotate the pipeline axis;
- being integrated into the main line using electric welding, they provide maximum connection reliability;
- are immune to temperature fluctuations, since steel has a low coefficient of thermal expansion;
- can be used in harsh operating conditions;
- have high mechanical strength;
- absolutely gas-tight.
Steel bends successfully withstand high operating pressures and are capable of operating in conditions of critically high and low temperatures. They are resistant to excess ambient moisture, reliable, and operate for a long time.
Types of bent elbows [edit | edit code]
Bent bends can be cold-formed, which are manufactured in accordance with GOST 24950-81 with a large bend radius (from 15 m), and hot-bent, which are manufactured in accordance with TU 102-488-95, TU 102-488-05, TU 51-515-91 and other OST and specifications with bending radii from 1.5 to 20Dn.
What types of plumbing fittings are used these days? We will look at the main types of pipes and methods of connecting them.
Alas, within the framework of a short article it is impossible to pay attention to all the details of the design and use of existing fittings, so our acquaintance with them will be somewhat superficial.
Only a small part of the modern range of connecting fittings is presented here.
For plumbing installation, two fundamentally different pipe connections are used:
- Pressure water pipes are designed to transport hot and cold water under pressure. The same pipes and methods of connecting them are used when installing heating systems.
- The specificity of sewerage is the movement of wastewater by gravity. Connections must be tight; but they are not designed for excess pressure.
In this order, we will consider the relevant sectors of the modern market.
Pipe rotator
In production, welding of bends to pipes is carried out using special equipment. Typically, these special equipment are rotators. The parts to be welded are clamped in the device and rotate around their axis, which makes it possible to perform high-quality welding of the outlet.
Let's consider the main advantages of using a rotator when welding a rotary product with a pipe:
- allow you to weld pipes with large diameters;
- the use of an autonomous drive in the rotator design allows you to regulate the rotation speed of the part;
- ensure precise alignment of pipes;
- can work not only with straight parts, but also with more complex, from a structural point of view, elements (for example, tees).
Today, there are many types of bends that allow you to solve any problem when installing pipelines. At the same time, a wide range of these products obliges specialists to study a large amount of information in order to know and comply with the features and rules for using all such products.
Plumbing and heating
Steel pipes
This category includes pipes made of black steel and galvanized, which are not afraid of corrosion. Most often they are welded by electric welding or gas, but not always.
Please note: galvanizing is strongly recommended to be assembled on threads. Welding breaks the protective zinc layer, making the seam vulnerable to corrosion.
To connect them, two types of fittings are used:
- Threaded _ Couplings, angles, tees, adapters and locknuts are made of brass (often chrome-plated) or cast iron. The advantage is the exceptional mechanical strength of the connection. The main disadvantage is the laboriousness of assembly and the need to precisely adjust the length of the pipes and threads.
Material used
There are no strict recommendations as to what alloy the steel elbow should be made of; GOST allows the use of various ferrous and corrosion-resistant steels. The raw material for basic products is predominantly low-alloy steel. The most popular brands are 09G2S, St20 and others.
If the product will work in highly loaded lines, it is better to use high-alloy steel (for example, 12ХН2А or 20G), as well as for work at high temperatures. And when the reinforcement comes into direct contact with chemically active substances, stainless steel alloys are chosen as raw materials: AISI 201, AISI 316 and others.
Galvanized variations of bends are also in demand on the market. For their production, a ready-made galvanized steel pipe is used, but its coating may be damaged during storage or transportation of the final product. Therefore, a newly manufactured elbow is often galvanized.
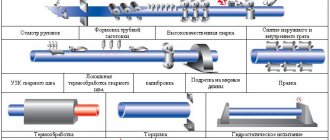
Production process
Depending on future operating conditions, choose one of five production methods:
- hot stamping (hot pressing);
- hot deformation;
- mechanical processing (bending);
- electric welding;
- combined technology (stamp welding).
With the hot-deformed method, the finished seamless pipe is cut into pieces of the required length, which are heated to +1000...+1100℃ (more precisely, the temperature is selected based on the steel grade used) in a hearth furnace or in another way and sent to a hydraulic press with a horn-shaped core. Each diameter has its own core. Then the product is sent for calibration, and its edges are trimmed on a special machine. The result of the work is seamless hot-deformed bends. This is the most expensive product in its class, because its production is the most labor-intensive and energy-consuming compared to analogues. However, the operational potential of these modifications is higher.
The hot stamping method is also carried out after preheating the workpieces. They are sent to a two-strand oval die, where they are given the appearance of an elbow with an elliptical cross-section. To prevent the stamp from damaging the edges of the future bend, a metal liner is driven into the workpiece to increase its rigidity. After leaving the oval die, the semi-finished product is sent to the molding die, where its shape is adjusted, turning it from oval to round. The final processing is carried out in a calibration stamp. If a bend with a diameter of more than 100 mm is made using this technology, the final molding is preceded by another operation - stretching the back. This is how seamless hot-stamped variations are produced.
In mechanical technology, a pipe bending machine is used; the operation can be carried out in a cold (more often) or hot (less often) version. Bending equipment can be automatic or manual. The fundamental difference between this technology and previous options is that the pipe is bent without preliminary cutting into individual products: first it takes the form of a snake, and then it is cut into segments. The output is bent bends, also without seams.
If the electric welding method is chosen, two or more closed ring parts of small height are first made (they are cut from a solid pipe or formed from tape). Then they are welded into a single piece by applying a girdle seam. This is how welded versions of products are produced; they are the most economical and practical among all, and their production takes the least amount of time.
With combined technology, stamping equipment produces two identical semicircular parts that mirror each other. The halves are combined and welded into a finished product, applying two parallel seams. These are stamp-welded modifications of fittings.
Sewerage
There are much fewer docking methods here.
Cast iron
Traditionally, chasing is used to connect cast iron sewers:
- The pipe is inserted into the socket of the fitting;
- The space between them is tightly caulked with kabalka - oiled organic fiber;
- Then the joint is covered with cement mortar or filled with molten sulfur.
Accordingly, fittings are a combination of bends with the same diameter as the pipes and sockets.
However, new cast iron sewer fittings and pipes are increasingly equipped with rubber seals, ensuring tightness during ordinary joining.
PVC and polyethylene
Both polyethylene and the much more common PVC pipes for sewerage, and fittings for them, are again equipped with rubber seals in the sockets.
There are two subtleties associated with docking:
- It is advisable to remove the outer chamfer from a pipe cut to size. Otherwise, it will be difficult to insert it into the rubber-sealed socket.
- A connection made with sealant is guaranteed not to leak due to drying of the rubber.
Tightness is ensured by a rubber seal; The sealant additionally fixes the pipe and protects against leaks when the rubber dries.
CONNECTORS
Couplings are used as an alternative to flanged connections in low-pressure, small-bore pipelines where pipe disassembly is required more frequently. Couplings can be threaded or welded. They consist of three parts: the nut, the female part and the male part. When the male and female ends are connected, the nuts provide the necessary pressure to seal the joint.
Purpose of the product
PVC bends for internal sewerage are needed to arrange the rotation of sewer pipes at a certain angle and are used for installing unclean water drainage systems in administrative and residential buildings.
Plastic connecting elements have a smooth interior, which greatly reduces the risk of clogging during operation, and virtually do not make noise when liquid flows through them.
In addition, their production uses material that is resistant to warm water (up to 95 degrees Celsius) and chemical detergents.
Dimensions of sewer plastic outlets: 110 and 50 mm (the diameter of the internal hole is measured).
As for angles, the standard values are:
Advice! By combining a sewer outlet and a half-outlet with different bending angles, it is possible to achieve a pipe rotation of 30, 45, 60, 75 and 90 degrees. But it is advisable to avoid excessively sharp bends so that blockages do not occur.
There is another option: a branch with a diameter of 110 mm with access to pipes of a smaller diameter. They are used for various non-standard configurations.
TEES
Tees are designed to separate or connect fluid flow. This is a short piece of pipe with a 90 degree branch in the center. There are two types of tees: equal (straight tee) and reducing tee.
Straight Tees
In a straight tee, the diameter of the branch is the same as the diameter of the pipe itself.
Reducing tees
In a transition tee, the diameter of the branch is less than the diameter of the pipe.
Lattice Tees
A grid tee, also known as a pig tee, is used in pipelines that are pigged. This tee has a special restrictive grid welded from the inside, which is necessary to prevent the scraper from getting into the branch. The grid is welded to the branch in such a way as to ensure free passage of the pig from the through pipe.
Skew tees
Such tees have a branch at an angle of 45° or at another angle other than 90°. An oblique tee allows you to connect one pipe to another at an angle of 45°. This reduces friction and turbulence that could impede flow.
Types of bends
Regardless of the name of the manufacturer producing PVC sewer outlets, all these products comply with accepted construction standards (GOST). This makes it easier to design sewer systems, purchase the necessary materials and install them into a single system.
There are a couple of different models of corner elements, which differ in price and some design features.
- Polyethylene . They are made of dark-colored material and are connected end-to-end or using couplings. In the first case, the ends of the pipe and the outlet are heated using special equipment and joined together until the plastic completely hardens. The couplings are already equipped at the factory with a special spiral, which is heated using a welding machine for a hermetically sealed connection.
- PVC bends . The most common type. They are connected by placing a socket on a smooth pipe. Advantages: no need to use different power tools and increased speed of installation of the sewer system as a whole. Structural elements intended for indoor use are painted gray. There is another sewer outlet - in a private house (at a time when the room is not heated or the pipes are installed outside) the parts are brown. (See also the article Pipes for internal sewerage: highlights.)
Note! It is forbidden to combine these two varieties into one system. It is necessary to use bends of the same type. Otherwise, high-quality and long-term operation of the sewer system is not guaranteed. It is extremely rare that it is necessary to include special adapters in the circuit.
- Polypropylene . In addition, they have sockets and smooth ends for joining each other. These products are only used in conjunction with pipes made of similar material. The main purpose is to drain groundwater and wastewater. They are capable of passing water flow at a speed of 4 to seven meters/s.
- Bends for corrugated pipes . These elements are joined by means of couplings and are equipped with sealing rings on each side. At the point of inflection, the outer part of the product has a reduced diameter. Scope of application: joining pipes made of different materials using sealing collars.
Independent installation of bends
As mentioned earlier, PVC bends are the most widely used. This is due to their low cost and ease of installation.
Docking is done using special seals. Quite often they are already inserted into the internal space of the bell. In another case, the rubber ring supplied with the corner element is placed in a special recess in front of the connection.
There is an alternative method - using glue. This type of docking is less common and more complex. For adhesive joints, rubber seals are not necessary.
From time to time it becomes necessary to join pipes made of different materials. In this case, it is necessary to use sealing collars and plumbing sealants. Such a connection will be reliable and will not allow leaks during operation.
Sealing joints
The reliability of its operation depends on the tightness of the corner connections of the sewer system. You should pay increased attention to this, especially at a time when installation is done with your own hands. (See also the article Connecting the toilet to the sewer: highlights.)
It is even more scrupulous to seal joints when laying pipes underground, which often happens during the construction of private houses. The cost of repairing leaks can be very large.
It is recommended to seal connections between bends and pipes using special sealants.
These substances contain many components and are divided into two main types:
- acidic (inexpensive compounds);
- neutral (more expensive).
Note! Acid sealants cannot be used when installing iron and cast iron pipes. Before purchasing, pay attention to the composition indicated on the packaging.
In addition, if you are joining PVC bends with rubber seals, additional treatment of the ring with sealant will only add reliability to the connection.
The use of one or another sealing compound is mandatory for processing connections of the sewer system with cast iron pipes. This material, by definition, cannot be completely smooth and therefore requires the use of current compositions. The best solution is liquid silicone.
Additional methods for sealing pipe joints and bends
In addition to using sealant, it is possible to use alternative methods.
| View | Description |
| Epoxy adhesive | Very reliable and durable connection. But after the composition has completely hardened, it will be impossible to disassemble the pipes without destroying them. |
| Hemp or resin strand | Used for joining PVC bends with pipes made of other materials. In this case, the end is wrapped with the selected material approximately two-thirds of the length, inserted into the socket and filled with cement or asbestos-cement mixture. The method is reliable and time-tested. |
| Technical sulfur | This method was used in 95% of cases quite recently. At the moment, it can be used to connect sewer systems of different materials to each other. |
| Bitumen mastic | More suitable for joining ceramic outlets with similar pipes, but can be used for sealing joints of external sewerage systems made of PVC pipes. |
| Sealing tape | Least reliable method. Suitable as a temporary measure until the damaged unit is replaced. |
Repairing leaks
Well, at a time when the sewer system is operated without accidents. But if leaks occur, you should not despair.
The instructions in this section will help you quickly resolve the problem.
- Leaks at junctions with old pipes. In this case, a liquid sealing compound will help: sealant or a mixture of cement and glue. In addition, epoxy glue or raw rubber, or, in extreme cases, plasticine, will do.
- Hole. Treated with a peg treated with sealant or a splint (clamp). An emergency option is to use a rubber bandage.
- Longitudinal crack. Sealed with epoxy glue or cloth impregnated with silicone. For metal pipes it is possible to use cold welding.
- The edge of the outlet is chipped. In this case, only replacing the damaged element will help.