The article, to help a novice welder, provides information on choosing a welding electrode for manual welding, choosing an inverter and welding mode - welding current, polarity.
Often, a novice welder faces many questions - which electrode to choose from the many brands and types on the market, how to connect an inverter, what current to use during the welding process, etc.
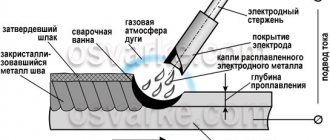
The welding electrode consists of two main parts - the core and the coating of the core - coating. The core melts during the welding process, and the coating burns, creating a protective gas layer (protection from oxygen). Electrode cores are made of various materials, depending on the metal being welded. There are electrodes for working with carbon, alloy, high-alloy steel, stainless steel, non-ferrous metals and their alloys. When choosing an electrode, first of all, we pay attention to the fact that the core material, in its composition, should be close to the metal being welded.
Types and purpose of welding electrodes
With welding you can:
- connect metal parts;
- manufacture metal structures of any size;
- cut metal;
- eliminate cracks;
- cut round and shaped holes;
- weld metal to restore wear areas;
- carry out repairs and other types of work.
The industry produces many types of electrodes, about two hundred of them. Each of them is most effective within the limited characteristics of these works, so the choice of electrodes for welding is a very important step. It should be done after thoroughly studying the topic or with the help of specialists.
The criteria for selecting electrodes are the design parameters, characteristics and purpose specified by the product manufacturer. The main ones are:
- electrode brand;
- appointment;
- core diameter;
- type of electrode coating;
- electrode length;
- the magnitude of the working current;
- type of current and polarity of connection;
- composition of the central rod;
- welding position;
- special technological characteristics of the welding process.
Metal preparation and joining
- Before butt welding thin metal sheets, they must be cleaned and processed. It is not advisable to leave rust or dirt behind. The better you prepare the metal, the better the quality of the seam. Remove traces of paint, oil, and dirt using a solvent. Using a grinder, sandpaper or file, clean the surface to a shine.
- The sheets must be placed next to each other without any gaps.
- Secure them with clamps. You can use any type of clamp, including magnetic ones.
- Using short seams, tack elements at intervals of 7-10 cm. This is done to ensure that the parts do not move and to reduce the likelihood of bending.
Purpose
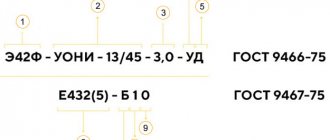
The brand of the electrode, as a rule, encrypts its purpose. For example, product types:
- UONI - designed for welding parts at low temperatures;
- ANO-21 - for performing work with thin (up to 4 mm) parts operated under low pressure;
- MP-3S - for welding rolled parts and medium-carbon steels up to 20 mm thick;
- LEZ - for surfacing worn parts;
- inexpensive universal-use OZS-12 electrodes are recommended for welding carbon steels and are easy to use;
- rutile products of the ANO-4 grade are used for welding low-alloy and low-carbon steels; work on both direct and alternating currents; They cook metal contaminated with rust well, have a stable arc, and are easily cleaned of slag.
Experts distinguish between electrodes for welding, tacking, surfacing and cutting. Universal products are in great demand, saving a lot of time when performing various types of work.
Dimensions
Electrodes are manufactured according to nominal diametrical dimensions . When ordering in bulk, some manufacturers can produce products with custom sizes. Sometimes the coating on the edge is not cleared, but both ends must remain in contact. In the total batch, no more than 10% of electrodes have a length deviation of 4 mm.
The electrode is made of several structural elements: 1 – rod; 2 – transition zone; 3 – coating; 4 – contact end.
The cleaning area has a conical, round or combined shape. The inclination of the cone is not regulated in any way, since it does not affect operation.
Ionizing elements are applied to the contacts, which facilitates the appearance of the welding arc. Product marking: electrodes E46 GOST 9466-75 with a diameter of 4 mm.
Diameter
The choice of electrode (core) diameter is determined by the thickness of the parts being welded and the maximum current of the welding machine used. The higher they are, the thicker the connected elements can be.
All three parameters are dependent on each other. Their values are indicated in special tables, which are convenient to use before work and purchasing electrodes. So, for parts with a thickness of 3-4 mm, you need to use electrodes with a diameter of 3 mm with adjustable operating current within the range of 80-160 A.
What functions does the electrode perform?
A consumable electrode is a metal core made of steel welding wire (GOST 2246-70) and has a special coating. Depending on the brand of metal being welded, select the appropriate wire for the core - low-carbon, alloyed, high-alloyed.
During welding, the core melts, filling the weld pool. Thanks to the elements included in the coating, a slag layer is formed, which protects the weld pool.
Coating of electrodes
The core coating is a solid composition, a kind of flux, designed to protect the molten metal from the harmful effects of oxygen, which, when it enters the liquid metal, forms oxides that deteriorate the quality of the connection.
Another function of the coating is to thermally insulate the melt to delay the solidification time (so that harmful gas and non-metallic inclusions have time to escape from it). Modern electrodes use several types of coating. The main ones are basic (in the marking of electrodes, indicated by the letter “B”) and rutile (letter “R”).
Basic coating
It is known that it contains calcium salts - carbonate and fluoride. Its advantage is considered to be a low hydrogen content. Typical representatives of electrodes with basic coating are UONI products. Their coating ensures a high-quality seam, both in appearance and in technical indicators: ductility, strength, impact strength.
The electrodes do not form crystalline cracks inside the seam, therefore they are recommended by specialists for critical welding operations and for products operated in harsh climatic conditions. They can be used when welding in any position except vertical.
Technical requirements
Metal consumable electrodes are manufactured in accordance with GOST 9466-75, but with modifications. The main element is made of special wire . The coating is durable, without pores, swelling, or cracks. The presence of minor irregularities is normal; deep dents and lingering scuffs are considered defective. The length of the damage does not exceed 3 times the diametrical size. The normal depth of dents is up to 50% of the total thickness of the coatings; there can be up to 4 of them with a total length of maximum 25 mm on the product.
Rutile coating
Rutile is titanium dioxide. In addition to it, the coating contains silicon and oxygen.
Rutile coating is characterized by the following properties:
- formation of a high-quality seam at any spatial position of the electrode;
- stable arc burning;
- minimal splashing of melt and coating;
- possibility of welding on both direct and alternating currents;
- possibility of welding rusty and dirty parts;
- quick and easy ignition of the electrode;
- easy removal of slag.
Current source
To weld metals with electrodes, welding transformers, rectifiers, inverters and other devices operating in manual arc welding mode are used. The inverter is widely used due to its compactness, light weight and wide capabilities.
It provides operation on both direct and alternating current, and its light weight is explained by the fact that voltage transformation is performed at a frequency not of 50 Hz, but of 100 kHz, for which the size and weight of the transformer core is reduced by an order of magnitude.
When welding with direct current, the polarity of the connection matters. With direct polarity, the ground (welding part) is connected to the “+” of the source, and the holder with the electrode is connected to “-”. With reverse polarity, the opposite is true. With direct polarity you can weld thin parts, and with reverse polarity you can weld massive parts.
When selecting electrodes, using the table and data on the welding machine, you can determine whether the source can provide the required amount of current.
Types of thin metal joints in manual arc welding.
- Using a continuous welding arc. In this case, the electrode must be directed at medium speed. If you move the electrode too quickly, not the entire seam will be welded, but only its upper part. If you move the electrode slowly, you can burn through the metal.
- With the cessation of the arc. This method is the most popular for joining thin metal.
- Spot welding.
As with manual arc welding, and when welding metal with an inverter, thin metal must be welded very quickly to prevent it from cooling.
Welding position
The spatial position of the electrode is also included in its marking. The number 1 denotes electrodes that are used for welding only in the lower position of the part (electrode on top).
The number 2 marks products used with a horizontal or vertical seam (ceiling is excluded).
Number 3 is used for ceiling electrodes (the electrode rests on the part from below). The welder must take these markings into account to avoid a poor-quality weld or injury.
Calcination of electrodes
Coating of electrodes requires tightness during storage, but this condition is not met everywhere. The sharp edges of the rods, as a rule, break the tightness of the plastic packaging already during the first transfer of packs. Thus, by the time of purchase, the electrodes are saturated with excess atmospheric moisture.
In this condition, due to the danger of obtaining a poor-quality seam and the possibility of too much metal spattering, welding cannot be performed with them. The electrodes need to be dried. The manufacturer gives clear recommendations regarding process parameters, setting drying time and maximum temperature. It usually does not exceed 260 ºС.
Techniques and methods for joining thin metal sheets
In each specific case, it is important to determine which technique should be used when joining thin-walled material.
electrodes for thin-walled materials
The flanging method involves bending the edges of the sheet to the required angle and fastening it with transverse seams every 5-10 cm. Then you need to lay a continuous seam from top to bottom.
However, it is not always possible to weld a continuous seam without burning through the material. In this case, you can try to tear off the arc for just a few moments and lower the electrode back to the same place, moving it a couple of millimeters. This is done so that the metal has time to cool during arc separation. The most important rule when carrying out such actions is not to let the metal cool too much.
Butt welding of thin iron is difficult to achieve. It is better to overlap it.
When butt welding, wire can be placed between the sheets. In this case, the arc must be drawn along it. It takes on the entire thermal load, while the sheets themselves do not overheat.
Instead of wire, copper plates can be placed between the sheets. Copper has good thermal conductivity, about 7 times higher than steel. The plates are placed under the welding site, and it “takes” the heat to itself, preventing the metal from overheating.
How to determine the quality of electrodes when purchasing?
The best option would be to test several electrodes from the purchased batch in the welding workflow. If this is not possible, you need to pay attention to the following factors:
- shelf life of products;
- name of the manufacturing company (for experienced welders this is important information);
- quality of coating in terms of uniform thickness of application around the rod, absence of crumbling.
If during testing there are signs of excessive moisture, the electrodes should be dried and the test repeated.
In order for the welding of parts to be carried out in accordance with all the rules of the regulations, and the quality of the seam not to be criticized, it is extremely important to study welding technologies well. The choice of electrode type is an integral part of this knowledge, which needs to be constantly replenished and improved.