Electrical power, designated in the diagrams by the letter P, is a physical quantity that characterizes the rate of conversion or transmission of electricity. The standard concept is the effort to move an electric charge along a route from point F1 to point F2.
The electrical power of a device is a key parameter that determines the potential for its operation in the electrical network. Used to calculate circuits and operating modes of equipment to ensure the safety of electrical networks. The greater the power of the device, the faster they perform the desired action.
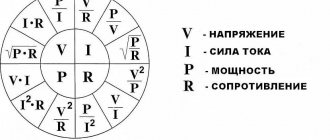
Formulas for calculating voltage, current, power, resistance Source amperof.ru
Electrical current through voltage and current
Since the potential difference calculated by the formula (F1-F2) determines the voltage (U), it is easy to conclude that the relationship established by Ohm’s law cannot be used. Electrical power (P) is also qualified by the current strength (I) on a specific section of the line. Final expression: P = U x I.
What is the load determined in terms of current and resistance?
Through a simple conversion, the electrical energy consumption is determined using the following formula: P = I2 x R. This shows the dependence of the power on the nominal value of the resistor connected to the line of the network element. For a complete circuit, the source resistance (internal) and the conductance of the connection point are indicated.
What is it and how to calculate the load
Electric current load is a quantity characterizing its properties. Shows how much energy is consumed by electrical appliances. The current power is measured using a special device - a wattmeter.
If you connect a meter in series, you can check the current strength. When connecting in parallel, the voltage is determined. The amount of circuit consumption is calculated using the formulas: P = I x U or P = U2/ R = I2 x R.
The electrical load is equal to the voltage across the consumer multiplied by the amount of current flowing through it.
P = U x I
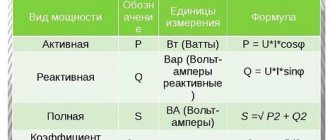
The formula indicates which measurements determine this parameter. If the load is active, it is measured in Watts, the reactive unit of electrical power is VA.
Reactive unit of electrical power - VA Source infourok.ru
Rules for calculating power consumption
In everyday life, when the need arises to independently determine the power consumption of electricity, do the following:
- determine the voltage required to power the device;
- find out the rated current from the passport data.
How to find out the power of an electrical appliance if not a single parameter is known? Household electrical appliances are designed for 220 V.
To determine power, it is permissible to measure current consumption. This can be done using an ammeter. It is connected to the circuit in series, having previously set the highest measurement limit - at least a hundred amperes. Current clamp meters will help you easily measure current, for which one of the conductors is grasped by the clamp sensor, and the readings are displayed on the display. Knowing the voltage, multiply it by the measured current to obtain the amount of power consumed.
Clamp meter
How to determine the maximum current load
The useful power shows the maximum value in a situation where the load resistance R is compared with the same parameter inside the source - r.
R = r.
P max = E2 / 4r, where E is the driving force of the current source.
To calculate the maximum current load for an electrical device, you need to know the rated load parameter and the AC input voltage. The technical data sheet of the device, manual or emblem contains the first indicator.
For example, when the appliance rating (P) is 12 W, the maximum current consumption at AC voltage will be for:
- 120 V – I = 12/120 = 0.100 A or 100 mA.
- 220 V – I = 12 / 220 = 0.055A or 55 mA.
If necessary, the amount of electricity consumed is expressed through a complex value. For this purpose, basic relationships are used, impedance is used instead of resistance.
Mathematical operations
The basic formula allows you to calculate an unknown quantity when the other two are known. For example, if the current consumed by the device is known I = 2 A and the network voltage U = 220 V, then the power consumption is equal to P = 2 * 220 = 440 W.
For example, it is known that the iron consumes 2 kW, and the voltage in the outlet is 220 V, then you can find the current strength for which the cross-section of the power cord is designed.
I = P/U = 2000/220 = 9.1 A.
In the case of fractional values, when using a calculator for calculations, the obtained values are rounded to tenths of the units of the desired value.
Basic formulas for calculation
Electrical Appliances Parameters
Every modern apartment must be equipped with electrical appliances. To connect them to the network, it is necessary to draw up a schematic diagram where the loads connected to individual lines will be distributed in coordination with each other. It is necessary to build in a circuit breaker based on the PUE to prevent emergency situations.
First, the electrical wiring parameters are clarified. Then they are checked according to the group diagram for connecting to the network of household electrical appliances.
Standard characteristics of electrical power consumption (W):
- desktop computer – 170-1,250;
- LCD TV – 120 – 265;
- laptop – 40-280;
- air conditioning – 1,200 – 2,500;
- iron – 450-1850.
To protect the network, you need an automatic machine; we choose it taking into account all the significant factors.
Automatic switch for protecting the electrical network Source vmasshtabe.ru
It is important to pay attention to loads that have increased reactive energy parameters.
Energy consumption
Calculating energy consumption for a house or apartment is not particularly difficult. To do this, you need to perform the following algorithm of actions:
- make a table of all electrical appliances used in the house, including lighting lamps;
- put in separate columns: device power, operating hours per day;
- for each energy consumer, calculate (by multiplying the power by the operating time) the average daily consumption;
- sum up all the obtained power values.
Such a calculation will give a real picture of electricity consumption. Using this data, you can control consumption and adjust the daily power consumption of each device.
It does not matter how power consumption is calculated or measured. The main task of the process is to correctly select the cross-section of conductors for wiring, supplying power cables and ensure that automatic protection is triggered. The cable supplying voltage to the room must withstand the simultaneous switching on of all consumers located in it for a long time. Its choice directly depends on the accuracy of determining the power of consumers.
What is it measured in?
The unit of measurement of electrical power is W for Russia. By international standards - W. This is the energy provided per unit of time. One W is equal to a joule per second (J/s). Moreover, a joule is a unit of electrical power, a second is a unit of time.
For small values, multiple prefixes are used: “milli-”, “micro-”, for large values - “mega-”. For example: 5,800 W = 5.8 kilowatts = 5.8 kW.
When you multiply 1 Kilowatt by 1 hour, you get a Kilowatt-hour (kW x h). This is a unit of measurement of the amount of electricity provided to subscribers. It is used by energy enterprises that own the appropriate equipment (generators and transformer substations). They generate and convert the produced electricity, which is then distributed to consumers.
In the same way, the energy capacity of batteries is measured in units of ampere hours (Ah). Portable types of energy storage batteries are measured in milliampere hours (mAh).
The energy in batteries is measured in milliamp hours (mAh). Source listtopa.ru
For the unit of measurement Watt, according to international standards, the letter designation W is allocated after James Watt. He was the first to use the term “horsepower,” which today is an obsolete unit of the W parameter.
Energy conversion indicators:
- horsepower (HP) - 746 W;
- kilo Watts (kW) – 1×1000 W;
- megawatts (MW) −1×1000000 W;
- gigawatt (GW) – 1×1000000000 W.
Today, "horsepower" is used to indicate the second measure of engine power in vehicles.
What determines the load of electric current?
Existing electrical wiring lines experience resistance during the movement of electrons, which characterizes voltage loss. Circuits where an alternating current source is present have one feature - the key role here is played by a sinusoidal oscillation of electrical indicators.
Sinusoidal oscillation of electrical indicators. Source urpsvet.ru
The following information will allow you to select the best calculation method based on actual network conditions.
Instantaneous electrical power: calculating the value
This indicator establishes the instantaneous values of the measured data. The key definition is considered taking into account the fact that a single simple charge (q) moves in a certain time Δt. To perform a specific action, the energy of electric current PF1-F2 = U/ Δt or (U/ Δt) x q = U x (q/ Δt) is expended. The formula takes into account the movement of q over the period Δt. Since the current, according to the classical definition, is equal to the charge moving from F1 to F2 (I = q/ Δt), the final expression is derived: PF1-F2 = U x I.
Conditionally assuming that the time period is very short, we obtain the instantaneous power for part of the electrical circuit P(t) = U(t) x I(t). The same conclusions can be drawn taking into account the corresponding resistance parameter: P (t) = (I (t))2 x R = (U(t))2/ R.
Electrical power: DC circuit
The previously mentioned formulas are shown without correction factors. They are used to calculate a circuit connected to a direct current source. Using an ordinary device - a multimeter, with the switch in the correct position, the resistance of the load connected to the network is set.
With its help, the load resistance is set. Source hammer-shop.ru
Electrical power: AC circuit
For such lines, it is unacceptable to use formulas that determine instantaneous parameters, since the final indicator changes from a minimum value to a maximum value with the network frequency. A typical single-phase 220 V network is characterized by a 50 Hz sinusoidal signal. It is allowed to use the simple formula P = U x I when connecting devices with resistive parameters:
- Heating elements of washing machines;
- spirals of infrared heaters;
- incandescent light bulbs.
Using this formula, the load is set.
Energy can be of two types: reactive and active.
Active is the true electrical power that produces real work in the load, W shows this parameter. It converts energy into mechanical, thermal and other forms.
If you turn on a powerful unit or capacitor, the voltage inside the network drops. Such loads create an oscillating circuit that receives energy from the power source. In this situation, only P act components perform useful functions. The active indicator is calculated in the following way:
- U x I – direct current (alternating current with a resistive load);
- U x I x cos fi – for a single-phase 220 V line;
- U x √3 x cos fi = U x 1.7321 x cos fi – 3-phase network, U x √3 x 380V.
There are other types of energy, but more on that later.
Active and passive energy Source ppt-online.org
Reactive power
This indicator shows the loads that are created in devices due to fluctuations in the energy of the electromagnetic field.
Reactive power, regardless of the absence of useful work, must be taken into account to correctly evaluate key network data. Cables and wires, when current passes through them in any direction, heat up. This happens quite cyclically. Energy effects at high intensity:
- damage cable cores and protective insulation;
- contribute to the occurrence of a short circuit;
- destroy the windings of transformers and drives.
Reactive power is expressed as VA (volt-amperes) and is calculated by multiplying the voltage by the current and the shear angle:
P r = U x I x sin fi.
When connecting a load with capacitive parameters, the value becomes negative, when inductive it becomes positive. Since the characteristics of the magnetic field change, the unit of measurement for reactive power is VA.
If the parameters of total electrical power are shown as vectors, a triangle appears. The length of its sides will be equal to the amount of electricity consumed by a particular component. The angle between the apparent power (Pap) and the active power (ϕ) is used for calculations. The total value is determined by the expression: P total = √((P act)2 + (P react)2).
General concept
Electric voltage is defined as the ratio of the work done by the field to transfer a test charge from one given point to another to the size of the potential. When a unit reserve is dislocated, work is performed that is equal to the voltage in the desired area. The total power is obtained by multiplying the work of the electric field for a unit charge by the number of potentials per specific unit of time.
In an alternating electrical circuit, 3 types of power are distinguished:
- active P;
- reactive Q;
- full type S.
In an alternating electricity circuit, the formula for calculating direct current is used only to calculate instantaneous power. This indicator undergoes changes over time and has almost no practical meaning for all other calculations. The power average requires time integration. The instantaneous power is combined over a certain period to calculate the magnitude in the line with periodic changes in the alternating flux strength and sinusoidal voltage.
The concept of complex numbers is used to relate all three types of power. This concept means that in an alternating circuit the load is expressed by a similar number so that the active variety appears to be a real component. The reactive indicator is an imaginary indicator, and the total power is shown in modulus form. These calculations take into account the phase angle φ, which is an argument for the power balance in the AC circuit.
Active power
The active conversion rate is also expressed through the mutual ratio of the flow force, voltage to the value of the active component of the resistance. In the line of sinusoidal and non-sinusoidal movement of electrons, the active load is equal to the sum of similar values in individual sections.
To determine the average periodic size, the active power of alternating current is used, the calculation formula P = U. I. cos φ (cosine), where:
- U is power.
- I is the flow force.
- φ is the phase shift angle.
The average instantaneous conversion rate in a single-phase circuit is taken as the rms value of current and voltage with a certain shift angle. In non-sinusoidal electricity circuits, power is equal to the sum of the corresponding indicators of individual movements. With the help of active power, the intensity of the irreversible modification of electricity into other types, for example, electromagnetic or thermal, is characterized.
The passing power is used as active power in the concept of long highways for the analysis of electromagnetic currents, the length of which is compared with the dimension of the wave. The required value is calculated as the difference between the decreasing and reflected powers. The resulting indicators of negative or positive load of the active type depend on the properties of the angular displacement coefficient.
Reactive characteristic
For designation, the additional unit volt-ampere reactive (var) is used. Russian analogues use var, and international experts use var. In the Russian Federation, the unit is allowed for electrical calculations in the form of a non-system value.
Finding is done using the formula P = U. I. sin φ (sine), where:
- U - rms power.
- I is the mean square flow force.
- φ - phase displacement angle, sine values are determined from tables.
When the indicator ranges from 0 to 90º (the current lags behind the voltage, and the load is active-inductive), the sine φ will have a positive value. With an angular shift from 0 to -90º (the electron flow is ahead of the load, the power has an active-capacitive property), the constant always shows a negative sign. Reactive power characterizes the tension that arises in electromechanical devices and circuits when energy field waves change in the main line of alternating sinusoidal flow.
In a physical sense, a reactive load shows the energy that is pumped from a current source to capacitors, inductors, motor windings, and subsequently returns to the source in one oscillatory period. Reactive power does not take part in the operation of electric current. In the case of a positive characteristic, the device consumes, and a load with a negative sign indicates energy production.
This circumstance is considered in a conditional context, since almost all energy-consuming devices, for example, asynchronous motors, as well as the payload supplied through a transformer, are of the active-inductive type. Synchronous motors in power plants simultaneously produce and consume energy depending on the maximum value of the excitation current in the rotor windings. This feature is used to coordinate the load level in a backbone in electrical engineering.
With the help of modern converters, reactive load compensation is performed to avoid overloads and to increase the power factor of electrical installations. The instruments more accurately estimate the amount of energy that flows in the opposite direction from the inductor to the AC source.
Full load
The indicator is used in physics to describe the power consumption that is applied to the supply units of the electrical network using resistors. The parameters of the EMF of distribution boards, cables, wires, power lines, and transformers are summed up.
The total load can be calculated using the formula S = U. I, where:
- S is the full load parameter (V/a).
- U is the design load in the generator.
- I is a complex indicator of current strength in combination with the winding value.
The conversion rate parameter depends on the characteristics of the applied current, and not on the properties of the load actually used. For this reason, the total power of electrical distribution panels and transformer units is measured in volt-amperes, and the value of watts does not apply to it.
What is power in electricity
Voltage is the work done to move a unit of charge. Current is the number of coulombs moved in 1 second. When multiplying the first parameter by the second, the total amount of work done in 1 second is obtained.
The strength of electricity is a numerical current meter that characterizes its energy qualities. The power indicator equally depends on voltage and current strength. How is current power measured? To measure this parameter, a Wattmeter is used; the unit of measurement is designated in the same way - W (Watt).
By using the dependence of the power parameter on current and voltage, specialists can transmit electricity over long distances. For these purposes, energy is converted at step-down and step-up transformer substations (transformer substations).
Calculation of light bulb power
The selection of incandescent lamp power depends on the desired level of illumination of the living space. One 100 W light bulb, working in the dark for at least 12 hours, consumes 1.2 kW of power. For a month this will be 36 kW, for a year - at least 432 kW. If there are 10 light bulbs in an apartment, then the total annual consumption will be 4320 kW. If the price for 1 kW of electricity is 5 rubles, the amount turns out to be decent – 21,000 rubles. Therefore, replacing incandescent lamps with energy-saving light sources: LED lamps, LED strips and the like allows you to save money. In addition, reducing the power of such light bulbs does not reduce the luminous flux. The reduced supply voltage of LED strips also reduces the amount of power consumed.
Electrical power and inactive power
Equipment certificates contain active load - power factor, which is an important characteristic. It shows how efficiently a household appliance consumes electricity.
Fig.8
This is a number from −1 to 1, it is never equal to one. This coefficient depends on the type of load: C, L or R. The first 2 negatively affect PF = cos φ of the system. If its parameter is large, the current consumed by the devices increases. Many power loads are inductive, causing the current to lag behind the voltage.
Inactive energy arises in electrical AC circuits of alternating current networks. It is calculated simply: the square root of the sum (Pa2 + Pr2). If the reactive load is zero, then the passive load is equal to the modulus |Pa|.
The presence of nonlinear current distortions in electrical networks is caused by non-compliance with the direction that occurs between U/I, since the energy has a pulsed nature. In nonlinear modes, the apparent current power (EP) increases. Such a load is inactive and consumes Pr and current distortion energy. The unit of measurement is the same as regular power W.
Negative effects of reactive load
Learn to easily calculate the power consumption of an electrical appliance
The reactive load does not perform any useful work. Fluctuations in the reactive component from source to consumer only cause parasitic losses. In addition, industrial enterprises are required to pay for the reactive energy supplied to them. This is due to the fact that most energy receivers are electric motors and transformers. The amount of electricity consumed (kWh) does not all go to useful work, but you also need to pay for its reactive component.
Capacitor compensation units will help solve this problem. After all, if you connect a capacitive load in parallel with an inductive load, you can reduce the effect of parasitic currents to a minimum. Such installations are installed at substations supplying consumers.