Basic information about brass
Brass can be double or multi-component in composition. It is always based on two metals: copper and zinc. In this alloy, zinc serves as the main alloying component. To impart different properties, various metals are added to its composition: tin, lead, manganese. Therefore, it is very important to know what composition of brass you have to work with. This is necessary to determine the conditions and specifics of soldering.
Brass
Modern brass is classified according to the following indicators:
Depending on the chemical composition:
- Two-component alloys. It contains only two metals, zinc and copper. The percentage of each may vary. This type is marked with the capital letter of the Russian alphabet “L” and a number. The number indicates what percentage of copper is contained in the alloy. For example, grade L85 - this alloy contains 85% copper and the remaining 15% is zinc.
- Multicomponent. They are also called special. Such alloys contain a large number of additives. They are marked with two capital letters and numbers. For example, brand LA77-2. She indicates that the composition includes 77% copper, 21% zinc and 2% aluminum. Therefore, very often special brasses get their name depending on the name of the alloying element with the highest percentage (aluminum, tin, nickel, manganese, and so on).
By degree and quality of processing:
- Deformable. These include brass in the form of wire, round tube, sheet and tape.
- Foundries. These are fittings, finished products made of brass.
According to the zinc content in the alloy:
- If the zinc content is in the range from 5 to 20%, then such an alloy is called red brass (tompak).
- If this percentage ranges from 21% to 36%, the brass is called yellow.
All brands of brass have similar properties. They are easy to process, have high anti-corrosion characteristics, and have sufficient strength. With a significant decrease in temperature, they retain their plasticity.
These properties have determined the wide range of uses of brass.
How to solder aluminum and aluminum-based alloys
In order for the work to be carried out at the proper level, the solder for soldering aluminum must contain silicon, aluminum, as well as copper, zinc and silver. Today you can find formulations on sale where all these components are in different proportions.
When choosing reliable solder, it is important to consider the following. The maximum resistance to corrosion and high strength will have the connection that was made with solder, which contains a lot of zinc.
Also for aluminum you can use compounds based on tin and lead. But it is important to properly prepare the work surface, clean it with a stainless steel brush and use active fluxes. But experts do not recommend using such an element.
Any solder for soldering aluminum is high-temperature. The most optimal ones, which allow you to obtain a reliable connection, are aluminum-silicon and aluminum-copper-silicon.
Application of brass
In addition to the listed positive properties, brass is a very durable and reliable alloy. Brass is used in the following areas:
- Manufacturing of pipeline fittings (adapters, valves, pipes).
- Plumbing fixtures (taps, mixers, washbasins)
- Furniture fittings (handles, latches, locks, decorative overlays).
- Production of electrical parts.
- Production of souvenirs.
- Production of tableware.
- Art casting.
- Jewelry production. Jewelers mainly use two-component alloys. It can be: yellow, red, green or golden brass.
Soldering brass pipes
Solders and fluxes: classification and selection methods
To obtain good soldering results, additives in the form of fluxes and various solders must be used.
Solder is a specific metal that, after melting, penetrates into metals prepared for soldering.
To achieve reliable contact, the brand of solder must have a melting point that will be significantly lower than the melting point of the brass itself. At the same time, it must have good adhesion to brass. Therefore, special solders are used for soldering brass.
Only as a last resort, if parts are soldered that do not bear much responsibility for the entire unit, and there are no high requirements for strength, ordinary tin-lead alloys are used.
Modern solders are classified as follows:
- By melting point. They are soft with a melting point reaching 400°C; semi-solid with the melting point of tin and solid. The melting point of hard solders exceeds 500 °C.
- By type of melting. Solders that melt completely or partially during the soldering process.
- According to the method of obtaining solder. We produce ready-made solders, and solders that are formed during the soldering process. This type of soldering is called contact reactive soldering.
- According to the list of chemical elements added to the composition. A fairly large number of such elements are used. From common metals zinc, tin, aluminum, to rare earth metals gallium, indium, palladium.
- According to solder manufacturing technology. They are: wire, stamped, rolled, cast crushed.
- By type of solder. They are produced in the form of wire, ready-made powder, in the form of tape and individual sheets, in the form of tablets and ready-to-use embedded parts.
- According to the method of flux formation. Solders are divided into two large categories: fluxed and so-called self-fluxing.
Solders, like brass, are marked with capital letters and numbers. By the marking you can determine which brass a particular solder is intended for. For example, if it is necessary to solder a part made of brass, in which there is a large percentage of copper, then it is proposed to use solder of the PSr12 or PSr72 brand. This solder contains a large percentage of silver. If there is a large percentage of zinc in brass, then it is advisable to use PSr40 solder. Therefore, in order to obtain a reliable connection after soldering, it is necessary to understand what loads are placed on the part being repaired. If the part is stationary and does not bear large vibration loads (for example, plumbing elements), you can safely use PMC solder. If it is necessary to ensure a strong connection, special hard solders are used, such as L-CuP6. This solder has a very high melting point - 730 ° C.
Solders for brass
To choose the right brand of solder, you can use the following method:
- Determine the melting temperature of the parts that are planned to be soldered.
- Determine the coefficient of thermal expansion. For brass that you plan to solder and the solder it should be very close.
- After soldering, the solder should not reduce the mechanical characteristics of the repaired part.
- The solder must form a galvanic couple with the main brass part. If this is not ensured, the corrosion process will quickly occur.
- The properties of the solder must comply with all technical and operational characteristics.
- The solder must ensure good wettability of the main part during the soldering process.
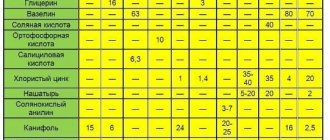
Flux is a special substance that allows you to prepare the surface of the metal, that is, remove the resulting oxide deposits, grease and water stains from it. Without the use of flux, it is impossible to qualitatively solder a brass part. Fluxes are selected depending on the chemical composition of brass.
Experience shows that in order to qualitatively solder parts made from common brands of brass LS59 and L63, it is enough to have a flux consisting of zinc chloride dissolved in boric acid. If you need to solder brass, which contains lead and silicon (for example, LKS80 brand), then you need a flux containing fluorine and potassium compounds. They are also dissolved in boric acid, or borax. A similar flux for soldering can be prepared at home, using the appropriate elements in the required percentage.
Flux paste for soldering brass
Today, the industry offers ready-made fluxes for brass soldering. These include: Borax flux; fluxes PV-209 and PV-209X.
Stainless steel
If you need to connect stainless steel parts, then professionals recommend using rods made of tin and lead. Materials containing cadmium also work well. Low-melting alloys based on zinc can be used. However, they should not be used together with carbon or low-alloy steels. The best solder for soldering stainless steel is a composition based on pure tin. In addition, only tin is allowed if the soldering area will be in contact with food.
If the work will be carried out in a dry or furnace atmosphere, then silver with manganese, chromium-nickel solders or pure copper (or even better, brass) should be used. When soldering has to be done in corrosive conditions, silver tinols with a small part of nickel are used.
Soldering methods
The brass soldering process has certain specifics. The brass heats up and the hot zinc elements evaporate. At this moment, an oxide film is formed, which is quite difficult to remove from the surface of the part and thereby deteriorates the quality of soldering. Usually brass is soldered in two ways: using a soldering iron and using a special torch.
Soldering with a soldering iron
To successfully solder brass, a soldering iron must have a power of at least 1000 W. Such a soldering iron will provide the required heating temperature for the parts themselves and the solder. It should be 500ºС and above. Low temperature soldering of brass is only possible if it has a high percentage of copper content.
Soldering brass with a soldering iron
The most convenient way is to solder using a soldering station, which has an adjustable soldering iron tip temperature. This adjustment allows you to set the optimal heating mode. The point is that during soldering it is necessary to avoid unnecessary overheating of the soldering area. The optimal temperature for heating the soldering iron tip is up to 350°C.
Necessary tool
If you have decided what to solder with, then you should also decide what to cook. When soldering brass, you will need the following tools and accessories:
- soldering iron with a power of 100 W and 0.5-1 kW;
- gas burner complete with gas cylinder;
- crucible;
- scales;
- vice;
- knife;
- scissors;
- file;
- pliers;
- clamp;
- sandpaper;
- brush;
- brush.
Brass is very often used in various household devices, so when they break, the question arises of how to solder brass. Such soldering is quite possible, but requires certain conditions and rules to be met.
Brass soldering is used when you need to connect small metal parts. For example, it is used in artistic forging when assembling a general composition or in a home workshop. In this case, ornamental steel with a flat or square cross-section is most suitable, where the contact area is larger than that of round rods. In addition to the fact that brass can be used as a solder to solder parts made from this material, there are also some tricks to get a high-quality seam.
Scheme of soldering metals with brass using a gas torch.