Home / Welding technique
Back
Reading time: 3 min
0
3931
Argon is a gas that is often used in welding. It is completely colorless, odorless and protects the metal from the bad influence of the atmosphere.
The main reason why it is so widely used in welding is its low price, because other protective gases sometimes have lower prices; craftsmen simply do not buy them, which reduces the quality of the weld.
- Introduction
- The most informative articles
- Advantages and characteristics of welding with argon
- How to weld aluminum with argon
- Features of welding ferrous metal with argon
- Welding stainless steel with argon
- Bottom line
Introduction
The use of argon is so widespread that it is used not only in factories and industries, but even at home, craftsmen have learned to use it, although working with gas is often unsafe and there is nothing good about it being in the garages of ordinary people, but this is not the same The argon option is completely safe; it does not explode. This gas is sold only in steel cylinders.
They come in different sizes, the manufacturer offers volumes from fifteen to forty liters, so if you have to brew a meter of land once a year, then you can just buy a small cylinder and it will last you for a very long time.
Another advantage of argon in terms of safety is that it is not explosive and also does not emit toxins when working with it, and this is important because if we are talking about home use, then there may be unqualified people or even children near the cylinder.
The most common areas of application are in arc, laser and plasma welding. If this is welding using an arc, then an electrode should be included with the gas; it can be with a melting or non-melting coating.
In our article we have made an extract from the main articles on this topic. If you find them interesting, you can read them in the full version.
Safety precautions
When carrying out work, it is necessary to take into account the presence of electric current, a bright glow of the arc, hot metal that can splash, and high temperatures. The welder must wear a special mask with a blue light filter. Gloves that protect your hands from melt splashes and clothing that can protect your entire body from them are required.
Electrical equipment must be reliably protected. It is necessary to use a residual current device and circuit breakers. The gas cylinder is equipped with a pressure reduction reducer. Before starting work, you must study the safety regulations and strictly follow them.
When welding aluminum one has to face difficulties caused by its specific properties. Argon welding, with the right approach and the use of high-quality materials and equipment, ensures a reliable connection.
Advantages and characteristics of welding with argon
Of course, argon welding has its advantages and characteristics, keeping up with all other types and technologies for welding metals.
This article will tell you about all the good and bad sides of argon welding, as well as some of the subtleties of working with such gas, and even about how to set up your welding machine so that the weld turns out to be of high quality.
This information is very useful to read; it will help you navigate the principles of argon and avoid mistakes. And this is important for beginners, or people who have not yet tried to work with this type of welding.
This article is very basic, it is highly recommended reading if you know nothing at all about argon cooking.
It will open the curtain for you on the processes that take place during this type of cooking and why this happens in principle. This article should be the first on your reading list, because without it you will not be able to navigate other articles.
Required technical information
Often the need for argon-arc welding arises not only in enterprises, but also at home. For example, you will need to repair a car or an electric boiler, where the tank is made of stainless steel, although there are many other units in the manufacture of which alloys and non-ferrous metals are involved. Therefore, knowing the technology of the process, you can learn to cook on your own.
What it is
This technology provides a seemingly strange hybrid combination of gas and electricity. However, the argon welding method works and allows you to work with almost all metals. This method is most in demand for welding stainless steel, cast iron, copper and aluminum - they are most often used to create various components and mechanisms. In everyday life, almost every person comes across products where the argon-arc method was used - these are small bronze hooks for hangers, various chandeliers, sconces and floor lamps, or the back of our refrigerator.
As you can see, argon-arc welding, or, more precisely, products that could not be made without its use, surrounds us in everyday life, therefore, this method can be very useful to any home craftsman. But, as you know, the birth of a good practitioner must always be confirmed by theoretical knowledge, and it cannot be otherwise. Here, of course, there is no need to study the composition of elements according to the periodic table, but there is no way to do without knowledge and understanding of the physical processes of melting metals in an inert environment.
The technology involves a hybrid combination of gas and electricity Source svarkalegko.com
Argon welding technology contains a solution to the dilemma: oxygen is needed to maintain combustion, but O2 promotes the oxidation of metals, which adversely affects the joint. When the weld pool hardens, many bubbles form there, which does not contribute to the strength of the seam, and if it is aluminum, then it simply burns out. Inert argon supplied to the bath envelops the welding site in a protective cloud, which minimizes the oxidation process. As you can see, an inert gas is an insulator from other elements that are found in ordinary air under natural conditions, that is, from the air we breathe. Ar is heavier than all the constituent gases of this composition, so the welding arc and part of the pool end up in its shell.
Note: in some cases, helium (He) is used instead of argon (Ar), which is also an inert gas. But this happens more as an exception than as a rule, since helium is much more expensive.
Please note why argon is preferred:
- Ar is heavier than all atmospheric gases, therefore, it is capable of displacing them from the bath;
- inert Ar does not react with substances that are present during the welding regime.
Note: in some cases, helium (He) is used instead of argon (Ar), which is also an inert gas. But this happens more as an exception than as a rule, since helium is much more expensive.
Now let's talk about the methods by which such a process is currently carried out. There are only three ways:
- Manual. When a welder works with manual argon arc welding, he needs to use both hands - one of them will have to hold the torch and the other the rod.
- Semi-automatic The welder holds and directs the torch by hand, and the rod is fed automatically.
- Machine. The movement of the torch and rod is automatic, but under the supervision of the operator. There are also lines where human functions are performed by a numerically controlled robot.
T-beam assembly-welding line Source google.com.ua
How to weld aluminum with argon
Aluminum is one of those metals that everyone has on their tongue, even a child knows that aluminum is a metal.
This metal is used in industrial enterprises; dishes and even elements for microelectronics are made from it, and this is a very specialized niche.
BUT even such wide popularity of this metal did not ensure that everyone knew how to handle it. In most cases, a beginner will not know which way to approach a metal such as aluminum.
The reason why seams on such metal often turn out weak and not beautiful is the oxide film that covers the metal.
It is because of this that working with one of the most common metals is so painstaking and not easy. We will tell you more about the oxide film in another article, since this is a very broad and painful topic.
Another article will tell you about igniting and maintaining arc stability and the formation of a weld pool. This article will give you all the necessary information on how to cook aluminum using argon even in the wild.
Welding materials used
TIG welding requires the following materials:
- protective gases;
- electrical conductors (electrodes);
- filler rods and wires.
Welding materials ensure stable combustion of the electric arc and obtain pore-free welds with high resistance to mechanical stress.
Shielding gases
Shielding gases for TIG welding affect metal transfer, shape and physical characteristics of the weld. They allow you to increase the speed and efficiency of welding. Argon is most often used as a shielding gas. It has low thermal conductivity and low ionization potential. When welding parts in an argon environment, the seam is deep and narrow.
Helium can also be used as a shielding gas for TIG welding. It conducts heat easily and has a high ionization potential. When welding products in a helium environment, the width of the seam increases. This inert gas ensures stable wetting of the workpieces being welded along the edges.
Electrodes
Electrodes for argon arc welding consist of durable tungsten, which is one of the most refractory chemical elements.
They improve the quality of the seam and heat up slightly when an electric arc burns. The following table shows the consumption of tungsten electrodes for argon arc welding of parts made of various materials: Electrode consumption
| Material to be welded | Surface thickness, mm | Diameter of electrical conductors, mm | Consumption per 100 m of seam, g | |
| For manual welding | During automatic welding | |||
| Stainless steels with high heat resistance | 1 | 1,5 | 8,3 | 3,9 |
| 2 | 2 | 23,4 | 10,9 | |
| 3 | 3 | 83,3 | 39 | |
| 4 | 4 | 132,2 | 125 | |
| 5 | 5 | 165 | 156 | |
| Magnesium and aluminum alloys | 2 | 2 | 23,4 | 10,9 |
| 4 | 3 | 83,3 | 39 | |
| 5 | 4 | 132,2 | 156 | |
| 7 | 5 | 165 | 156 |
Tungsten electrodes for argon welding do not require the use of additives and various wires. To improve the technical characteristics of electrical conductors, it is necessary to pre-sharpen them. This procedure will ensure a stable arc while welding workpieces.
Features of welding ferrous metal with argon
Ferrous metals are classically considered to be iron and its alloys. Such metals rarely act independently; more often they are taken as raw materials, produced, for example, cast iron, or used for processing for steel production.
Rarely, but sometimes situations arise when you need to deal with pure iron.
This is a very difficult task, but this gas makes it a lot easier. Like any method, argon welding has advantages and disadvantages. And if you need to get a passable result, you will have to strictly adhere to the technology.
This article talks about all this, it will also talk about how to choose a welding mode, what safety rules should be followed, and in particular fire safety. Because welding is not a simple matter and unsafe situations often arise.
The influence of current polarity on the tig welding process
The polarity of the welding current significantly affects the nature of the process of arc welding in an inert gas with a tungsten electrode. Unlike welding with a consumable electrode (which includes MMA and MIG/MAG welding), when welding with a non-consumable electrode in a protective atmosphere of an inert gas, the differences in the nature of the welding process in reverse and direct polarity are of the opposite nature.
So, when using reverse polarity, the TIG welding process is characterized by the following features:
– reduced heat input into the product and increased heat input into the electrode (therefore, when welding with reverse polarity, the non-consumable electrode must be of a larger diameter at the same current; otherwise it will overheat and quickly collapse); – the melting zone of the base metal is wide but shallow; – the effect of cathodic cleaning of the surface of the base metal is observed, when, under the influence of a flow of positive ions, the oxide and nitride films are destroyed (the so-called cathode sputtering), which improves the fusion of the edges and the formation of the seam.
While when welding with straight polarity the following is observed:
– increased heat input into the product and reduced heat input into the electrode; – the melting zone of the base metal is narrow but deep.
As in the case of MMA and MIG/MAG welding, differences in arc properties for direct and reverse polarity in TIG welding are associated with the asymmetry of energy release at the cathode and anode. This asymmetry, in turn, is determined by the difference in the voltage drop in the anode and cathode regions of the arc. Under non-consumable electrode welding conditions, the cathode voltage drop is much lower than the anode voltage drop, so less heat is generated at the cathode than at the anode.
Below is the approximate amount of heat generated in different sections of the arc in relation to TIG welding at a welding current of 100 A and when using straight polarity (as the product of the voltage drop in the corresponding area of the arc and the welding current):
– in the cathode region: 4 V x 100 A = 0.4 kW at a length of ≈ 0.0001 mm – in the arc column: 5 V x 100 A = 0.5 kW at a length of ≈ 5 mm – in the anode region: 10 V x 100 A = 1.0 kW over a length of ≈ 0.001 mm.
Due to the fact that when welding with direct polarity there is an increased heat input into the product and a reduced heat input into the electrode, when welding with direct current, direct polarity is used. At the same time, due to the fact that heat is released mainly in the anode region, only those areas of the base metal to which the arc is directed melt, i.e. where the anode is located.
Welding stainless steel with argon
This article will tell you how to weld stainless steel using all the nuances and features. Those who are involved in welding know that stainless steel is far from being a simple metal, when working with which many problems often arise, you need to cut, digest, and sometimes you don’t even have to cut, the seams themselves crack and come apart, but how to deal with this?
That is why you should read our article where we will tell you how to cook stainless steel with your own hands using argon.
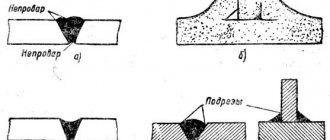
An important stage of welding is the preparation of the metal, the quality of the weld depends on this, what you get in the end, the metal must be thoroughly cleaned and checked for defects.
This article describes how to most advantageously use gas to the burner position. Here you will find tips that the masters have honed during practice, and you will no longer have to repeat someone else’s mistakes.
Just take and adopt the experience of a person who already knows how good it will be and how bad it will be. For example, how to cook metal with argon so that it does not oxidize, or how to cook thin metal, because this is filigree work that requires care.
Even GOSTs do not write such advice, although you can find very informative operating instructions there that will help both beginners and experienced welders.
Electrode selection
The technology of welding aluminum with argon also requires the correct choice of a tungsten electrode, the diameter of which should be as close as possible to the thickness of the parts being welded. Sharpening is done in the classic way, but without a sharp tip, as is the case with stainless steel welding. During the first seconds of combustion, the electrode will take the shape of a drop at the end and the seam will have to be made this way. The projection from the nozzle is required to be 3-5 mm to avoid overheating of the tungsten. When welding, small spatters of aluminum will stick to the electrode, requiring re-sharpening.
Learning to weld aluminum is not easy. But knowing the above principles and watching videos with lessons from experts, you can confidently try your hand at practice.
Bottom line
If you need your seams to be reliable and neat, without having to re-sew a hundred times, or spend a lot of money on expensive consumables, then you need to read these articles.
They tell you all the nuances of welding with argon, a variety of metals that are quite difficult to work with. If you work with stainless steel or aluminum, then these nuances are many times greater than when working with other metals.
You need to try hard to ensure that your seams are strong, beautiful, without sagging or welding. Read all the pros and cons of welding with this gas that we have given and evaluate whether it is worth using it, but most often this metal justifies itself.
If you are an experienced craftsman, then write what you think about this, whether you had to work with argon, whether it made your work easier, or perhaps even vice versa.
Tell us about gas consumption, it will be very useful for entrepreneurs who make money by welding. Your experience will be useful to us for future articles and to beginners who are just learning. We wish you good luck and new successful works!
Necessary equipment
Argon arc welding of copper and other metals requires special equipment. Minimum technical equipment includes:
- Current sources.
- Oscillator.
- Inverter.
- Argon cylinder.
- Gearbox.
- Burner.
- Connecting cables.
- Tungsten electrodes.
- Filler wire.
For full TIG welding, the machine requires constant ignition. The simplest sources for TIG welding produce direct current. They can weld metals - stainless steel, ferrous metal, brass, copper, bronze. But you cannot weld metals that have an oxide film - aluminum and magnesium. They require the source to have an AC function. These are more complex sources that have the function of both direct and alternating current. For AC there are settings such as current balance.
In modern models, there are sources with modes for different material thicknesses and different spatial positions. The most common function is pulse mode. One of the characteristics is heart rate. There are sources with pulse frequencies up to 15 thousand Hz. The higher the frequency, the higher the functionality.
When choosing a machine for TIG welding, you need to decide where it will be used and for what purposes. This will determine whether the required functions are available:
- power supply voltage;
- availability of modes with direct and alternating current;
- possibility of changing polarity;
- the presence of a mode for steel with high viscosity;
- the ability to weld thick metal for a long time;
- inclusion of a water-cooled burner in the kit;
- presence of stationary type cooling;
- the ability to control operation using the display;
- Ability to work on production lines.
The advantages include additional functions:
- the possibility of contactless ignition of the arc;
- DOWN POST GAS – allows you to smoothly turn off the arc;
- BALANCE – the ability to change the polarity balance when welding with alternating current.
There are many models of welding machines for TIG welding. The TIGER 170 DC model is ahead of its competitors in terms of the ratio of device weight and performance. The device has a wide range of applications - from steel sheets with a thickness of 0.2 mm to 6 mm. The additional function of adjusting the current value allows you to weld thin sheets without burns. The device has microprocessor control and a large amount of memory. A simple and convenient interface allows you to set the necessary parameters and modes.
The HAMER TIG-200DC device can operate in two modes. This is an option for welding ferrous metals and stainless steel. The main advantage is the low price combined with the presence of all the necessary functions.
The ELAND TORS-200 welding machine has similar characteristics. There are a large number of additional functions available. A distinctive feature is that it is equipped with devices and consumables for work both for TIG and MMA welding.
GOST 5.917-71 sets out the requirements for manual torches for argon arc welding. According to this regulatory document, burners of the RGA type must be used. The most common models are RGA-150 and RGA-400. The choice of electrode diameter and thickness for TIG welding depends on the type of metal being welded.