To change the basic performance properties of metals, an alloying process is quite often carried out. It involves the inclusion of additional chemical elements in the basic composition of the metal that can change certain properties. The alloying process is so widespread that most modern metals belong to this group. An example is 20x steel. It is a representative of the group of structural steels, but chromium was added to the composition to change some of the performance properties of the metal. Let's take a closer look at 20x steel, its characteristics, application and many other qualities.
Decoding the brand
Deciphering the markings of structural steels is quite simple. The metal in question has the following composition:
- Carbon content ranges from 0.17 to 0.23%. This element determines the hardness and brittleness of the metal.
- Alloying in this case is carried out by adding chromium to the composition. The fact that there is no number after the letter designating the element indicates the concentration of chromium in the composition is no more than one percent.
- There are also other elements characteristic of structural steels.
Alloying of the metal in question is carried out in order to increase the hardness of the surface layer, leaving the core less strong and more flexible.
20G2
Download the full price list of ProfProkat LLC
Characteristics of the material.
Steel 20Х2Н4А. Brand
| Steel 20Х2Н4А | |
| Classification | Alloyed chromium-nickel structural steel |
| Substitute | Steel 20KhGNR, Steel 20KhGNTR |
| Other designations | Steel 20Х2Н4А; Art.20X2H4A; 20Х2Н4А; 20Х2Н4А-ВД |
| Foreign analogues | USA 3120.3316H; Germany (DIN, WNR) 19crni8; France (Afnor) 20nc6; England (BS) 822M17; Italy (UNI) 20CRNI4; Bulgaria (BDS) 20CH2N4A; Poland (PN) 20H2N4A; Czech Republic 16231. |
| general characteristics | High quality chromium-nickel case-hardened steel . |
| Application | Steel 20 X 2 N 4 A is used: for the manufacture of gears, gear shafts, fingers, solid-rolled rings and other cemented, especially critical, highly loaded parts, which are subject to the requirements of high strength, ductility and toughness of the core and high surface hardness, working under the influence of shock loads and at negative temperatures. |
| Type of delivery | |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 1133-71, GOST 8319.0-75, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006, GOST 2879-2006 |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 103-2006 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 1051-73, GOST 4543-71, GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78, GOST 14955-77, TU 14-1-2118-77, TU 14-136-367-2008, TU 14 -1-1271-75, TU 14-11-245-88, TU 3-173-83, TU 14-1-1433-75, TU 14-1-1732-76, TU 14-1-1885-85, TU 1-83-77-90 |
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | OST 1 90005-91, GOST 4543-71 |
| Blanks. Blanks. Slabs | OST 3-1686-90, TU 14-1-4944-90 |
Chemical
composition in % of material 20Х2Н4А.
| Chemical element | According to GOST 4543-71 , in% | According to TU 14-1-1885-85, in % |
| Carbon (C) | 0,16 — 0,22 | 0,16 — 0,22 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 1,25 — 1,65 | 1,25 — 1,65 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 3,25 — 3,65 | 3,25 — 3,65 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0,30 — 0,60 | 0,30 — 0,60 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0,17 — 0,37 | 0,17 — 0,37 |
| Copper (Cu), no more | 0,30 | 0,25 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0,15 | — |
| Phosphorus (P), no more | 0,025 | 0,025 |
| Sulfur (S), no more | 0,025 | 0,015 |
| Tungsten (W), no more | 0,20 | — |
| Vanadium (V), no more | 0,05 | |
| Titanium (Ti), no more | 0,03 | |
| Iron (Fe) | the basis | the basis |
| According to GOST 4543-71, the content in especially high-quality steel is regulated: P≤0.025%; S≤0.015%; Сu≤0.25%. According to TU 14-1-1885-85, the chemical composition is given for steel grade 20X2H4A-VD. To ensure the required grain size, it is allowed to introduce vanadium during steel smelting based on its content in steel not exceeding 0.10%, the content of which in steel is not determined. The presence of tungsten up to 0.20%, molybdenum up to 0.15%, titanium up to 0.030% is not a rejection sign. The permissible deviation for manganese content in steel is ±0.010%. | ||
A brief
description of .
Cementation (carburization) is a chemical-thermal treatment consisting in the diffusion saturation of the surface layer of steel with carbon when heated in a carburizing medium (carburizer). The final properties of cemented products are acquired after hardening and low tempering. The purpose of carburization and subsequent heat treatment is to give the surface layer high hardness and wear resistance, to increase the contact endurance limit and the bending endurance limit while maintaining the viscous core. Cementation is widely used to harden medium-sized gears, automobile gearbox shafts, individual steering parts, high-speed machine tool shafts, spindles and many other machine parts. Parts are received for cementation after machining with an allowance for rough and final grinding of 0.05-0.010 mm. In many cases, only part of the part is subjected to carburization, then the areas that are not subject to hardening are covered with a thin layer of low-porosity copper (0.02-0.04 mm), which is applied electrolytically, or is isolated with special coatings consisting of a mixture of refractory clay, sand and asbestos mixed with liquid glass. To ensure stability and quality, it is recommended that parts be washed in a 3-5% soda solution before cementation. Case-hardened chromium-nickel steels (12ХН3А, 20ХН3А, 20Х2Н4А), chromium-manganese titanium (18ХГТ, 25ХГТ), chromium-nickel-molybdenum steels (18Х2Н4МА, 18Х2Н4ВА). used for parts of medium and large sizes that are exposed to wear under high loads (gears, piston pins, axles, rollers, etc.). Chrome-nickel steels are little sensitive to overheating, can be calcined well, but their use is limited due to the scarcity of nickel. Therefore, in all cases where there is no emergency, chromium-nickel steels are replaced with steels without nickel. For the manufacture of parts, large-sized bearings (with a diameter of more than 400 mm), operating in difficult conditions with high shock loads, case-hardened steel 20Х2Н4А is used. Parts of large-sized bearings (rings, rollers), made from steel 20Х2Н4А, are subjected to carburization at a temperature of 930-9500C for 50-170 hours to obtain a layer 5-10 mm deep. Simultaneous alloying with chromium and nickel increases the strength, ductility and toughness of the core. Nickel, in addition, increases the strength and viscosity of the cemented layer. Chromium-nickel steels are insensitive to overheating during prolonged carburization and are not prone to supersaturation of surface layers with carbon. The greater stability of supercooled austenite in the region of pearlitic and intermediate transformations ensures the high hardenability of chromium-nickel steel. 20Х2Н4А – structural alloy steel, insensitive to overheating during prolonged carburization and not prone to oversaturation of surface layers with carbon. The greater stability of supercooled austenite in the region of pearlitic transformation ensures the high hardenability of chromium-nickel steel. The critical diameter when quenching in oil is 25-70 mm. After carburizing and quenching in oil, the core of the part has a low-carbon martensite structure, which provides a combination of increased core strength (σ in = 800 − 1300 MPa) and toughness.
Mechanical
properties of steel 20Х2Н4А at a temperature of 200С
| Delivery status | Section, mm | σ t/σ0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KCU, J/m2 | HB | H.R.C. |
| Quenching in oil from 860 °C + quenching in oil from 780 °C + tempering at 180 °C, cooling in air or in oil | ||||||||
| Long products (rod) | ≤15 | ≥1080 | ≥1270 | ≥9 | ||||
| Rods made of steel 20X2H4A according to TU 14-1-1885-85. Quenching in oil from 850-870 °C + Quenching in oil from 770-790 °C + Tempering at 180 °C, cooling in air or in oil. The KCU column shows the values of KCU along the fiber/KCU across the fiber | ||||||||
| Sample 15x15 | ≥1080 | ≥1270 | ≥9 | ≥45 | ≥784 | 363-444 | ||
| Carburization at 900-920 °C, air cooling + oil quenching from 780-810 °C + tempering at 180-200 °C, air cooling | ||||||||
| Long products (rod) | 20-50 | ≥1050 | ≥1220 | ≥12 | ≥45 | ≥1158 | 360 | 57-64 |
| Cementation at 920-950 °C + normalization at 900-920 °C, air cooling or quenching in oil from 880-920 °C + tempering at 630-660 °C, air cooling. Quenching in oil from 780-820 °C + tempering at 150-200 °C, air cooling | ||||||||
| Rolled products, forgings | 150 | ≥830 | ≥1080 | ≥9 | ≥35 | ≥765 | 321-420 | 57-64 |
Mechanical
properties of grade 20X2H4A depending on the cross-section of round bars
| Heat treatment | Section (mm) | σ t/σ0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | HB |
| Quenching + Tempering | 120-160 | ≥760 | ≥880 | ≥12 | ≥50 | ≥262 |
| 15-30 | ≥820 | ≥940 | ≥12 | ≥50 | ≥277 | |
| 160-200 | ≥740 | ≥860 | ≥12 | ≥50 | ≥262 | |
| 200-240 | ≥720 | ≥860 | ≥12 | ≥50 | ≥255 | |
| 30-50 | ≥820 | ≥940 | ≥12 | ≥50 | ≥277 | |
| 50-80 | ≥820 | ≥940 | ≥12 | ≥50 | ≥269 | |
| 80-120 | ≥780 | ≥900 | ≥12 | ≥50 | ≥262 |
Mechanical
properties of steel 20 X 2 N 4 A depending on the tempering temperature
| Heat treatment | holiday temperature (°C) | σ t/σ0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % |
| Quenching in oil from 840 °C + Tempering | 200 | ≥1360 | ≥1500 | ≥7 | ≥56 |
| 300 | ≥1280 | ≥1400 | ≥7 | ≥60 | |
| 400 | ≥1140 | ≥1300 | ≥7 | ≥63 | |
| 500 | ≥970 | ≥1170 | ≥10 | ≥67 | |
| 600 | ≥790 | ≥1000 | ≥11 | ≥72 |
Mechanical
properties of steel 20 X 2 N 4 A at elevated temperatures
| test t, °C | σ t/σ0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % |
| Sample 10 mm in diameter, 50 mm long, forged and annealed. Deformation speed 5 mm/min. Strain rate 0.002 1/s. | ||||
| 700 | ≥63 | ≥120 | ≥56 | ≥78 |
| 800 | ≥45 | ≥56 | ≥64 | ≥95 |
| 900 | ≥36 | ≥56 | ≥58 | ≥100 |
| 1000 | ≥22 | ≥37 | ≥63 | ≥100 |
| 1100 | ≥20 | ≥27 | ≥59 | ≥100 |
| 1150 | ≥16 | ≥26 | ≥65 | ≥100 |
| 1220 | ≥16 | ≥22 | ≥71 | ≥100 |
Technological properties of steel 20Х2Н4А
| Forging temperature | Start - 1200 °C, end - 800 °C. Sections up to 100 mm are cooled in air, 101-350 mm - in a pit. |
| Weldability | difficult to weld. Welding methods: RDS, submerged arc welding, ESW. Heating and subsequent heat treatment are required. |
| Machinability | After normalization and tempering at HB 259 σ V=880 MPa Kn tv.all.=0.72 Kn b.st.=0.63 |
| Tendency to release ability | less inclined |
| Flock sensitivity | Sensitive. |
| Macrostructure and contamination | When checking for fractures in the longitudinal direction and transverse templates taken from finished rolled products, the macrostructure of steel should not have shrinkage cavities, friability, bubbles, cracks, delaminations, slag inclusions and flakes, as well as fracture defects listed in Appendix 3 of GOST 10243. Central porosity, point heterogeneity and segregation square should not exceed 1 point; layer-by-layer crystallization and light contour - 3 points of the GOST 10243 standard scales. All other defects provided for by GOST 10243 are not allowed. Contamination of steel with non-metallic inclusions should be no higher than the average score (in points): for point oxides 1.5, for line oxides 2.0, for brittle silicates 1.0, for plastic silicates 1.0, for non-deformable silicates 2.5 , for sulfides 2.5, for nitrides line and dot 1.0. |
Temperature of
critical points of steel 20 X 2 N 4 A
| Critical point | Ar1 | Ac1 | Ac3 |
| °C | 640 | 710 | 800 |
Impact strength of steel KCU, J/cm2 steel 20Х2Н4А
| Delivery condition, heat treatment | +20 | -20 | -40 | -70 |
| Quenching in oil from 820 °C + tempering at 500 °C | 1442 | 1442 | 1540 | |
| Longitudinal samples from forgings (Oil quenching at 880 °C + oil quenching at 780 °C + tempering at 200 °C) | 638 | 598 | 618 | 608 |
| Transverse samples from a forging (Oil quenching at 880 °C + oil quenching at 780 °C + tempering at 200 °C) | 314 | 324 | 343 | 294 |
Hardness
Hardness of rolled steel 20Х2Н4А after annealing: HB=269
Endurance limit of steel 20Х2Н4А
| Strength characteristics | σ-1, MPa | t-1, MPa | ||
| σB, MPa | σ t/σ0.2, MPa | HB | ||
| 1220 | 1050 | 360 | 617 | 372 |
| 730 | 610 | 238 | 333 | 230 |
| 960 | 680 | 322 | 382 | |
| 940 | 850 | 421 | ||
Hardness for hardenability strips HRCe steel 20Х2Н4А according to
GOST 4543-71 with heat treatment according to the regime: normalization at 850 °C + quenching in oil from 840 °C.
| Distance from the end, mm | 3 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| Hardness HRCе | 41.5-49.5 | 40.5-48.5 | 35.5-45.5 | 31-40 | 28-36.5 | 25-33 | 23.5-31 | 23-30.5 | 22.5-30.5 |
Physical properties of steel 20Х2Н4А
| Test temperature, °C | 0 | 20 | 100 | 400 |
| Modulus of normal elasticity, E, GPa | 203 | 203 | ||
| Steel density, pn, kg/cm3 | 7850 | 7850 | ||
| Thermal conductivity coefficient W/(m °C) | 24 | 18 |
Designations:
| Mechanical properties : | ||
| σ in | — Short-term strength limit (temporary tensile strength, tensile strength), [MPa] | |
| σ T | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] | |
| σ0.05 | — elastic limit, MPa | |
| σ0.2 | — conditional yield strength, MPa | |
| σсж0.05 and σсж | — compressive yield strength, MPa | |
| ν | — relative shift, % | |
| δ 5 | — Relative elongation at (after) rupture, [%] | |
| ψ | — Relative narrowing, [%] | |
| KCU | — impact strength, determined on a sample with concentrators of the type U, [kJ/m2] | |
| KCV | — impact strength determined on a sample with concentrators V, [kJ/m2] | |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, [MPa] | |
| H.V. | Vickers hardness | |
| HRC uh | — Rockwell hardness, scale C | |
| HRB | — Rockwell hardness, scale B | |
| HSD | - Shore hardness | |
| σtТ | — long-term strength limit, MPa | |
| G | — modulus of elasticity during torsional shear, GPa | |
| ε | — relative settlement at the appearance of the first crack, % | |
| J | — ultimate torsional strength, maximum shear stress, MPa | |
| σben | — ultimate bending strength, MPa | |
| σ-1 | — endurance limit during bending test with a symmetrical loading cycle, MPa | |
| σ | — endurance limit during torsion testing with a symmetrical loading cycle, MPa | |
| n | — number of loading cycles | |
| Physical properties : | ||
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] | |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] | |
| ά | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o - T), [1/degree] | |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] | |
| p | — Material density, [kg/m3] | |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o — T), [J/(kg deg)] | |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] | |
| Weldability: | ||
| no limits | — welding is performed without heating and without subsequent heat treatment | |
| limited weldability | — welding is possible when heated to 100-120 degrees. and subsequent heat treatment | |
| difficult to weld | — to obtain high-quality welded joints, additional operations are required: heating to 200-300 degrees. during welding, heat treatment after welding - annealing | |
Buy steel 20Х2Н4А.
Structural high-quality chromium-nickel alloy steel with an average carbon content of 0.20%, chromium 1.5%, nickel 3.4%, manganese 0.4; and silicon 0.25%. Pipe Angle Channel Strip Circle Hexagon Reinforcement Square Beam Sheet
Normative documents
GOST 103-2006. Hot-rolled long-rolled steel strip. Assortment. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 1051-73. Calibrated rental. General technical conditions. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 1133-71. Forged steel round and square. Assortment. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 2590-2006. Hot-rolled round steel products. Assortment. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 2591-2006. Hot-rolled square steel products. Assortment. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 2879-2006. Hot-rolled hexagonal long steel. Assortment. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 4543-71. Rolled alloy structural steel. Technical conditions. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 7417-75. Calibrated round steel. Assortment. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 8319.0-75. Hot-rolled steel profiles, periodic longitudinal rolling. Technical conditions. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 8559-75. Calibrated square steel. Assortment. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 8560-78. Rolled calibrated hexagonal. Assortment. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
GOST 14955-77. High-quality round steel with special surface finishing. Technical conditions. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
TU 14-1-1433-75. Rods made of steel grade 20Х2Н4А-Ш electroslag remelted. Technical conditions.
TU 14-1-1271-75. High precision shaped steel profiles. Technical conditions. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
TU 14-1-1732-76. Steel rods. Brand 20Х2Н4А. Technical conditions.
TU 14-1-1885-85. Hot-rolled, forged and calibrated rods from structural alloy steel of vacuum-arc remelting. Technical conditions.
TU 14-1-2118-77. Hot-rolled bars in profiles measuring 250 mm or more from structural carbon and alloy steel. Technical conditions. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
TU 14-1-4944-90. Continuously cast square billet for pipes and long products. Technical conditions. Steel 20X2H4A.
TU 14-11-245-88. High precision shaped steel profiles. Technical conditions. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
TU 14-136-367-2008. Rolled hot-rolled, turned, round sections with a size of more than 200 mm. Technical conditions. Steel 20X2H4A.
TU 1-83-77-90. Solid-rolled rings made of steel grades 20X2H4A, ШХ15СГ, ШХ20СГ, 20X2H4A-Ш. Technical conditions.
TU 3-173-83. Hot rolled steel grade 20Х2Н4А. Technical conditions.
OST 1 90005-91. Steels and alloys. Indicators of tensile strength and hardness of finished parts. Layer depth during chemical-thermal treatment of carburized, nitrocarburized, nitrided steels. Steel 20X2H4A.
OST 3-1686-90. Structural steel blanks for mechanical engineering. General technical conditions. Steel 20Х2Н4А.
Additional Information.
Correspondence between Soviet and Russian steel grades.
International analogues of steels
Correspondence table HB - HRC.
Tool materials.
The influence of the main alloying elements on the properties of steel.
Basic properties
The distribution of the metal in question is due to the fact that it has a relatively low cost and is suitable for the manufacture of a wide variety of parts . The main properties include the following information:
- Normalization is often carried out as a heat treatment. It makes the material more resistant to mechanical stress.
- The specific gravity is 7830 kilograms per cubic meter.
- The surface hardness is relatively low, but often this is quite enough for the manufacture of various non-critical parts.
- It is possible to carry out cutting processing, for which the metal is preheated.
- By adding chromium to the composition, the degree of weldability is significantly increased. An exception is the case when it is necessary to weld parts that have previously undergone a chemical-thermal treatment process.
- No tendency to temper brittleness.
In addition, do not forget that the presence of a small amount of chromium in the composition does not lead to increased corrosion resistance. Therefore, steel is not suitable for the manufacture of parts that will be used in an aggressive environment.
Steel 20X - structural alloy
Substitutes
Steels 15Х, 20ХН, 12ХН2, 18ХГТ.
Foreign analogues
| Germany DIN | 20Cr4, 20CrS4 | |
| USA (AISI, SAE, ASTM) | 5120, 5120H | |
| UK (BS) | 207 | |
| Japan (JIS) | SCr420, SCr420H | |
IMPORTANT!!! The possibility of replacement is determined in each specific case after assessing and comparing the properties of steels
Type of delivery
Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 4543-71, GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88, GOST 10702-78, GOST 2879-88.
Calibrated rod GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78, GOST 7417-75, GOST 1051-73.
Polished rod and silver GOST 14955-77.
Thick sheet GOST 1577-93, GOST 19903-74.
Strip GOST 82-70, GOST 103-76.
Forgings and forged blanks GOST 1133-71, GOST 8479-70.
Pipes GOST 8731-87, GOST 8732-78, GOST 8733-74, GOST 8734-75, GOST 13663-86.
Purpose
Bushings, gears, cages, sleeves, disks, plungers, levers and other cemented parts, which are subject to the requirements of high surface hardness with low core strength, parts operating under friction wear conditions.
Decoding steel 20X
The number 20 means that the carbon content of the steel is 0.2%.
The letter X means that the steel contains chromium in amounts up to 1.5%.
Application of 20X steel bodies, covers, flanges, membranes and valve assembly made from rolled products, forgings (stampings) (GOST 33260-2015)
| steel grade | ND for supply | Temperature of the working medium (wall), °C | Additional instructions for use |
| 20X GOST 4543 | Forgings GOST 8479. Long products GOST 4543. Sheets GOST 1577, categories 2, 3. Pipes GOST 8731 gr.V, GOST 8733 gr.V | -40 to 450 | For welded reinforcement assemblies operating in non-aggressive environments |
The use of 20X steel for parts of valves and pneumatic actuators that do not operate under pressure and are not subject to welding, intended for operation at low temperatures (GOST 33260-2015)
| steel grade | Quenching + tempering at temperature, °C | Approximate strength level, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) | Application temperature not lower, °C | Use in thickness no more than, mm |
| 20X | 200 | 900 (90) | -60 | 15 |
NOTE
- When heat treated for strength below that specified in column 3 or when used in parts with a wall thickness of less than 10 mm, the operating temperature may be reduced.
- The maximum thickness indicated in column 5 is due to the need to obtain through hardenability and uniformity of properties across the cross section.
Temperature of critical points, °C
| Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar3 | Ar1 | Mn |
| 750 | 825 | 755 | 665 | 390 |
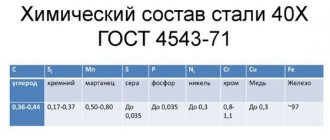
Chemical composition, % (GOST 4543-71)
| WITH | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Cu | S | P |
| no more | |||||||
| 0,17-0,23 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,5-0,8 | 0,7-1,0 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,035 | 0,035 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 4543-2016)
| steel grade | Mass fraction of elements, % | |||||||||
| WITH | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Al | Ti | V | B | |
| 20X | 0,17-0,23 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,5-0,8 | 0,7-1,0 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
NOTE: the sign “-” means that the mass fraction of this element is not standardized or controlled unless otherwise indicated.
Hardness (GOST 4543-2016)
- The Brinell hardness of metal products in the annealed (HT) or high-tempered (HT) state, as well as hot-rolled and forged metal products, normalized with subsequent high tempering (H + HT), with a diameter or thickness of over 5 mm must comply with the standards specified in the table
steel grade Hardness HB, no more 20X 179 NOTE The hardness of calibrated metal products in the annealed (HT) or high-tempered (HT) state, as well as hot-rolled and forged metal products, normalized with subsequent high tempering (H+HT), can be 15 HB more than indicated in the table above.
- The hardness of hot-rolled and forged metal products supplied without heat treatment is not standardized or controlled.
- The hardness of calibrated metal products and metal products with special surface finishing with a diameter or thickness of over 5 mm, supplied in a cold-worked state (NG), must comply with the standards specified in the table below.
steel grade Hardness NV, no more 20X 229
Mechanical properties of rolled products (GOST 4543-2016)
| steel grade | Heat treatment mode | Mechanical properties, no less | Sectional size of workpieces for heat treatment (circle diameter or square side), mm | ||||||||
| Hardening | Vacation | Yield strength σt, N/mm2 | Tensile strength σв, N/mm2 | Relative | Impact strength KS U, J/cm2 | ||||||
| Temperature, °C | Cooling medium | Temperature, °C | Cooling medium | elongation δ5,% | narrowing Ψ, % | ||||||
| 1st hardening or normalization | 2nd hardening | ||||||||||
| 20X | 880 | 770— 820 | Water or oil | 180 | Air or oil | 635 | 780 | 11 | 40 | 59 | 15 |
Mechanical properties of rolled products
| GOST | Delivery condition, heat treatment mode | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | Ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness, no more |
| no more | ||||||||
| GOST 4543-71 | Bar. Quenching from 880 °C in water or oil, quenching from 770-820 °C in water or oil; holiday at 180 °C, cool. in water or oil | 15 | 640 | 780 | 11 | 40 | 59 | — |
| GOST 10702-78 | Cold-worked steel - calibrated and calibrated with special finishing without heat treatment | — | — | 590 | 5 | 45 | — | HB 207 |
| Bar. Cementation at 920-950 °C, cooling. on air; hardening at 800 °C in oil; holiday at 190 °C, cool. on air | 60 | 390 | 640 | 13 | 40 | 49 | HB 250; HRC 5 55-63 | |
Mechanical properties of forgings (GOST 8479-70)
| Heat treatment | Section, mm | KP | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | Ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness HB , no more |
| no less | ||||||||
| Normalization | Up to 100 | 195 | 195 | 390 | 26 | 55 | 59 | 111-156 |
| 100-300 | 23 | 50 | 54 | |||||
| 300-500 | 20 | 45 | 49 | |||||
| Up to 100 | 215 | 215 | 430 | 24 | 53 | 54 | 123-167 | |
| 100-300 | 20 | 48 | 49 | |||||
| Up to 100 | 245 | 245 | 470 | 22 | 48 | 49 | 143-179 | |
| Quenching+tempering | 100-300 | 19 | 42 | 39 | 143-179 | |||
| Up to 100 | 275 | 275 | 530 | 20 | 40 | 44 | 156-197 | |
| 100-300 | 275 | 275 | 530 | 17 | 38 | 34 | 156-197 | |
| 100-300 | 315 | 315 | 570 | 14 | 35 | 34 | 167-207 | |
| 100-300 | 345 | 345 | 590 | 17 | 40 | 54 | 174-217 | |
Mechanical properties depending on tempering temperature
| totp. °C | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | Ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 |
| 200 | 650 | 880 | 18 | 58 | 118 |
| 300 | 690 | 880 | 16 | 65 | 147 |
| 400 | 690 | 850 | 18 | 70 | 176 |
| 500 | 670 | 780 | 20 | 71 | 196 |
| 600 | 610 | 730 | 20 | 70 | 225 |
Note: Rod with a diameter of 25 mm; hardening at 900 °C, in oil.
Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures
| tsp. °C | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | Ψ, % |
| 700 | 120 | 150 | 48 | 89 |
| 800 | 63 | 93 | 56 | 74 |
| 900 | 51 | 84 | 64 | 88 |
| 1000 | 33 | 51 | 78 | 97 |
| 1100 | 21 | 33 | 98 | 100 |
| 1200 | 14 | 25 | — | — |
NOTE: Sample 6mm diameter, 30mm long, forged and normalized; deformation speed 16 mm/min; strain rate 0.009 1/s.
Endurance limit at n = 107
| Heat treatment | σ-1, MPa |
| Normalization, σ0.2 = 295-395 MPa, σв = 450-590 MPa, HB 143-179 | 235 |
| Hardening + high tempering, σ0.2 = 490 MPa, σв = 690 MPa, HB 217-235 | 295 |
| Cementation + hardening + low tempering, σ0.2 = 790 MPa, σв = 930 MPa, HRCе 57-63 | 412 |
Impact strength KCU
| Delivery status | KCU , J/cm2, at temperature, °C | |||
| +20 | -20 | -40 | -60 | |
| Rod with a diameter of 115 mm; hardening + tempering | 280-286 | 280-289 | 277-287 | 261-274 |
Technological properties
Forging temperature, °C: start 1260, end 750. Workpieces with a cross-section of up to 200 mm are cooled in air, with a cross-section of 201-700 mm subjected to low-temperature annealing.
Cutting ability - K
v tv.spl = 1.3 and
K
v b.st = 1.7 in the hot-rolled state at HB 131 σw = 460 MPa.
Flock sensitivity is insensitive.
Tendency to temper brittleness - not prone.
Weldability
Steel 20X can be welded without restrictions (except for chemical-thermal treated parts). Welding methods: RDS, KTS without restrictions.
Critical diameter d
| Critical hardness HRC3 | Amount of martensite, % | d, mm, after hardening | |
| in water | In oil | ||
| 32-36 | 50 | 26-48 | 8-24 |
| 38-42 | 90 | 12-28 | 3-9 |
Physical properties
Density ρ kg/cm3 at test temperature, °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 20X | 7830 | 7810 | 7780 | — | 7710 | — | 7640 | — | — | — |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ W/(m*K) at test temperature, °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 20X | 42 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 38 | 36 | 33 | 32 | 31 | — |
Linear expansion coefficient α*106, K-1, at test temperature, °C
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 | 20-700 | 20-800 | 20-900 | 20-1000 |
| 10,5 | 11,6 | 12,4 | 13,1 | 13,6 | 14,0 | — | — | — | — |
Specific heat capacity c, J/(kg*K), at test temperature, °C
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 | 20-700 | 20-800 | 20-900 | 20-1000 |
| 496 | 508 | 525 | 537 | 567 | 588 | 626 | 706 | — | — |
Modulus of normal elasticity E, GPa, at test temperature, °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 20X | 216 | 213 | 198 | 193 | 181 | 171 | 165 | 143 | 133 | — |
Modulus of elasticity in torsional shear G, GPa, at test temperature °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 20X | 84 | 83 | 76 | 74 | 71 | 67 | 62 | 55 | 50 | — |
Find out more
Steel X12MF tool stamping...
Spring steel 65
Steel 45Х22Н4М3 (EP48) heat-resistant, heat-resistant...
Steel 7X3 tool die…