Application of CVG
The very name “instrumental” determines the use of this brand. But what properties provide it with such a purpose? First of all, its resistance to warping during hardening, to which it is necessarily subjected, and corrosion resistance.
- Since HVG steel does not deform, high-precision measuring instruments of any length are made from it.
- Resistance to scale formation allows products made from this steel to be subjected to thermal operations in an already ground form, which also makes it possible to produce tools without allowances for final machining (i.e. grinding).
- The wear resistance of the surface and the toughness of the middle are determined as steel for the manufacture of parts subject to dynamic loads, for example, spring shock absorber rings.
- The corrosion resistance of HVG is ensured by the chromium content; it is relevant in the manufacture of almost any tool and spare part.
- High strength is used for the manufacture of parts for rolling mills and cold drawing. These are punches, rolls, thread gauges, etc.
- Wear resistance and strength are the main characteristics used for all parts, including lock washers.
What the HVG steel grade does not have is heat resistance, the ability to retain its properties, in particular hardness, at high temperatures. This condition is necessary for cutting and high-speed tools, where the edge temperature can reach 650 ºC. The softening of the cold hardening agent occurs at a temperature of 200 ºC, so it is used only for parts operating in the low temperature range.
HVG steel is supplied to:
- calibrated and ground rods;
- silver coin;
- thick sheets;
- stripes;
- forgings;
- blanks;
- slabs.
GOST
To learn in more detail about what the steel we are interested in is, let’s turn to the regulatory documents that mark the HVG grade as alloy tool steel. Even this seemingly very short formulation gives us some information. The fact is that tool steel is the steel in which the carbon content exceeds 0.7%. Alloy steel is an alloy of iron, carbon and some other additives designed to improve the structure of the steel.
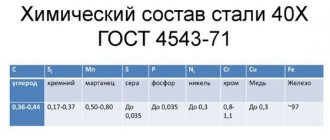
Oddly enough, we can also find out a little about the alloying elements present in the composition of cold gases. To do this, you should turn to the GOST system, which states that each such element is assigned a specific letter designating it. Thus, we know that the composition of HVG steel includes:
- X – chromium;
- B – tungsten;
- G – manganese.
Decoding steel HVG
The HVG grade is the base grade for analog pearlitic steels. Its chemical composition is ensured by a minimum amount of alloying elements (4 in total):
- carbon - ± 1.0%;
- chromium - 0.9-1.2%;
- silicon - 01-0.4%;
- tungsten - 0.2-1.6%.
The remaining elements are of secondary importance and are maintained in the following concentration:
- manganese - 0.8-1.1%;
- molybdenum up to 0.3%;
- nickel - up to 0.35%;
- copper - up to 0.3%.
Since HVG grade steel belongs to the high-quality class, the content of harmful impurities of phosphorus and sulfur is regulated to 0.03% (this is the minimum possible limit). Residual oxygen is deoxidized with the introduction of alloying elements Si and Mn.
Influence of elements on properties
The properties of steel are influenced by two components:
- concentration of chemical elements, i.e. chemical composition of steel;
- their interaction with each other, as well as in relation to the main element (in this case Fe), which is determined by heat treatment.
Modifying materials are introduced into the melt in order to fill the crystal lattice in a certain way and thereby determine its properties. These concepts include:
- Strength - any distortion of the crystal lattice increases this characteristic;
- Increasing the hardening layer - uniform temperature distribution;
- Reduction of deformations - complete crystal lattice;
- Tendency to crack formation - here we mean strong intercrystalline bonds, i.e. the formation of carbides along grain boundaries, it can also be the formation of segregations.
The main element that increases strength and defines an alloy as steel is carbon. Not much smaller in size than the Fe molecule, it is placed in a metal lattice to form carbides. Their shape, location and dimensions are of primary importance for the characteristics of the metal during subsequent processing.
The main alloying element of HVG is chromium. Its atoms are small in size and compact the lattice, giving it even greater density and stability. The peculiarity of chromium atoms to form oxides almost the same size as the atom itself is used in the smelting of an alloy with the properties of stainless steel, but this is when its content is above 10.5%, and up to this limit it improves hardenability well.
To increase the hardening layer and reduce the CVG grain (which increases the quality of steel), the following two elements are used: molybdenum and tungsten. In addition to the fact that they form even stronger carbides than carbon, these metals are very refractory and are centers of crystallization, crushing the grains, which increases the ductility of the metal without changing its hardness, and also increases the hardenable layer.
Alloying with silicon and manganese (this element is not indicated in the labeling due to its secondary influence in importance). Silicon is not a carbide-forming element; it pushes carbides to the grain boundaries, thus strengthening the metal. Manganese in this case is used for balance, since in this concentration it increases viscosity and ductility, and reduces the undesirable consequences of such an increase in strength.
Foreign analogues
Metallurgical plants smelt steel not only in the CIS countries, but also far abroad, and it just so happens that the same steel, or its “relatives” of similar composition, is found every now and then in some distant country. This is no longer uncommon and, for example, those who are forced to work with certain foreign suppliers are forced to know what material they are actually dealing with. Well, for people who are less burdened, you can use the following list of foreign analogues of HVG steel:
- USA - 01 or T31507;
- Europe - 107WCr5;
- China - CrWMn;
- Japan - SKS2 or SKS3.
With this small list at hand, anyone will be able to determine what kind of steel a particular tool made abroad is made of.
Source
Heat treatment of the HVG brand
HVG steel is subjected to the following types of heat treatment:
- Annealing - used to soften steel before machining. This procedure is used if necessary, namely, if the workpieces have been subjected to cold deformation.
- Hardening is carried out after final machining, i.e. after manufacturing a part (tool, etc.), giving it its final shape, without taking into account grinding. The workpiece is heated to temperatures of 830 ºC and cooled by immersion in oil. After this, the crystalline bonds change and the martensitic structure, very strong and brittle, predominates. To break such a part, it is enough to apply muscular force.
- Relieve internal tension and eliminate unwanted consequences with the help of vacation. This is heating and holding the metal at a temperature below ... transformations, specifically for this steel it is 180 C with cooling in air. Coagulation of martensite needles occurs and the formation of a sorbitol or troostite structure, which is the most durable and ductile.
HVG steel has a successful combination of strength and corrosion resistance. Relatively low cost and good machinability allow it to be widely used in production. Disadvantages include a narrow range of quenching and annealing temperatures (steel is easy to burn out) and softening at temperatures above 200 ºC.
Rate this article:
Rating: 5/5 — 2 votes
Physical and mechanical properties
The chemical composition of the metal includes 1-1.6% tungsten, which gives the element additional resistance to wear. To achieve the required hardness, chromium and carbon are added to the composition in a ratio of 1%. The presence of silicon (0.4%) increases tempering resistance, and manganese (1-2%) ensures the integrity of the structure.
CVG itself has the following characteristics:
- at T=20 °C the density of the product will be 7850 kg/m3;
- with a temperature of 100 °C, the coefficient of linear expansion (a10 6) will be 11 DEGREES, and the density will decrease by 20 units;
- at T=200 °C a10 6 will be 12;
- when heated to 600°C, the expansion will reach 14.5 degrees, and “p” will decrease to 7660.
It is important to note that carbon is the main component of CVG , which should be at least 1%. This value turns out to be overestimated, which distinguishes this brand from the rest.
An important indicator is corrosion resistance, which makes it possible to use rolled metal to create complex units. The general chemical structure is as follows:
All compounds are added in such a proportion as to provide the ingots with better hardenability, reduce deformation and eliminate the likelihood of cracks. The result is high-grade carbon steel.
Steel 60ХГ / Auremo
Barrels of rolls of rail and beam mills and section mills in delivery condition
500 – – – – – 255-302 –
Rolls with a diameter of up to 600 mm. Planting in an oven at 650 °C (holding for 4 hours), heating at a rate of 100 °C/h to 820-860 °C (holding for 4 hours), cooling in air to 400 °C, then with the oven to 360 °C (holding 10 hours), heating at a rate of 100 °C/h to 630-660 °C (holding time 50 hours), cooling at a rate of 40 °C/h to 400 °C, then from 15 °C/h to 120 °C (holding time 4 h), cooling in air (the place where samples are cut is indicated)
– 460-520 810-900 15-18 30-38 240-390 229-255 –
Barrels of rolls of rail and beam mills and section mills in delivery condition
950 – – – – – 229-285 –
Rolls with a diameter of up to 600 mm. Planting in an oven at 650 °C (holding for 4 hours), heating at a rate of 100 °C/h to 820-860 °C (holding for 4 hours), cooling in air to 400 °C, then with the oven to 360 °C (holding 10 hours), heating at a rate of 100 °C/h to 630-660 °C (holding time 50 hours), cooling at a rate of 40 °C/h to 400 °C, then from 15 °C/h to 120 °C (holding time 4 h), cooling in air (the place where samples are cut is indicated)
– 510-550 860-910 15-17 32-36 270-290 241-255 –
Rolls as delivered
600 440-550 800-910 ≥18 ≥38 ≥350 – –
Rolls with a diameter of up to 600 mm. Planting in an oven at 650 °C (holding for 4 hours), heating at a rate of 100 °C/h to 820-860 °C (holding for 4 hours), cooling in air to 400 °C, then with the oven to 360 °C (holding 10 hours), heating at a rate of 100 °C/h to 630-660 °C (holding time 50 hours), cooling at a rate of 40 °C/h to 400 °C, then from 15 °C/h to 120 °C (holding time 4 h), cooling in air (the place where samples are cut is indicated)
– 440-550 800-910 15-20 36-41 270-440 229-255 –
– 430-540 810-920 12-18 28-36 240-340 229-255 –
Mill rolls Surface hardening with HFC heating + Low tempering + Cooling
– – – – – – – 51-63
Rolls with a diameter of over 600 mm. Planting in an oven at 630-660 °C (holding time 8 hours), cooling in air to 330-360 °C, heating at a rate of 100 °C/h to 820-860 °C (holding time 4 hours), cooling in air to 330 -360 °C (holding time 6 hours), heating at a rate of 100 °C/h to 630-660 °C (holding time 40-50 hours), cooling in air (location of sample cutting is indicated)
– 390-580 710-950 14-21 28-51 150-590 207-269 –
Mill rolls Surface hardening with HFC heating + Low tempering + Cooling
– – – – – – – 42-57
Rolls with a diameter of over 600 mm. Planting in an oven at 630-660 °C (holding time 8 hours), cooling in air to 330-360 °C, heating at a rate of 100 °C/h to 820-860 °C (holding time 4 hours), cooling in air to 330 -360 °C (holding time 6 hours), heating at a rate of 100 °C/h to 630-660 °C (holding time 40-50 hours), cooling in air (location of sample cutting is indicated)
– 390-580 710-940 14-20 28-52 180-590 207-255 –