Aluminum industry
- a branch of non-ferrous metallurgy, uniting enterprises producing aluminum metal. In terms of the scale of production and consumption, aluminum ranks first among the sub-sectors of non-ferrous metallurgy, and among the metallurgy sectors in volume it is second only to steel production. The most important consumers of aluminum industry products are: aviation, electrical engineering, automotive and a number of other branches of the mechanical engineering and metalworking industries, as well as construction, railway transport, chemical and food industries.
TOP 10 aluminum producing countries
Today scientists know about 300 types of aluminum compounds. The main feature is wear resistance and the ability to be processed without loss of quality. Many countries are engaged in the extraction and smelting of aluminum.
USA
Metal production in the USA is in jeopardy due to the unprofitability of maintaining technical premises. Today, only seven companies operate throughout America. At the same time, the country still remains on the list of leaders in production. Thus, 910 thousand tons were smelted last year.
Saudi Arabia
Due to the increase in demand for metal, the government of Saudi Arabia is considering the option of developing this industry by opening new factories. Most of the material produced is used within the state. A smaller part is spent on sales to other countries. In 2022, 936 thousand tons of metal were produced.
Bahrain
The end of last year showed how rapidly the amount of metal produced in Bahrain is increasing. It is planned that in 2022 the figures will increase by 20%. At the same time, 1,115 million tons were produced in 2022.
Norway
Factories of other countries, for example, Germany, Denmark, Brazil, etc., are located on the territory of the state. Production indicators for last year, according to statistical data, were as low as possible and led to large losses. Despite this, Norway remains on the list of leading countries, producing an average of 1,640 million tons per year.
Australia
Aluminum production in Australia is gradually increasing every year, occupying a leading position in the list of producers. According to the Australian Department of Industry, 2021-2021 will be a consistently high year in terms of performance. On average, production will be 1,680 million tons per year.
United Arab Emirates
The UAE has expanded significantly in scale over the past decades. At the same time, developing within the state, its influence on the global industrial market increases. The largest metal production company, Emirates Global Aluminum (EGA), showed good results last year, producing 2,940 million tons of aluminum.
Canada
Despite the conflict between the union of the Canadian aluminum smelter Aluminerie de Becancour (ABI) and American shareholders, metal production was almost at full capacity last year. By the end of 2022, it is planned to fully resume all sectors of the enterprise and increase the result by at least 5%. So, last year, a plant in the province of Quebec produced 3,200 million tons of metal.
India
Vedanta Group, an aluminum manufacturing company in India, plans to begin construction of a new plant in the fourth quarter of 2022. Today, India is one of the three world leaders in providing other countries with metal. Last year, 3,540 million tons were produced.
Russia
Most of the aluminum production enterprises in the Russian Federation are located in Siberia. The exported portion increased by 13% compared to last year. The total amount of aluminum produced was 3,620 million tons.
China
At the end of the first quarter of 2022, aluminum production in China fell by 2%. At the same time, without in any way affecting its leading position in the world. At the end of last year, according to RUSAL, China produced 35 million 710 thousand tons. With such indicators, no country can come close to China in terms of production volume.
Source
Aluminum: properties, production and application
Physical properties:
- High thermal and electrical conductivity.
- Resistant to low temperatures.
- Density – 2712 kg/m3.
- Melting point: 6580C – technical metal; 6600C – pure metal.
- Plastic. It can be used to produce thin sheets and foil.
- Good weldability.
- Has good reflective ability.
Chemical properties:
- Aluminum is highly active.
- In air it forms an oxide film, which further provides protection against corrosion and does not allow it to react with a number of oxidizing agents.
- Under normal conditions, it reacts with bromine and chlorine.
- When the temperature rises, it forms compounds with nitrogen, iodine, oxygen, sulfur, phosphorus, and carbon.
- Interacts well with alkalis.
- Forms many alloys with metals.
Natural aluminum compounds
Aluminum is almost never found in its pure form (the only exception may be special reducing conditions that form, for example, when magma comes out of volcanic vents). Much more often its compounds are present in the earth's crust:
- Corundum (mineral varieties: ruby, sapphire, padparadscha, star ruby, leucosapphire, common corundum and emery)
- Boehmit.
- Diaspora.
- Chrysoberyl (Alexandrite).
- Gibbsite.
- Kyanite.
- Kaolinite.
- Muscovite.
- Alunites.
- Anorthitis.
- Andalusite.
- Nephelines.
- Spodumene.
- Sillimanite.
- Cryolite.
- Albite.
- Otroclase.
- Beryl.
- Spinel.
- Feldspars.
- Mica.
- Bauxite.
- Alumina.
In reservoirs, the aluminum content varies within:
- From 0.001 to 10 mg/l – freshwater basins of rivers and lakes.
- 0.01 mg/l – sea water.
Aluminum production
Aluminum is one of the most sought-after metals in modern industry. However, for its production it is necessary to go through several stages, spend a significant amount of energy, transport and raw materials, and use a lot of personnel.
Bauxite mining
The main type of ore for producing aluminum is bauxite, and they are of high quality when the content of the desired mineral is 50% or more. In nature, bauxite is presented in a clay-like form, a mass of red-brown brick color. Industrial use is determined by the morphology, composition of rocks, and conditions of occurrence of ore bodies of deposits.
This mineral is extracted using both open (the most common) and closed methods (used at significant depths, about 500 m and below). Carrying out drilling and blasting operations, using selective methods and using milling technologies.
Alumina production
The next stage of aluminum production is the Bayer method, which produces 90% of the world's alumina - aluminum oxide Al2O3, which is a white powder. The method is quite simple and economical, but is applicable only for bauxites of high quality and low impurity content (silica is best suited for these purposes).
Splitting up
First of all, the mined bauxite is subjected to crushing, that is, crushing, splitting and impact in order to obtain a material of the required size and then grind it using abrasion. This makes it possible to bring the material to the opening of the grains of the desired component, so that in the future the raw material can completely release the aluminum contained in it.
Leaching
After which the crushed aluminum oxide is dissolved in concentrated alkali. To achieve maximum effect, lime is added to the solution. As a result of this technological process, a pulp is obtained containing sodium aluminate and foreign impurities that were originally part of bauxite - red mud. The ballast is removed, and the useful composition is decomposed.
Decomposition
The process of “twisting”—the separation of crystalline sodium aluminate into a precipitate—is called decomposition. A rather complex and lengthy procedure, including dilution with water followed by cooling of the solution in tubular heat exchangers, is divided into two stages:
- Hydrolysis of the solution to produce aluminum hydroxide.
- Crystallization accelerated by seeding and stirring.
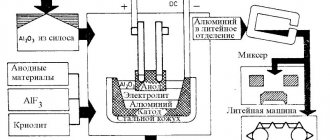
Electrolysis
The next stage of production is electrolysis, performed at a temperature of 9500C in baths with molten cryolite. An electric current of more than 400 kA passed through the solution frees aluminum from oxygen. Liquid metal is collected at the bottom of the bath for further use either as ingots sent to consumers, or for the production of alloys.
Foundry
The use of aluminum in its pure form is difficult due to insufficient strength, so impurities are used to increase it. Chemical compounds of this metal obtained in metallurgical processes are divided into two types of alloys:
- Foundry.
- Structural - obtained as a result of deformation, which may or may not be subsequently subjected to thermal effects.
Casting alloys
The main additives (alloying elements) in the production of cast aluminum alloys are:
- Magnesium, manganese, copper, silicon, zinc.
- Beryllium, lithium, zirconium, and titanium are used to a lesser extent.
High performance of the resulting casting is determined by:
- The ability to fill complex shapes with the melt, which is a manifestation of good casting properties.
- Insignificant mass of manufactured products, due to the low specific gravity of aluminum itself.
- Resistant to corrosion.
- Increased mechanical strength and hardness compared to the original material.
- Compliance to processed influences.
According to the resulting qualities, aluminum alloys can be classified into three types:
- Structural sealed. They have good anti-corrosion and casting properties.
- Corrosion resistant. Resistant to aggressive chemical environments and water. They are quite easy to process during the cutting process and are easy to weld.
- Heat resistant. Retain their properties at elevated temperatures and mechanical stress.
Rental
Using hot or cold rolling in rolling mills, aluminum is given a shape suitable for further use. This can be foil, sheets of various thicknesses, tires. In the future, rods, pipes, and various profiles can be made from these products, which are widely used in various sectors of the economy.
Extrusion
Extrusion is the pressing of metal softened as a result of the melt through a forming profile. This process is most clearly demonstrated by an ordinary household meat grinder. The process makes it possible to compact and increase the strength of the material of the extruded profile product compared to the original raw material.
Aluminum recycling
Modern economic conditions and environmental standards have created a number of requirements, the fulfillment of which is best ensured by the technology of recycling aluminum waste. The fact is that the metal is preserved for quite a long time without being subject to corrosion, and, if necessary, in a compressed state. Also, the processing process does not require much energy consumption.
The market for secondary aluminum raw materials is represented by waste products:
- Electrical profile. As a rule, this material contains a minimal amount of impurities.
- Food sector – dishes and containers.
- Profile format, this material is often used when cutting furniture and construction parts.
- Motor - usually silumin.
- Means of aviation and water transport - airplanes, helicopters, boats.
The collected aluminum scrap is sorted, pressed, dried, and melted. After which it is sent to consumers.
As a reducing agent
Due to its chemical properties, aluminum is a strong reducing agent, as it reacts well with oxygen. This property is used for the reduction of halides and rare metals.
In ferrous metallurgy
Steel production uses aluminum and its alloys as deoxidizers, allowing not only to get rid of oxygen, but also to eliminate the possible porosity of finished products under the influence of carbon monoxide bubbles. Also in this industry it is used as alloying additives and modifiers in the form of granules, powder and powder.
Aluminum alloys
There are whole series of aluminum-based alloys that are in great demand as structural materials. These are mainly compounds with magnesium, manganese, copper, alloyed in turn with magnesium, manganese, iron and silicon. Aluminum alloys have ductility, strength, manufacturability, resistance to vibration and corrosion resistance.
Aluminum as an additive to other alloys
Aluminum is also used in alloys of other metals:
- magnesium,
- aluminum bronze,
- fechral,
- become.
Jewelry
Recently, silver-white metal has again, like a century and a half ago, begun to attract the attention of jewelers who want to add some variety to the standard set of materials used. And not only as cheap jewelry, but also as the basis for precious products, as well as independent exquisite products.
Cutlery
Aluminum cutlery is currently not as popular as before, due to reasons of harm to human health and loss of appearance during use. Although a certain number of them are present in public catering. Also, some utensils, such as spoons, forks, pots, flasks, are used as army utensils and tourist equipment.
Glass making
In the glass and glass products industry, aluminum and its compounds are widely used:
- Alumina (aluminum oxide) increases strength, hardness and resistance to temperature and chemical influences.
- Aluminum salts are necessary for the production of special types of glass.
Food industry
In addition to the food additive in E173 food products, aluminum is included in antacids intended to coat the gastrointestinal tract for pain relief in a number of diseases.
Military industry
Due to its properties: lightness and flexibility, aluminum is widely used in the designs of various types of weapons: from pistols and machine guns to tanks, missiles and aircraft. Even such exotic products for our time as crossbows, swords, rapiers, and sabers cannot do without this mineral.
In rocket technology
In addition to using aluminum as a material for making rockets, satellites and other spacecraft; powder from this metal, as well as an oxidizer based on it, are important components of solid fuel - fuel for launching shuttles and rockets.
Aluminum energy
The intermediate role of aluminum in enhancing the production of primary energy carriers or directly thermal and electrical energy manifests itself in a relatively new industry - aluminum energy. It is here, in the process of oxidation of this unique mineral, that:
- Hydrogen from water.
- Electricity - due to exposure to oxygen in the air in electrochemical generators.
Deposits in Russia and the world
50 aluminum ore deposits are located in Russia. The largest of them are located in the Arkhangelsk, Belgorod, Leningrad and Sverdlovsk regions, as well as in the Komi Republic.
The world's bauxite deposits are located in 7 regions of the world:
- Africa - Guinea and a number of countries in the center and west of the continent.
- South America - Brazil, Venezuela, Guyana and Suriname.
- Caribbean Islands - Jamaica.
- Europe – Greece and a number of regions of Russia.
- Asia – India, China, Türkiye.
- Australia.
World reserves
Proven reserves of aluminum ores are estimated at 30 billion tons; resource estimates from the US Geological Survey bring this figure to 75 billion tons.
Aluminum producing countries
In 2022, global aluminum smelting reached 60 million tons, distributed by country as follows:
- China – 33 million tons.
- Russia – 3.71 million tons.
- India – 3.68 million tons.
- Canada - 2.9 million tons.
- UAE – 2.6 million tons.
- Australia – 1.6 million tons.
- Norway – 1.35 million tons.
- Bahrain – 0.995 million tons.
- Saudi Arabia - 0.916 million tons.
- USA – 0.89 million tons.
Aluminum occupies a leading position among the non-ferrous metals produced on the planet, second only to steel in the general metallurgical list.
Aluminum ore - from mining to metal production. Leading countries in aluminum production
Hello, dear readers of the Tyulyagin project! Today we will talk about aluminum. In the article you will learn why aluminum is smelted and where it is used. But, mainly, the article will focus on comparing different countries in the production and smelting of aluminum. In the article you will find out which country is the largest aluminum producer in the world , as well as the largest exporters and importers of aluminum in the world . In addition, we will talk about the smelting of primary aluminum in Russia. Here you will find unique statistics on aluminum smelting in the USSR and Russia since 1932. Make yourself comfortable and enjoy reading.
What is aluminum produced for and where is it used?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal. Aluminum is the most abundant metal in the world. Due to its lightness, strength, functionality and resistance to corrosion, aluminum has become popular and is used in many structures.
If you look closely, you can find aluminum almost anywhere you go. It is used in homes, in transport, in various equipment, including mobile phones and computers, and in other household items - refrigerators, microwaves, furniture and so on.
Bauxite ore is the basis of global aluminum production
The silver metal itself is directly obtained from alumina. This raw material is aluminum oxide (Al2O3), obtained from ores:
The most common source of starting material is bauxite, which is considered the main aluminum ore.
Despite the more than 130-year history of discovery, it has still not been possible to understand the origin of aluminum ore. It is possible that simply in each region the raw materials were formed under the influence of certain conditions. And this makes it difficult to derive one universal theory about the formation of bauxite. There are three main hypotheses about the origin of aluminum raw materials:
- They were formed due to the dissolution of certain types of limestone as a residual product.
- Bauxite was obtained as a result of weathering of ancient rocks with their further transport and deposition.
- The ore is the result of chemical processes of decomposition of iron, aluminum and titanium salts, and fell as sediment.
However, alunite and nepheline ores were formed under different conditions from bauxite. The former were formed under conditions of active hydrothermal and volcanic activity. The second - at high magma temperatures.
Bauxite
As a result, alunites generally have a crumbly porous structure. They contain up to 40% of various aluminum oxide compounds. But, in addition to the aluminum-bearing ore itself, the deposits, as a rule, contain additives, which affects the profitability of their mining. It is considered profitable to develop a deposit with a 50 percent ratio of alunites to additives.
Properties of aluminum ore
Bauxite is a complex compound of oxides of aluminum, iron and silicon (in the form of various quartz), titanium, as well as with a small admixture of sodium, zirconium, chromium, phosphorus and others.
Copper ore: properties, application, mining
The most important property in aluminum production is the “breakability” of bauxite. That is, how easy it will be to separate unnecessary silicon additives from it in order to obtain the feedstock for metal smelting.
The basis for producing aluminum is alumina. To form it, the ore is ground into a fine powder and heated with steam, separating most of the silicon. And this mass will become the raw material for smelting.
To obtain 1 ton of aluminum, you will need about 4-5 tons of bauxite, from which, after processing, about 2 tons of alumina are formed, and only then you can get the metal.
Aluminum mining methods
Aluminum is a relatively young metal, first mined just over a century ago. Throughout time, aluminum mining technology has been constantly improved, taking into account all chemical and physical properties.
The production of metal is possible only from alumina, for the formation of which the ore is crushed to a powder state and heated with steam. This way it is possible to get rid of most of the silicon and leave the optimal raw material for subsequent smelting.
Aluminum ore is mined using an open-pit method if its occurrence is shallow. Bauxite and nepheline, due to their dense structure, are usually cut using a surface miner using a milling method. Alunites are a type of loose rock, which is why a quarry excavator is optimal for removing it. The latter immediately loads the rock onto dump trucks for further transportation.
After the extraction of primary raw materials, several mandatory stages of rock processing follow in order to obtain alumina:
- Transportation to the preparatory workshop, where crushing equipment crushes the rock to a fraction of about 110 mm.
- The prepared raw materials, along with additional components, are sent for further processing.
- The rock is sintered in furnaces. If necessary, the aluminum ore is leached. This produces a liquid aluminate solution.
- The next stage is decomposition. As a result, an aluminate pulp is formed, which is sent for separation and evaporation of the liquid.
- Cleaning from excess alkalis and oven calcination.
The result is dry alumina, ready for aluminum production. The final stage is hydrolysis treatment. In addition to the method described above, aluminum is also mined using the mine method. This is how the rock is cut out from the layers of the earth.
Technology for the development of aluminum deposits. Aluminum ore mining methods
Methods of mining aluminum ore If the depth of occurrence of aluminum-bearing rocks is insignificant, they are mined using open-pit mining. But the process of cutting off ore layers will depend on its type and structure.
- Crystalline minerals (usually bauxite or nepheline) are removed by milling. Mineral miners are used for this purpose. Depending on the model, such a machine can cut a layer up to 600 mm thick. The rock thickness is developed gradually, forming shelves after passing through one layer.
This is done to ensure the safe position of the operator’s cabin and running gear, which in the event of an unexpected collapse will be at a safe distance.
- Loose aluminum-bearing rocks preclude the use of milling. Since their viscosity clogs the cutting part of the machine. Most often, these types of rocks can be cut using mining excavators, which immediately load the ore onto dump trucks for further transportation.
Transportation of raw materials is a separate part of the entire process. Usually, whenever possible, enrichment plants try to be built near mining sites. This allows the use of belt conveyors to supply ore for processing. But, more often, confiscated raw materials are transported by dump trucks. The next stage is the enrichment and preparation of rock to obtain alumina.
- The ore is moved using a belt conveyor to the raw material preparation workshop, where a number of crushing devices can be used, crushing the minerals one by one to a fraction of approximately 110 mm.
- The second section of the preparatory workshop supplies prepared ore and additional additives for further processing.
- The next stage of preparation is sintering the rock in furnaces.
Also at this stage, it is possible to process raw materials by leaching with strong alkalis. The result is a liquid aluminate solution (hydrometallurgical processing).
- The aluminate solution goes through a decomposition stage. At this stage, an aluminate pulp is obtained, which in turn is sent for separation and evaporation of the liquid component.
- After which this mass is cleaned of unnecessary alkalis and sent for calcination in ovens. As a result of this chain, dry alumina is formed, which is necessary for the production of aluminum by hydrolysis treatment.
The complex technological process requires large amounts of fuel and limestone, as well as electricity. This is the main factor in the location of aluminum smelters - near a good transport interchange, and the presence of nearby deposits of the necessary resources.
However, there is also a mining method of extraction, when rock is cut out from the layers according to the principle of coal mining. After which the ore is sent to similar plants for enrichment and aluminum extraction.
One of the deepest “aluminum” adits is located in the Urals in Russia, its depth reaches 1550 meters!
How is aluminum ore mined and where is it used?
Aluminum is a metal coated with a matte silver oxide film, the properties of which determine its popularity: softness, lightness, ductility, high strength, corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity and lack of toxicity. In modern high technologies, the use of aluminum is given a leading place as a structural, multifunctional material.
The greatest value for industry as a source of aluminum is natural raw materials - aluminum ore , a component of rock in the form of bauxite, alunite and nepheline.
The industrial scale of the “winged” metal began only in the 20th century. Today, it is one of the sought-after materials in various industries from electronics to the space and aviation industries.
Aluminum ore was first obtained in the form of a silvery metal in 1825 in a volume of just a few milligrams, and before the advent of mass production, this metal was more expensive than gold.
For example, one of the royal crowns of Sweden contained aluminum, and D. I. Mendeleev in 1889 received an expensive gift from the British - scales made of gold and aluminum.
What raw materials are needed to produce aluminum ore? How is one of the most essential materials of our time produced?
Bauxite ore is the basis of global aluminum production
The silver metal itself is directly obtained from alumina.
This raw material is aluminum oxide (Al2O3), obtained from ores:
- Bauxite;
- Alunitov;
- Nepheline syenites.
The most common source of starting material is bauxite, which is considered the main aluminum ore.
Despite the more than 130-year history of discovery, it has still not been possible to understand the origin of aluminum ore. It is possible that simply in each region the raw materials were formed under the influence of certain conditions. And this makes it difficult to derive one universal theory about the formation of bauxite.
There are three main hypotheses about the origin of aluminum raw materials:
- They were formed due to the dissolution of certain types of limestone as a residual product.
- Bauxite was obtained as a result of weathering of ancient rocks with their further transport and deposition.
- The ore is the result of chemical processes of decomposition of iron, aluminum and titanium salts, and fell as sediment.
However, alunite and nepheline ores were formed under different conditions from bauxite. The former were formed under conditions of active hydrothermal and volcanic activity. The second - at high temperatures of magma.
As a result, alunites generally have a crumbly porous structure. They contain up to 40% of various aluminum oxide compounds. But, in addition to the aluminum-bearing ore itself, the deposits, as a rule, contain additives, which affects the profitability of their mining. It is considered profitable to develop a deposit with a 50 percent ratio of alunites to additives.
Nephelines are usually represented by crystalline samples, which, in addition to aluminum oxide, contain additives in the form of various impurities. Depending on the composition, this type of ore is classified into types. The richest contain up to 90% nephelines, second-rate 40-50%; if the minerals are poorer than these indicators, then it is not considered necessary to develop them.
Having an idea of the origin of minerals, geological exploration can quite accurately determine the location of aluminum ore deposits. Also, the formation conditions, which influence the composition and structure of minerals, determine the extraction methods. If the deposit is considered profitable, its development is established.
Properties of aluminum ore
Bauxite is a complex compound of oxides of aluminum, iron and silicon (in the form of various quartz), titanium, as well as with a small admixture of sodium, zirconium, chromium, phosphorus and others.
The most important property in aluminum production is the “breakability” of bauxite. That is, how easy it will be to separate unnecessary silicon additives from it in order to obtain the feedstock for metal smelting.
Natural deposits of bauxite, nepheline, alunite, clay, and kaolin can serve as a source of raw materials. Bauxite is the most saturated with aluminum compounds. Clays and kaolins are the most common rocks with a significant alumina content. Deposits of these minerals are found on the surface of the earth.
Aluminum ore in nature exists only in the form of a binary compound of metal with oxygen. This compound is extracted from natural mining ores in the form of bauxite, consisting of oxides of several chemical elements: aluminum, potassium, sodium, magnesium, iron, titanium, silicon, phosphorus.
The basis for producing aluminum is alumina. To form it, the ore is ground into a fine powder and heated with steam, separating most of the silicon. And this mass will become the raw material for smelting.
To obtain 1 ton of aluminum, you will need about 4-5 tons of bauxite, from which, after processing, about 2 tons of alumina are formed, and only then you can get the metal.
Technology for the development of aluminum deposits. Aluminum ore mining methods
When the depth of occurrence of aluminum-bearing rocks is insignificant, they are mined using open-pit mining. But the process of cutting off ore layers will depend on its type and structure.
- Crystalline minerals (usually bauxite or nepheline) are removed by milling. Mineral miners are used for this purpose. Depending on the model, such a machine can cut a layer up to 600 mm thick. The rock thickness is developed gradually, forming shelves after passing through one layer.
This is done to ensure the safe position of the operator’s cabin and running gear, which in the event of an unexpected collapse will be at a safe distance.
- Loose aluminum-bearing rocks preclude the use of milling. Since their viscosity clogs the cutting part of the machine. Most often, these types of rocks can be cut using mining excavators, which immediately load the ore onto dump trucks for further transportation.
Transporting raw materials is a separate part of the entire process. Usually, whenever possible, enrichment plants try to be built near mining sites. This allows the use of belt conveyors to supply ore for processing. But, more often, confiscated raw materials are transported by dump trucks. The next stage is the enrichment and preparation of rock to obtain alumina.
- The ore is moved using a belt conveyor to the raw material preparation workshop, where a number of crushing devices can be used, crushing the minerals one by one to a fraction of approximately 110 mm.
- The second section of the preparatory workshop supplies prepared ore and additional additives for further processing.
- The next stage of preparation is sintering the rock in furnaces.
Also at this stage, it is possible to process raw materials by leaching with strong alkalis. The result is a liquid aluminate solution (hydrometallurgical processing).
- The aluminate solution goes through a decomposition stage. At this stage, an aluminate pulp is obtained, which in turn is sent for separation and evaporation of the liquid component.
- After which this mass is cleaned of unnecessary alkalis and sent for calcination in ovens. As a result of this chain, dry alumina is formed, which is necessary for the production of aluminum by hydrolysis treatment.
The complex technological process requires large amounts of fuel and limestone, as well as electricity. This is the main factor in the location of aluminum smelters - near a good transport interchange, and the presence of nearby deposits of the necessary resources.
However, there is also a mining method of extraction, when rock is cut out from the layers according to the principle of coal mining. After which the ore is sent to similar plants for enrichment and aluminum extraction.
One of the deepest “aluminum” adits is located in the Urals in Russia, its depth reaches 1550 meters!
Leading countries in aluminum ore production
The main deposits of aluminum are concentrated in regions with a tropical climate, and most of the 73% of deposits are found in just 5 countries: Guinea, Brazil, Jamaica, Australia and India. Of these, Guinea has the richest reserves, more than 5 billion tons (28% of the world share).
If we divide reserves and production volumes, we can get the following picture:
- 1st place – Africa (Guinea).
- 2nd place - America.
- 3rd place – Asia.
- 4th place – Australia.
- 5th – Europe.
The top five countries in aluminum ore production are presented in the table
| A country | Production volumes million tons |
| China | 86,5 |
| Australia | 81,7 |
| Brazil | 30,7 |
| Guinea | 19,7 |
| India | 14,9 |
Also, the main producers of aluminum ores include: Jamaica (9.7 million tons), Russia (6.6), Kazakhstan (4.2), Guyana (1.6).
Development of aluminum ore deposits in Russia
In our country there are several rich deposits of aluminum ores, concentrated in the Urals and in the Leningrad region. But the main method of extracting bauxite in our country is the more labor-intensive closed mine method, which extracts about 80% of the total mass of ores in Russia.
The leaders in deposit development are the joint-stock company Sevuralboxitrude, JSC Baksitogorsk Alumina, and the South Ural Bauxite Mines. However, their reserves are running out. As a result, Russia has to import about 3 million tons of alumina per year.
| Field | Reserves |
| Little Red Riding Hood (Ural) | For 19 years of production |
| Gornostayskoye and Gornostaysko-Krasnooktyabrskoye | For 18 years of production |
| Blinovo-Kamenskoye | 10 years |
| Kurgazskoe | 10 years |
| Radynsky quarry | 7 years |
In total, 44 deposits of various aluminum ores (bauxite, nepheline) have been explored in the country, which, according to estimates, should be enough for 240 years, with such mining intensity as today.
The import of alumina is due to the low quality of the ore in the deposits, for example, bauxite with a 50% alumina composition is mined at the Red Cap deposit, while in Italy rock with 64% aluminum oxide is extracted, and in China 61%.
Applications of Aluminum Ore
Basically, up to 60% of ore raw materials are used to produce aluminum. However, the rich composition makes it possible to extract from it other chemical elements: titanium, chromium, vanadium and other non-ferrous metals, which are necessary primarily as alloying additives to improve the quality of steel.
As mentioned above, the technological chain for producing aluminum necessarily passes through the stage of formation of alumina, which is also used as fluxes in ferrous metallurgy.
The rich composition of elements in aluminum ore is also used to produce mineral paint. Also, the smelting method produces alumina cement - a quickly hardening, strong mass.
Another material obtained from bauxite is electrocorundum. It is obtained by smelting ore in electric furnaces. It is a very hard substance, second only to diamond, making it popular as an abrasive.
Also, in the process of obtaining pure metal, waste is formed - red mud. The element scandium is extracted from it, which is used in the production of aluminum-scandium alloys, which are in demand in the automotive industry, rocket science, production of electric drives, and sports equipment.
Alternative to aluminum ores
The development of modern production requires increasingly large volumes of aluminum. However, it is not always profitable to develop deposits or import alumina from abroad. Therefore, metal smelting using recycled materials is increasingly being used.
For example, countries such as the USA, Japan, Germany, France, and the UK mainly produce secondary aluminum, amounting to up to 80% of global smelting.
Secondary metal is much cheaper compared to primary metal, the production of which requires 20,000 kW of energy/1 ton.
Today, aluminum, obtained from various ores, is one of the most popular materials for producing durable and lightweight products that are resistant to corrosion. No alternatives to metal have been found yet, and in the next decade.
Sources:
Leading countries in aluminum ore production
The main deposits of aluminum are concentrated in regions with a tropical climate, and most of the 73% of deposits are found in just 5 countries: Guinea, Brazil, Jamaica, Australia and India. Of these, Guinea has the richest reserves, more than 5 billion tons (28% of the world share).
If we divide reserves and production volumes, we can get the following picture:
- 1st place – Africa (Guinea).
- 2nd place - America.
- 3rd place – Asia.
- 4th place – Australia.
- 5th – Europe.
The top five countries in aluminum ore production are presented in the table
| A country | Production volumes million tons |
| China | 86,5 |
| Australia | 81,7 |
| Brazil | 30,7 |
| Guinea | 19,7 |
| India | 14,9 |
Also, the main producers of aluminum ores include: Jamaica (9.7 million tons), Russia (6.6), Kazakhstan (4.2), Guyana (1.6).
Rating of world countries for aluminum production and smelting for 2021
Since 2002, the leader in aluminum smelting in the world has been China . Today China smelts more than half of the world's aluminum production. At the end of 2022, China smelted 36,000 thousand tons , while 64,000 thousand tons of aluminum were produced worldwide. Following China are India and Russia ; they smelt approximately equal amounts of aluminum per year - 3,700 and 3,600 thousand tons, respectively.
For a long time, the United States was the leader in aluminum production in the world, until 2000. Today they are only at the end of the top ten with primary aluminum production at about 1,100 thousand tons. A complete list of countries by primary aluminum smelting can be found in the table below. USGS (United States Geological Survey) data was used as the main source of statistics.
| Rank | A country | Aluminum smelting, thousand tons | Year |
| World | 64000 | 2019 | |
| 1 | China | 36000 | 2019 |
| 2 | India | 3700 | 2019 |
| 3 | Russia | 3600 | 2019 |
| 4 | Canada | 2900 | 2019 |
| 5 | UAE | 2700 | 2019 |
| 6 | Australia | 1600 | 2019 |
| 7 | Bahrain | 1400 | 2019 |
| 8 | Norway | 1300 | 2019 |
| 9 | USA | 1100 | 2019 |
| 10 | Saudi Arabia | 916 | 2017 |
| 11 | Iceland | 870 | 2018 |
| 12 | Malaysia | 760 | 2017 |
| 13 | South Africa | 716 | 2017 |
| 14 | Brazil | 660 | 2018 |
| 15 | Qatar | 650 | 2017 |
| 16 | Mozambique | 577 | 2017 |
| 17 | Germany | 550 | 2017 |
| 18 | Argentina | 433 | 2017 |
| 19 | France | 430 | 2017 |
| 20 | Spain | 360 | 2017 |
| 21 | Iran | 338 | 2017 |
| 22 | New Zealand | 337 | 2017 |
| 23 | Romania | 282 | 2017 |
| 24 | Egypt | 279 | 2017 |
| 25 | Kazakhstan | 256 | 2017 |
| 26 | Oman | 253 | 2017 |
| 27 | Indonesia | 219 | 2017 |
Dynamics of aluminum production by year in the USSR and Russia since 1932
Above I attach a graph with unique statistics on aluminum smelting in the USSR and Russia since 1932. It was in 1932 that aluminum production began in the country. Until now, aluminum was only imported. Imports of aluminum were also high during the Second World War; at that time, our own capacities were still not enough, and aluminum was actively imported from foreign countries, including the USA, Great Britain and Canada. However, aluminum production grew rapidly in the post-war years. By the end of the 1980s, primary aluminum smelting in the USSR reached 3.5 million tons. Like other industries, after the collapse of the USSR, the production of non-ferrous metals in Russia decreased. This happened in the flesh until 1995. Then the smelting of primary aluminum began to grow and by 2004 Russia exceeded the record smelting of the USSR. Despite this achievement, in recent years, aluminum smelting in Russia has begun to decline, reaching its peak in 2008 at 4.19 million tons; smelting at the end of 2022 amounted to only 3.6 million tons.
Development of aluminum ore deposits in Russia
In our country there are several rich deposits of aluminum ores, concentrated in the Urals and in the Leningrad region. But the main method of extracting bauxite in our country is the more labor-intensive closed mine method, which extracts about 80% of the total mass of ores in Russia.
Foreign investment in Russian industry
The leaders in deposit development are the joint-stock company Sevuralboxitrude, JSC Baksitogorsk Alumina, and the South Ural Bauxite Mines. However, their reserves are running out. As a result, Russia has to import about 3 million tons of alumina per year.
| Field | Reserves |
| Little Red Riding Hood (Ural) | For 19 years of production |
| Gornostayskoye and Gornostaysko-Krasnooktyabrskoye | For 18 years of production |
| Blinovo-Kamenskoye | 10 years |
| Kurgazskoe | 10 years |
| Radynsky quarry | 7 years |
In total, 44 deposits of various aluminum ores (bauxite, nepheline) have been explored in the country, which, according to estimates, should be enough for 240 years, with such mining intensity as today.
The import of alumina is due to the low quality of the ore in the deposits, for example, bauxite with a 50% alumina composition is mined at the Red Cap deposit, while in Italy rock with 64% aluminum oxide is extracted, and in China 61%.
Notes
Sociology Life expectancy · Quality of life · Human potential · Overall happiness · Salary (average) · Income inequality · Intentional homicide · Suicide · Age of sexual consent · Adulthood · Prisoners · Charity · Consumption of: alcohol (beer) · cigarettes · coffee · cars Education Education · Literacy · High school education · Reading · Math and science · Computer literacy Information Technology ICT Development Index · List of countries by number of mobile phones used · List of countries by number of Internet users · List of countries by number of broadband Internet users · List of countries by number of computers per 1000 people Business Economics Ease of doing business · Innovation · Number of patents · Production and extraction of: oil · gas · coal · uranium · electricity · automobiles · iron ore · steel · cast iron · bauxite · copper · aluminum · zinc · manganese · bismuth · cement · cellulose · paper and cardboard · wheat · rye · rice · barley · buckwheat · corn · potatoes · milk · fish · wine · apples · Consumption: oil · Transport: railways · roads · pipelines · inland waterways · shipping · airports · metro Macroeconomics Global competitiveness · GDP (nominal): per person · GDP (PPP): per person, forecast · Budget · External debt · Gold and foreign exchange reserves · Gold reserves · Oil reserves · Gas reserves · Coal reserves · Uranium reserves · Current account balance · Trade balance · Export · Import · Economic complexity Politics, Army, Aerospace Great Powers · Economic Freedom · Freedom of Speech · Democracy · State Failure · Peacefulness · Armed Forces · Military Budget · Nuclear Club · Space Club · Satellites · Astronauts · Police · Doctors Ecology Environmental efficiency · CO2 emissions · CO2 emissions per person
Leading countries in aluminum export and import
As I already wrote, aluminum today is used in many industries, in connection with this, not only its smelting is developed, but also trade. Countries around the world actively export and import aluminum for their own needs.
Thus, the largest exporter of aluminum in the world at the beginning of 2022 is Canada . In dollar terms, Canada exported more than $5.3 billion worth of aluminum. Also among the top five largest aluminum exporters in the world are the Netherlands, the UAE, Russia and India. You can see the full list of aluminum export countries
| № | A country | Aluminum exports, million $ |
| 1 | Canada | 5349 |
| 2 | Netherlands | 5115.8 |
| 3 | UAE | 5113.2 |
| 4 | Russia | 4640.9 |
| 5 | India | 3819.7 |
| 6 | Norway | 2802.1 |
| 7 | Australia | 2775.2 |
| 8 | Malaysia | 2003.2 |
| 9 | Bahrain | 1931.5 |
| 10 | Iceland | 1429.3 |
| 11 | Qatar | 1291.6 |
| 12 | China | 1100.5 |
| 13 | USA | 1050.4 |
| 14 | South Africa | 1009.7 |
| 15 | Saudi Arabia | 967.8 |
| 16 | Germany | 957.7 |
| 17 | Mozambique | 940.3 |
| 18 | Italy | 751.1 |
| 19 | New Zealand | 652.9 |
| 20 | France | 578.2 |
| 21 | Spain | 574.9 |
| 22 | Great Britain | 516.6 |
| 23 | Kazakhstan | 513.3 |
| 24 | Poland | 466.6 |
| 25 | South Korea | 445.5 |
| 26 | Slovakia | 385.1 |
| 27 | Slovenia | 372 |
| 28 | Sweden | 362 |
| 29 | Austria | 323.2 |
| 30 | Oman | 296.3 |
| 31 | Romania | 291.9 |
| 32 | Argentina | 264.7 |
| 33 | Luxembourg | 262.7 |
| 34 | Greece | 256.5 |
| 35 | Belgium | 254.1 |
| 36 | Brazil | 236.1 |
| 37 | Vietnam | 231.7 |
| 38 | Türkiye | 219.9 |
| 39 | Egypt | 196 |
| 40 | Singapore | 187.6 |
| 41 | Switzerland | 187 |
| 42 | Taiwan | 185.6 |
| 43 | Chech republic | 176.5 |
| 44 | Tajikistan | 175.2 |
| 45 | Hungary | 137.1 |
| 46 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 121.1 |
| 47 | Ghana | 106.6 |
| 48 | Cameroon | 100 |
| 49 | Indonesia | 88.7 |
| 50 | Thailand | 88.5 |
| 51 | Azerbaijan | 84.6 |
| 52 | Montenegro | 76.6 |
| 53 | Iran | 76.4 |
| 54 | Japan | 56.6 |
| 55 | Venezuela | 54 |
| 56 | Nigeria | 51.7 |
| 57 | Finland | 31.7 |
| 58 | Albania | 23.4 |
| 59 | Ukraine | 22 |
| 60 | Portugal | 16.5 |
| 61 | Bulgaria | 16 |
| 62 | Serbia | 11.8 |
| 63 | Hong Kong | 11.1 |
| 64 | Ireland | 10.4 |
| 65 | Georgia | 10.3 |
| 66 | Angola | 9 |
| 67 | Iraq | 8.5 |
| 68 | Lebanon | 8 |
| 69 | Estonia | 7.3 |
| 70 | Mongolia | 7.1 |
| 71 | Latvia | 5.7 |
| 72 | Mexico | 5.5 |
| 73 | Syria | 5.3 |
| 74 | Sri Lanka | 5.2 |
| 75 | Jordan | 4.8 |
| 76 | Morocco | 4.2 |
| 77 | Tunisia | 3.9 |
| 78 | Libya | 3.8 |
| 79 | Armenia | 3.4 |
| 80 | Denmark | 2.9 |
| 81 | Kuwait | 2.9 |
| 82 | Croatia | 2.5 |
| 83 | Gabon | 2.3 |
| 84 | Myanmar (Burma) | 2.1 |
| 85 | Cambodia | 2 |
| 86 | Mauritius | 1.8 |
| 87 | Algeria | 1.8 |
| 88 | Pakistan | 1.3 |
| 89 | Kyrgyzstan | 1.2 |
| 90 | Zambia | 1.2 |
| 91 | Colombia | 1.1 |
| 92 | Uzbekistan | 1.1 |
| 93 | Congo | 1 |
| 94 | Afghanistan | 0.9 |
| 95 | North Macedonia | 0.9 |
| 96 | Belarus | 0.8 |
| 97 | Peru | 0.6 |
| 98 | Philippines | 0.4 |
| 99 | Andorra | 0.4 |
| 100 | Tanzania | 0.4 |
| 101 | Lithuania | 0.3 |
| 102 | Equatorial Guinea | 0.3 |
| 103 | Kenya | 0.3 |
| 104 | Yemen | 0.2 |
| 105 | DR Congo | 0.2 |
| 106 | Laos | 0.2 |
| 107 | New Caledonia | 0.2 |
| 108 | Israel | 0.2 |
| 109 | Costa Rica | 0.2 |
| 110 | Virgin Islands | 0.1 |
| 111 | Moldova | 0.1 |
| 112 | Ecuador | 0.1 |
| 113 | Chile | 0.1 |
| 114 | Somalia | 0.1 |
| 115 | Samoa | 0.1 |
Applications of Aluminum Ore
Basically, up to 60% of ore raw materials are used to produce aluminum. However, the rich composition makes it possible to extract from it other chemical elements: titanium, chromium, vanadium and other non-ferrous metals, which are necessary primarily as alloying additives to improve the quality of steel.
As mentioned above, the technological chain for producing aluminum necessarily passes through the stage of formation of alumina, which is also used as fluxes in ferrous metallurgy.
How are the costs of supporting industry distributed?
The rich composition of elements in aluminum ore is also used to produce mineral paint. Also, the smelting method produces alumina cement - a quickly hardening, strong mass.
Another material obtained from bauxite is electrocorundum. It is obtained by smelting ore in electric furnaces. It is a very hard substance, second only to diamond, making it popular as an abrasive.
Also, in the process of obtaining pure metal, waste is formed - red mud. The element scandium is extracted from it, which is used in the production of aluminum-scandium alloys, which are in demand in the automotive industry, rocket science, production of electric drives, and sports equipment.
Aluminum and its role in industry
Aluminum is one of the elements in the periodic table; it belongs to light metals. It is the most common metal, and as a chemical element it ranks third in terms of content in the earth’s crust.
Aluminum can be obtained from aluminum ores, primarily from bauxite, containing from 28 to 80% aluminum oxides. Nepheline syenites, alunite, nepheline-apatite rocks are also raw materials for the production of aluminum, but they have a lower percentage of aluminum oxides than bauxites and are raw materials of poorer quality.
If we consider the production volumes of non-ferrous metals in the modern economy, aluminum ranks first. This is primarily due to the fact that it is widely used in people’s lives, affecting a fairly wide range of industries, such as transport engineering, construction, packaging production, and the production of consumer goods. Aluminum is also used to make cables or other products used in electrical engineering.
The physicochemical properties of aluminum allow it to be used for the manufacture of special tanks in which liquid gases such as methane, oxygen, hydrogen, as well as nitric acid and clean water can be stored and transported. Aluminum is widely used as a structural material for nuclear reactors. In steel production, aluminum is also of great importance, acting as a deoxidizing agent.
In our everyday life, we quite often come across objects for the manufacture of which aluminum was used, for example, parts of electrical appliances for refrigerators and washing machines are made from it. Quite often in everyday life you can find aluminum dishes, furniture, and various sports equipment. Aluminum is also used to produce various types of packaging, cans or disposable containers made from foil.
Such widespread use of aluminum in life is influenced by its advantages in properties over other structural metals:
— first of all, we can highlight the fact that aluminum has a fairly small specific gravity;
— secondly, its advantages over other metals include high corrosion resistance;
— aluminum is easy to process, is 100% recyclable, and saves energy by 95%;
— in addition, the metal has high electrical conductivity and fire resistance;
— aluminum is resistant to low temperatures, at which its strength, ductility and toughness are much higher.
Alternative to aluminum ores
The development of modern production requires increasingly large volumes of aluminum. However, it is not always profitable to develop deposits or import alumina from abroad. Therefore, metal smelting using recycled materials is increasingly being used.
Import substitution is a factor in the economic security of the country
For example, countries such as the USA, Japan, Germany, France, and the UK mainly produce secondary aluminum, amounting to up to 80% of global smelting.
Secondary metal is much cheaper compared to primary metal, the production of which requires 20,000 kW of energy/1 ton.
Today, aluminum, obtained from various ores, is one of the most popular materials for producing durable and lightweight products that are resistant to corrosion. No alternatives to the metal have yet been found, and in the coming decades the volumes of ore mining and smelting will only increase.
The main reserves of explored bauxite and the largest aluminum producers.
Aluminum is a lightweight metal that can handle almost all metals.
It is also an important metal for aviation, machine, ship, and carriage building. The Second World War was the starting point for the development of this industry. The main raw material for aluminum production is bauxite, which is concentrated in 18 countries. These are mainly countries with a hot and humid climate. But in addition to bauxite, there are also substitutes that are currently less profitable. These are, for example, alunite, anorthosite, coal waste and oil shale and other raw materials.