The development of industry and the creation of synthetic materials cannot detract from the advantages and benefits of traditional materials. These include cast iron and steel. These are some of the oldest familiar alloys to human civilization.
The technology of repair and design work often includes various types of processing. It could be:
- mechanical
- chemical
- thermal
- electrolytic
- plasma and other types of processing.
Despite the fact that cast iron and steel differ from each other by a tiny difference in carbon content, the methods and methods of influencing factors on these alloys differ and require different ways of the same method to influence the shape and structure of the metal.
How much does 1 kg of cast iron cost?
Cost of cast iron scrap
| Category | Price per kg | Price per ton |
| 17A - cast iron scrap overall | 6-7 rubles | 9000-10000 rubles |
| 19A - dimensional cast iron scrap, in pieces | 6-7 rubles | 8500-9000 rubles |
| 20A - oversized scrap, piece weight no more than 5 tons | 6-7 rubles | 9000-10500 rubles |
| 22A - oversized scrap (plumbing waste) | 6-7 rubles | 8500-9000 rubles |
Factors affecting the processing of steel and cast iron
In order not to waste money and resources, it is very important to know how to identify cast iron or steel.
- Selecting a welding electrode
- drill sharpening angle
- drilling and milling mode
These are not all the factors that can complicate the life and work of a person who incorrectly determines the type of metal. Reducing mechanical, strength and violating guaranteed repair intervals is a much greater evil that can damage production and the budget in the event of an error.
How to distinguish cast iron cookware from aluminum?
Cast iron is a dark metal, almost black. Aluminum - light gray, silver. And, besides weight, the difference can be... fragility.
Interesting materials:
Can a tablet be used as an e-reader? Can old asphalt be used? Can I use just the base and top? Is it possible to leave Car Sharing at the airport? Is it possible to go to the movies for 18+? Is it possible to wear an autumn coat in winter? Can you wear Yeezy Boost in winter? Is it possible to bury a relative in the grave? Can pancake batter be stored in the refrigerator? Is it possible to lay laminate flooring on a wooden floor?
How to distinguish cast iron from metal - Metalist's Handbook
Among the metals produced in one technological process, some of the most common are steel and cast iron. Despite the fact that one is made as a result of alteration of the other, these metals differ significantly from each other, both in their composition and in their use in the economy.
How steel is made
Steel is an iron-carbon alloy in which the carbon content does not exceed 3.4 percent . The usual figure is in the range of 0.1-2.14% .
It reduces the plastic characteristics of steel, while making it harder and stronger. Alloyed and highly alloyed contain more than 45% iron.
The elasticity of steel determines its demand for the creation of engineering products, primarily power springs and springs, shock absorbers, suspensions, braces and other elastic parts.
Regardless of the forms and operating conditions of the elastic parts of machines, mechanisms and devices, they have a common remarkable quality. It lies in the fact that, despite large shock, periodic and static loads, they have no residual deformation.
Steels are classified according to their purpose, chemical composition, structure and quality. There are many categories of appointments, including the following:
- Instrumental.
- Structural.
- Stainless.
- Heat resistant.
- Resistant to ultra-low temperatures.
Steels can vary in their carbon content, from low-carbon, in which it is up to 0.25%, to high-carbon with 0.6-2%. Alloyed ones can contain from 4 to 11 or more percent of the corresponding additives. Depending on the content of various impurities, they are classified into steels with ordinary qualities, high-quality and those with especially high qualities.
In its production, the main thing is to reduce to the required level the content of sulfur and phosphorus, which make the metal brittle and brittle. In this case, different methods are used for carbon oxidation, which can be open-hearth, converter and electrothermal.
The open-hearth method requires a lot of thermal energy, which is released when gas or fuel oil is burned. Arc or induction furnaces are heated using electricity. The converter version does not require an external heat source.
Here, molten pig iron is usually separated from impurities by blowing oxygen through it.
The raw materials for steel production are metal, pig iron, and additives that form slag and provide steel alloying. The smelting process itself can be carried out in different ways. It happens that it begins in an open-hearth furnace and ends in an electric one.
Or, in order to obtain steel that is resistant to corrosion, after melting in an electric furnace, it is poured into a converter. In it, it is purged with oxygen and argon to minimize carbon content. Steel melts at a temperature of 1450–1520 °C .
How to get cast iron
An alloy of iron and carbon can also be called cast iron. However, unlike steel, it must contain at least 2.14% carbon, which gives this very hard material high brittleness. At the same time, it becomes less ductile and viscous. Depending on the content of cementite and graphite in it, cast iron can be called white, gray, malleable and high-strength.
The first contains 4.3-6.67% carbon . It is light gray at the break. It is used primarily to produce malleable cast iron using annealing technology. Cast iron is called gray because of the gray color of its fracture due to the presence of graphite in lamellar form and the presence of silicon.
As a result of prolonged annealing of white cast iron, malleable cast iron is obtained. It has increased ductility and toughness, impact resistance and greater strength. Complex parts for machines and mechanisms are made from it.
It is marked with the letters “K” and “H”, after which numbers are placed indicating the tensile strength and relative elongation.
High-strength cast iron is distinguished by the presence of spheroidal graphite, which prevents stress concentration and weakening of the metal base.
A laser is used to strengthen it, which makes it possible to obtain critical machine parts of increased strength.
For industrial needs, there are various classifications of pig iron, anti-friction, alloy and graphite-containing cast iron. Its melting point is between 1,150 and 1,200 °C.
Cast iron has proven itself to be
a versatile, inexpensive and durable material .
Complex and massive parts of machines and mechanisms, as well as unique artistic products are made from it. Cast iron decorations and monuments decorate many cities around the world. Fences of ancient buildings, steps in them, and water and sewer pipes skillfully made from it have served people for centuries. Cast iron hatches cover communication wells on the streets of many settlements. Bathtubs, sinks and sinks, heating radiators made of this material are reliable and durable. Crankshafts and cylinder blocks of internal combustion engines, brake discs and other automobile parts are cast from cast iron.
Typically, cast iron parts undergo additional machining after casting.
What makes them different
Steel and cast iron are materials widely used in industry, transport and construction. Outwardly they are very similar.
However, there are these main differences between them:
- Steel is the final product of steelmaking, and cast iron is the raw material for it.
- Steel has higher strength and hardness than brittle cast iron.
- It contains much less carbon than cast iron.
- Steel is heavier than cast iron and has a higher melting point.
- Steel can be processed by cutting, rolling, forging, etc.; cast iron products are mainly cast.
- Cast iron products are porous and have a thermal conductivity significantly lower than steel
- New steel parts have a silver shine, cast iron matte and black.
- To give steel special properties, it can be hardened; this is not done with cast iron.
Difference between steel and cast iron
The metallurgical industry products often used in everyday life are cast iron and steel. Both materials are a unique alloy of iron and carbon. But the use of identical components in production does not endow the materials with similar properties. Cast iron and steel are two different materials. What are their differences?
articles
To make steel, you need to fuse iron, carbon and impurities. In this case, the carbon content in the mixture should not exceed 2%, and the iron content should not be less than 45%.
The remaining percentage in the mixture can be alloying elements (substances that bind the mixture, for example, molybdenum, nickel, chromium and others). Thanks to carbon, iron acquires strength and extreme hardness.
Without his participation, a viscous and plastic substance would be obtained.
Differences
In metallurgy, a fairly large number of varieties of steel are distinguished. Their classification depends on the amount of one or another component in the mixture. For example, a high content of binding elements produces high-alloy (more than 11%) steel. In addition there are:
- low alloyed – up to 4% binding components;
- medium alloyed - up to 11% of connecting elements.
carbon in the alloy also gives its classification to the metal:
- low-carbon metal – up to 0.25% C;
- medium carbon metal – up to 0.55% C;
- high carbon – up to 2% C.
And finally, depending on the content of non-metallic inclusions that are formed as a result of reactions (for example, oxides, phosphides, sulfides), classification is carried out according to physical properties:
- especially high quality;
- high quality;
- quality;
- ordinary steel.
This is far from a complete classification of steel. The types are also distinguished by the structure of the material, production method, and so on. But no matter how the main components are fused, the result is a hard, durable, wear-resistant and deformation-resistant material with a specific gravity of 7.75 (up to 7.9) G/cm3. The melting point of steel is from 1450 to 1520°C.
Unlike steel, cast iron is more fragile; it is distinguished by its ability to collapse without noticeable residual deformations. In this case, the carbon itself in the alloy is presented in the form of graphite and/or cementite; their shape and, accordingly, quantity determine the types of cast iron:
- white - all the necessary carbon is contained in the form of cementite. The material is white when broken. Very hard, but fragile. It can be processed and is mainly used to produce the malleable variety;
- gray – carbon in the form of graphite (plastic form). It is soft, easily processed (can be cut) and has a low melting point;
- malleable - obtained after prolonged annealing of a white appearance, resulting in the formation of graphite. Heating (over 900°C) and the cooling rate of graphite negatively affect the properties of the material. This makes welding and processing difficult;
- high-strength - contains spherical graphite formed as a result of crystallization.
The carbon in the composition determines its melting point (the more it is, the lower the temperature) and the higher the fluidity when heated. Therefore, cast iron is a fluid, non-plastic, brittle and difficult to process material with a specific gravity of 6.9 (7.3) G/cm3. Melting point – from 1150 to 1250°C.
Features of the delivery of cast iron scrap
This type of ferrous scrap metal is the most in demand, and it is classified as metal waste. It is recycled, melted down in smelters, and even recycled into steel by reducing its carbon concentration. Most of the cast iron scrap is of industrial origin.
Outdated machines, equipment, and dismantled metal structures are sold for scrap metal. The cost of such scrap is relatively low, but due to the large mass, these items can fetch good money.
You can distinguish cast iron from aluminum, steel, and iron by color, weight, and even sound (cast iron products are the most resonant, so when struck they make loud, sharp sounds). But the most reliable way is to send a metal sample to our laboratory equipped with a spectrometer. We will accurately determine the composition of the alloy and offer the best price for scrap metal!
Cauldron shape
A real cauldron, which came to us from Asian culture, has a spherical shape. This configuration is quite understandable from a practical point of view. Nomadic peoples dug a hole to lay coals, and placed a round cauldron on top - it turned out stable and convenient for cooking.
At the same time, the spherical shape allows the flames to heat the entire area of the cauldron at once, and not just the very bottom. The heat is distributed evenly, the products reach their condition at the same time and do not burn. With a flat bottom, this effect is impossible to achieve.
Nowadays, pilaf cauldrons made of cast iron with a flat bottom are often found on sale. It would be a stretch to call it a real cauldron. Rather, it is a model adapted for modern kitchens that can be used on a regular stove.
Remember: a real cauldron for pilaf should have an ideal hemisphere shape.
What should you be wary of when purchasing?
By what signs can you determine that you are being sold a low-quality product:
- Suspiciously low price. If you are offered to buy an inexpensive pilaf cauldron for a few hundred rubles, refuse without hesitation. Cast iron, by definition, cannot be cheap. The market price for small cauldrons with a volume of 3 liters starts from 2 thousand rubles.
- Light weight. Remember that cast iron is a heavy metal, it is not aluminum or even steel, so the weight of a cast iron cauldron must be impressive. For example, a 10-liter container with a lid will weigh about 8 kg.
- Chips and cracks. Before purchasing, inspect the product from all sides - its shape should be spherical and the surface should be smooth. Only slight roughness characteristic of the alloy is allowed, but there should be no traces of soldering or welding. Modern high-quality cauldrons are produced using the continuous casting method, which eliminates the appearance of nicks and other defects.
How to recognize a real cauldron
Nowadays, a variety of raw materials are used in the production of cauldrons - from steel and copper to aluminum and Teflon. But since real pilaf cauldrons are made exclusively from cast iron, the main task is to determine that this is cast iron. In principle, no difficulties should arise because cast iron is easily identified by its appearance - it should be black or dark gray, with a characteristic porous surface.
Cauldrons made of copper will have a reddish tint, and aluminum cauldrons will have a white tint. Metallurgists also smelt white cast iron (iron carbide), but in its pure form, and especially not for making dishes. So you definitely won’t find real white cast iron cauldrons.
Before you buy a real pilaf cauldron, try it by weight. Cast iron by its nature has a high density, so products based on it are always very heavy. And the thicker the walls of the dish, the heavier the pilaf cauldron will be. Speaking of walls, their thickness plays a key role in proper cooking. In a cauldron, dishes should simmer slowly, and this is only possible if the wall thickness reaches at least 4 mm.
Main characteristics
The properties of cast iron can be classified according to the following points:
- Chemical.
- Thermal.
- Technological.
- Hydrodynamic.
The chemical characteristics of the metal are its tendency to corrode. It depends on the composition of the alloy and the elements that are included in it, as well as on environmental factors. Elements in the composition of the alloy can either reduce the susceptibility of the metal to corrosion or increase it, it all depends on their effect on the structure of the metal.
The thermal conductivity of iron decreases due to an increase in impurities in its composition. The thermal conductivity of the alloy changes due to the degree of its graphitization.
Fluidity is classified as a technological property; its degree is determined in various ways. This property increases with decreasing viscosity.
The viscosity of the metal decreases with an increase in the content of manganese in the composition, as well as with a decrease in the amount of sulfur and other non-metallic inclusions in the alloy. Viscosity also depends on temperature. It is proportional to the absolute temperature and the experience of contact with it.
There are also magnetic properties of cast iron, which mainly depend on the structure of the metal. They are divided into primary and secondary.
Primary characteristics include:
- magnetic transformation temperature;
- saturation;
- induction;
- permeability in strong fields.
Main characteristics
In addition to carbon, manganese, sulfur, phosphorus, silicon, molybdenum, etc. are added to the alloy. The carbon in it is in the form of graphite or cementite (iron carbide), and their quantity determines the type of metal. All types of alloy are characterized by high density - about 7200 kg / cubic meter. m.
Cast iron can be distinguished from other metals by its poor weldability. During the heating process, oxidation of silicon in the iron alloy occurs. Due to its higher melting point, silicon oxide makes the welding process more difficult, so permanent joints are difficult to form. At the same time, cast iron alloys have a relatively low melting point (from 1150 to 1200 °C, which is lower compared to steel and pure iron).
Where to buy a cauldron for pilaf?
There are several options where to buy a real cauldron. You can go to a flea market - sometimes you can find very interesting used items there, made back in Soviet times.
If you like to choose from a large assortment and prefer new dishes, then an online store is the best solution. Here you can instantly get information, look at photos of cast iron cauldrons in detail and communicate with consultants. As a rule, the entire model range is always available - both in terms of volume and configuration, which market sellers often cannot offer. Doubting buyers can read reviews, think carefully and take into account all the nuances before placing an order.
Now you know what a real cauldron should be like - cast iron, heavy, spherical in shape, without defects. All that remains is to choose the appropriate volume and configuration.
Differences from aluminum
A magnet can be used to distinguish cast iron not only from steel, but also from aluminum - a silvery-white light metal. This substance is paramagnetic, therefore it has external magnetic susceptibility (in the absence of an external magnetic field, the magnetic moments of atoms are non-zero). The relative magnetic permeability of the metal is slightly greater than unity, and the magnetic field in it increases insignificantly. Accordingly, aluminum is magnetic, but very weakly. This is not visible visually, so it is generally accepted that it is not magnetic. In addition to magnetic properties, metals have other differences: color, mass, density, hardness and flexibility. Therefore, you can distinguish them from each other in other ways.
Which cauldron is the best?
Rating of the best cauldrons
| Nomination | place | Name of product |
| The best cast iron cauldrons for pilaf | 1 | Dobrynya, with lid, 7 l (DO-3306) |
| 2 | Kazan Kama cookware, 7 l, with lid (k71) | |
| 3 | Bekker 3.1 l (article BK-641) | |
| The best aluminum cauldrons | 1 | Kukmara “Tradition”, 4.5 l |
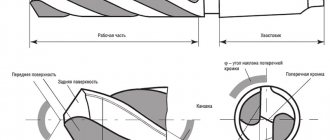
Mechanical determination by drilling
High-strength cast iron with nodular graphite is very similar in quality and visually to steel products. Testing a product by tearing it using a tensile testing machine is not entirely justified or reasonable. To do this, you can select a non-working, inconspicuous area on the product and drill it not to the full depth with a drill of minimum diameter. The structure of cast iron is such that the chips are not able to form into a twisted loach. Graphite inclusions, even if they are not visible, crumble the chips at the stage of their formation. Such shavings grind into dust in your hands and leave a black mark on your hands, like the lead of a simple pencil.
How much should a cast iron cauldron weigh?
Weight
45 kg.
Diameter 78 cm. Wall thickness: 9 mm. Included: cast iron cauldron
.
Interesting materials:
What is the best shampoo to use for oily hair? Which massager is better, Kuznetsov or Lyapko applicator? What is the best rice to use for pilaf? Which separator is better? Which pendulum is better, longitudinal or transverse Komarovsky? Which brand is best to buy baby food? What brand of shampoo is best to use? What is the best towel material? What material is best for car covers? What material is best for jeans?