It is difficult to imagine high-quality production of metal products without the use of welding. Semi-automatic welding is one of the most common methods used for welding ferrous and non-ferrous metals of various thicknesses.
The use of special technologies in semi-automatic welding can significantly improve the quality of the weld and speed up the process. This type of welding is actively used at many car service stations to perform body repairs.
What is semi-automatic welding?
Before you start mastering the technology of semi-automatic welding, you should know the structure of the equipment.
The electromechanical tool, called semi-automatic welding, includes:
- the main unit responsible for supplying power and electrode wire;
- welding sleeve or hose;
- a burner with a wire inside;
- conductive tip;
- shielding gas supply system.
Some large enterprises use semi-automatic stationary models that provide fast welding speed, uniform seams and low electrical energy consumption.
Semi-automatic welding machine.
All types of semi-automatic machines according to the method of operation are divided into:
- equipment for welding in an inert gas environment;
- a device that uses flux for the base;
- devices using cored wire;
- universal semi-automatic machines.
All types of semi-automatic welding machines are ideal for performing work on joining products made of non-ferrous or ferrous metal.
According to the method of feeding electrode wire, semi-automatic welding machines are divided into:
- Stationary. The equipment is rigidly fixed on a stand or a special console.
- Portable. The device is made in the form of a portable cabinet.
- Mobile. A special trolley adapted for moving around one room.
Based on the location of the feed rollers, semi-automatic machines can be divided into:
- pushing;
- pulling;
- push-pull.
Semi-automatic welding without gas
Among the vast number of types of welding, welding without the use of gas is becoming the most promising and in demand.
Semi-automatic welding of this type is carried out using flux-cored wire or, as experts call it, flux-cored welding wire.
Flux-cored wire is a steel tube, but inside this tube there is a special powder - welding flux, similar to the coating of conventional electrodes.
By exposing the flux-cored wire to high temperature, the flux is burned, which provides a protective gas cloud at the welding site. The process itself is very similar to conventional electrode welding.
The main advantage of this method is the absence of the need to carry gas cylinders with you, a huge selection of materials with different types of chemical compositions, with the help of which you can form the necessary arc properties and change the characteristics of the seam.
Since semi-automatic welding is similar to conventional electrode welding, slag from the burnt flux gets into the welding zone, so it is necessary to ensure sealing of the welding surface. To do this, you need to put a few more new ones on top of the finished seam.
Flux-cored wire has low rigidity, so it must be fed to the welding zone with a slight increased pressure; bends in the semi-automatic welding hose are simply unacceptable.
It is extremely necessary to observe the polarity conditions of the phase wire and the “ground”
On the left you see the polarity of welding without using gas, and on the right with using gas when welding.
In order to start the process, you need to connect the power source in the following way: minus to the torch holder, and plus to the surface to be welded. In the case of welding using shielding gas, the connection occurs in the reverse order.
This method of power connection provides a high temperature for melting the flux and the formation of a protective gas environment.
The main advantages of gasless welding:
- Easy welding process
- No need for a gas cylinder
- Fast speed of work
Features of the technology
Semi-automatic welding allows you to weld even rusty or galvanized metal with high quality. When connecting products made from materials that are difficult to weld, it is best to use copper or aluminum wire, since these metals allow you to obtain a strong and uniform seam.
In general, gas shielded or flux welding technology includes the following preparatory steps:
- cleaning and degreasing surfaces to be welded using popular solvents;
- checking gas equipment;
- performing a test seam to adjust the welding equipment settings;
- fine selection of current and voltage.
Welding in a shielding gas environment is the simplest option for using the equipment. Any gas is suitable for semi-automatic welding: carbon dioxide, helium, nitrogen or argon. The welding technique is the same for all gases.
Most often, novice welders choose carbon dioxide for welding due to its low cost and fairly good parameters.
Advantages of semi-automatic welding in a carbon dioxide environment:
- maintaining the appearance of the product;
- the ability to process even the most difficult to reach areas;
- minimum amount of waste;
- strong and thin weld seam;
- fast speed of work.
Welding in a carbon dioxide environment is one of the simplest methods of joining metal products.
Selecting current for semi-automatic welding.
The quality of the weld may depend on the following subtleties:
- wire guiding method;
- maintaining the required interval between connected parts;
- failure to comply with work standards.
Welding with semi-automatic equipment without gas is an alternative option for joining metals, which allows you to prevent the occurrence of oxides and control the production of a high-quality seam.
The gasless welding method involves the use of direct current supply and the use of flux-cored or flux-cored wire. During the welding process, when the wire burns, a gaseous environment is formed that is sufficient for high-quality work.
Connecting steel products using gasless semi-automatic welding is divided into stages:
- purchase of welding steel wire with flux;
- turning on the wire feed;
- turn the switch to the on position;
- placing flux inside the funnel;
- opening the protective flap to release flux;
- starting the device with the start button;
- waiting for the appearance of an electric arc;
- direct execution of work.
It is important to note that semi-automatic welding devices allow you to weld even aluminum parts with non-standard characteristics. To connect aluminum products, it is necessary to use argon as a shielding gas.
Due to the presence of an inert atmosphere, the aluminum oxide film, after its destruction, cannot appear again and nothing will interfere with the work being done quietly.
Rating of universal semi-automatic machines TIG, MIG/MAG, MMA
Multifunctional semi-automatic inverters that allow additional welding of metals with non-consumable electrodes in an atmosphere of protective gas or gases.
1
Fubag IRMIG 200 SYN 31447 + torch 38443 (TIG, MIG/MAG, MMA)
Rating:5.0
- welding inverter
- argon arc welding TIG
- manual arc welding MMA
- semi-automatic welding (MIG/MAG)
- Max. welding current: 180 A (MMA), 200 A (MIG/MAG), 200 A (TIG)
Setting up the welding machine
High-quality semi-automatic welding for beginners cannot do without fine-tuning the equipment.
Before using the device, the welder must install:
- current strength;
- wire feed speed;
- required shielding gas pressure.
Most semi-automatic welding machines are supplied with accompanying documentation containing optimal settings for certain operating modes. There are parameters that should be used as a starting point when fine-tuning the equipment.
You can check the correct settings of the parameters on separate unnecessary pieces of metal. To set the correct parameters when working in a protective gas environment, it is necessary to ensure that the weld is smooth and uniform, without drips or interruptions.
The optimal working gas pressure should generally be between 1-2 atmospheres.
Preparing the semiautomatic device for operation includes the following steps:
- Selecting the optimal wire radius. Most of these consumables come with a radius from 0.03 to 0.06 centimeters. The best choice for most materials is a wire radius of 0.04 centimeters.
- Pulling the wire until it exits the torch and adjusting the degree of its pressure.
- Preparation of optimal shielding gas. The two most commonly used gases are carbon dioxide and argon. The first option is cheap, common and great for welding steel parts. Argon is a more expensive shielding gas that ensures high stability of the electric arc and reduces the amount of metal splashes during work.
- Connecting the gas cylinder to the equipment.
Semi-automatic welding in a protective gas environment.
When setting up the equipment, you must adhere to certain rules that allow, if you have certain skills, to obtain an even and high-quality seam:
- ensuring uniform arc burning;
- installation of electrode wire forward direction;
- cleaning seams from accumulated slag.
The most optimal equipment settings are indicated in the accompanying documentation for the welding installation. However, you should not always completely trust the factory parameters.
Thus, the operating properties of the device can be affected by:
- various operating modes;
- quality of the electrical network;
- composition of the alloy being joined;
- ambient temperature;
- thickness and composition of filler wire;
- spatial positions of work;
- composition of the shielding gas.
The most common errors when setting up welding equipment are:
- Loud extraneous sounds resembling crackling. Similar symptoms can occur if the solder supply speed is insufficient. To avoid such misunderstandings, the feed rate of filler materials should be increased.
- Heavy splashing of metal droplets. The malfunction occurs when there is insufficient shielding gas. The problem can be resolved by checking the reducer or increasing the power of the gas flow.
- Poor penetration and low quality seam. Fault due to incorrect voltage and inductance settings.
- Uneven roller width. The defect may occur due to incorrect choice of burner speed.
Semi-automatic machines at reasonable prices
Many citizens who often have to perform welding-type work pay attention to the need to purchase the appropriate device at a relatively reasonable cost.
One of the optimal models in this case is ZUBR Master PS – 200, the main advantages of which are:
- The existence of significant prerequisites for operating at high currents;
- Possibility of adjusting inductance;
- High level of resistance to voltage surges.
At the same time, the main disadvantages can be considered: the relatively low level of quality of the cables, which, based on the opinion of a number of experts, need to be replaced almost immediately, the lack of standard capabilities for carrying out high-quality work with various types of wire.
An alternative option is the Resanta Saipa-200 model, one of the undeniable advantages of which is a significant current reserve, which is especially important if we take into account the specifics of using the corresponding devices.
At the same time, one should not ignore the existence of many negative characteristics, the main ones being: Not too responsible attitude of the manufacturer, which is inextricably linked with poorly written instructions and creates many problems for use; a high level of sensitivity to dust pollution, quite high if taken into account attention to the indicated disadvantages, cost level.
Types of welds in semi-automatic welding
Semi-automatic welding technology allows you to obtain different types of seams, depending on the equipment settings.
According to the type of connection, seams produced by semi-automatic machines are divided into:
- butt;
- T-bars;
- overlap;
- corner.
Features of semi-automatic welding.
According to their spatial position, welds are usually divided into:
- horizontal;
- vertical;
- ceiling;
- lower ones.
Popular ceiling seams are usually made in two stages:
- Welding the root seam. The preparatory seam is usually performed with three-millimeter electrodes with low current.
- Full completion of the seam.
The second welding stage of the ceiling seam can be performed in two ways:
- Welding using short, jerky seams or spot welding. This welding method prevents drops of molten metal from falling on the operator. When performing such a procedure, additional welding may be required at the beginning and end of the seam.
- Cooking with the shortest possible arc. This approach will allow the metal to quickly harden, immediately after the electric flame is removed.
Bottom connections, made using semi-automatic or manual arc welding, are often used in factories and industries. Such welds provide high mechanical characteristics due to the uniform distribution of molten metal.
Semi-automatic welding modes when making corner joints can be different.
Table of characteristics of semi-automatic welding machine.
Semi-automatic gas welding of corner metal structures can be performed:
- With a perpendicular arrangement of two workpieces. This technique allows you to weld only the internal joint. Cooking perpendicularly located tubes should include making a concentric weld around the circumference.
- With an angle of less than 60 degrees between the parts being welded. The best option for performing a fillet weld. In this case, the workpieces are completely boiled.
The butt weld is the most popular method of joining pipelines or steel sheets.
This type of welding is divided into:
- one-sided welding;
- one-sided welding and processing;
- double-sided welding.
One-sided welding in shielding gases is used for product thicknesses of no more than 4 millimeters. If the parts have a thickness of more than 8 millimeters, it is necessary to perform double-sided welding.
The best method for ensuring high strength of a thick product when welding one side is to groove the edges. The cutting is carried out using a grinder or a file. During the processing of the joined ends, a bevel of 45 degrees is formed.
An overlap joint is usually performed to ensure high tensile strength of the product. The seam should be made on both sides of the contacting surfaces to avoid moisture accumulation.
A T-joint is in most cases used to secure the base of a metal structure. When the metal thickness is more than 4 millimeters, it is recommended to use a double-sided weld.
Vertical
The technology of semi-automatic welding of a vertical seam has several important principles:
- Molten drops of metal should solidify faster than with conventional welding. This condition is necessary due to the gradual flow of molten metal downward under the influence of universal gravity. The required droplet size can be ensured only by reducing the size of the welding arc.
- Vertical welding is done from bottom to top. The welding method ensures the absence of sagging and unevenness when making a vertical seam.
There are several rules that can be followed to guarantee a high-quality vertical connection when welding from top to bottom:
- use of a short arc;
- perpendicular position of the electrode at the beginning of welding;
- the location of the electrode at an acute angle relative to the weld seam.
Welding wire feeder.
Although such steps make it possible to obtain a vertical seam by welding semi-automatically from top to bottom, as the lessons learned by experienced welders show, such joints have much more meager characteristics.
There are three technologies for welding vertical seams using semi-automatic machines:
- Triangle. It is used when connecting parts with a thickness of less than 2 millimeters. The essence of the method is as follows: during the operation of the welding arc, liquid metal flows from bottom to top onto the already solidified metal. In this case, the flowing slag moves at a certain angle, depicting a triangle.
- Herringbone. Method used to join 2-3mm gaps. Welding begins from the plane of one of the edges. Then, using an electrode, the metal is melted throughout the entire thickness of the workpiece, after which the arc is drawn to the very depth of the gap.
- Ladder. The best option for eliminating large gaps between parts. The method involves performing welding work using a zigzag movement of electrodes from edge to edge.
Horizontal
Semi-automatic welding allows you to perform high-quality horizontal seams. Performing such operations is not much different from creating vertical connections. The welding process can be performed both from right to left and from left to right.
You can get a high-quality horizontal seam by taking into account these subtleties:
- the arc burning force must be equal to the gravity force of the metal drops;
- the speed of movement of the electrode must be selected separately for a horizontal seam;
- Welding work should be carried out continuously in order to keep the melt under control.
Arc welding sometimes makes it impossible to complete a seam in one go. In this case, you can use the welding technique with periodic arc extinguishing. When metal thickness is up to 4 millimeters, the use of various welding patterns is allowed.
Otherwise, the quality of making a horizontal connection using semi-automatic or manual equipment completely depends on the skill of the welder.
Semi-automatic welding machine.
The process of creating a horizontal welding seam can be divided into four stages:
- Creating a root roll. The root weld bead is made with a short electric arc. The angle of inclination of the electrode to the surface should be about 80 degrees. The primary roller, as a rule, is created with the maximum current allowed for the equipment.
- Formation of the secondary roller. The process begins with setting the average current strength. The secondary roller is made in one pass, in which it is advisable to use an electrode with a large diameter. The second welding bead should be formed using the forward angle technology.
- Getting the third roller. The tertiary bead can be created in two ways, depending on the success of the previous stage. If the secondary roller has a large area, then the third should lie exactly in the center. If the second roller turned out to be standard, then the third stage is performed in two approaches.
- Final welding of parts.
During the work process, you should carefully monitor the upper part of the seam being formed, since it is in this area that various welding defects appear.
Why choose semi-automatic?
Many beginners who are generally familiar with welding may ask a completely expected question: Why are automatic settings not recommended? It would seem that both devices have a similar operating principle and, therefore, the second option would be preferable. Automating the process reduces the risk of errors to a minimum. The absence of human factor influence on production significantly speeds up and allows you to obtain a stable result throughout the entire work cycle. In other words, it is enough to set the parameters for the installation, and it will begin to perform the task. Semi-automatic equipment requires the direct participation of the operator in welding parts.
It is unreasonable to compare both settings without taking into account the situation at hand. The complexity and planned scope of work play a decisive role in making the choice.
For workshops, small companies, service and repair enterprises, private craftsmen, and especially for home use, purchasing a machine is not advisable. The acquisition will result in significant financial expenses. Failure to maintain a continuous work cycle will negatively impact performance. In addition, it may be difficult to set up, since you need to know all the subtleties and nuances of the process. A semi-automatic welding machine can be moved on a special wheelbarrow with a cylinder to the desired location. It is impossible to perform such manipulations with an automatic analogue. If we talk about welding technology, it is identical in both cases.
Welding thin and thick metal
The nature of semi-automatic welding depends on the type of product being welded.
The connection of thin metal, depending on the type of product, is made in two ways:
- Regular sheet metal can be welded by any method.
- Riveted thin metal should be overlapped and welded through pre-prepared holes in the top sheet.
Electrical circuit of a semi-automatic machine.
When welding thin metal products, you need to remember the following subtleties:
- the current, voltage and wire exit speed must be adjusted downward;
- It is forbidden to hold the electric arc in one place, as this may result in burning of the product or influx of the welding bead;
- It is important to weld thin rivet metal starting from the center of the lower workpiece in order to avoid flooding of the prepared holes.
If the weld does not need to be airtight, spot welding can be done at intervals of 1 to 5 centimeters.
Thick metal with a wall thickness of more than 4 millimeters is joined by chamfering the surfaces to be welded. Such preparation allows you to obtain an even seam and qualitatively boil the workpieces.
Welding work with thick metals should be carried out using small oscillating movements of the torch. The table of welding modes that comes with each semi-automatic machine contains extensive information about the optimal parameters for welding thick metal products.
Basic rules for connecting thick metal products:
- the gap between the parts should be no more than 2 millimeters;
- the width of the weld should be equal to the thickness of the workpiece;
- The choice of welding materials should be made depending on the metals being joined.
If the task is to thoroughly weld metal products with a width of more than 5 millimeters, then the work should be done in several approaches. First, you need to create a welded joint in the center of the workpiece, and in the second and third approaches you can weld the parts from above and below.
Welding work is recommended to be performed outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
How to choose a semi-automatic welding machine?
When choosing a semi-automatic welding machine, first of all you need to decide on the scope of its use..
Inexpensive devices are suitable for household use, but for a small workshop it is better to choose more expensive models with expanded functionality and advanced technical characteristics.
The main criteria for choosing a semi-automatic welding machine include:
- Voltage and output current adjustment range . For domestic use, a device with modest characteristics will be sufficient. But, if you plan to use the device to perform a large volume of work with wire of the maximum permissible diameter, it is better to choose a device with a high level of outgoing current.
- Power . The lower this indicator, the less network subsidence will occur during welding. To ensure that the device can operate even from a network with an unstable voltage, it is better to choose a model with modern IGBT or MOSFET transistors.
- Dimensions and weight . This criterion is especially important if the welding is planned to be frequently transported or stored in a small room. But it should be borne in mind that compact devices usually have reduced power, although they are quite sufficient for domestic needs.
Be sure to take into account the possibility of connecting the device to a household electrical network, as well as the type and thickness of the metals with which they will work.
Features of wire welding
Features of welding with wire using semi-automatic equipment are as follows:
- the filler material must correspond to the chemical composition of the product being welded;
- the wire must meet government standards and be made from the correct components;
- The terms and conditions for storing filler wire must be strictly observed.
A review of the features of work using filler wire should begin with welding basics. Most metals welded in production or at home are steel and manganese. Wire for connecting such products is the most in demand.
Welding of ferrous metals is usually carried out using the following types of filler material:
- Wire Sv-08GS for joining low-carbon and alloy steels.
- Wire Sv-08G2s for welding high-carbon steel.
Flux-cored wire is often used for welding ferrous metal products. This filler material allows welding to be carried out without additional gas supply to the welding zone.
Self-fluxing wire is a low-carbon steel tube with a powder core. When the metal melts, powder is released, forming a gaseous environment to protect the weld. As a rule, the fluxing powder contains rutile and metal dust.
Stainless steel is welded with wire grades Sv.-06Х19Н9Т, Sv.-04Х18Н9 or Sv.-01Х19Н9. This filler wire provides good mechanical and physical properties of the weld.
The connection of aluminum parts is carried out using SV-AK5 wire. A characteristic feature of this filler material is the unique color of the weld. Immediately before joining aluminum products, preparation should be carried out.
Semi-automatic welding using flux-cored wire.
This procedure is divided into steps:
- Creating bevels or chamfers.
- Mechanical cleaning of surfaces.
- Washing with caustic substances to slow down the formation of a refractory oxide film on the surface of an aluminum product.
- Preparation of a Teflon channel to reduce friction of the filler wire on the walls of a semi-automatic welding device.
Step-by-step instructions for using carbon dioxide welding for beginners include the following subparagraphs:
- removing all foreign objects from the workplace;
- turning on maximum lighting;
- preparation of material and tools;
- checking cable connections and functionality of extension cords.
After completing the above points, you should proceed to preparing the electric arc welding machine.
To do this you need:
- unwind the welding sleeve;
- connect the gas cylinder;
- check the burner nozzle;
- conveniently place all the parts to be connected and fasten them securely;
- dress in welder's work clothes;
- connect semi-automatic equipment to the network;
- bring the torch to the intended connection site.
Upon completion of welding work using wire, you should:
- remove your fingers from the wire feed buttons;
- shut off the gas supply;
- turn off the power to the equipment;
- Allow the seam to cool for several minutes;
- If defects are found, repeat welding.
The semi-automatic welding machine allows you to use all types of filler wire.
When performing work, it is important not to forget about protective equipment.
Semiautomatic welding machine with thyristor control.
The most complete welder equipment consists of:
- Eye protection. The ideal equipment to protect a welder's vision is a mask, face shields and goggles.
- Respiratory protection. Special filter masks will help the master to significantly reduce the impact of harmful fumes on internal organs.
- Splash protection. Full body protection should include a flame retardant jacket and trousers. You can use overalls.
Safety precautions when performing welding work include the following rules:
- Carrying out work from wooden scaffolding. The use of metal protective masks and helmets is prohibited.
- Providing light flux from a 12 volt power source.
- Providing insurance for the welder using a string attached to the belt. The rope size must be at least 2 meters.
- Providing the workplace with a special hood that ensures the removal of harmful fumes from the work area. In cases where it is impossible to provide exhaust, the welder must work in a hose gas mask or respirator.
- Do not touch the workpiece to be welded with bare hands.
- It is prohibited to carry out work in open areas during precipitation.
Specifics of choosing a semi-automatic machine
Given the diversity of this category of equipment, it is necessary to pay attention to such factors as, in particular, the availability of a warranty and its duration, the availability of special service centers for additional maintenance, as well as the purchase of parts if such a need arises.
In addition, it is extremely important to take into account the reviews left by users.
Thus, now there are many models of semi-automatic welding machines, and to ensure their correct selection, it is necessary to take into account, in particular, the technical characteristics.
What are they?
- Household. A simple device with a minimum number of settings. The limited power is enough for use in the country house or garage. Requires alternating voltage with a value of 220 Volts. The best option for use is within 2 - 3 hours. As the duration increases, the device heats up. It takes time to cool down. The permissible cross-section of the metal is in the range of 3 - 5 mm. Compatible with thin wire. The material cassette received 2 rollers. Household equipment is suitable for carrying out minor body repairs, welding a fuel or water tank, and self-manufacturing gates, frames and other types of small metal structures. The device is unpretentious in maintenance. Weaknesses include low maximum current strength.
- Semi-professional. Mid-level equipment. Available power has increased. Despite the simple interface, the number of permissible settings has increased. The maximum penetration thickness is 10 mm. Depending on the configuration, the feeding device can have 1 or 2 rollers. Wire diameter ranges from 0.8 - 1.6 mm. In demand in private auto repair shops, service stations and small industries. They are used to lay pipelines, repair thick-walled parts and larger metal structures. Operation is allowed for 6 hours a day. Disadvantages include increased cost compared to household ones and problems with maintaining current up to 20 A.
- Professional. Massive heavy equipment installed permanently or on a trolley. In the latter case, a mount for a gas cylinder is provided. This makes transportation easier. The universal wire feeder and cable duct is compatible with a variety of material diameters. Semi-automatic devices are actively used in production. It is possible to process metals with a thickness of 20 mm and more. The device is not afraid of moisture and dust. You can work with it outdoors. The cable length depends on the model. The equipment will require a connection to a 380 V network. It is advisable to purchase it in places with permanent employment. In addition, difficulties with transportation and repair may arise. The cost of replacing components will result in serious financial losses.
About the device
The semi-automatic device is widespread, primarily because of its ease of interaction. Compared to manual welding, the performer does not need to stop to periodically replace a burnt electrode. This greatly improved productivity.
The maximum permissible seam length ranges from 2 to 4 m. It is not affected by the position of the worker in space. This was made possible thanks to the built-in wire feed mechanism, which is implemented by a compact electric motor, started by pressing a button. The unwinder sends it through a metal channel to the welding zone at a constant speed. Together with the motor, the valve for supplying argon, carbon dioxide or a mixture of them into the weld pool moves. The speed can be changed at your discretion. The wire acts as a filler material and a contact for igniting the arc. The performer sets the feed at the mark and maintains a certain distance to the surface.
Technical modification has increased productivity. To work with large diameter pipes, simply place them on rollers and make one continuous weld.
Practical features include the standard nozzle length and distance to the seam. The opposite situation is with electrodes; as they burn out, they become smaller, requiring control over the size of the arc and the filler material. Semi-automatic wire cutting equipment does not have this kind of complexity. You don't need to be highly qualified to work productively. Unified materials are distributed at an affordable price. All this, combined with the need for minimal processing of the finished seam, makes the device one of the most popular on the market. The last factor is explained by the fact that no slag remains on the surface; you can immediately begin painting the product.
Semi-automatic devices are used for:
- creating tacks;
- pulse welding;
- scalding;
- adding carbon steel;
- welding cast iron;
- applying seams to stainless steel;
- working with thin metals;
- processing of galvanized products.
How is it arranged?
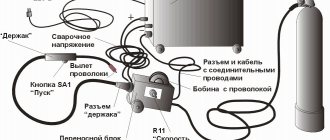
Any device, regardless of the scope of application, consists of a number of basic components. Depending on the retail network and the manufacturer’s equipment, the semi-automatic machine may include: unwinding tools, equipment for pipeline welding, hose stands, hoods, protective screens, etc.
The main nodes include:
- Power supply. Rectifiers and inverters are common. Transformer modifications are practically not used. This is because they are bulky and more suitable for permanent installation. They are characterized by a simple design and a unified layout. The most affordable option. Rectifiers are not without the disadvantages of the group described above. They have limitations on current regulation and difficulties arise with its ripple. Strengths include: a powerful electric arc and almost complete sealing of the seam. Inverters are a modern technology that does not consume much energy. Spot adjustment of shapes and levels of welding currents. The device received automatic inductance adjustment. Widely distributed in garage auto repair shops. Significant disadvantages include the high cost and complexity of repairs. To weld aluminum and magnesium alloy, alternating current with balanced polarity is required. Its formation is possible only with inverters.
- Welding sleeve (cable hose). Visually, the element resembles a flexible hose with a filler wire feed channel located in the center, surrounded by a tube for shielding gas and coolant (depending on the model). The power cable cores and control system wires are located nearby. Connects the burner to the device itself. The main task is to supply the above listed materials to the shielding gas welding zone. The functionality and efficiency of performing assigned tasks in conditions of difficult access to the place depend on the length. The part is expensive because it must meet high performance characteristics.
- Burner. A tool on which the quality of performance depends. Tubes and wires passing through the welding sleeve are brought out through it. Main parts: handle and guide tube. The handle received a welding mode switch. The guide tube is equipped with a gas diffuser, nozzle and contact tip. The latter is responsible for the output of the material and must correspond to its diameter. The part can be replaced. The nozzle is also considered a replaceable element. Its choice is influenced by the size of the tip and the welding mode.
- Wire feed mechanism. The material is distributed in reels of various sizes, coils, with or without copper coating. The mechanism is represented by a reel installation unit with a mechanical unwinding stabilizer and a feed roller. The drive rollers have special grooves, they are identical to the diameter of the wire. The system is driven by an electric motor, controlled by a semi-automatic controller. Pressing and tension are carried out manually. The feeding mechanism is available in 2 versions: 2 rollers (drive and pressure), 4 rollers. The latter is relevant when working with soft and cored wires. Depending on the manufacturer, the reel is placed outside or inside the equipment. In the first case, the equipment will take up less space. The second one is suitable for working with large coils.
- Control Panel.
- Cylinder with reducer.
- Gas valve.
- Ground cable with clamp.
To work smoothly with metal (cast iron, stainless steel, steel, aluminum), the voltage must undergo certain changes. Initially, you need to get 220 or 380 V, then they are converted to 30 - 90. In this case, the number of amperes increases to 120 - 500. Unlike electrode welding, the technique does not leave slag on the surface of the seam. The joint does not even require mechanical processing.
To carry out the transformation, the mechanical, electrical and gas parts of the semiautomatic device are used. The electric motor supplies the filler material to the torch with a mouthpiece and nozzle. The speed varies depending on the diameter, amperage and required weld thickness. Through the wires, through the mouthpiece, the voltage reaches the wire.
The second contact is connected to the object using a ground cable with a clamp. After pressing the button located on the torch, the wire extends towards the surface to be treated. The electric arc melts the material and the edges of the connection. To form an even seam, the burner is moved from one edge to the other. Sharp and oscillating movements are excluded.
The gas protects the weld pool from contact with the environment. The substance in an inert state is supplied automatically after pressing the button. The tubular shape of the nozzle ensures uniform delivery in the required direction. Otherwise, the gas would disperse randomly, and the resulting seam would be porous and not airtight.
Types of burners
The division is based on how the part interacts with the wire.
- For pushing mechanisms. The burner is without a drive; the movement of the material is carried out by a mechanism installed in the main block.
- Driven. The burner handle is equipped with a motor. Its design is identical to the mechanisms on the main unit.
- Combined (push-pull). The design received both mechanisms described above.
What modes do they work in?
- Mig. Welding is carried out with argon. Inert gas flows through high-pressure pipes into the burner from a cylinder. The optimal option for welding complex groups of metals.
- MAG. The process is based on carbon dioxide. He is classified as an active group. They perform a similar task (protects oxygen).
- MMA, or RDG (mma). Manual arc welding with a fusible conductor. Refers to additional functionality. The hot conductor enters the welding cup. At the same time, the coating melts, forming a top protective layer.
- TIG. Semi-automatic welding in an argon environment using a conductor. An additional feature for most premium quality models. The constant length of the electrode simplifies the process. The absence of impurities improves the quality of the seam.