No welding takes place without the main element - the electrode. It is worth choosing a certain optimally suitable electrode for a specific welding machine. But there are types that are suitable for almost any brand of welding unit and have a number of advantages. Such convenient and easy-to-use electrodes include rutile ones, the main thing is that the welding seams after their operation are distinguished by accuracy and subtlety. What are rutile electrodes and when should they be used - in the text.
Rutile electrodes: what are they and what are they for?
All electrodes are made according to the same principle: a special coating is applied to a metal rod made of a special alloy. As a rule, the type of coating determines where the electrodes of this type will be used.
Rutile coated electrodes are designed for manual arc welding.
The coating is made primarily from titanium dioxide. This allows you to achieve high quality welding seams and also has a beneficial effect on the entire welding process. REFERENCE: This type of coating is one of the safest, as it does not emit harmful substances during combustion that can be inhaled by the welder.
How to choose electrodes for inverter welding
First of all, the composition of the core is selected: it must be similar to the type of metal being welded. Structural steel is the most commonly used material in households. The electrodes should be made from the same wire. Sometimes you still have to cook stainless steel. Then the core should also be made of stainless steel, and for highly alloyed and heat-resistant ones it is made of metal with the same characteristics.
You can perform all the work around the house or at a construction site using just a few brands of electrodes:
- MR-3
- SSSI 13/55
- ANO 21
- OK 63.34
They are recognized by many as the best electrodes for beginners who work with inverter welding machines: they are easier to work with, at the same time, they allow you to weld high-quality seams even without significant experience. Below are the characteristics and general application of those consumables that many experts consider good electrodes for an inverter. In any case, they are often recommended for beginning welders to gain experience.
Electrodes with rutile coating MP 3
MP-3 is perhaps the most popular welding electrodes for inverters among beginners.
Most often, beginners are advised to start mastering welds with MP-3 electrodes. They light up easily, even with a not very good current-voltage characteristic of the welding machine, provide good protection for the weld pool, and make it quite easy to control its position. If the electrode does not ignite, calcine it at a temperature of 150-180° for 40 minutes.
They are used in devices with alternating current (welding transformers) and direct current (welding rectifiers and inverters). Inverters are usually connected with reverse polarity (+ on the electrode). Suitable for any type of seam, except vertical from top to bottom.
Read about the types of welding machines here.
MP 3 electrodes are not picky about the quality of the surfaces being welded. They can be used even on untreated, rusty and wet parts. Welding is carried out with a medium (2-3 mm) or short arc.
The MP 3 feature is very important for novice welders: they “hold” the arc well and are easy to work with. This is why not all professionals love this brand: they call them sparklers. They cook too softly: slow movements are necessary for good heating. What the pros don't like, is just what beginners need. Try to start learning welding with MP3. Everything should work out for you.
| Electrode diameter LEZ MR-3, mm | Length, mm | Recommended welding current, A | Pack weight, kg | Price, rub |
| 2,0 | 250 | 40-60 A | 1,0 | 146 |
| 2,5 | 300 | 60-100 A | 1,0 | 120 |
| 3 | 350 | 70-100 A | 1,0 | 95 |
| 4 | 450 | 80-170 A | 1,0 | 91 |
| 5 | 450 | 130-210 A | 1,0 | 91 |
UONI 13/55 with basic coating
Electrodes preferred by professionals for the UONI 13/55 inverter (click on the picture to enlarge the size)
These are, perhaps, the most widespread and popular electrodes with a basic coating. They are recommended for welding carbon and low-alloy steels. Suitable for connections of critical structures. The seams are resistant to shock loads and ductile, and withstand low temperatures well.
The disadvantage of these electrodes is that they ignite well only when the idle value of the inverter is sufficiently high (above 70 V). The second significant drawback: high requirements for stripping and processing of welded metals. If rust, dust, oil or other contaminants remain on the edge, the seam will be porous.
You can work with UONI 13/55 only on DC welding machines, including those with inverters, with reverse polarity (+ applied to the electrode), and with a short arc (keep the tip of the electrode closer to the surface to be welded). Minimum open circuit voltage 65 V.
| Electrode diameter UONI 13/55 (manufacturer: Mezhgosmetiz) | Electrode length, mm | Recommended welding current, A | Retail price of a pack, rub |
| 2,0 | 250 | 30-60 A | |
| 2,5 | 300 | 40-70 A | 127 RUR |
| 3 | 350 | 80-100 A | 116 RUR |
| 4 | 450 | 130-160 A | 111 rub. |
| 5 | 450 | 180-210 A | 110 rub. |
ANO 21
This type of rutile-coated electrode is designed to work with thin carbon steels. (Read about welding thin metals here.) When using them, the arc is easily ignited (including when re-igniting), the weld is fine-scaled (made up of small waves), and the slag is easily separated. ANO 21 electrodes can be used for welding water or gas pipes.
Try ANO 21 electrodes to work on the inverter
They work with both alternating and direct current of any polarity. Before welding, heat treatment is required: they are calcined at a temperature of 120°C for 40 minutes.
| Diameter, mm | Low electrode position | Vertical electrode position | Ceiling electrode position |
| 2 | current 50-90 A | current 50-70 A | current 70-90 A |
| 2,5 | current 60-110 A | current 60-90 A | current 80100 A |
| 3 | current 90-140 A | current 80-100 A | current 100-130 A |
Stainless steel electrodes OK 63.34
If you need to weld stainless steel, try OK 63.34. They can also cook structural steel. This produces a seam with a small wave with a smooth transition to the main surface of the metal. The amount of slag is small and can be easily removed.
This electrode is good for welding vertical seams in metal 6-8 mm, passing from top to bottom. Suitable for multi-pass welding of butt and overlap joints. Works with direct and alternating current of any polarity, minimum open circuit voltage is 60 V.
Welding electrodes OK 63.34
For welding you will also need a mask. To make your work easier, take a chameleon welding mask.
Why so popular
Rutile electrodes are considered one of the best. They have a number of advantages, thanks to which a welder with any experience can obtain an even and high-quality seam.
- Can be used with both AC and DC current . The welding arc in any case maintains combustion stability.
- You can weld metal joints coated with a light layer of primer .
- Ideal for use when welding short seams or in awkward places. The arc is easy to ignite and just as easy to re .
- Allows you to form a seam with a high impact strength . This is achieved due to the increased alkalinity of the slag.
- The rutile welded seam has excellent durability and fatigue strength . Even under prolonged exposure to alternating loads, it retains its qualities.
- a low spatter coefficient is characteristic . This makes the welding process more convenient for the welder.
- Convenient to reuse the electrode. After welding is completed, carbon residue remains on the tip of the rod, which does not need to be cleaned off (unlike other types of coatings). The carbon deposits of rutile electrodes are a semiconductor, so you can continue working without additional problems.
- Less harm to health . During the combustion of rutile coating, no hazardous substances are released. Therefore, there is less negative impact on the welder’s respiratory system.
IMPORTANT: Low requirements for the hob. Even with strong surface moisture, the seam does not lose its properties. Welding is also allowed in the presence of a corrosion layer (up to 30%).
DC Electrode Rating
Differences in welding with different current polarities.
Types of electrodes used for DC welding:
- UONI - 13/55 - famous electrodes of their kind for direct current, applicable for steel alloys - with low doses of alloying elements and with the addition of carbon. They have significant advantages: the welding seam is very plastic and tough for mechanical stress, very durable. Almost no impurities and gases are formed. The arc is easily ignited. A wire of parameters Sv-08 or Sv-08A is placed in the rod.
- UONI - 13/45 are also used for joining workpieces made of carbon and low-alloy steels. The seam is not inclined to form cracks - neither hot nor cold. It is very ductile and tough, with ideal tightness, which makes it a suitable option for welding containers that will subsequently be subject to high pressure. Seams made with these electrodes do not age much longer.
- OZL – 6 are distinguished by their narrow focus: they are used in working with heat-resistant steels. Pores and cracks do not form in the seams, they are not subject to further corrosion and have the same heat resistance as the base metal. Suitable for metals with different structures.
- OZS-12 are intended for steel alloys with a low proportion of alloying additives and carbon. It is possible to work in any spatial position and is tolerant of surfaces with rust. The weld is formed with excellent characteristics: strength and durability. Stable arc. There are no releases of toxic substances during operation.
- TsL - 11 are also highly specialized electrodes, which are intended for steel alloys with additions of chromium and nickel, as well as corrosion-resistant steels. Welded seams are resistant to corrosion. The metal hardly spatters, the arc is stable, and the slag in the form of a crust is easily separated.
- ANO - 21, despite the fact that they are also intended for carbon and low-alloy steel alloys, like previous brands of electrodes, these consumables are extremely popular among craftsmen of various levels of professional training. Their features are a fine-scale structure of the weld metal, excellent arc ignition, softness, slight metal spattering, and so on.
- LB – 52U are distinguished by the high productivity of the welding process with their help. The arc is stable, the metal hardly spatters, work is possible in any position in space, and almost no cracks form in the seam.
- MR - 3 typical universal electrodes, which are rightfully present in both lists - for both alternating and direct current. Pores and hot cracks practically do not form in the weld, the arc is powerful and stable, there is little spattering of metal, and easy separation of slag in the form of a crust.
- OZCH – 2 are intended for welding cast iron. Despite their seemingly narrow functional focus, they have solid advantages in the form of versatility, ease of use, an excellent arc with excellent characteristics, ductility of the weld without cracks, and a well-separated crust with slag at the end of the process.
Rutile electrode coating - characteristics
Electrodes with this type of coating can most often be of two main types: E42 and E46 (according to the state standard). The type must be indicated on the packaging label. Weld metal welded with E42 type electrodes has the following technical characteristics:
- Tensile strength - 410 MPa;
- Relative elongation - 22%;
- Impact strength - 80 J/cm2.
A seam welded with E46 electrodes has more durable characteristics:
- Tensile strength - 450 MPa;
- Relative elongation - 20%;
- Impact strength - 147 J/cm2.
In the manufacture of rutile electrodes, low-carbon welding wire (SV-08 or SV-08A) is used. A rutile coating is applied to it. The marking of such electrodes contains the letter “P”, which indicates the type of coating. As a rule, the letter “P” is always followed by two numbers:
- The first indicates in what spatial positions welding can be performed. Most rutile electrodes can be welded in any position.
- The second indicates the type of welding current: alternating or direct, its polarity and open circuit voltage.
Distinctive features
Rutile electrodes have a number of positive characteristics that distinguish rutile and basic electrodes. Here are some differences:
- Non-toxic gas when welding.
- Strong arcing even during voltage surges in the network.
- Minimal spatter with minimal metal loss.
- The seam is neat, reliable, high quality with a fine pattern.
- The seams do not bend or break later.
- It is easy to separate the slag crust.
- Allows welding in any position - both vertically and horizontally.
Important! Due to their composition, rutile electrodes during welding help to increase the viscosity of the metal, which prevents deformation, porosity and cracks in the weld.
Marking
Depending on the manufacturer and the specific type of product, package markings may differ slightly. However, most rutile electrodes are labeled almost the same. Let's take a closer look at the example of marking MP-3 electrodes.
On their packaging you can see the following markings: E 46 – MR-3 – UD E 430 (3) - P26.
Let's look at everything in order:
- E46 - indicates the type according to GOST. This means that this model is designed for welding low-alloy and carbon steels. Tensile strength - 46 kgf/mm2.
- MP-3 is a brand from the manufacturer.
- U - indicates the purpose of the electrode. For welding carbon steels, tensile strength is 60 kgf/mm2.
- D is the coating thickness coefficient (thick).
- E - international marking. Indicates the type of electrode with a consumable coating.
- 43 - tensile strength (430 MPa).
- 0—relative elongation index (20%).
- (3) - temperature indicator -20°C. This is the minimum temperature at which the weld metal retains an impact strength of at least 34 J/cm2.
- P - type of coating. In our case - rutile.
- 2 - shows in what positions welding work can be carried out. This indicator means that you can cook in any direction except vertical “top to bottom”.
- 6 - for high-quality work you need to use a current of reverse polarity, constant. The open circuit voltage should be approximately 70V.
[ads-pc-2][ads-mob-2]
Types of electrodes
E42A
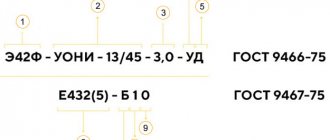
-UONI-13/45-3.0-UD ———————————— E432(5)-B 1 0
The marking consists of a group of letters and numbers, behind which there are certain characteristics. For clarity of explanation, let’s take as an example common electrodes with the following markings:
The first indices E42A indicate the type of consumable element. There are several of them and they explain to the welder which metal is best welded with certain electrodes.
| Surfacing of the surface layer of metal | E-10, E-10G3, E-12G4, E-15G5, E-16G2ХМ, E-30G2ХМ - in total there are 38 types of this group |
| Welding structural carbon and low alloy steel | E38, E42, E46, E50, E55, E60 |
| Welding of carbon and low-alloy steels with increased requirements for impact strength and weld ductility | E42A, E46A, E50A |
| Welding of alloy structural steels | E70, E85, E100, E125, E150 |
| Welding of high-alloy structural steels | E-12X13, E-06X13N, E-10X17T, E-12X11NMF, E-12X11NVMF |
| Welding heat resistant steel | E-09M, E-09MH, E-09X1M, E-05X2M, E-09X2M1, E-09X1MF, E-10X1MNBF, E-10X3M1BF, E10X5MF |
In our example, type E42A is indicated, where:
- E - electrodes for RDS.
- The number 42 is the tensile strength, measured in kg per mm?.
- A - the weld metal will have increased ductility and impact strength.
Thanks to knowledge of this part of the marking, you can easily select electrodes based on the strength of the seam - the higher the number, the stronger the connection. For example, in our case, 42 means that the welded seam will withstand a load of 42 kg per 1 square millimeter. When resistance to sudden loads is required, choose consumables with the prefix “A” in the type.
Physico-chemical composition
Depending on the manufacturers and various modifications, the composition of the rutile coating may differ slightly. However, in most cases the composition is as follows:
- Rutile concentrate (titanium dioxide) - 48%.
- Feldspar - 20%.
- Ferromanganese - 15%.
- Magnesite - 15%.
- Dextrin - 2%.
Some types of electrodes may also contain additional elements: for example, cellulose. Such coatings are marked with the letters “RC”, which stands for “rutile-cellulose coating”.
What does the electrode coating consist of?
To create an electrode coating with specified properties, various ingredients and their combinations are used. All of them can be divided into categories according to the role they perform in welding.
The main component of the electrode coating
- Gas-forming. When welding, they create a gas cloud around the arc. This gas prevents oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen from the atmosphere from penetrating the metal. This category includes: cellulose, food flour, wood flour, dextrin, starch and carbonates.
- Slag-forming. A slag layer is formed, which protects the metal from the atmosphere and slows down its cooling. These include: dolomite, marble, kaolin, manganese ore, quartz sand, chalk, feldspar, titanium concentrate and other substances that can be converted into slag.
- Alloying. These additives give the weld metal special properties: strength, ductility, resistance to oxidation, high and low temperatures. Among these substances: tungsten, molybdenum, titanium, manganese, nickel, vanadium and chromium.
- Deoxidizing. Oxygen in welded joints increases the brittleness of the metal. You can remove it by adding aluminum, silicon, titanium or manganese to the molten metal.
- Stabilizing. They could also be classified as gas-forming, since they also emit gas. But this gas is not intended to protect the weld pool, but to maintain the arc. This includes chromate, saltpeter, potash and other potassium compounds.
- Binders. The purpose of these coating components is to connect the coating elements to each other and to the welding wire. Liquid glass is most widely used as a binding component.
- Shaping. They improve the plastic properties of the coating, which is important when applying the coating by machine. These substances include kaolin, bentonite and others.
To increase the efficiency of the welding process, iron powder can be added to the electrode coating.
Some ingredients can perform more than one function: for example, create a protective gas cloud that supports the arc, and then turn into slag that protects the weld metal.
Rutile electrodes: application
Due to its excellent qualities, rutile coatings are widely used in various conditions and are considered one of the most practical types. We list the main applications in which electrodes of this type do an excellent job:
- Welding of low carbon steel structures . The chemical composition of the coating allows you to effectively work with ferrous and low-alloy metals. In such cases, the seam is smooth and without cracks.
Welding of pipelines. Excellent for repairing pipes that carry liquids. In this case, it is difficult to completely dry the working surface of the metal. However, the welding arc of rutile electrodes burns stably even when drops of water enter the combustion zone.- Widely used for repairing parts or tools that wear out over time . Rutile electrodes make it possible to deposit welds of considerable thickness as efficiently as possible. Due to small splashing, material savings are achieved.
AC Electrode Rating
Types of electrodes for welding with alternating and direct current.
The type of current is indicated in all markings of consumables - this is always the last digit. The main thing is to remember that if the last place in the marking is 0, then the electrode is not suitable for welding with alternating current.
- OZS – 12 with rutile coating. The most common type of electrodes for welding with alternating current, which is used on almost all Russian-made machines. Excellent welding of carbon steel parts, suitable for connections of critical structures. Significant advantages of these electrodes are the ability to work in any position in space, the absence of pores in the seam, a stable arc, and a completely acceptable dose of toxic gases released during the welding process.
- MP – 3 are designed for welding low-carbon steels. The advantages are similar: excellent arc stability, acceptable metal spatter. The slag crust comes off very easily. With these consumables you can cook even rusty, damp and poorly cleaned workpieces.
- ANO – 4 are also used for carbon steels. Excellent arc that ignites quickly and easily. You can cook wet and rusty products. There are no pores or cracks during seam formation. Easy separation of slag crust. There is virtually no metal spattering.
- MP-3C are distinguished by their high versatility: they are suitable for both low-alloy and carbon steels. The arc is ignited easily and instantly, the seam is protected from slag and oxides due to the rutile coating. The seams are smooth and durable, they can withstand significant loads. You can work with them in any position in space.
- ANO – 6 are used for connecting parts made of low-carbon steels. They are not afraid of rust, scale and dirt. The arc is stable and easily ignited, the seam is formed correctly.
- OZS – 4 for carbon steels, can be welded in any spatial position. The arc ignites easily. You can weld metal workpieces with edges of medium and large thickness at high temperatures. Attention! Doesn't like dirt on the surfaces being welded - they stop working.
- ANO – 21 are also intended for steels with carbon additives and low-alloy alloys. They are very easy to handle, can be worked in any position, and are also used in conjunction with an inverter and a semi-automatic transformer. The metal hardly splashes during operation, and the slag in the form of a crust is easily separated. An arc with excellent qualities - stable and soft.
- OZS – 6 are intended for carbon steels. They are characterized by a high throughput speed, which gives high labor productivity with a welding seam of excellent quality. Capable of welding oxidized surfaces.
Rutile coated electrodes: pros and cons
Compared to other types of coatings, rutile has a number of advantages:
- Seam durability . Welded metal is not susceptible to cold or hot cracks.
- In contrast to the acid coating, the rutile welding arc burns with alternating current as intensely as with direct current.
- Easy to process areas where short seams are needed . If the main coating requires continuous welding, since the welding arc is difficult to re-ignite, then with rutile it is easier. The arc ignites easily, and there is no need to clean carbon deposits from the tip of the rod.
- It is not necessary to prepare the work surface . Other types of electrodes are susceptible to oxidation and rust, resulting in a weak weld. Rutile electrodes allow you to form a stable and durable seam, regardless of the quality of the surface.
- After welding, the slag is easily separated , and the surface of the weld practically does not require grinding.
There are also disadvantages:
- Not suitable for all designs. The small range of metals with which this type of coating can be used imposes certain restrictions on their operation. Such electrodes cannot be used for welding high-carbon steel .
- The properties deteriorate sharply with increasing voltage. Therefore, you will have to monitor compliance with the nominal indicator.
- It is necessary to carry out preparatory work - drying and calcination .
[ads-pc-4][ads-mob-4]
What is special about rutile electrodes?
To understand all the advantages and disadvantages, you must first say that a rutile electrode is a rod into which, like all others, there is a metal core. But there is a difference - rutile coating, and rutile is a natural mineral that will make the welding seam not only high-quality, but also very neat.
However, only manual arc welding is assumed here.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the advantages of rutile electrodes for welding:
- The harmful effects of caustic fumes are reduced by titanium oxide - the mineral rutile is obtained from it.
- The arc burns more stable and ignites faster and easier.
- Rutile slag can be removed more easily.
- The seams become more resistant to tears and breaks.
- Pores due to oxygen ingress are much smaller thanks to rutile.
- The welding is good, even if the metal requires cleaning.
- The metal is sprayed in small quantities, so that vertical and even ceiling joints can be easily made.
Moreover, the welding itself will be simple, so it can be carried out with any placement of materials; even with sudden movements, the arc will maintain its combustion.
Sometimes iron powder is added to the coating, which increases the amount of welded metal and reduces the risk of defects.
Among the disadvantages that you may encounter when using rutile electrodes:
- Before use, you need to dry and calcinate, and after calcination you need to wait another 24 hours.
- It is important to maintain the accuracy of the modes so that the quality of the rods does not decrease.
Such rods have much more advantages than disadvantages, which easily explains their popularity.
The best brands of rutile coated electrodes
ESAB-SVEL OK 46.00
Produced in Russia by the Swedish concern ESAB. This model is one of the best in its category and has the following advantages:
- Low requirements for preliminary preparation. Even damp products can be calcined at a temperature of 70-90°C.
- They are not afraid of moisture. The arc burns stably upon contact with a moistened surface.
- The minimum threshold of the required current, which is needed for reliable combustion, is significantly lower than that of other types of electrodes.
- Forms a strong and impact-resistant seam.
Lincoln Electric Omnia 46
They are produced by the American company Lincoln Electric, which has been producing electric welding products since 1927. Electrodes are affordable and are an excellent choice for beginners. The welding arc does not require precise control; if it is slightly extended, combustion stability is not lost.
When operating the Omnia 46, a relatively small amount of sparks are generated. A strong seam allows them to be used for welding critical structures (for example, pipelines operating under high pressure).
OZS-12
Electrodes of this brand have a NAKS certificate, which allows them to be used for welding work at critical and hazardous facilities. Among the advantages of the brand:
- The seam is made easily and smoothly, even without special welding skills.
- After cooling, a thin slag crust remains on the surface, which is easily separated.
But there is also a drawback . Despite the fact that rutile coatings are usually not susceptible to moisture, electrodes of this brand are sensitive to dampness . This entails additional requirements for storage, calcination (at a temperature of 150 ° C before each use), as well as cleaning the weld pool from large contaminants.
MR-3
MP-3 type electrodes are one of the most common. The Resanta brand managed to preserve all the advantages of rutile coating and avoid the disadvantages that are found in other manufacturers of products of this type.
MP-3 are easy to ignite, form a strong and even seam, and work effectively with different currents. The disadvantage is increased sensitivity to moisture. Before use, they must be calcined for at least an hour at a temperature of 150-170°C.
What is alternating current in welding
Is it good or bad, which current is better? Variable or constant? No one will give you a definite answer.
Welding classification.
To begin with, it is better to understand the features of processes with alternating current, they are as follows:
- The behavior of the arc leaves much to be desired: with alternating voltage it is the most unstable.
- The welding seam is not of the highest quality due to deviation from the axis of the welding arc.
- If the arc goes out, its combustion can only be resumed when the voltage increases.
- The metal is splattered to a large extent.
Despite all these complexities, the equipment required for AC welding is simple and inexpensive. These are, first of all, transformers - devices that are still very popular among welding masters.
It would seem that electrodes for alternating current should gradually lose their relevance: after all, many rectifiers have appeared on the market - inexpensive and with small dimensions convenient for use. However, these consumables are still in demand in many industries and handicraft workshops.
Most of the brands are universal, which is also extremely suitable for older generation domestic welders.
If you look at it, the best consumables for “change” have and show very serious production advantages. First of all, this concerns the resulting electric arc: its durability and easy ignition. Another feature of such electrodes is the low level of metal spattering during welding.
Welding transformer
Electrode diameter and steel thickness.
To carry out welding using a transformer, the following mandatory structural elements are required:
- Windings primary and secondary. The primary is made of a special insulated wire; there is no insulation on the secondary winding.
- Magnetic wire.
- Screw for controlling the position of two windings and changing the distance between them.
- Protective housing for the entire unit.
- Screw handle, running nut.
- Fan and other elements depending on the transformer model.
Despite the fact that many welding professionals regard transformers as equipment of the “outgoing generation,” they are presented on the market in the form of a wide range of models of very different values and for wallets of any thickness.
Transformers differ according to the following criteria:
- dimensions and weight;
- output current strength;
- output voltage level at idle;
- volume of electricity consumed;
Welding generator
It is assessed as an independent device, necessary for operation if there is no full-fledged network electricity.
Electrode markings.
The generator design includes the required structural elements:
- The most important part - the converter consists of an electric generating element with an alternating voltage motor. They provide changes in current indicators.
- Drive internal combustion engine.
- Indicator for monitoring and recording current strength.
- Mode switches.
- Special circuit breaker.
- Regulators for current and arc behavior.
- Terminals for connecting cables and 230V outlets.
These types of generators are available in two versions:
- Collector generators.
- Valve generators.
The main advantages of a gas generator in comparison with other welding machines are:
- Compact and therefore highly mobile.
- Convenience, relative cheapness, noiselessness.
- Wide functionality and high reliability.
- Quite high technical characteristics.
Welding with rutile coated electrodes
Several nuances that must be taken into account when carrying out welding work:
- Check what material the electrode is made of. And now we are not talking about the coating, but about the rod itself. To achieve the highest quality weld, the metal of the rod must match the metal of the structure that is being welded.
- It is also important to consider the thickness of the electrodes. It must correspond to the thickness of the metal of the structure, although it may be thicker or thinner, which is compensated by the current strength and the skill of the welder.
Video
Watch a couple of videos where a craftsman shares his experience of working with rutile electrodes.
Calcination of electrodes with rutile coating
Electrodes of this type require pre-calcination before use. Common requirements for calcination: at least an hour in an oven at temperatures up to 350°C.
These are general requirements, and exact guidelines vary by brand. Some models are slightly sensitive to moisture and can be calcined at relatively low temperatures (up to 90°C), or do not require calcination at all. Although there are brands that can become damp and lose their properties. The exact calcination mode is indicated by the manufacturer .