Cutting Features
The cutter must be moved smoothly along the cutting line and monitor the angle of inclination, which deviates 5-6 degrees against the movement of the tool. When the metal thickness is more than 0.95 m, the deflection is increased by cutting through the metal to a depth of about 20 mm, and the deflection angle decreases again. We have already explained in detail how to cut with a cutter so that the cut is even in the previous section.
How much gas is consumed?
Gas consumption when cutting metal with a propane-oxygen cutter depends on the thickness of the structure and the configuration of the cut. For clarity, we present the table below:
| Workpiece size (thickness), mm | Hole time, sec | Cut size (width), mm | Consumption, per m3 cut | |
| propane | oxygen | |||
| 4,0 | 5—8 | 2,5 | 0,035 | 0,289 |
| 10,0 | 8—13 | 3,0 | 0,041 | 0,415 |
| 20,0 | 13—18 | 4,0 | 0,051 | 0,623 |
| 40,0 | 22—28 | 4,5 | 0,071 | 1,037 |
| 60,0 | 25—30 | 5,0 | 0,087 | 1,461 |
Gas consumption is significantly reduced when surfacing or soldering is performed.
Nuances
The main task of the performer is to maintain the speed correctly:
- normal mode - sparks fly at right angles relative to the surface of the workpiece;
- low speed - flying away from the performer and an angle of less than 85 degrees.
After the process is completed, the oxygen supply is turned off first, and the propane is turned off last.
T. N. Ishkulov, education: vocational school, specialty: fifth-class welder, work experience: since 2005: “Performers who perform cutting for the first time using oxygen equipment must remember that they must start a new cut after a sudden stop from a different point, and not where the process was over."
Negative deformation
Beginning welders are concerned with the question of how to properly use a propane-oxygen cutter so that warping of the surface of the part does not occur. First you need to figure out what factors contribute to the occurrence of these defects:
- with uneven heating of the surface;
- a high cutting speed was selected;
- there was a sharp cooling of the heating area.
To eliminate the occurrence of the listed factors on the workpieces, they are first securely fixed and heated, and the speed is increased gradually. If warping does occur, then the original shape can be returned by firing or tempering, and the sheets can be straightened on rollers.
Kickback hazard
If the jet burns in an incorrect mode, a bang occurs and the flame is drawn inside the product, which leads to an explosion, as the fire spreads through the hoses and reaches containers with gases. To prevent a dangerous situation, the cutter is equipped with a non-return valve, which cuts off the flame and prevents it from spreading.
Terms of use
They are similar to safety precautions when welding, but have specific additions:
- It is not recommended to neglect protective equipment, as this leads to injury in the form of skin burns or damage to the cornea of the eyes from flying sparks, so goggles and gloves with long bells up to the elbow are required.
- The performer's clothing and shoes are made of non-flammable material.
- Gas cylinders are located no closer than five meters from the cutting site.
- The flame of the cutter is directed only in the direction opposite to the hoses.
- Cutting is carried out in rooms equipped with strong ventilation or in open areas.
If the equipment is idle for a long time, it is necessary to carry out preventive maintenance before using the cutter for its intended purpose.
Beginning of work
How to cut metal with a gas cutter - having completed the preparation, the performer slightly opens the propane valve, ignites a gas stream, and the nozzle of the product rests on the surface of the metal. Now you need to adjust the flame strength by alternately adding propane and oxygen. After setting the optimal force of the jet of the burning mixture, the product is located at a right angle to the surface of the part, the nozzle is located no closer than 5 mm.
If the cut begins in the middle of the sheet, then the starting point is set at the beginning of the cut. The surface is heated to a temperature of at least 1000 0 C, in appearance it becomes wet, then the oxygen supply is increased to form a powerful, narrowly directed jet.
A cutter instead of a soldering iron melts tin and copper
A standard oxygen torch has not only a maximum, but also a minimum burner power. It can cut steel sheet, angle or I-beam or weld them together, but is not suitable for delicate work or spot welding.
In addition to the already mentioned ultra-portable cutter with a reservoir located in the handle, which is enough for several minutes of work, there are miniature cutters that are connected to a standard collet cylinder with a flexible hose.
Unlike the ultra-portable version, they have slightly less mobility, but significantly longer continuous operation time.
Most mini-cutter models have two operating modes:
- Wide cone with a diameter and length of up to 5 cm. Used for melting solder, soldering tin and copper products.
- Short and narrow high-temperature torch. It is used for spot soldering of small parts and for soldering electrical and radio components.
Micro burner
It is also not suitable for cutting steel sheets and profiles, despite the high temperature of the torch - up to 1300 °C. Low pressure and low flame intensity have an effect. The device is very economical - gas consumption is 12 g/hour.
Basic methods of cutting metal with gas
Spear cutting - this operation is used to process stainless steel, cast iron and low-carbon steel of large diameters. The essence of cutting is that the spear is heated to the melting temperature and pressed against the workpiece being cut. The method is common in the field of mechanical engineering and metallurgy. Oxygen-flux cutting is used to work with high-alloy chromium and chromium-nickel alloys. This method is characterized by the fact that powdered flux is introduced into the gas (oxygen) stream; it serves as an additional source of heat.
Air arc cutting is based on melting metal using an electric arc. When using this method, gas is supplied along the entire electrode.
Propane cutting is performed when it is necessary to cut titanium, low-alloy and low-carbon steel alloys. Equipment of this type cannot cut metal thicker than 300 mm.
| Material thickness, cm | Penetration, sec. | Cutting width, cm | Propane consumption, m3 | Oxygen consumption, m3 |
| 0,4 | From 5 to 8 | 0,25 | 0,035 | 0,289 |
| 1,0 | From 8 to 13 | 0,3 | 0,041 | 0,415 |
| 2,0 | From 13 to 18 | 0,4 | 0,051 | 0,623 |
| 4,0 | From 22 to 28 | 0,45 | 0,071 | 1,037 |
| 6,0 | From 25 to 30 | 0,5 | 0,071 | 1,461 |
Necessary equipment
To perform various steel processing tasks, it is necessary to prepare equipment and appropriate tools. Operation is carried out using:
- oxygen and propane cylinders;
- cutting tool;
- mouthpiece of a certain size;
- hoses.
Safety precautions require the presence of a control valve on each cylinder. The propane cylinder has a reverse thread, so installing an additional reducer is impossible. The equipment has similar designs, both for home use and for industrial purposes. Before cutting metal, it is necessary to check the functionality and presence of all adjustment elements.
Hoses for oxy-propane cutter
The supply of ozone is marked in blue; the valves are located both directly on the cylinder and on the cutter. The propane stream is marked like all other gases and explosive substances, in red or yellow.
After connecting the torch, a process begins in which oxygen and propane merge in the mixing chamber, resulting in the formation of a flammable mixture. The design provides for the replacement of units for scheduled repairs and maintenance; if one of the units fails, it is possible to replace it and continue working. The mouthpiece is selected depending on the type of tasks performed, has different indications and differs in numbers.
Advice from experienced people: how to use
Instructions on how to use a gas cutter can be divided into general provisions and professional “minor” notes, which in fact are the most valuable practical assistants.
Table of cutting metals with a gas cutter.
First the general points:
Only with a mask! We carry out any work with any gas cutter only in a welder’s mask or special glasses. Working with an autogen is an activity with a sea of risks; safety precautions must be carried out for real and not childishly. We choose clothing and gloves with fire-resistant properties. If there are none, well: at least the minimum requirement is not to wear synthetic clothes. There must be a fire extinguisher at the workplace with all the correct expiration dates, etc.
Fire extinguishing equipment must also be placed nearby in accordance with fire safety regulations. Before work you need to stock up on: a ruler, a special pencil, a square and a tape measure; a special lighter, which is usually included with the equipment. When working, it is important to choose the right location. The torch flame should be located frontally in relation to the supply hoses
The hoses, in turn, should be positioned so that they do not interfere with you during the process. Another safety rule: gas cylinders should not be closer than 5 meters to you during operation. Ventilation should be excellent throughout cutting, preferably working outdoors. The floor in the workshop should be either concrete or earthen. If you haven't worked with your cutter for a long time, or are starting to use a new device, check the channels: they should be clean. In addition, always check the vacuum level in the chamber that is formed by oxygen. First, remove the propane hose - this must be done with the valves on both the cutter and the cylinder tightened. Then open the oxygen and gas valve on the cylinder at operating pressure. The injector is checked simply: put your finger on the gas nipple, if everything is correct, you will feel air being sucked into this nipple. Close the oxygen, all the valves and then connect the hose with flammable gas to the cutter: you can work.
Scheme of cutting metal with a cutter.
Stages of action during cutting, propane cutters:
First, an oxygen cylinder: set the operating pressure. Then a cylinder with flammable gas: we also set the working pressure. The reference point is oxygen pressure. The propane pressure should be about ten times less. If the device is three-pipe, then the difference will be five times. Slowly open the oxygen and gas valve, ignite the gas and use the valves to create the pressure of the heating flame. The manual gas cutter is ready for work, now the actual cutting of the metal with the cutter. A stream of igniting oxygen begins to flow to the combustion site. If the metal is heated sufficiently, the desired reaction will begin immediately. In this case, the oxygen supply pressure can be further increased until the metal is completely cut through. Now the autogen can be moved in the desired direction - along the line of the planned cut. The speed of movement must be determined as you go, it will depend on how the sparks and slag flow or are blown down from the burner. After cutting, carefully inspect the work area for any remaining pieces of molten metal.
God forbid you step on these - they will even burn through the thick soles of your boots. Cooling of parts is carried out either with water or naturally. After finishing cutting, you need to finish the work process, which is no less important than starting work. First we tighten the oxygen valve. The flame valves are closed next - the propane valve first, the oxygen valve next. We tighten the valves on the cylinders. We release the hoses from the gas: open and then alternately close the valves of the heating mixture on the device.
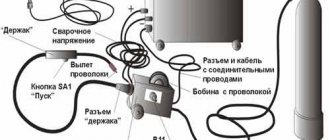
Cutter design
If a welder works independently, he may often need to quickly switch from cutting to welding. And the hoses can be disconnected quickly. You can save time by using a special insert cutter for burners. Mouthpieces can be used with “Sotki”; when changing, you can get holes in thicknesses of up to 100 millimeters.
If we talk about the cutter device, it looks like this:
- gas enters the cutter body through the hoses through the nipples. Propane goes to the western valve, and oxygen splits into two streams, one of which will go to the heating oxygen valve, and the second to the cutting oxygen valve, it is located outside the handle;
- when the heating oxygen valve is opened, it is supplied under pressure into the key hole of the injector, and propane is supplied to it through a series of peripheral holes due to vacuum;
- in mixed form, gases move along the lower tube of the tip towards the mouthpieces;
- internal and external mouthpieces with external threads are screwed into the head of the cutter tip;
- oxygen is supplied through the first valve with a central channel;
- the heating gas comes out of the annular gap, which is formed outside;
- When a flame appears, it is directed to the initial cutting location of the workpiece. The cutting oxygen valve opens when the area is heated to the desired temperature. A gas jet under pressure burns the metal and immediately blows it out with oxide.
Next, the acetylene or propane cutter is held at a certain distance from the metal product, leaving a narrow slot at the back, which is limited by the side and frontal planes.
As for such a structural element as a mouthpiece, the outer one should always be copper. But the internal mouthpieces for an acetylene cutter should be copper, and for a propane cutter - brass, respectively. When choosing the correct internal nozzle, depending on the thickness of the workpiece being processed, it is necessary to optimize the oxygen consumption in the cutting jet.
The mouthpiece is a consumable item because it quickly wears out and becomes clogged with molten metal residues.
The hose nipple should be made of brass. If you are planning to purchase a budget gas cutter along with hoses, then its components may be partially aluminum, which makes the product wear out quickly, and covered with brass or copper on top.
Burner device
A torch for welding with propane consists of a handle with valve devices located on it, which provide regulation of the supply of gases and mixing them in the required proportion. Gas supply hoses that comply with current standards (GOST 9356) are connected to them using special nipples.
According to this standard, each of the hoses (sleeves) is equipped with a replaceable tip with a mixing chamber, which in turn is equipped with a built-in injector.
The hose chamber indicates the type (number) of the tip and the name of the gas for which it is designed to work. The convenient and ergonomic arrangement of the valves allows you to hold the torch handle with one right hand, while performing all the necessary work operations during the welding process with the other.
Read also: Voltmeter for measuring alternating voltage
The tip of a typical gas burner consists of a mouthpiece, an injector and a special supply tube. The dimensions of the holes in the mouthpiece and in the injector (more precisely, their ratio) are designed for the use of these units only for a specific type of gas (propane or oxygen).
The temperature developed in the combustion zone of propane with oxygen can reach approximately 2300 °C, and therefore the mouthpieces of these prefabricated structures are most often made of copper.
This is explained by the fact that copper materials have greater thermal conductivity (compared to brass mouthpieces, for example), and cool faster during the welding process.
How to choose the right gas cutter: expert advice
Gas cutting is widely used for dismantling metal products and structures. This is one of the easiest ways to cut metal. It involves the use of cylinders filled with flammable gas and oxygen, and a cutting torch. The principle of operation of such equipment is the formation of a powerful gas jet, under the influence of which the metal burns, resulting in oxidation products remaining in the cutting area.
1 / 1
Device
Gas cutters for flame cutting of metal presented today generally have a similar design. The main elements include:
- injector/ejector – designed for mixing substances (gases);
- inlet connectors and nipples – necessary for connecting gas hoses: flammable gas and oxidizer (oxygen);
- mixing chamber – a flammable mixture is formed in it;
- valves - allow you to regulate the supply of components of the combustible mixture;
- nozzle (mouthpiece) - the tip of the gas cutter tube.
Using a gas cutter is quite simple, the main thing is to follow safety precautions. A standard gas cutter works as follows: the cutter connects the flammable gas and oxygen supply hoses from the cylinders, then opens the valves until the required pressure is formed, ignites the mixture and regulates the burning power of the flame by rotating the valves on the handle of the gas cutter
As a result of these simple manipulations, oxygen and gas are mixed into a single stream, during the combustion of which a powerful stream simultaneously burns the metal and blows away the straightened drops of metal. This scheme is similar for most models for gas cutting; the only differences are in ejector devices.
The ejector device differs from the injection device in that it has a separate channel for supplying oxygen and a head with two replaceable mouthpieces.
Types of gas cutters
To avoid making a mistake in choosing the right model, consider and study the existing types of gas cutters. They are classified according to the following criteria:
- Type of flammable gas: acetylene, propane, methane, etc.
- Type of cutting: separation and surface.
- Purpose: manual and mechanized.
- Oxygen supply: low and high pressure.
- Power: low (up to 100 mm of the thickness of the metal being cut), medium (up to 200 mm), high (over 200 mm).
In addition, there is a classification of devices by design. This includes dimensions, number of tubes and other characteristics.
How not to make a mistake with your choice
The choice of cutting torch directly affects the quality of work
If certain parameters are not taken into account, safety and performance may be impaired. Do not forget that the flammable mixture used for cutting metal products is explosive.
When purchasing a gas cutter, pay attention to the following points:
- The handle must be made of aluminum alloys. Plastic is used in the manufacture of cheaper devices, so it is recommended to avoid choosing it, because... Over time, it begins to collapse and lose its original shape.
- When choosing nipples, give preference to brass. This material will last longer than its aluminum counterpart, because... has great resistance to deformation.
- The valves should rotate with a slight force to stop the cutting process in an unusual situation. It is advisable that the valve size be at least 4 cm.
- The cutter should have a collapsible design, which will allow for regular maintenance, which will contribute to long-term operation.
- The outer mouthpiece should be made of pure copper or chrome bronze. For an acetylene torch, the internal tip must also be copper.
- Make sure the body and connection tubes are made of stainless steel, brass or copper.
- It's good if the cutters are not painted, because... paint is usually decorative. It can hide various defects in the metal and soldering flaws.
- The most reliable valves are made of stainless steel - on average they can withstand up to 1500 opening and closing cycles without replacement. Brass analogues last no more than 500 cycles and subsequently do not provide tight locking, which threatens oxygen and flammable gas leaks.
Welding technique
Propane welding involves the use of the following two techniques:
- high-temperature heating of the edges of the workpieces, their subsequent melting and final joining;
- formation of a working seam by surfacing or spraying.
In the second case, a special soft metal filler wire is used to ensure that the weld pool remains fully saturated.
When carrying out work operations using the first of these methods, a large amount of propane is consumed, since high temperatures are required to melt the metal edges. Therefore, preference is most often given to the second welding method, in which noticeably less energy is spent on heating the filler wire made of low-melting metals.
Both of these approaches when working with propane generally lead to the same result. However, they differ fundamentally in terms of gas mixture consumption, time spent on operation and functionality (in other words, in their efficiency).
Welding by surfacing, in addition to saving money and time, provides increased strength of the seam and looks more aesthetically pleasing. It is this technique that is used when laying and equipping main pipelines, as well as when welding various products and elements of building structures.
Advantages and disadvantages
The gas burner is designed for cutting products in production conditions, with a large volume of tasks
Before using the device, it is important to understand what key features metal cutting with propane and oxygen has:
- The mechanism of action is convenient when making curved cutting lines. Stable power allows you to separate metal products of various thicknesses into parts. In situations where it is impossible to use a tool such as an angle grinder, a gas torch is used. The task of making a round product or a blind hole is performed with a gas torch without requiring much effort.
- A gas cutter has an advantage over gasoline models. In addition to being lightweight, the mechanism does not produce excessive noise during operation and is also compact.
- The use of a device based on the influence of flammable gas makes it possible to double the speed of execution, which is beyond the power of mechanical tools.
- Propane, as a liquid gas, has a low price. Therefore, it is used not only when processing products for production needs, but also when recycling metal and other activities.
- The use of propane as a flammable mixture allows for high-quality cutting. Cutting is carried out along a narrow line, which is the main factor in quality work.
Read also: Circulation pump in the heating system of a private house
The disadvantages are that some materials cannot be processed with a propane cutter, such as cast iron and high-alloy steels.
Setting up a cutting torch
Setting up a cutting torch is carried out at the manufacturer as the final operation of the assembly process. It is prohibited to engage in any additional amateur “tuning on your knees”, as it can lead not only to a deterioration in operating parameters, but also to an explosion of the equipment.
Before starting work, you should assemble the equipment and check its functionality in accordance with the “Operating Instructions”. Only after this can the metal processing process begin.
Attention! It is strictly prohibited:
- blow oxygen through the propane hose;
- change sleeves with each other.
If you do not have access to the “Instructions”, then proceed in the following sequence. Before assembly, it is necessary to carry out an external inspection of the components and parts:
- Check the condition of all rubber gaskets. If there are the slightest defects, they must be replaced;
- carefully inspect the oxygen valve. The slightest traces of oil or fat are not allowed on its surface - their presence can lead to an explosion;
- carefully inspect the fittings. The flammable gas connection must have a check valve. Defects on the fittings should be carefully corrected with a “velvet” file. If this is not done, then the rubber gasket of the gearbox will “poison” with all the ensuing consequences.
After inspection, gearboxes should be installed:
- blue – for an oxygen cylinder;
- red - for a propane tank.
If the cutter has injection, you should check its functionality:
- the check is carried out before connecting the flammable gas hose;
- the oxygen hose is connected to the corresponding fitting;
- open the oxygen reducer valve;
- open the oxygen and flammable gas valves on the cutter;
- Place your finger on the flammable gas fitting. If everything works, then it should be “sucked in”. In this case there will be no backlash.
Next, a propane hose is installed and gas is connected. The ratio of propane and oxygen is set to 1:10. For example, if the oxygen pressure is 5 atm, then the propane pressure should be set to 0.5 atm.
It is necessary to open and stop the gas supply in the following sequence:
- open each oxygen and flammable gas valves by 0.5 turns (the sequence cannot be changed). Set the mixture on fire;
- bring the torch to the metal and add oxygen until a “crown” appears;
- upon completion of work: the supply of flammable gas is stopped first, then oxygen (the sequence cannot be changed).
Preparatory work
How to set up a cutter for cutting metal - first of all, you need to make sure that the product is in good condition and ready for work, then perform the following procedure:
- The hoses from the cylinders are connected to the cutter, having previously purged the product to remove foreign inclusions from the inside.
- Oxygen is connected to a right-hand thread fitting, and propane is connected to a left-hand thread fitting.
- Set the propane supply level to 0.5, and oxygen to 5.0 atmospheres.
- We check connections for leaks, as well as the operation of gearboxes and pressure gauges.
If gas leaks are detected, tighten the nuts or change the gaskets.
The diagram shows the correct connection of the cylinders to the cutter.
Cutting metal with an oxygen-propane cutter: pros and cons, technology, features
Gas cutting seems to be a simpler process than gas welding work, and therefore even a person who does not have special skills can cope with it. For this reason, almost any of us can master working with a cutting torch.
The main thing here is to understand the essence of gas cutting technology. In modern conditions, propane cutters are increasingly used.
Working with them requires the use of both propane and oxygen, since the combination of such substances provides the maximum combustion temperature.
Features of use
Such tools are not suitable for cutting high-carbon steels for the reason that they have a fairly high melting point, which is almost the same as the flame temperature.
This leads to the fact that instead of the release of scale, which looks like a column of sparks, from the back side of the sheet, it mixes with the molten metal along the edges of the cut.
As a result, oxygen cannot reach the thickness of the metal, which is why it fails to burn through the material.
Difficulties when cutting cast iron are created by the shape of the grains, as well as the graphite between them. True, this does not apply to malleable cast iron. It is impossible to solve the problem if you have to deal with aluminum, copper and their alloys.
It is important to dwell on the following point: the category of low-carbon steels is represented by grades from 08 to 20G, medium-carbon steels - grades from 30 to 50G2. A characteristic feature of carbon steel grades is the presence of the letter U in front of their names.
Let's get started
First, you need to move the oxygen reducer to the position corresponding to 5 atmospheres, the gas reducer to 0.5. You also need to make sure that each valve is in the closed position.
After that, you need to take a propane torch and open the propane slightly, and then light it. The cutter nozzle must be positioned so that it rests on the metal, after which you need to slowly open the oxygen control. Next, you should adjust these valves one by one, thereby ensuring the required flame supply force. During such a setup, you need to sequentially open gas, oxygen, gas, oxygen.
When choosing the flame strength, you need to focus on the thickness of the metal. As the thickness of the sheet increases, the strength of the flame will have to increase, which will lead to an increase in the consumption of oxygen and propane. After adjusting the flame strength, you can start cutting metal.
The nozzle must be held in relation to the edge of the metal so that it is removed from the object being cut at a distance of 5 mm, and it itself must be located at an angle of 90 degrees. In some cases, it may be necessary to cut through the sheet or product in the center.
In this case, the starting point is chosen to be the place from which the cut will go.
The essence of the procedure is to heat the top edge to a temperature of 1000-1300 degrees Celsius. The exact temperature is determined taking into account the metal. In practice, such work will look like the surface appears to be “wet.” The heating itself will take no more than 10 seconds. After waiting for the metal to ignite, you need to open the cutting oxygen valve, after which a powerful, narrowly directed jet will begin to flow.
Cutting Features
When opening the valve of a propane cutter, do not rush. In this case, the ignition of oxygen will occur naturally as a result of interaction with the heated metal. By acting this way, you will eliminate the risk of a flashback of the flame, during which you may see a pop. It is necessary to slowly guide the oxygen stream strictly parallel to the given line
It is important not to make a mistake with the angle of inclination.
First, it is maintained at 90 degrees, after which it is necessary to create a slight deviation of 5-6 degrees in the direction opposite to the movement of the cutter. If you have to deal with metal whose thickness is more than 95 mm, then it is allowed to increase the deviation to 70 degrees. After the cut in the metal reaches 15-20 mm, the angle of inclination begins to increase to 20-30 degrees.
Oxygen consumption
Different flammable gases require different amounts of oxygen. Below is the ratio of oxygen consumption to the consumption of each of the three combustible gases (the so-called combustible mixture composition) required to form a normal cutting flame.
| Flammable gas | Mixture composition (oxygen consumption/fuel gas consumption) |
| Acetylene | 1,1 |
| Propane | 4,0 |
| Natural gas | 1,8 |
Application area. Only when using acetylene is it possible to change the composition of the gas mixture to obtain a neutral or reducing flame. At the temperatures used in industry, all other combustible gases produce only an oxidizing flame. For this reason, natural gas and propane are not used for welding.
For general heating, gas with a large supply of energy per cubic meter is required. For such purposes, propane is the most suitable gas.