These electrodes are used for welding carbon and low alloy steels. Scope of application: metal structures of special reliability, which must operate under large variable loads, including in cold climates or in refrigeration units, which makes them suitable for shipbuilding purposes. They are suitable for pressure vessels, thick sheet materials and for repairing casting defects.
This type includes the following brands: VN-48, OZS-2, SM-11, UONI 13/45, UONI 13/45A, UP-1/45, UP-2/45, TsU-6. (See also the neighboring type E42 in terms of characteristics).
Specifications
E42 electrodes are designed for welding with both direct and alternating current. They can have either acidic or rutile coating. Flux coating, burning in the flame of an electric arc, releases protective gases that prevent the access of air oxygen to the weld pool. It also helps to increase arc stability and delivers alloying additives to the work area. When working with an acidic coating, the suture material is susceptible to cracking, especially if welding conditions are not followed. The rutile coating eliminates this risk; the suture material, in its degree of deoxidation, is close to mild or semi-mild steel.
Electrode welding
According to their chemical composition, E42 electrodes belong to the group of conventional electrodes and contain the following elements:
- C - 0.08%;
- Mn7%;
- Si1%;
- S035%;
- P035%.
The electrodes have the following physical, mechanical and performance characteristics:
- Tensile strength - 420 MPa.
- Length with a diameter of 4 millimeters - 45 cm.
- Welding temperature range: -20 °C - +20 °C.
- Consumption per 1 kg of seam - 1.6 kg of electrode.
- The impact strength of the suture material is 150 J/cm2.
- The relative elongation of the seam is up to 22%.
- Diameter range - from 4 to 12 mm.
The specified parameters are achieved subject to compliance with welding technology and welding modes.
Analogues of electrodes E42
Application area
Electrodes of type E42 of various diameters are widely used for welding structural low-carbon steels. In addition, they can also be used to weld alloyed alloys 14G2 and 09G2.
They are popular both among home craftsmen and when installing industrial metal structures.
In addition, GOST allows their use for welding thin-walled pipes and low-pressure tanks.
Stainless steel welding
There are the following restrictions on use:
- Not suitable if arc welding is performed in a vertical position (top to bottom).
- Not suitable for use on stainless steel, copper and other non-ferrous metals.
- Incompatible with high alloy steels.
- Not suitable for cast iron.
Download GOST 9467-75
In addition, it is unacceptable to try to cook with damp electrodes.
Cost of electrodes
Considering the fact that for manual arc welding, performed in a home workshop or garage, electrodes of the fairly common ANO 6 brand are most often used, it makes sense to provide data on their cost. On average, the price of E42 electrodes remains at 65–70 rubles per kilogram. For comparison, you can provide data on the cost of electrodes of other brands, for example, MP3. The cost of such products, which have average technical characteristics, starts at 60 rubles per kilogram.
Taking into account the universal technical characteristics of E42 brand electrodes, we can conclude that they should be used to perform work of varying degrees of complexity, carried out by both beginners and professional specialists. If you need electrodes to perform work around the house or in the garage, then products of the E42 brand of the ANO 6 series are optimal.
Distinctive features and specific application
Type E42 is a universal product for mass use. However, some features of E42 electrodes can be noted for it:
- The resulting welded joint is strong and ductile, and is highly resistant to fracture loads.
- The resulting slag crust is easily separated from the suture material.
- The connection is characterized by a highly homogeneous structure, low porosity and the absence of cavities.
- The product does not require high qualifications and experience for successful use; it is enough to strictly follow the welding modes and welding technology.
- Easy arc ignition.
- Low material consumption per kilogram of seam.
- Wide range of flux coatings.
- Wide range of diameters – up to 12 mm.
- Excellent price/quality and price/functionality ratio.
Electrodes of small diameters are successfully used for welding structures at home, both with an inverter welding machine and with outdated bulky welding transformers and rectifiers. As long as the specified distance from the tip of the rod to the part is maintained, voltage surges in the network have a negligible effect on the stability of the arc.
Electrodes E42 diameter 5.0 mm
Diameters of 6-12 mm are used mainly in industrial environments, together with professional high-performance welding stations that develop operating currents of up to 600-800 amperes. E42 electrodes with a diameter of 8 mm allow you to weld parts with a thickness of over 8 mm in one pass, which makes them competitive in performance with semi-automatic machines that use welding wire.
E42 is not recommended for working on high-alloy alloys, stainless steel, non-ferrous alloys, and cast iron.
Choice
Let's start with the diameter. Everything is simple here: usually the diameter of the electrode is equal to the thickness of the metal you are going to work with. Thus, electrodes with a diameter of 4 mm or electrodes with a diameter of 6 mm are excellent for thick parts, and 2 mm or less are indispensable when welding thin steels.
As for brands, focus on your needs. If quality is more important to you, then buy OK 46.00. If price is more important - ANO-6. Consult with the seller in the store and read the GOSTs for each individual brand to better understand this issue.
Choosing a manufacturer should not be a problem either. If you are not ready to spend money on electrodes, then choose Russian-made products. If quality comes first and price comes last, then take a closer look at foreign electrodes. For example, to the Kobelco company.
Much more important is the quality certificate that you can request from the seller or manufacturer. The certificate confirms that the electrodes you purchased meet all modern standards and are genuine. There is one “but”: at the moment the manufacturer is not required to undergo quality control. This is a voluntary event. But, on the other hand, if the company has provided its products with certificates, then it really vouches for their decent quality.
Therefore, if, when purchasing electrodes, one manufacturer has a certificate and another does not, then of course it is better to prefer the first.
Restrictions on use
There are also restrictions on use. The main one is the unsuitability of the electrode for making vertical connections in the “top to bottom” direction, especially with large diameters. This is indicated by the number “2” in the type designation. When the weld pool moves vertically, part of the molten metal will flow into the space of the unwelded seam. The larger the diameter of the electrode, the greater the mass of the weld pool and the easier it is for the melt to overcome surface tension forces and flow down.
Also, electrodes of this type are unsuitable for welding stainless and high-alloy steels, cast irons and non-ferrous metal alloys.
It is also important to select the correct electrode diameter based on the thickness of the workpieces being welded.
In addition, it is unacceptable to try to cook with damp electrodes. The coating becomes a conductor under such conditions, and it will be very difficult to ignite an arc. The suture material will absorb hydrogen and form unwanted pores. Maintaining a stable arc will also be difficult due to frequent sticking of the electrode.
Analogs
E42 electrode rods are produced simultaneously by at least ten companies. Finding electrodes that fit into your budget and work scenario will not be difficult due to their prevalence.
In this case, there is no point in looking for a replacement, but there are different situations. And, if one of these happened to you, choose E42A rods. Their coating creates an acidic environment on the product, preventing the appearance of pores.
But keep in mind that hot cracks are dangerous for products welded with E42A.
If E42A does not satisfy you, look at the wire material from which similar rods are made. Compare the material with the composition of the alloy or steel of the parts being welded.
The electrode must be similar in composition to the elements in order for compatibility to be high. You can also look for an analogue by electrode coating. For E42 it is made of rutile.
Weld metal or surfacing
Surfacing is a welding operation in which a layer of molten metal (called filler material) is applied to the internal or external surface of a part. Surfacing is performed for the purpose of:
- restore the original dimensions of the worn part;
- bring the dimensions to the design ones when manufacturing a part and detecting a removable defect;
- create a coating of one metal with a layer of another in order to increase corrosion resistance or impart special physical or chemical properties;
- strengthen the surface layer.
Surfacing
The electrode is guided along the surface of the part at a given location. The top layer of metal of the part melts and, together with the metal of the electrode, forms a surfacing layer. If necessary, several layers are deposited. Despite the fact that there are special surfacing electrodes, E42 can also be used for surfacing relatively small volumes of metal.
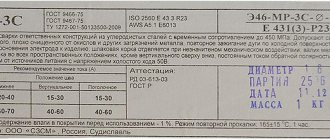
Certificate of Quality
The legislation of the Russian Federation requires that this document be obtained only for electrodes intended for work:
- In the navy. Certificates are issued by river and sea registers.
- In hazardous industries. The papers are issued by Rostechnadzor.
Manufacturers are not required to certify general purpose electrodes. But many do this on their own initiative in order to convince the buyer of the high quality of their products. Before purchasing consumables, it is recommended to ask the seller whether they have a certificate. Its presence will serve as a solid argument in favor of purchasing this brand.
Certificate for electrodes.
Coverage options
The working qualities of the electrode and the features of its use are largely determined by the material of the flux coating. There are several options:
- Sour. Based on silicon and iron oxides, manganese oxide is used as an additive. A connection made using such a coating is prone to the formation of hot microcracks.
- Rutile. Based on titanium dioxide. Compared to the previous option, the likelihood of the formation of hot microcracks is significantly reduced. Allows you to obtain a more stable and powerful electric arc. Reduces melt spattering and associated metal losses. Improves the formation and uniformity of the seam, forms an easily removable slag crust, which reduces the labor intensity of subsequent cleaning operations.
- Basics. It is based on bases - fluorine compounds mixed with carbonates. According to the degree of deoxidation, it corresponds to calm type steels. The suture material acquires high ductility and impact strength, both at room and at low temperatures. The likelihood of hot microcracks appearing is also reduced.
Electrodes "Tien Shan" type E42
For any type of coating, the requirement for use only in dry form remains. If you try to use wet electrodes, manufacturers disclaim their warranty on the quality of the seam. The products are supplied in hermetically sealed boxes with cellophane; they should be printed immediately before starting work. If the electrodes do become wet, they must be dried and calcined in a muffle furnace.
Also, regardless of the coating option, it is necessary to carefully follow the technology and welding modes.
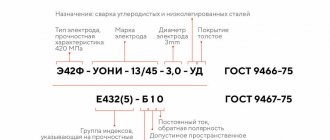
GOST requirements
Requirements for type E42 electrodes are set out in GOST-9567-75-E42. It defines such parameters as the linear dimensions of the rod and coating, a number of diameters, weight, material consumption per 1 kg of seam, impact strength of the seam and relative elongation, listed at the beginning of the article.
In addition, GOST 9467-75-E42A puts forward increased requirements for suture material, primarily for impact strength and elongation. There are no increased requirements for tensile strength; a number of diameters also remain unchanged. Thus, a seam using type E42A will be just as strong, but more malleable and flexible. The requirements for the percentage of sulfur, phosphorus and their compounds have also been increased.