The configuration and operational characteristics of sawmill equipment largely determine the success of wood processing production, both large and small, including home-based ones. It would seem that if you take the most expensive and “sophisticated” one, you won’t go wrong. However, it is important for each enterprise to select its own set of equipment that corresponds not only to its scale, but also to the volume of processed raw materials, its properties, and the characteristics of the finished product.
A striking example is the choice of an angle saw. Manufacturers and dealers place emphasis on cutting speed and quality of finished lumber. “You will receive high-quality products with excellent mechanical parameters,” “impeccable lumber geometry,” sounds tempting, doesn’t it? But we must remember that manufacturers are generous with their promises, and statements about the absolute superiority of one technology over another often turn out to be a marketing ploy, nothing more.
Buying equipment, especially unknown equipment, is possible only after a careful analysis of the needs of production and the entrepreneur’s own capabilities. The temptation to purchase a coal saw appears, as a rule, at the stage of modernization of an enterprise. But sometimes beginners also believe that it is better to invest in complex, productive equipment at the start.
Typically, this strategy is chosen by those whose finances allow them not to save. Although the price of the issue makes you think: the cost of a saw blade sawmill is several times higher than the cost of a band sawmill, and the cutting tool for it is not cheap. And this is the case when it is not the stingy person who pays twice, but the too generous one who can irrationally manage his investments.
Is it profitable to purchase an angle saw?
Disc sawmills are traditionally used for the production of edged lumber, parquet, laminated veneer lumber, blanks for molded products, and furniture panels. It is advisable to use charcoal saws for those who work with deciduous and coniferous forests up to 1000 mm in diameter and plan to produce radial lumber from them.
An angle saw is special equipment, and not a general-purpose machine. It is intended primarily for radial cutting of boards. This machine is best suited for those who plan to produce small, specially cut lumber, since it can be used to implement any log cutting pattern.
Boards obtained by radial cutting are often more expensive. Such lumber holds a more stable shape and is less subject to transverse warping when dried than, for example, those obtained as a result of tangential sawing. In addition, they are less susceptible to both swelling and drying out. It is not for nothing that the great Stradivarius preferred to use radially cut wood for his violins.
“Many beginners believe that with one such machine they will be able to export, without having their own timber lease and further deeper processing of wood,” says Andrey Noak, author of a professional blog about woodworking.
But you also need to take into account the productivity of such equipment: the final yield of boards during radial cutting, taking into account all technological features, is up to 35%, and often does not exceed 15%. The characteristics of the raw materials used play an important role: the angle saw cuts wood with a diameter of up to a meter of any curvature and with large branches that conventional sawmills cannot handle. Therefore, the smaller the log, the less such a machine is needed.
Flipping the log
If the turn is made 180 degrees, unedged boards are obtained that require additional processing on the sides, and then the half-beam is sawn into an edged board.
For efficient cutting, the log must be turned 180 degrees.
With a 90-degree turn, unedged and semi-edged boards are obtained with the need for trimming on one side. The 180° flip sawing method will produce more valuable wide boards. But if the edger has only one saw, turning it 90 degrees is convenient.
After cutting the opposite edges, the worst of the remaining ones is cut first, but this option does not take into account the taper. But a high-quality edge must be sawed parallel to the bark, which increases the yield of high-quality lumber.
In different planes
“It is believed that radial saws are intended only for the production of radial lumber. This is incorrect due to the nature of the miter sawing method itself. It would be correct to say that the method of miter sawing, along with the production of conventional edged lumber, makes it possible to simultaneously produce radial lumber from one log.
The possibility of individual cutting of a log using the angular sawing method allows you to simultaneously obtain radial lumber from defect-free zones of the log and regular edged lumber (but a different cross-section is also possible) from the area of defects. The thickness and width of sawn timber sequentially is limited only by the diameter of the saw blade.
By obtaining at least 20% of radial lumber from raw materials from the total volume of lumber produced, the woodworker significantly increases his profit at the same costs,” says one of the woodworking equipment manufacturers.
What do the users of this equipment—the woodworkers themselves—think? It should be noted that they are rarely ready to openly comment on their experience of working with a particular machine, citing either a lack of experience or certain “related factors” that are different for each wood product manufacturer.
Numerous industry forums become a source of information in this situation - here foresters do not mince words, and if the machine has any shortcomings, they will describe it in the best possible way. But they will not be stingy with praise if there is something to praise for. And at the same time, they will share the problems they encountered when operating this or that model, and their ways of solving them.
For reference, Angle sawing (longitudinal radial cutting of logs using an angular method) is performed on circular saws, when the direction of sawing the disks occurs in two mutually perpendicular planes. This is a new technology in the field of primary wood processing.
This method is simple: circular saws located in the vertical and horizontal planes sequentially cut lamellas from the log, at the end of which the annual rings are located “radially”, that is, at an angle of 45° to the largest plane of the lamella. The log is fixed on the stationary frame of the machine; a portal with a saw unit moves along it along the guides.
Secondly.
As soon as the width of the cut reaches the required size, and the remaining height of the log has reached the desired size, it is turned over. That is, if you cut a beam, for example, at 150, then both the width of the cut and the height of the remaining log should correspond to this value, even be greater, taking into account the removal of the slab.
Next, we know the final size of the material that needs to be obtained, and we will obtain it.
To do this, after turning the log over, start calculating from the final size until the full height of the log is used, but do not forget to take into account the size of the cut, which, as we already know, ranges from 2 to 5 mm.
For example, you have a log on your overpass that you have cut to a size of 260 mm. Let's turn the log over and continue.
The final result we want to achieve is a carriage with a thickness of 150 mm. Next, in a simple way, calculate that 260 mm-150 mm = 110 mm. We get as much as 110mm of extra material thickness. And it is precisely this that needs to be calculated correctly.
We take this additional size and calculate it to get the block, which has a size of 50 mm, 110-50 = 60, don’t forget the cut, and for us it is 2 mm, 60-2 = 58 mm, then the plank, equal to 25 mm, 58 -25-2=31 mm, hump 20 mm, 31-20-2=9 mm.
As you can see, from our calculations, we get 9 mm slab, 20 mm slab, 25 mm gorge and 50 mm block. And the final size will be 150 mm.
Opinions are divided
“An angle saw is a working tool. It is desirable that the possibility of sawing both in angular mode and in camber mode be implemented. Then there will be more opportunities to change the technological chain at different stages of development,” this is how one of the woodworkers spoke about his experience of working with a angle saw on a forestry Internet forum.
His opponent believes that buying an angle saw for camber or other simple cutting is “a crazy investment of money and shooting sparrows with a cannon.”
“I don’t see the point of using it as an alternative to a sawmill frame or a “ribbon”. The installed power is large, the tool is expensive, the machine will not accept crooked hands, the productivity is low. Therefore, when raising the question of for what purposes they buy coal cutting machines, you need to determine these goals for yourself. The first question, of course, will be the availability of suitable raw materials, the second is the availability of a contract under which the sawn products can be sold profitably,” says a sawmill equipment user.
“An angle saw is good when the area is limited and the dimensions of the lumber are close to the dimensions of the beams 100x100x6000, 150x150x6000. That’s when real economic feasibility appears,” his colleague supports.
For reference, radial lumber is used in the production of laminated window timber and supplied to the countries of the European Union.
Tools and equipment
Trunks and large branches are used for production. All material is divided into groups according to thickness and presence of bark. Often, timber processing enterprises have workshops near the harvesting site, in which machines for the initial processing of wood are installed.
Manual debarking of wood
Wood that has not passed the debarking stage can be used on floors or as ridge beams in the corresponding interior, or as a supporting device during construction.
Industrial debarking of forests
If another option for using the wood is planned, then sawing is carried out, resulting in the following segments:
- unedged and semi-edged (rough material from which the bases of the floor, walls or ceiling are mounted);
- edged (intended for finishing flooring).
The cutting can be carried out by a mobile organization that has all the necessary tools.
Wood cutting map
Rational use of the material is ensured by compliance with the cutting map. This allows you to reduce costs due to waste, the percentage of which the card can significantly reduce. The tools and types of forest processing equipment used depend on the volume, desired quality and size of the finished lumber.
Wood sawing machine
The most commonly used are a circular saw and various machines:
- The circular saw allows you to make precise cuts in various directions. Suitable for both professional and home use, it copes well with above-average round timber diameters;
- chainsaw;
- machines for clean bark removal;
- sawing on a band sawmill makes it possible to process dense logs; it is considered the most popular, since the output is high-quality material and a small amount of waste;
- disk machine: production of double-edged timber and unedged boards;
- a frame sawmill does not require a foundation, the technology using it allows you to install the equipment in close proximity to the felling site;
- the fine gauge is processed by universal machines, the output is high-quality building materials even from low-grade logs;
- sawing of round timber at a large woodworking enterprise should be carried out with the largest amount of lumber, differing from the rest in its special quality and precise dimensions. For this purpose, special lines are installed for sawing.
At the sawmill, timber and edged boards are obtained by cutting logs up to 7 m long and 15-80 cm in diameter along the longitudinal line. A circular saw has one or more disks and processes wood of different diameters according to their number.
Sawmill
If you need to process a small amount of wood at home, you can use a regular chainsaw.
We take into account all factors
What does the area have to do with it? And despite the fact that the use of an angle saw allows you to abandon the machines of the second row: with its help you can get all the edged lumber at once, while after the “ribbon” you will need to install an edger. Therefore, timber merchants recognize the rationality of its use in cases where there is a lack of space on the industrial site.
There is also an opinion that it makes sense to think about purchasing an angle saw for those who have problems with personnel: less equipment means less need for specialists to service it. However, this is not entirely true: the number of workers may be decreasing, but at the same time the requirements for their qualifications are increasing.
“It all comes down to the operator. The value of this frame is much greater than the machine itself. The operator gives you pure money, and he needs to be raised like a child, cared for and cherished. Take care of it like the apple of your eye. You can grow it from scratch. I raised four in a year. First, you will run together with a ruler along the logs, cube, how to saw them, and then the process will begin,” a user of the forest forum with the nickname Oleg shared his experience.
“It’s not easy to find machine operators. The fusion of mechanics and computer technology is difficult for the older generation. Young people have their own problems with learning ability, concentration, and work discipline,” complains another angle saw owner, Evgeniy.
Construction of traditional sawmills.
When designing all through-type machines, the main attention is paid to the feed mechanism. Its main function is to feed the log into the cut so as to exclude any displacement across the plane of the saws
Given the imperfections of real logs, this task is perhaps the most difficult in forestry engineering.
At the slightest misalignment of the log feed, the rear edge of the saw touches the cut surface and spoils the surface of the lumber, and with a more significant misalignment, the saw blade rubs against the cut surface, which can lead not only to disruption of the cutting geometry, but also to overheating and failure of the saws. These phenomena are well known to most owners of such machines; they always have a lot of “burnt” and deformed saw blades in their saw blades.
Only carriage-type machines cope with the problem absolutely effectively, where it is not the log that moves, but the carriage with the log or sawing mechanism. However, such sawmills are bulky, expensive and significantly less productive due to the loss of time for installing logs and reversing the carriage. Accordingly, carriage machines are less suitable for continuous sawing.
The feed mechanisms of pass-through type machines in the overwhelming majority use either an end pusher or a toothed chain to impart longitudinal movement to the log:
The log is pushed into the end and slides along the guides or tray. Pressure rollers are sometimes used. The log lies on a toothed chain and moves with it, usually pressed from above by rollers.
| Pusher | Chain |
These simple and inexpensive solutions, however, cannot be called satisfactory for real Russian conditions. If the geometry of the log is close to ideal, everything is fine. Problems begin when sawing logs with poorly cut branches, significant curvature, complex curvature, etc. Unfortunately, it is impossible for us to avoid this. Even with a slight displacement of the log to the side from the axis (with a “sideways” curvature, complex curvature, centering errors), the cutting force, greater on the side of the overhang of the log, tends to rotate the log around the fulcrum. When a knot hits a guide or chain, the stability of the log also decreases. Such feed mechanisms are not able to effectively counteract this. The guide knives don't help much either.
It is possible to somewhat smooth out the consequences of feed misalignment by increasing the thickness of the saw blade and increasing the spread (widening). In this case, the saws also take on the function of a guiding element. However, heating of the saws is inevitable, which means the need for straightening increases and the service life decreases. Increasing the kerf thickness also affects economic efficiency.
In Europe, the problem is usually solved through meticulous preparation, sorting of raw materials and cross-cutting into 3-4 m sections, and most importantly, through long-term, competent forest management. Simply put, they try not to grow crooked forest there, and its share is small. Needless to say, this approach is still problematic for Russia.
The staff decides
Modern models of such machines are equipped with software and an automatic cutting optimization system, which calculates the optimal log cutting scheme according to the criterion of maximum yield of lumber with specified parameters. However, experienced sawmill managers point out that a qualified operator, having opened a log, can change the cutting combination at any time depending on the presence of knots and internal defects that are not visible from the outside. The computer is not capable of this.
“It’s better to raise an operator on site himself and from scratch. His previous experience of working on a corner of another model is absolutely unnecessary, and sometimes gets in the way. A person gets used to the machine within a month and begins to saw on his own. At a minimum, he must know the structure of wood and its defects, and not just the iron part of the machine.
The operator reaches the design productivity of the machine by the end of the first year of operation. He gains basic experience, learns all the intricacies of sawing, goes through the first mistakes in work, and begins to feel the work of the saw by ear. After all, no one needs a simple “push-button operator” who will chop a mountain of all kinds of noodles from a log,” forum member Oleg continues the recommendations.
Some modern models of angle saws are also equipped with an automatic lumber release system, which allows you to work in a fully automatic mode (when using saw logs of a certain diameter). When removing a sawn board using automatic reset, all manipulations can be done by one operator. Of course, the finished lumber will not fall into his hands on its own, but it will be dumped in a fairly compact area.
In the absence of such a system, the productivity of the equipment directly depends on the efficiency of the operator’s assistants. As a rule, two assistants carry the boards a decent distance, trim them if necessary and place them in bags. The operator waits until they move to a safe distance, and only then starts a new sawing cycle. Accordingly, the difference between removing material manually and automatically resetting is significant.
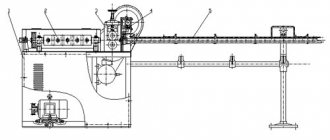
Design features of the Arctant CLS-631D circular sawmill.
The feeding mechanism of the Arctant CLS-631D circular sawmill is equipped with two tracks, four horizontal and two vertical rollers with pneumatic clamping, and a protective claw curtain. The caterpillar carries out basing and movement of the log, the rollers press the log to the caterpillar. The claw curtain prevents the back ejection of wood fragments.
The sawing mechanism of the Arctant CLS-631D circular sawmill is equipped with two movable supports with saw shafts, a guide knife assembly, and a mechanism for moving saw supports. The position of the saw was hard. The guide knives are adjusted by rotating the handle. Both shafts can move in the vertical direction, which allows the use of saws of different diameters, evenly distributing the load between the shafts and eliminating the “sill” effect that is inevitable during double-shaft sawing. Each saw shaft is driven by its own electric motor. The sawmill can be equipped with a main drive with a power of 2x45, 2x55, 2x75 and 2x90 kW.
The transmission of torque to the saw shafts is carried out by cardan shafts, which allows you to move the saw shafts when the engines are stationary. In addition, this design allows the replacement of engines with more powerful ones if there is a desire to increase productivity during operation of the sawmill. Each saw shaft is driven by its own electric motor. The machine can be equipped with a main drive with a power of 2x45, 2x55, 2x75 and 2x90 kW.
The most important advantage of the Caterpillar machine over other machines, after the caterpillar, is the opposite direction of cutting on both shafts; accordingly, the dullness of the saws is practically independent of the contamination of the logs and debarking is not required. Let's illustrate this statement:
| Single shaft system. Counter or downcut sawing. Dirt from the bark is captured by the saw teeth and carried into the cut. The dullness of the saw is mainly determined by the contamination of the raw material. | |
| Twin shaft system. The lower shaft is for up-cut sawing, the upper shaft is for down-cut sawing. The lower saw cuts from the middle of the log outwards. The top saw cuts from the edge of the log to the middle. Dirt from the bark is captured by the teeth of the upper saw, carried into the cut and partially transferred to the cut of the lower saw. The dullness of the top saw is mainly determined by the contamination of the raw material. | |
| Caterpillar double-shaft disc sawmill system. The lower and upper shafts are counter-sawing. The lower and upper saws cut from the middle of the log outward. Dirt from the bark does not get into the cut. The dullness of saws does not depend on the contamination of the raw material. |
European manufacturers of through-type circular sawmills do not use counter-sawing on the upper shaft, since this tightens the requirements for the feeding mechanism and, accordingly, increases the cost. Dirt in the bark is not relevant for them, since all enterprises are equipped with debarking machines.
It should be noted that there is nothing fundamentally new in the design of the Caterpillar machine. All of the above “innovations” were invented and tested no later than the middle of the last century. We are talking only about selecting the optimal layout solution for specific tasks and conditions.
Crawler disc sawmills are widely used in America. One of the leading manufacturers of such machines is the USA www.conemachinery.com
On the Russian market there is a simplified and lightweight version of the tracked disc sawmill - “TT-5/500/320G” from Poland www.brodpol.pl. Using a caterpillar has an amazing effect. An indicative example is one of the institutions of the GUIN of the Komi Republic, where we delivered this machine in 2003. There, saws with a blade thickness of 2.8 mm (recommended 3.5-4.2 mm) with a diameter of 500 mm work quite successfully without any adjustments until they are completely worn out and the tooth tips are replaced. At the same time, the quality of the sawlogs there is extremely low, the branches stick out by 3-7 cm, and there is no sorting of raw materials at all.
The main differences between the TT-5 and the Caterpillar are as follows:
- The maximum diameter of raw materials in the butt is 32 cm;
- downcut sawing on the upper shaft;
- fixed saw shafts;
- non-standard main drive motors.
Thanks to its unique resistance to low-quality and contaminated raw materials, ease of operation, high productivity and quality of lumber, the Arctant CLS-631D circular sawmill is the best choice for industrial sawmilling in Russia.
Sawing methods
During the sawing process, you need to take into account the thickness of the board, compensation for the taper, and the turning of the log. Craftsmen can saw on a band sawmill in three ways.
Simple sawing
The log must be cut to the end to obtain unedged boards, but no turning is carried out. The method is simple and fast, but has disadvantages. The resulting boards must then be cut from the sides.
The lumber comes out of low quality with a lot of waste. The central boards crack easily; the method is suitable for working with low-grade wood.
Circular sawing
Having made a cut, the sawyer turns the log over to the other side, and so on in a circle until the remaining central part. For medium and high grades of wood raw materials, this is the best method, but on separate sawmills it is difficult to turn the log over. Suitable for sawmills with hydraulics.
Options for circular sawing of wood
Sawing timber
The beginning of the cut is made in a circle, and the central part is left in the form of a certain size of timber. Sawing timber ensures maximum productivity of the sawmill; the method is used for sawing medium and low grade logs.
How to make sawmills with your own hands
The most common types of sawmills are corner, band and chain, as well as devices assembled using a chainsaw.
Band sawmill
band sawmill
Assembling the sawmill with your own hands is carried out on a site of the required size, which should be prepared in advance. The device will require special wheels and band saws. Then, in accordance with the drawings, the frame of the future unit is assembled. Work on the frame begins with the manufacture of special rails. To do this, you can pick up a corner and install one of the sides up. Then the wheels are installed, maintaining maximum strength.
Between two corners, set parallel, sleepers are made from a profile pipe, which are designed to ensure their reliable fastening to each other. Fasteners for logs that move freely in all directions are welded to this profile pipe. Then, according to the drawing, the cart is assembled and the wheels are attached to it.
Finally, the electric motor is installed, connected through a special pulley to the operating mechanism of the device.
Chain sawmill
resembles a band sawmill
Assembling a chain device begins with making a frame from a metal profile. Having assembled the main part, they make several technological holes, while maintaining extreme accuracy. The number of holes depends on the step length. Then they begin to assemble the racks and install the frame on them, after which additional stiffeners are made. This creates the basis of a chain structure.
In addition, it is necessary to assemble a movable cart for the sawmill with your own hands. To do this, prepare the base and attach the stop, gaskets, clamping plates and mounts for the electric motor to it.
Then the cart is mounted to the frame, the engine and saw are secured, the chain is tensioned and that’s it, the DIY chain sawmill is ready.
Latest posts Ingenious tricks for growing tomato seedlings from experienced gardeners 6 ideas on how to use cut branches in the country and at home What to put in the ground when planting cucumbers for seedlings so that powerful vines will form by the summer season
Corner or disc sawmill
The corner sawmill has many functions and is used for large volumes of work. It is best to make such a design yourself, because finished equipment is very expensive. To assemble it, you should use the appropriate drawings, and before starting work you need to purchase all the necessary components and components.
First, a frame is assembled from metal pipes and high-strength guides. All joints are fastened by welding. It is best to use rails as guides. Then the carriage is assembled
During assembly, special attention should be paid to the accuracy of all dimensions indicated in the drawing
A high-power gasoline engine is installed in a corner or circular sawmill, which effectively affects the process of sawing wood. The engine is mounted on the structure frame and connected to the working elements through special holes. Most often, a chain drive is installed on such sawmills, but in some cases this leads to overheating of the drive itself
When assembling the drive, it is necessary to pay due attention to safety precautions and eliminate possible risks during its operation.
Chainsaw sawmill
most often such a large sawmill is not required
To make a mini sawmill from a chainsaw with your own hands, you will need:
- two channels;
- corners;
- rails.
To strengthen the frame, several stiffening ribs are installed. Then the movable cart is assembled from a steel plate. Two corners are welded at the bottom of this plate, after which it is placed on bearings or rollers. Two corners are welded to the top of the movable cart, intended for mounting a chainsaw.
Finally, a special structure is installed for fastening the processed logs.
DIY sawmill video.
Characteristics of the Arctant CLS-631D circular sawmill
| Name | Unit | Meaning |
| Diameter of sawn logs: minimum (at the top) maximum (at the butt) | mm | 120 460 |
| Minimum length of sawn logs | m | 3,5 |
| Feed speed (smooth adjustment) | m/min | 1-24 (40**) |
| The estimated productivity of raw materials per shift is 8 hours. With an average diameter of raw materials of 30 cm. | cubic meters | 150* |
| Maximum number of cuts | PC. | 6 |
| Saw diameter minimum maximum | mm | 500 650 |
| Main drive power (2 motors) | kW | 2x55 (45, 75, 90) |
| Total power of feed drives (4 drives) | kW | 9,5* |
| Saw shaft rotation speed | rpm | 1475 |
| Overall dimensions: length width height | mm | 7200 3400* 2360 |
| Machine weight | kg | 8800* |
| * - with main drive power - 2x55 kW | ||
| ** — option, by default in the 2x90 kW option |