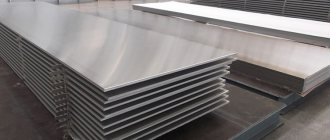
When choosing materials for construction, it is impossible not to familiarize yourself with the knowledge base of hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel. Knowing the differences between them will help you choose the right material for your building project. While hot rolled steel allows for a variety of shapes, cold rolled steel is more or less limited to a few shapes.
Cold rolled steel is usually created at temperatures close to normal. This helps increase the strength of the finished product. Cold rolled steel is gray in color and feels smooth when touched. While with hot rolling you cannot be sure of the dimensions of the finished product, the results of cold rolling are always closer to the dimensions of the finished product since it has already gone through the cooling process.
Physical properties
The characteristics of cold-rolled sheets are determined by the properties of the manufacturing material and the features of the technological process.
Among the physical features:
- High mechanical strength; is achieved by using a sequence of technological processes aimed at eliminating internal tension between layers in the alloy;
- Small thickness - from 0.35 mm; to obtain such a thin sheet, the workpiece is rolled many times without heating under a press; with increasing thickness, increasing mechanical forces are required, so the maximum value is limited to 5 mm;
- neat appearance of the surface; it is clean, smooth, with a characteristic metallic sheen, there is no soot, scale, or traces of temperature or chemical treatment;
- The process of rust formation on the surface of cold-rolled sheets is significantly slowed down; this is facilitated by heating the products at the last stage of processing followed by recrystallization; During long-term use of products made from cold-rolled sheets, they are more resistant to corrosion.
Learn the benefits of each type of steel and which one to choose for your project!
Steel metal can be widely used in shipbuilding, auto and aircraft manufacturing, household appliances, construction, etc...
But improving the properties of steel is not only about changing the chemical composition. The processing of steel during production can significantly affect the products being manufactured, even if the brand and technical characteristics are identical. One of the main differences between finished products is the difference between the types of steel rolling: hot-rolled and cold-rolled.
Production Features
The entire technological process is conventionally divided into three stages: initial preparation, rolling with pressing, and final processing. The main task of preliminary preparation is to clean the surface after hot rolling and remove the film of iron oxide (scale). Mechanical cleaning can be manual or automated grinding.
- Manual cleaning of the surface is performed by workers using power grinding tools. Mechanical cleaning is performed by directing a stream of abrasive particles under pressure onto the surface. For chemical cleaning, concentrated solutions of hydrochloric (HCl), nitric (HNO3), sulfuric (H2SO4), and phosphoric (H3PO4) acids are used.
- The workpieces are placed for a short time in a container with an acid solution. Next, they are removed, washed to remove any remaining solution, wiped, and dried. All operations are carried out in compliance with the strictest safety regulations.
- The cleaned billets are fed to a rolling mill equipped with several sequential presses and equipment for automatic cutting and welding. Each mechanism produces crimping, trimming, and the workpieces become thinner. At the last stage, the strip is rolled into rolls.
Additional processing consists of heating to 680-690°C in an oven. In this case, recrystallization of the metal occurs, the strength threshold increases, the waviness of the products and the fluidity index decreases. After cooling, a stamp is placed on the finished product.
Hot rolled steel: advantages
Hot-rolled steel is much cheaper than cold-rolled steel because it undergoes less processing. Because hot rolled steel can be cooled at room temperature, it is essentially normalized, meaning it contains no internal stresses that can result from quenching or hardening.
Hot rolled steel is ideal in applications where dimensional tolerances are not as important as the overall strength of the material, and where a flawless surface finish is not a major concern. The surface can be cleaned by grinding, sandblasting or acid bath etching. Then, once the roughness and imperfections have been removed, various brushes or mirror coatings can also be used. A cleaned surface is better for painting and other coatings.
Application area
Cold rolled steel sheet is used in the automotive industry. The bodies of passenger cars, fuel tanks, truck cabins, pallets, engine covers, fasteners, and protective devices for the engine compartment are made from rolled products of 1-2.5 mm thickness.
- Tin has a thickness of up to 0.5 mm. It is obtained by cold deformation on heavy-duty roller-type presses. The resulting sheets are cut with industrial scissors into strips up to 1.5 m wide. Banks, partitions are stamped from them, fencing, and decoration elements are made.
- To produce household enamel cookware, steel sheets are annealed in special furnaces at high temperatures. The steel becomes more ductile and less effort is required for stamping. After annealing, the sheets are cleaned chemically; stamped forms are covered with a layer of enamel.
Corrugated sheeting is a thin sheet of metal coated with a protective layer of zinc. To increase mechanical strength and protect against damage, additional stiffeners are formed.
Corrugated sheeting is widely used in construction for constructing fences, creating fences, temporary barriers, installing roofs, sloping surfaces, and for protecting the outer walls of buildings from precipitation.
Main stages of cold rolling
The source material (roll) supplied to the cold rolling mill may have scale on the surface, which must be removed in the most convenient way:
- using shot blasting;
- dissolving oxides with acids - hydrochloric or sulfuric; hydrochloric acid is more effective;
- by combining the two methods mentioned above.
After pre-treatment, the hot-rolled product is supplied to the cold rolling mill, which includes:
- four or five stands in which compression is carried out to the specified parameters;
- winder;
- scissors;
- loop-forming mechanism and other devices.
After the cold rolling operation, a hardened layer is formed on the surface of the sheet, which has high strength and low ductility. To eliminate work hardening, heat treatment is used - annealing at a temperature of +700°C - which allows the plasticity characteristics to be restored. The equipment used is bell-type or broaching furnaces.
One of the final operations is training, which is a small compression that provides the following positive aspects:
- increasing the strength of steel;
- reduction of strip waviness;
- improvement of surface quality;
- slight decrease in yield strength;
- after training, shear lines do not appear, which necessarily appear during stamping.
Photo of cold rolled sheet
How to calculate the mass of a steel sheet using a calculator?
To quickly determine the mass of a sheet, we use the formula:
H*B*L*7.85, in which
H – sheet thickness in mm,
B – sheet width in m,
L – sheet length in m,
7.85 kg/dm 3 is the density of black steel, corresponding to the weight of a sheet with a thickness of 1 mm and an area of 1 m 2.
Attention! When you substitute the length and width of the sheet in meters into the formula, and the thickness in millimeters, you will get the mass of the sheet in kilograms.
Having calculated the mass of one sheet, it is easy to calculate how much a pack containing a certain number of sheets weighs.