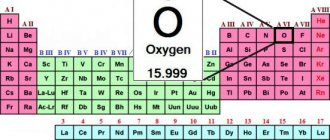
Historical information
The chemical element has been known to people since ancient times. One of the first methods of metal extraction mastered by man was the smelting of lead. The first archaeological finds confirming this were lead beads found from the times of Çatalhöyük (modern Turkey). The items date back to 6400 BC.
The oldest lead figurine of a girl in long clothes was excavated in Egypt. It dates back to the time of the first dynasty of the pharaohs (3000 BC).
Lead pipes made up the ancient Roman water supply system. In the Ancient Roman Empire, up to 80 thousand tons of this metal were smelted annually. In Rus', since ancient times, lead has been used as roofing for cathedrals and churches.
Since time immemorial, the low melting point of lead has made it possible to obtain the metal and manufacture products of any shape from it.
Note! Over the course of 20 years, the Industrial Revolution since 1840 has raised the volume of annual lead smelting in the world from 100 to 250 thousand tons per year.
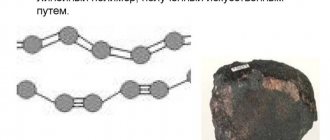
Lead crystal lattice:
| 500 | Crystal cell | |
| 511 | Crystal grid #1 | |
| 512 | Lattice structure | Cubic face centered |
| 513 | Lattice parameters | 4.950 Å |
| 514 | c/a ratio | |
| 515 | Debye temperature | 88K |
| 516 | Name of space symmetry group | Fm_3m |
| 517 | Symmetry space group number | 225 |
Being in nature
Soldering aluminum
Plumbum is usually not found in its pure form. It is found in more than 100 different minerals in the form of intermetallic agglomerates. Lead is present in uranium and thorium veins. Large accumulations of lead-zinc ores have been discovered and are being developed in Transbaikalia and the Primorsky region. Lead is mined in various deposits in the Urals and Norilsk.
The largest deposit with a high content of lead is located in the uranium ores of the Kohistan Ladakh arc (northern Pakistan).
Fossil lead
How to smelt lead at home
Melting lead is not very difficult. You can do this yourself, using a container made of aluminum or thin-walled steel.
This metal melts at a low temperature, which can be achieved using an ordinary gas burner or electric stove.
Lead Characteristics
Our planet contains 0.0016% of this metal from the total mass of the earth's crust. Although this figure is small, however, when compared with other chemical elements - bismuth, gold, mercury, lead is in a much higher position.
The predominant source of raw materials is sulfide polymetallic ores . Metal has the following qualities:
- softness;
- low melting point;
- You can process this metal yourself.
This material is characterized by a dirty grayish tint . In the cut area, the metal has a bluish tint, which gradually becomes dull. This is due to the oxidation process, which occurs due to the influence of oxygen. An oxide layer is formed on the cut.
It is a heavy metal, its density is 11.34 g/cm³ . This figure is approximately one and a half times higher than that of ordinary iron. Among other things, lead is also one of the softest metals.
Its surface can be easily scratched even with an ordinary knife or fingernail. Lead is extremely flexible; this metal can be flattened with an ordinary mallet or hammer. It is also often used for casting or melting with your own hands.
Receipt
How to solder a wire without a soldering iron
The raw materials for lead extraction are rocks that include helenite. The heavy metal smelting process consists of several phases. From the initial raw material, a concentrate containing from 40 to 70 percent plumbum is isolated by flotation. Next, manufacturers take different paths.
One of the ways to transform the product into werkbley (blank lead) is smelting using the regeneration method. Another method is that the metal is restored from the oxide by melting the raw material in a water jacket heater.
The resulting werkley containing 90% lead is purified from copper. Then arsenic and antimony are removed by alkaline refining. Then silver and zinc are isolated. The effects of magnesium and calcium exclude bismuth. As a result, lead with a purity of 99.8% is obtained.
Global lead production based on research by international organizations for 2005
| Manufacturer country | Volume, kilotons |
| Countries of Europe | 2220 |
| China | 1430 |
| Russian Federation | 1120 |
| South Korea | 650 |
| Kazakhstan | 570 |
| Ukraine | 410 |
Environmental characteristics
Lead pollution of the environment is considered one of the most dangerous. All products that use lead require special disposal, which is carried out only by licensed services.
Unfortunately, lead pollution is caused not only by the activities of enterprises, where it is at least regulated. In city air, the presence of lead vapor ensures the combustion of fuel in cars. Against this background, the presence of lead stabilizers in such familiar structures as a metal-plastic window no longer seems worth attention.
Lead is a metal of industrial importance. Despite its toxicity, it is used too widely in the national economy for the metal to be replaced with anything.
This video will tell you about the properties of lead salts:
Technological properties and characteristics
The characteristics of the metal can be represented by the list:
- Lead density and mass;
- Lead smelting temperature;
- Mechanical properties;
- Corrosion resistance.
Lead density and mass
The density of the metal is 11342 kg/m3. This means that a metric cube of lead weighs 11.342 tons. Its large specific gravity allows it to be used as payloads in various devices.
Lead smelting temperature
Molten metal in its pure form has a temperature of about 400 degrees. In this state, lead has fluid properties. The casting qualities make it possible to pour lead in a liquid state into molds of complex configurations.
Pouring a mold with lead
The metal boils when heated to 1750 degrees. During boiling, volatile fumes arise in the form of lead dust and oxide vapors, which can cause severe poisoning to the human body.
Mechanical properties
The chemical element has softness and ductility, which allows cold rolling to achieve the state of thin foil. Cold deformation does not affect the change in mechanical properties.
Corrosion resistance
The chemical inertness of the element is close to that of noble metals. In the air, plumbum practically does not corrode. The rapidly forming oxide film on the surface of lead puts an insurmountable barrier to corrosion processes.
Aggressive environments for lead are hydrogen sulfide, coal anhydrite and sulfuric acid. Under their influence, the metal is actively destroyed.
Physical properties
Lead has a rather low thermal conductivity, it is 35.1 W/(m K) at a temperature of 0 °C.
The metal is soft, can be cut with a knife, and is easily scratched with a fingernail. On the surface it is usually covered with a more or less thick film of oxides; when cut, a shiny surface is revealed, which fades over time in air. Melting point - 600.61 K (327.46 °C), boils at 2022 K (1749 °C). Belongs to the group of heavy metals; its density is 11.3415 g/cm3 (at +20 °C). As temperature increases, lead density decreases: Change in lead density depending on temperature
| Temperature, °C | Density, g/cm3 |
| 327,6 | 10,686 |
| 450 | 10,536 |
| 650 | 10,302 |
| 850 | 10,078 |
Tensile strength - 12-13 MPa (MN/m2).
At a temperature of 7.26 K it becomes a superconductor.
Application areas of lead alloys
Lead compounds are divided into high-alloy and low-alloy alloys. The former are formed by adding a large number of chemical elements that provide high strength, abrasion resistance and low shrinkage at a lower melting point.
Low alloy lead compounds are produced by small inclusions of substances such as tin, antimony, copper and cadmium. This achieves increased resistance of the alloy to corrosion processes in a polluted atmosphere, inorganic acidic environment.
The alloys are used in acid and alkaline batteries, as shells for both high-power and low-voltage cables. Compounds of antimony or copper with lead are used for the production of pipelines, sheet lining of various devices and protective mats against radiation damage.
Security measures
When working with molten metal, it is imperative to protect the skin from thermal burns. During work, be sure to wear fireproof gloves and cloth or linen clothing that can withstand the ingress of molten substances.
In addition, it is necessary to wear a respirator or gauze bandage to protect the respiratory system - lead is a toxic substance.
So, by following these tips and using the information about the melting process, it won't be much of a problem to cast a fishing sinker or melt down the remains of an old battery into one ingot.
Home and industrial methods
Without tin-lead solders (PLS), the existence of such an industry as radio engineering is impossible. Many industrial products contain POS coatings.
Tin-lead solders
The industry supplies the market with solder product:
- cast pigs;
- wire;
- foil tape;
- solder tubes with flux;
- powder or paste.
Alloys containing 90% tin and 10% lead are used for soldering products, which are then electroplated with gold or silver. The melting point of pure tin is 2310 C. Therefore, the solder will melt when heated to 2200 C.
Tubular solder with flux
Tin-lead POS with a predominance of tin in its composition (61%) has a lower melting point - 191%. POS 61 is used to cover contact groups in various devices; it is also used to process thin wire for windings of electric motor armatures and transformer coils.
Important! Taking into account the temperature at which tin melts, the % lead content in the alloy is regulated. This achieves a comfortable temperature regime, at which the tin-lead solder quickly turns into a liquid state.
POS 30 melts at 256 degrees. The compounds are less durable than products with a higher tin content.
10 percent solder is far from the temperature threshold at which tin melts. Therefore, POS 10 is used as a durable material for tinning large metal surfaces.
Melt preparation and pouring
In industrial conditions, the melt is prepared in special crucibles, which are placed in electric furnaces (equipment equipped with electronic measuring equipment that maintains the desired melting mode).
In radio engineering production, special heating baths are used to prepare solder for printed circuit boards of radio circuits.
In workshops and at home, solder is melted with a soldering iron tip. To prepare a large volume of molten metal, it is placed in a copper vessel on an electric stove. The alloy in the form of scrap is loaded into the melting bath gradually, as the next layer of metal melts.
Fishing varnishes
Avid fishermen at home cast fishing sinkers and spoons by pouring molten tin into clay molds. The spoons are then coated with waterproof varnishes.
Interesting. Fishing varnish is used to protect against the appearance of oxides on various figurines and other products.
Fishing varnish
Preparing to smelt lead
First you need to find a container. It would be great if the handle of the vessel was made of some heat-resistant material. For this purpose, you can use an old coffee pot or kettle.
The material can also be melted in an outdated container made of cast iron, using a deep and long spoon for pouring.
If there is no suitable container nearby, then you can use an ordinary tin can. However, here you should use pliers, which will be used to remove the hot pan from the flame and pour the material into the mold.
Do not forget that you need to be extremely careful while working. To simplify the procedure, you can make a small groove on one side of the jar. In this case, the red-hot metal will pour out in a thin stream clearly into the required place.
The material, cleared of impurities, can be crushed so that it melts as quickly as possible. The container must be securely placed over the burner and heated properly. This must be done in order to rid the surface of excess impurities and moisture.
Melting procedure
There is no need to try to melt all the prepared lead at once, because only the very bottom layer will interact with the hot surface of the container.
Melt two or three pieces first to form a puddle, then gradually add new material. This will give you the opportunity to make your work area more voluminous.
After melting, a layer of debris, impurities and slag must be removed from the surface of the metal. Pouring must be done into a heated mold. Lead is also characterized by rapid solidification. The material quickly loses its fluidity, becomes thicker, and therefore cannot completely fill the mold.
Methods for getting rid of oxide
When exposed to air, lead products become covered with an oxide film. This is the result of the ionic interaction of oxygen and lead atoms. The oxide becomes not only protection against an aggressive environment, but also a barrier to electric current.
Important! Mechanical cleaning will not bring the desired result. The film will recover quite quickly. Sunflower oil, graphite grease or varnish can help get rid of oxides.
At home, the product is placed in a vessel with sunflower oil for about five minutes. After which it is removed from the vessel and allowed to dry.
In industrial conditions, graphite lubricant is used. The lead surface treated with the product retains its shiny appearance for a long time.
How to melt lead at home?
Melting lead is not very difficult. You can do this yourself, using a container made of aluminum or thin-walled steel.
This metal melts at a low temperature, which can be achieved using an ordinary gas burner or electric stove.
Our planet contains 0.0016% of this metal from the total mass of the earth's crust. Although this figure is small, however, when compared with other chemical elements - bismuth, gold, mercury, lead is in a much higher position.
The predominant source of raw materials is sulfide polymetallic ores . Metal has the following qualities:
- softness;
- low melting point;
- You can process this metal yourself.
This material is characterized by a dirty grayish tint . In the cut area, the metal has a bluish tint, which gradually becomes dull. This is due to the oxidation process, which occurs due to the influence of oxygen. An oxide layer is formed on the cut.
It is a heavy metal, its density is 11.34 g/cm³ . This figure is approximately one and a half times higher than that of ordinary iron. Among other things, lead is also one of the softest metals.
Its surface can be easily scratched even with an ordinary knife or fingernail. Lead is extremely flexible; this metal can be flattened with an ordinary mallet or hammer. It is also often used for casting or melting with your own hands.
Melting temperature
The temperature at which lead begins to boil is 1751 degrees.
This metal begins to melt at a temperature of 327.46 degrees Celsius . Its casting qualities are fully preserved within the range from four hundred to four hundred and fifty degrees.
And the oxide film, which protects the material from corrosion, begins to melt only at a temperature of 850 degrees Celsius, which makes it difficult to weld this type of metal with others. In addition, the volatility level of lead increases significantly at a temperature of 700 degrees.
The material is perfectly processed even when chilled. You can make a thin layer of foil from it. If this metal is subjected to a pressure of 2 tons per square centimeter, then it takes on the appearance of a monolith.
Wire is made from it by pressing in a die. The low degree of tensile strength does not allow the use of ordinary drawing for this purpose.