Aluminum is an extremely light metal, but due to its characteristics, the raw material is used in many industries. It is used in aviation, shipbuilding, as well as the production of cars and ships. The use of aluminum became truly widespread during the Second World War.
To obtain the metal, bauxite is used, a resource whose extraction sources are found in 18 countries. As a rule, they are all characterized by a hot climate with sufficient moisture. In addition to bauxite itself, substitutes can also be used, but their use is less cost-effective. These include anorthosite, alunite, oil shale and other resources.
The main reserves of explored bauxite and the largest aluminum producers.
Aluminum is a lightweight metal that can handle almost all metals.
It is also an important metal for aviation, machine, ship, and carriage building. The Second World War was the starting point for the development of this industry. The main raw material for aluminum production is bauxite, which is concentrated in 18 countries. These are mainly countries with a hot and humid climate. But in addition to bauxite, there are also substitutes that are currently less profitable. These are, for example, alunite, anorthosite, coal waste and oil shale and other raw materials.
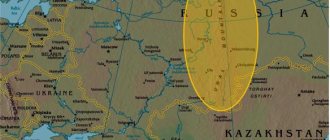
The largest deposits in Russia
The most powerful is rightfully the Kursk magnetic anomaly, with reserves of 250 billion tons. Considering the fact that the world's proven reserves amount to up to 500 billion tons, we can conclude that more than 50% of the raw materials are contained in the country, and it is the leader in iron ore reserves.
A special difference from other deposits is the presence of iron quartzite. This is a rare mineral of igneous origin, and its reserves here are almost inexhaustible. Another notable feature is the location of the deposits close to the ground (35 - 500 meters), which significantly reduces the cost of producing raw materials. Magnetite minerals of this deposit contain up to 50% iron, and hematite-martyr minerals – up to 65%.
The following deposits are of great importance in the iron ore industry:
- Beloretskoe;
- Kerch;
- Mikhailovskoe;
- Lebedinskoe;
- Stoilenskoe;
- Olegorskoe;
- Eno-Kovdorskoe;
- Kostamuksha.
One of the most interesting is the Kachkanar deposit, where in addition to iron, titanium, a particularly valuable metal, is obtained from raw materials.
Main reserves of explored bauxite
Reserves in thousand tons
In total, the world's proven reserves of bauxite amount to more than 30 billion tons, which should be enough for many centuries. The TOP 5 have more than 70% of the world's bauxite reserves.
Aluminum (bauxite) is included in the list of 35 critical minerals compiled by the US Department of the Interior
Aluminum production requires a very large amount of electricity. Fortunately, bauxite is a transportable raw material. As a result, the geography of bauxite production and consumption varies markedly. The main consumers of bauxite are developed countries with a good energy base (as a rule, aluminum smelters are clustered near hydroelectric power stations). Thus, the territorial gap between the stages of aluminum production increases noticeably.
Australia is the leader in bauxite mining (75 million tons), followed by China (70 million tons) and Guinea (50 million tons).
Source
Areas of application of the mineral
This is a valuable raw material for industry. Alumina is obtained from bauxite. It is used in different ways, for example, they do the following:
- Molding material.
- Flux for ferrous metallurgy.
- High-quality refractories that are not afraid of temperatures or loads.
- Special dense cement with excellent physical properties. The solution hardens quickly and bonds perfectly to the reinforcement. The resulting concrete is resistant to high temperatures and acidic environments.
- Alumina is ground and used in the production of anti-oil spill products.
- Pure aluminum for various products.
Bauxite has also been used in other areas. From them we get:
- electrocorundum is an excellent jet abrasive for industry;
- metal compounds for the production of pigments.
Bauxite is a valuable find for humanity. The ore is used in the chemical industry, construction, and metallurgy. The world's reserves will last for a long time. Due to its use in the military-industrial sector, the breed is considered strategically important.
Most popular
Bauxite is a soft limonite iron ore rock with some of its iron composition replaced by aluminum. Bauxite forms when silicon is leached from lateritic soil. Bauxite does not have any specific composition, but is only a collection of clay minerals, aluminum hydroxides and hydrous aluminum oxides. Although insoluble minerals are also part of its composition, namely siderite, magnetite, quartz, goethite and hematite. It is found primarily in humid subtropical or tropical climates and is a major source of raw material for the global aluminum industry. The main sources of aluminum are bochmite, diaspora and gibbsite ores. It has a pisolite structure and reddish-brown color, as well as a low specific gravity of 2.0-2.5.
How is bauxite aluminum ore formed?
Bauxite is formed from alumina monohydrate, boehmite and diaspore, trihydrate hydrargillite and associated minerals hydroxide and iron oxide.
Depending on the composition of nature-forming elements, three groups of bauxite ores are distinguished:
- Monohydrate bauxite – contains alumina in monohydrate form.
- Trihydrate - such minerals consist of alumina in trihydrate form.
- Mixed - this group includes the previous aluminum ores in combination.
Deposits of raw materials are formed due to the weathering of acidic, alkaline, and sometimes basic rocks or as a result of the gradual deposition of large quantities of alumina on the sea and lake beds.
Main bauxite mining areas
Mineral ore mining
Bauxite is one rock that is found in large quantities in many countries around the world. In fact, some countries have more than 100 years worth of bauxite reserves. The stone is easily mined by open pit mining. Blasting or drilling is used to uncover a layer of bauxite beneath the topsoil, which is then crushed and loaded onto trucks for crushing and washing before being transported to alumina refineries. The following data on bauxite production volumes by country are given in 2014.
Australia
Today, the number one producer of bauxite in the world is Australia, where 81,000 metric tons of bauxite are mined annually. It is produced from five mines, which supply seven refineries, which supply six smelters, all in Australia.
China
The second place is occupied by China, where about 47,000 tons of bauxite are mined annually. China's bauxite reserves have shrunk due to increased global demand for aluminum and its by-products. China has agreed to import bauxite from India, Australia and Malaysia.
Brazil
Brazil ranks third, producing 32,500 metric tons of bauxite annually. Brazil is home to the world's largest alumina refinery, which receives supplies from two mines in the state of Pará. It has a unique underground pipeline to transport bauxite raw materials to oil refineries.
Features of processing
The quality of the stones, on which the processing method depends, is determined in the laboratory. The “silicon module” is calculated using the formula MSi = Al2O3/SiO2. Then do the following with the mined ore:
- Higher quality bauxites (with high results) are processed using the Bayer method. As a result, alumina becomes sodium aluminate. Next, the resulting solution is cleaned of red mud. The alumina precipitates and is leached. The output is aluminum.
- For the rest, the sintering method is used. The treatment is carried out at high temperature: +1250 °C. Special rotary kilns are used. Crushed bauxite, soda and limestone are thrown there. All this is sintered and then leached. Aluminum hydroxide is precipitated and filtered.
What is bauxite used for?
French geologist Henri Rouvere discovered bauxite rock in 1821 in Les Baux de Provence in southern France. Rouvere named his stone discovery after the village of Les Baux. Today, bauxite is used in many ways, such as aluminum-based chemicals, aluminum metal, cement, abrasives, and refractory materials. Aluminum-based chemicals are used in deodorants and other cosmetics. It is also used in wastewater treatment plants. Aluminum metals are used to make electrical cables, car bodies, aircraft casings, beer cans and electronic casings. Refractory materials are used in stoves, stoves, fireboxes and fireplaces. Abrasives containing aluminum are used for grinding carbon and high-speed steel. It is also used in electrical insulators and sandpaper products.
Which country produces more bauxite?
Australia is the world's leading producer of bauxite, an aluminum ore that is used as a major source of the metal.
Source
Import and export
Despite the fact that many countries mine ores, this does not mean that they do not purchase it from outside. A huge amount of minerals from Russia and Brazil is supplied to China, since the quality of raw materials there is slightly lower, which affects the metallurgical industry. In addition, the needs for hardware are sometimes not equal, and there is not enough of it to implement all plans.
Most iron-rich minerals are exported from India, Brazil and Australia. This can be explained by the countries' reduced demand for this raw material and its high quality, due to which iron processing requires fewer resources.
What is bauxite
Bauxite stone is aluminum ore, a complex raw material. The composition contains about 40–60% aluminum-containing substances. It is a dense porous rocky formation. Sometimes in the form of earthy, loose or clay-like masses.
Externally it resembles clay. Most often it is brick-red in color, but there are also other red shades from light to brown, less often - yellow, white, gray, black.
Varieties
According to their chemical composition, mono-, trihydroxide and mixed varieties are distinguished.
Monohydroxide are divided into:
Trihydroxide are gibbsite. Mixed ones combine both options.
Based on their structure, they are classified as clastic (in the form of fragments) and concretionary (in the form of a rounded mineral formation). They may have different textures (layered, uniform, etc.).
Watch a video on the topic:
Varieties
Externally, bauxite is a clay-like and often rocky rock. There are porous, dense, with a cellular or earthy fracture.
Based on their chemical composition, the following compounds are distinguished:
- monohydroxide. These are boehmite and diaspore species, where the rock-forming mineral is boehmite or diaspore. Alumina comes in one form;
- trihydroxide (gibbsite). Alumina is contained in trihydrate form;
- mixed (combine two types).
According to the structure, they are distinguished as clastic (in the form of fragments) and concretionary (rounded formations). Also, the rock may differ in texture (uniform, layered, etc.).
History and origin of the stone
The history of the discovery of the rock begins in 1821. French geologist Pierre Berthier accidentally discovered an unusual rock while on vacation. The scientist has been engaged in mineralogical surveys and research for many years, so he decided to study the composition. Having found nothing surprising, he lost interest in the find.
But years later, the rock became famous and in demand. The first evidence of the demonstration of bauxite dates back to 1855, where a beautiful silvery specimen called "clay silver" was presented at a Paris exhibition.
Recommendations
- Glossary Clay Minerals Society for Clay Science Project Archived 2016-04-16 in the Wayback Machine
- P. Berthier (1821) "Analyze de l'aluminehydratée des Beaux, département des Bouches-du-Rhóne" (Analysis of hydrated alumina from Les Baux, department of the Rhône Estuary), Annales des mines
, 1st episode,
6
: 531-534. Notes:- In 1847, in the summary index of the third volume of his Traité de minéralogie
, French mineralogist Armand Dufresnoy listed hydrated alumina from Les Beaux as "bauxite".
(See: A. Dufresnoy, Traité de minéralogie
, vol. 3 (Paris, France: Carilian-Goeury et Vor Dalmont, 1847), para. 799.)
In 1861, H. St. Clair Deville credits Berthier with the name "bauxite" on p. 309, “Chapitre 1. Minerais alumineux ou bauxite”: H. Sainte-Clair Deville (1861) “De la présence du vanadium dans un minerai alumineux du midi de la France. "Études analytiques sur les matières alumineuses." (On the presence of vanadium in an alumina mineral from the Midi of France. Analytical studies of aluminous substances.) Annales de Chimie et de Physique
, 3rd series,
61
: 309-342. - In 1847, in the summary index of the third volume of his Traité de minéralogie
- ^ a b
Bardosi, G. (1982).
Karst bauxite
. Amsterdam: Elsevier. paragraph 16. ISBN 978-0-444-99727-2. - ^ a b
"Bauxite and Alumina Annual Publication 2020" (PDF).
US Geological Survey
. January 2022. Retrieved June 29, 2022. - ^ a b c d f g
Production during 2016 “Bauxite and Alumina Annual Publication 2022” (PDF).
US Geological Survey
. January 2022. Retrieved June 29, 2022. - "Mining Journal - Vietnam's bauxite reserves could reach 11 billion tons." Archived from the original on 2011-06-16. Retrieved 2010-11-28.
- "BBC - GCSE Bitesize: Aluminum Manufacturing." Archived from the original on 2018-02-25. Retrieved 2018-04-01.
- Michael Quinion (23 January 2006). "Aluminum vs. Aluminum" Worldwidewords.org. Retrieved 2011-12-19.
- "Gallium Resource Data Compendium for Bauxite Deposits Author: USGS" (PDF). Retrieved 2017-12-01.
- ^ a b
Frenzel, Max;
Ketris, Marina P.; Seifert, Thomas; Gutzmer, Jens (March 2016). "On the presence of gallium at present and in the future." Resource Policy
.
47
: 38–50. Doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2015.11.005. - Moskalyk, R. R. (2003). "Gallium: the basis of the electronics industry." Mineral Engineering
.
16
(10): 921–929. Doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2003.08.003.
Bauxite deposits
According to modern data, the main reserves of bauxite (up to 90%) are located in 18 countries. The most important are:
- The country that ranks first in rock reserves (20 billion tons) is Guinea.
- Australia ranks second in the world (7 billion tons).
- Third place (6 billion tons) – Brazil.
- Fourth place (3 billion tons) – Vietnam.
- Fifth place (2.5 billion tons) – India and Indonesia.
Smaller volumes are mined in Jamaica, Mali, and Cameroon.
Bauxite mining is carried out in some regions of Russia:
- Arkhangelsk;
- Sverdlovsk;
- Belgorodskaya;
- Leningradskaya;
- Komi Republic.
But Russian reserves are minimal (250 million tons - about 1% of world production) and are imported. Some CIS countries also mine rock. Mining is carried out in Uzbekistan and Azerbaijan. But stocks are also minimal.
Watch a video about the deposit in the Komi Republic:
Iron ore importing countries
The largest states in the world not only export and mine minerals. They also import raw materials. This trend is typical for Italy, the United States of America, and China. Large importers are the Republic of Korea, European countries, and Japan. The most powerful cargo flow carrying ore is the Australia-Japan flow. Asian, American and Indian ore also moves along it.
The common European market receives imports from countries such as Brazil, Africa, and Sweden. Canada supplies raw materials to the United States and supplies West Africa and Latin America.
Rock processing
Rock is mined in two main ways:
Processing of high-quality rock is carried out chemically using the Bayer process:
- When crushed bauxite is treated with sodium hydroxide, sodium aluminate is formed.
- The resulting compound in liquid form is purified from unnecessary impurities.
- Then aluminum hydroxide (alumina) is precipitated from it.
Low-quality crushed rocks are processed in another way (electrolysis):
- The crushed raw materials are combined with soda and limestone.
- Sent to a special rotary kiln.
- The workpiece removed from the furnace is treated with alkali. A chemical reaction occurs with the precipitation of hydroxide.
- The hydroxide is separated and then filtered.
The designation of bauxite on the map looks like a black square with an inscribed white circle. This is how all types of aluminum ore are designated.
Video review on the topic of aluminum mining and processing:
Technologies and related problems
At the initial stage of the technological cycle, the extracted ore is crushed and exposed to an alkali solution in order to obtain alumina directly from it. Aluminum is obtained from it, which is released during electrolysis in a ratio of 1 to 2 - that is, the final product - aluminum - is formed by weight two times less than the initial raw material - alumina. The resulting mass is melted into ingots. This is done to remove remaining impurities.
The most serious problem in the production of aluminum is the significant consumption of electrical energy (150-200 kWh per 1 ton of finished products made from raw metal). Which makes it necessary to combine metallurgical capacities with the generation of electrical energy. And this, in turn, leads to CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, in addition to the CO2 emissions generated during the electrolysis process, is 280 thousand m3 per ton of finished product.
It is clear that aluminum producers cannot ignore such a dangerous problem in terms of environmental protection. One of the most promising developments in this area, being mastered by the leading Russian company, is the use of an inert anode in the electrolysis process, which eliminates carbon dioxide emissions directly during the production process. Prototypes of the resulting products are already being tested by consumers.
Properties and applications of bauxite
The main direction of use is the production of pure aluminum from bauxite and its salts. Minor areas:
- production of flux - a group of substances that remove oxides from surfaces intended for soldering;
- paint and varnish production;
- during oil refining as a sorbent;
- production of aluminous cement used in construction at low temperatures;
- creation of electrocorundum - a fireproof, resistant superhard material used as an abrasive substance.
Physicochemical characteristics
The formula of the chemical substance varies greatly depending on the amount of impurities, the basic formula is Al2O3 × nH2O. Bauxite contains the following basic substances:
- aluminum hydroxides;
- iron compounds;
- silicon.
Additional impurities are found in varying amounts: titanium, magnesium and calcium carbonates, compounds of sodium, potassium, chromium and other elements.
The most valuable ore is considered to be one that predominantly contains alumina and a minimal amount of silica.
- Color: red shades from light pink to brown, shades from white to black, sometimes yellow.
- Transparency: opaque.
- Hardness: 6 points.
- Density: 1.8–3.2 g/cm3.
- Cleavage: perfect.
- Fracture: earthy (dense rocks), cellular (porous rocks).
- Electrical conductivity: dielectric.
If you run bauxite over glass, it leaves a brown or brown mark.
Share your knowledge about bauxite in the comments. Have you ever found such stones? Repost on social networks. All the best.
Source
Physicochemical characteristics
The breed has a complex composition. Consists of various chemicals (aluminum hydroxide, silicates and oxides of iron, silicon). It may also contain manganese, magnesium, calcium oxide, titanium dioxide, rutile, etc. Sometimes calcium, magnesium carbonate, zirconium, sodium, phosphorus, chromium, gallium, potassium, vanadium compounds are found, and there may be pyrite impurities. That is, the chemical component fluctuates greatly. The indicators differ primarily depending on the mineralogical form of aluminum hydroxide and the amount of various impurities.
A bauxite deposit is valuable when the stone has a lot of silica and alumina. The openability of the ore, simplicity and ease of extraction are important.
Bauxite differs in physical properties and appearance, so it is difficult to determine quality by visual signs. This causes difficulties in finding the mineral, which is why rocks are examined under a microscope, and then a decision is made about mining.
The main physical and chemical indicators of the mineral are as follows:
- hardness 2–6 on the Mohs scale;
- opacity;
- lack of syngony, amorphous mineral;
- perfect cleavage;
- electrical conductivity: dielectric;
- density 2500–3500 kg/m3.
If you run the mineral across glass, it leaves a brown or brown mark. The specific gravity varies depending on the location of extraction. For example, if there is a lot of silica, then the indicator is 1.2 g/cm3. For dense samples with a high iron content, the specific gravity is 2.8 g/cm3.
TOP 10 countries for bauxite mining
The existence of metal deposits in the amount of about 30 billion tons has been proven. This amount of raw material for aluminum production should be enough for many centuries. Moreover, five countries have reserves of 70% of all bauxite.
Aluminum production requires a large amount of electricity. At the same time, bauxite is a transportable raw material, because it is mined in geographically remote countries. Consumers of the resource are developed countries with a huge energy base. It is not for nothing that most industrial enterprises operate near hydroelectric power stations. This makes it possible to reduce the territorial accessibility between mines for aluminum production and factories for its production. Among the leaders in aluminum production is Australia, whose annual share of production is 75 million tons. It is followed by China with 70 million, as well as Guinea with 50 million tons.
| N | A country | Production in 2004 (million tons) | Reserves at the end of 2004 (billion tons) | Share in world production (%) |
| 1 | Australia | 56 | 4,4 | 35,90 |
| 2 | Brazil | 18,5 | 1,9 | 11,86 |
| 3 | Guinea | 15,5 | 7,4 | 9,94 |
| 4 | China | 15 | 0,7 | 9,62 |
| 5 | Jamaica | 13,5 | 2 | 8,65 |
| 6 | India | 10 | 0,77 | 6,41 |
| 7 | Venezuela | 5,5 | 0,32 | 3,53 |
| 8 | Russia | 5 | 0,2 | 3,21 |
| 9 | Suriname | 4,2 | 0,58 | 2,69 |
| 10 | Greece | 2,4 | 0,6 | 1,54 |
| 11 | Guyana | 1,7 | 0,7 | 1,09 |
| Other countries | 9 | 3,72 | 5,77 | |
| Total worldwide | 156 | 23 | 100,00 | |
Iron ore exporting countries - list
Among the significant participants in the international iron ore market, it is worth noting the states that are not included in the top five:
- Venezuela. The country is located on the mainland of South America. Its unique topography provided a huge amount of iron ore reserves. The raw material is suitable for making alloy or steels. You can find it in magnetite, chamosite, hematite.
- USA. The volume of iron ore in the deposits is about seven billion tons. Most of them are located near the largest Lake Superior and Michigan. Iron ore is of low quality and needs beneficiation.
- Canada. The main ore reserves are located in the Canadian crystalline shield. The Iron Belt - Labrador, is of global importance in the field of ore mining. Its width reaches hundreds of kilometers. It stretches from the northern region to the southern shores. Length - one thousand three hundred kilometers. Unlike the USA, Canada produces high-quality raw materials.
- Iran. Large deposits are located in the central regions of the country. The extraction of such minerals as ferrous metal, iron ore, gold and others is completely monopolized by the largest companies.
- Sweden. The country is rich in mineral resources, including iron ore deposits.
further reading
- Bardossi, G. (1982): Karst bauxites: bauxite deposits on carbonate rocks.
. Elsevier Sci. Publ. 441 p. - Bárdossy, G. and Aleva, G. J. J. (1990): Lateritic bauxites
. Developments in Economic Geology 27, Elsevier Sci. Publ. 624 pp. ISBN 0-444-98811-4 - Grant, C.; Lalor, G., Vuchkov, M. (2005) Comparison of bauxites from Jamaica, Dominican Republic and Suriname
. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry p. 385–388 Volume 266, No. 3 - Hanilci, N. (2013). Geological-geochemical evolution of the Bolkardağı bauxite deposits, Karaman, Turkey: shale to bauxite transformation
. Journal of Geochemical Research