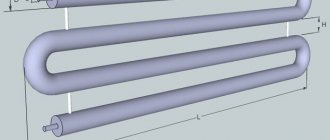
For the heating system of large premises, it is not advisable to use conventional factory batteries and radiators. They have very little heat output and power. As an alternative, heating registers can be considered.
Heating devices called registers are several folding pipes located parallel to each other and connected to each other by jumpers. The coolant moves through the pipes, transferring heat to the iron walls of the register, which heat the air space in the room.
Water or antifreeze can be used as a coolant , which prevents the pipes of a disconnected system from freezing during the cool season. In independent heating registers with a cylindrical electric heater (TEH), the coolant can also be oil, then the independent register is considered the most powerful analogue of domestic oil radiators. They have become widespread due to their simplicity of design, reliability and a number of other advantages.
Serpentine registers (S-shaped)
Such registers have become quite popular. The design of these devices is quite simple: there are several sections that are connected by arcs, the diameter of which is close to the sectional ones. Due to this, the hydraulic pressure inside the device is significantly reduced. As a result, the register becomes a single unit, the entire surface of which is working, which significantly increases the efficiency of such devices.
Such heating registers made of smooth pipes usually contain a large amount of carbon. In addition, registers made of other materials can be found on the market: cast iron, alloy or stainless steel.
Sectional registers made of smooth pipes
Sectional registers are in very good demand among owners of private houses. Such devices consist of pipes that are interconnected and closed with plugs. The energy carrier passes through the top pipe, enters the next one, and ultimately ends up in the discharge line. To increase heat transfer, they try to make transitions between sections as close to the edge as possible. Interpipe plugs can be elliptical or flat. The inlet pipe can be made with a flange, thread or welding. The design of sectional registers includes a threaded fitting, to which a special vent is attached to remove air from the system. Pipes for sections can have different diameters (from 25 mm to 40 cm), so choosing the appropriate option is not difficult. Transition pipes usually have a smaller diameter. In addition, one of the most important operating conditions for such installations is the pressure in the system not exceeding 1 MPa.
Design features
Essentially, a register is one or more pipes connected to each other in parallel
Here it is important to create conditions so that the coolant flows sequentially from one pipe to another, releasing heat into the room. Therefore, two types of registers are made
Sectional
Several parallel pipes, the ends of which are closed with plugs. Jumpers are installed between them, through which the coolant flows from one section to another. It moves from top to bottom, that is, it enters the upper pipe and comes out of the lower one.
Important! The jumpers are installed in a checkerboard pattern. If between the first and second sections the jumper is installed on the left, then between the second and third - on the right
The diameter of the jumpers is much smaller than the diameter of the sections. For example, if the diameter of the main register element is 80 mm, then the jumpers are 32-40 mm.
Serpentine, their drawing
This is the same design, only the sections are connected to each other by double 90° bends of the same diameter as the main pipes, and a continuous pipe structure of one large diameter along the entire length is obtained. The heat transfer of this type of register is much higher than that of the previous version.
Photo 1. Drawing of a coil-type register, which is a continuous pipe structure of the same diameter along the entire length.
The advantages of the design include the low hydraulic pressure of the coolant inside the device, which allows a sufficiently large volume of hot water to pass through it.
Reference! The coil can be installed either horizontally or vertically.
Location options
Heating registers, depending on placement options, can be divided into two groups: portable and stationary. Portable systems are quite mobile, and they can be moved absolutely freely - if only there was power. And such systems are usually powered by electricity. Inside portable registers there are usually heating elements of different power, which provide heating of the energy carrier. Such units can be used both in the house and in the garage, at the dacha, at a construction site, etc. Stationary registers are demanding in terms of their location. Firstly, they require permanent mounting, and secondly, they need to be connected to a boiler, which will ensure heating of the coolant and its circulation through the system.
Reduced heat transfer.
In order to save energy, it becomes important to reduce the heat transfer of pipes in those sections of communications that are not used for their intended purpose, for example, when moving from one building to another or in an unheated room.
There are many options for using thermal insulation materials for this. Manufacturers offer a fairly wide range to choose from, ranging from cheap fiberglass to more expensive types of polystyrene foam. You can purchase pipes with insulating elements already built into them.
To summarize, we conclude that the use of such calculations helps to significantly save money and avoid many technical obstacles when designing water and heat supply systems.
Actually, you are a desperate person if you decide to undertake such an event. The heat transfer of a pipe, of course, can be calculated and there are a great many works on the theoretical calculation of the heat transfer of various pipes.
Let's start with the fact that if you decided to heat your house with your own hands, then you are a stubborn and purposeful person. Accordingly, a heating project has already been drawn up, pipes have been selected: either metal-plastic heating pipes or steel heating pipes. Heating radiators have also already been looked at in the store.
But, before acquiring all this, that is, at the design stage, it is necessary to make a conditional relative calculation. After all, the heat transfer of heating pipes, calculated in the project, is the key to warm winters for your family. There is no room for error here.
Methods for calculating heat transfer from heating pipes
Why is the emphasis usually placed on calculating the heat transfer of heating pipes? The fact is that for commercially manufactured heating radiators, all these calculations have been made and are given in the instructions for use of the products. Based on them, you can easily calculate the required number of radiators depending on the parameters of your home: volume, coolant temperature, etc.
Tables.
This is the quintessence of all the necessary parameters collected in one place. Today the Internet contains a great many tables and reference books for online calculations of heat transfer from pipes. In them you will learn what is the heat transfer of a steel pipe or cast iron pipe, the heat transfer of a polymer or copper pipe.
All that is needed when using these tables is to know the initial parameters of your pipe: material, wall thickness, internal diameter, etc. And, accordingly, enter into the search the query “Table of heat transfer coefficients of pipes.”
This section on determining the heat transfer of pipes also includes the use of manual reference books on heat transfer of materials. Although they are becoming more and more difficult to find, all information has migrated to the Internet.
Formulas.
The heat transfer of a steel pipe is calculated according to the formula
Qtr=1.163*Str*k*(Twater - Air)*(1-efficiency of pipe insulation), W where Str is the surface area of the pipe, and k is the heat transfer coefficient from water to air.
The heat transfer of a metal-plastic pipe is calculated using a different formula.
Where is the temperature on the inner surface of the pipeline, °C; t
c is the temperature on the outer surface of the pipeline, °C;
Q—
heat flow, W;
l
—pipe length, m;
t
—coolant temperature, °C;
t
inc—air temperature, °C;
a n is the external heat transfer coefficient, W/m 2 K; d
n - outer diameter of the pipe, mm;
l—thermal conductivity coefficient, W/m K; d
in
-
internal diameter of the pipe, mm; a int - internal heat transfer coefficient, W/m 2 K;
You understand perfectly well that calculating the thermal conductivity of heating pipes is a relative value. The formulas include the average parameters of certain indicators, which may, and do, differ from those that actually exist.
For example, as a result of the experiments, it was found that the heat transfer of a polypropylene pipe located horizontally is slightly lower than that of steel pipes of the same internal diameter, by 7-8%. It is internal, since polymer pipes have a slightly thicker wall thickness.
Many factors influence the final figures obtained in tables and formulas, which is why the footnote “approximate heat transfer” is always included. After all, the formulas do not take into account, for example, heat loss through the building envelope made of different materials. There are corresponding tables of amendments for this purpose.
However, by using one of the methods for determining the heat output of heating pipes, you will have a general idea of what kind of heating pipes and radiators you need for your home.
Good luck to you, builders of your warm present and future.
Material of manufacture
If you make a selection depending on the material of manufacture, then the registers can be classified into the following categories:
- Steel;
- Aluminum;
- Cast iron.
Which heating registers are best to choose? Steel registers became the most common. Their connection to the heating system is carried out by threading or welding. Such devices have good heat transfer and reasonable cost. Aluminum registers are much lighter than steel registers. In addition, they are resistant to corrosion, are made without connecting seams and have good heat dissipation. The main disadvantage of such devices is their very high price. Read also: “What types of heating registers are there – selection, calculation, characteristics.” Registers made of cast iron are connected to the heating system using a flange connection. They are quite easy to install and inexpensive. The disadvantages of cast iron products include low inertia, which significantly reduces the heating time of the registers.
Choosing a welding machine and electrodes
Selection of electrodes and welding mode depending on the thickness of the metal
Currently, manufacturers offer several models of welding machines that can be used to make high-quality metal joints of various brands. But before you properly weld the heating, you need to choose the optimal model. Let's look at the most popular types of devices and their main characteristics.
Transformer
The operating principle is based on increasing the frequency of the incoming current. Step-up transformers are used for this. Despite the relatively large dimensions, this type of welding machine is best adapted to power surges. With its help, you can properly weld a heating boiler following the manufacturing technology.
Inverter
The generation of current according to the established parameters occurs due to the operation of electronic circuits. They are characterized by a stable arc, which ultimately produces a high-quality seam. This must be taken into account before you properly learn how to weld heating yourself. However, they are extremely sensitive to voltage drops in the network.
It is recommended to purchase a voltage stabilizer as additional equipment for inverter devices.
Is it possible to weld a boiler with your own hands for water heating using an inverter apparatus? Yes, but its characteristics must correspond to the parameters of the metal used. Carbon steels are most often used for the manufacture of heating elements.
Heating welding material table
You also need to know the dependence of the diameters of the electrodes on the thickness of the metal being welded
As for choosing a welding machine, experts recommend choosing inverter models that operate on alternating current. Their cost is slightly higher than that of transformer ones, but they are smaller in size and can be used to make a high-quality weld
This is important to consider, since self-welding of a heating boiler must be of high quality
The cost of a device with a power of 7 kW, a welding current of up to 200 A and a maximum electrode diameter of 3.6 mm will be about 16 thousand rubles.
Calculation of the number of ribs
Heating registers must be calculated before purchasing them. The diameter of the pipes is very important: experts believe that pipes with a cross-sectional diameter in the range from 3 cm to 8 cm are suitable for a private house. This decision is determined by the fact that a conventional heating boiler is not capable of producing a larger amount of heat, so too large surfaces will not warm up completely . When making calculations, you need to pay attention to the length of one register rib and the heat transfer per meter of this length. For example, a meter-long pipe with a 6-centimeter cross-section can heat one square meter of area. When calculating the required number of edges, the result must be rounded up. The calculation of the number of heating registers must also take into account the characteristics of the building. For example, if a building has a large number of windows and doors, or if the walls are thin and poorly insulated, then the number of registers can be increased by 20-50%.
Types of radiator connections
The main methods of connecting heating system devices are several types:
- Lateral (standard) connection;
- Diagonal connection;
- Bottom (saddle) connection.
Side connection
Lateral radiator connection.
Connection from the end of the device - supply and return are located on one side of the radiator. This is the most common and effective connection method; it allows you to remove the maximum amount of heat and use the entire heat transfer of the radiator. As a rule, the supply is at the top and the return is at the bottom. When using a special headset, it is possible to connect from bottom to bottom, this allows you to hide the pipelines as much as possible, but reduces the heat transfer of the radiator by 20 - 30%.
Diagonal connection
Diagonal radiator connection.
Connection diagonally to the radiator - the supply is on one side of the device from the top, the return is on the other side from the bottom. This type of connection is used in cases where the length of a sectional radiator exceeds 12 sections, and a panel radiator is 1200 mm. When installing long radiators with side connections, there is uneven heating of the radiator surface in the part furthest from the pipelines. To ensure that the radiator heats up evenly, a diagonal connection is used.
Bottom connection
Bottom connection from the ends of the radiator
Connection from the bottom of the device - supply and return are located at the bottom of the radiator. This connection is used for the most hidden installation of pipelines. When installing a sectional heating device and connecting it using the bottom method, the supply pipe approaches on one side of the radiator, and the return pipe on the other side of the bottom pipe. However, the heat transfer efficiency of radiators with this scheme is reduced by 15-20%.
Bottom radiator connection.
In the case when the bottom connection is used for a steel panel radiator, then all the pipes on the radiator are located at the bottom end. The design of the radiator itself is made in such a way that the supply flows through the manifold first to the upper part, and then the return flow is collected in the lower radiator manifold, thereby not reducing the heat transfer of the radiator.
Bottom connection in a single-pipe heating circuit.
Heating register installation
Installing heating registers usually does not require the help of a qualified specialist, but carrying out the operation yourself requires careful preparation. The most important thing is to ensure a reliable connection between the registers and the pipeline. The connection must be able to withstand a load of 10 MPa. When welding, it is very important to maintain good quality. For clarity, you can look at the photo, which shows a diagram of connecting heating registers.
It is best to place registers along the walls. A prerequisite for installing heating devices is maintaining a constant slope, which for registers is 0.05% of its length. In addition, registers should be installed closer to the floor surface.
The efficiency of the device will depend on a large number of factors. For example, a reduced main pipe diameter will increase resistance to the energy carrier, which will affect performance. The most commonly used systems are with the following parameters:
- pipe diameter: 25-160 mm;
- sectional adapters: from 30 mm;
- distance between main pipes: from 50 mm;
- maximum pressure: 10 MPa;
- material: steel.
Operating rules
There are no special requirements for the operation of registers compared to radiators:
They must be securely mounted on legs or strong brackets.
Any heating devices with water should not freeze.
If corrosion occurs, the damaged areas should be cleaned, covered with an anti-corrosion primer and painted in several layers.
Registers must not serve as a support for any loads.
It is necessary to ensure that the heating system does not become airy - this impairs its performance.
Advantages of heating registers
Heating registers have a number of advantages:
- possibility of using an individual drawing;
- The coolant can be not only water, but also heated steam;
- connecting the heating register to the system is extremely simple;
- excellent for heating large buildings because they have very good heat transfer;
- They're pretty cheap.
A homemade heating register is shown in the video: Conclusion Registers have already become good competitors to conventional heating radiators. Do-it-yourself heating registers allow you to save a lot, and these designs can work even in rooms with an aggressive environment.
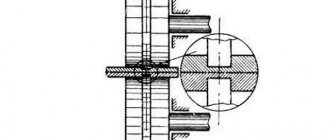
Self-installation
Split bolt mounting
Two mounting methods:
- detachable bolted connection;
- non-detachable welding connection.
The choice should be based on the weight and size of the device, and also take into account the characteristics of the heating system.
You can take the rules for installing heating radiators as a basis; there is no fundamental difference. Slope indicator - it is important to take into account, when connecting to a gravity system, the slope along the flow of the coolant.
In systems where pumping equipment is not used and where the driving force is the difference in its partial pressure, there are no such problems.
Installation rules:
- The recommended distance, in accordance with the technological process, from the wall and windows is at least 20 cm.
- Detachable installation requires the use of only paranite pads or flax used in plumbing work;
- All steel heating registers must be painted to avoid rusting.
- It is better not to carry out installation during the heating season.
A comparative analysis of the calculated and actual power of the register can be carried out at the end of the test launch of the system, and if necessary, design changes can be made.