How to make an electromagnetic table from a microwave transformer - for plumbing and welding work
In this review, we want to share with you an interesting idea on how to make an electromagnetic table for welding and plumbing work with your own hands.
This idea (and its implementation) was shared by the author of the YouTube channel Gianni Pirola Fai Da Te.
The advantage of an electromagnetic table is that there is no need to use a vice, clamps or other devices for fixing metal workpieces.
On a homemade electromagnetic table you can both weld workpieces and process them: cut with a grinder, grind, etc.
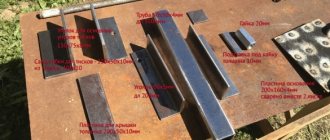
- transformer from a microwave oven (microwave);
- power unit.
DIY magnetic table
Tools for grinding flat surfaces
When grinding, parts can be secured directly to the machine table using clamping bars. However, such fastening is used in cases where the parts cannot be fixed to a magnetic plate or other devices.
Pattern vices (Fig. 10.9a) differ from conventional machine ones in manufacturing precision and the ability to turn. The fixed jaw of the vice is integral with the base 1. The body has grooves for the passage of the movable jaw 2, which is moved by a screw 3. The base of the body has threaded holes for attaching the vice to various devices. All vise planes are machined at an angle of 90°. The pressed-in cylindrical measuring pin 4 is used to measure inclined planes.
Article on the topic: How to make a table from boards with your own hands
Rice. 10.9. Pattern vice (a) and electromagnetic plate (b)
Electromagnetic plates . The design of the electromagnetic plate (Fig. 10.9b) is based on the following principle. If a wire is wound around an iron core (Fig. 10.10a) and a direct current is passed through it, the core will be magnetized. If you now bring a steel object to one of the ends of the core, it will be strongly attracted to the core. After the current in the winding stops, the magnetic action of the core will also stop.
You can bend such a core in the form of a horseshoe (Fig. 10.10b) and also pass current through its winding. In this case, the magnet will be even stronger. By combining horseshoe-shaped magnets into a group, we get an electromagnetic plate.
Rice. 10.10. Diagram of the magnetic action of current (a) and a horseshoe magnet (b)
The magnet poles located on the top of the plate are carefully insulated from its body with non-magnetic alloys (babbitt, zinc), due to which the magnetic forces are not dissipated in the body of the plate, but are directed directly into the body of the part. Only magnetic metals (for example, steel, iron, cast iron) can be attracted to the electromagnetic plate.
Electromagnetic plates are used in various sizes, round and rectangular. Only direct current is suitable for powering them, so machines are installed with devices that convert alternating current into direct current.
Electromagnetic plates provide reliable and quick fastening of the parts to be ground. To maintain the functionality of the plate, it is necessary to protect it from shocks and shocks, and also to ensure that no coolant gets on the windings. Upon completion of work, you should immediately wipe the working surface of the stove dry.
Magnetic plates
In addition to electromagnetic plates, magnetic plates with permanent magnets are used on grinding machines. This type of stove does not require special generators and rectifiers with wiring and distribution devices. However, as a rule, the force of their attraction is weaker than the force of attraction of electromagnetic plates.
Article on the topic: Do-it-yourself multi-touch table
The design of a rectangular magnetic plate and its operating principle are shown in Fig. 10.11. Its upper part is made of steel plates 1 with non-magnetic layers 2 between them (Fig. 10.11a). Strong permanent magnets 4 can be moved, closing them either to the iron plates or to the part being fixed. In Fig. 10.11b shows the position of the magnets when fastening parts 5, and in Fig. 10.11c – during their removal or installation. The magnets are switched using handle 3. The lower part of the plate 6 is fixed on the machine table.
Rice. 10.11. Magnetic plate:
a – general view; b – position of the magnets when securing the part; c - the same when installing and removing the part
Segmented grinding wheels for grinding flat surfaces
Surface grinding with solid grinding wheels of large diameter is economically unprofitable due to large waste, increased heat generation and the possibility of breakage during transportation. In addition, if a crack appears or partial destruction of the wheel, it is necessary to replace it entirely and lose a significant amount of usable abrasive material. These inconveniences are eliminated when using wheels made from inserted abrasive segments (Fig. 10.12). If one or more of them breaks, such segments can be easily replaced with new ones.
The insert segments are used until they are almost completely worn out. By releasing 1 clamp, you can remove 2 segments at once. As they wear, the height of the segments decreases, so spacers are placed under them.
Rice. 10.12. Segment grinding
DIY magnetic plate - Metals, equipment, instructions
Magnetic plates for grinding machines are a special class of metalworking equipment that is designed to hold steel workpieces on the working surface under the influence of electromagnetic attraction forces.
It would seem, why use such a sophisticated design when you can use traditional cams as a clamp, which reliably clamp the workpiece and provide maximum rigidity during processing? In fact, electromagnetic fixation using magnetic plates for grinding machines has a number of advantages, which we will discuss below.
The key advantage is the ability to operate the equipment in multi-threaded mode. The master can simultaneously fix several workpieces on one installation, thereby increasing the productivity of his work by an order of magnitude. In addition, the magnetic plate for the grinding machine can ensure extreme precision in machining the workpiece.
This is due to the fact that during the grinding process the metal part heats up and, accordingly, expands. In this case, the workpiece clamped in a vice is deformed, while the workpiece mounted on the electromagnetic plane expands freely on the working surface.
It is worth remembering that the plate is not capable of providing as much force as the locking cams. In addition, if an emergency interruption of the power supply occurs, the workpiece will fall off the working surface. That is why the scope of application of magnetic plates for grinding machines excludes work that requires high cutting forces.
Another disadvantage of such installations is the phenomenon of residual magnetism inherent in steel workpieces that were processed in this way. Fortunately, you can cope with the problem using a demagnetizer, which in most cases allows you to close your eyes to the above-described drawback.
How to make a simple electromagnet - step-by-step instructions with diagrams
Such a device is convenient because its operation is easy to control using electric current - changing the poles, changing the force of attraction. In some matters it becomes truly indispensable, and is often used as a constructive element of various homemade products. It’s not difficult to make a simple electromagnet with your own hands, especially since almost everything you need can be found in every home.
What you will need
- Any suitable sample made of iron (it is highly magnetic). This will be the core of the electromagnet.
- The wire is copper, always with insulation to prevent direct contact of the two metals. For a homemade electric magnet, the recommended cross-section is 0.5 (but not more than 1.0).
- DC source - battery, battery, power supply.
Additionally:
- Connecting wires for connecting an electromagnet.
- Soldering iron or electrical tape to secure contacts.
Device and principle of operation.
3.1. The plate consists of three main parts: movable and fixed magnetic blocks and a housing. Magnetic blocks are assembled from steel plates, between which ceramic permanent magnets are located. The free space between the steel plates is filled with non-magnetic material.
Rice. Magnetic plate device
3.2. When switched on, poles 2 of the power unit lie on non-magnetic elements 5 of housing 1, directing the entire magnetic flux of magnets 3 through adapter 4 and parts 6. when switched off, poles 2 are located under non-magnetic spacers of the adapter. As a result, the magnetic flux has a new direction.
Article on the topic: Do-it-yourself loft-style table
3.3. The movable magnetic block is located inside the housing and can be moved using an eccentric wolf to the right or left by turning the handle 180˚. In the off position, magnetic circuits with different polarities are combined; there is no non-magnetic flux on the working surface.
Compared to electromagnetic plates and hydraulic or pneumatic devices, they have the following advantages:
- do not require connection to an energy source;
- allow you to achieve higher precision when processing workpieces;
- provide absolute reliability of fastening;
- maintain the main technical parameters during the entire service life at the original level;
- do not require periodic repairs and maintenance
Magnetic tables. Coordinate tables
- Dovetail guides.
- The flywheel division value is 0.05 mm.
- Millimeter scale, 2 stops.
- Chutes for draining coolant.
Table model
| KT120 | KT179 | KT180 | KT210 | |
| Working surface length | 400 | 500 | 700 | 730 |
| Working surface width | 120 | 180 | 180 | 210 |
| X-axis travel, mm | 220 | 287 | 480 | 480 |
| Movement along the Y axis, mm | 165 | 175 | 175 | 210 |
| Width of T-shaped grooves, mm | 10 | 12 | 12 | 14 |
| Maximum load, kg | 70 | 120 | 120 | 150 |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 483x430x250 | 840x510x330 | 955x485x140 | 1050x535x180 |
| Weight, kg | 22 | 32 | 49 | 84 |
| Availability | stock | order | stock | stock |
| Price, rub. | 40412 | 53097 | 65074 | 75573 |
2 x- COORDINATE ROTARY TABLE FA
Rotate 360°
| vendor code | Size | Weight | Price | Availability |
| K 588 | 100x100x115 | 6.5 | 8 740 | in stock |
| K 589 | 150x150x115 | 13.5 | 11 643 | in stock |
2 x- COORDINATE TABLE RKA
Longitudinal feed - 80mm; cross feed - 50mm; table groove width - 10mm; distance between grooves - 35mm; the distance between the mounting holes is 115x100mm.
CNC installation possible
| vendor code | Size | Workers field | Price | Availability |
| P 77884 | 185x100x102 | 100×80 | 9 685 | in stock |
2 x- JOINT TABLE BKA
Longitudinal feed - 180mm; cross feed - 100mm; table groove width - 16mm; distance between grooves - 65mm; the distance between the mounting holes is 182mm.
CNC installation possible
| vendor code | Size | Workers field | Price | Availability |
| P 38884 | 300x140x123 | 180×100 | 15 685 | in stock |
1 x- COORDINATE TABLE AKA 180
Longitudinal feed - 180mm; table groove width - 16mm; distance between grooves - 65mm; distance between mounting holes - 182mm
CNC installation possible
| vendor code | Size | Workers field | Price | Availability |
| P 28884 | 300x140x85 | 180 | 8 585 | in stock |
2 x- COORDINATE TABLE WITH CLAMPS KKA
Longitudinal feed - 220mm; cross feed - 160mm; table groove width - 10mm; distance between mounting holes - 200x160mm
CNC installation possible
| vendor code | Size | Workers field | Price | Availability |
| P 008884 | 400x120x145 | 220×160 | 27 685 | in stock |
| P 58165 | 700x180x151 | 480×175 | 49 230 | in stock |
2 x- COORDINATE TABLE WITH KAN CLAMPS
Longitudinal feed - 225mm; cross feed - 150mm; table groove width - 12mm; distance between grooves - 72mm; distance between mounting holes - 250x240mm
CNC installation possible
| vendor code | Size | Workers field | Price | Availability |
| P 08884 | 425x244x150 | 255×150 | 21 240 | in stock |
2 x- COORDINATE TABLE CF
Longitudinal feed - 270mm; cross feed - 120mm; table groove width - 14mm; distance between grooves - 62.5mm; the distance between the mounting holes is 170x152mm.
CNC installation possible
| vendor code | Size | Workers field | Price | Availability |
| P 48884 | 473x156x134 | 270×120 | 16 182 | in stock |
COORDINATE ROTARY TABLE RK-3A
Longitudinal feed - 105mm; cross feed - 90mm; table groove width - 12mm; distance between grooves - 72mm; the distance between the mounting holes is 195mm.
CNC installation possible
| vendor code | Size | Working fields mm. | Price | Availability |
| P 87884 | 225x175x138 | 105×90 | 12 274 | in stock |
| P 97884 | 330x220x155 | 190×100 | 18 240 | in stock |
| P 08884 | 425x245x165 | 225x150 | 25 529 | in stock |
COORDINATORY ROTARY TABLE PK
Longitudinal feed - 400mm; cross feed - 150mm; table groove width - 12mm; distance between grooves - 72mm; distance between mounting holes - 250x250mm
CNC installation possible
| vendor code | Size | Workers field | Price | Availability |
| P 18884 | 600x240x150 | 400x150 | 31 243 | in stock |
MAGNETIC TABLE RM-300T
The PM-300T magnetic table is designed for securing workpieces made of materials during their processing on metal-cutting machines, metalworking and during control operations.
Clamping occurs when the handle is turned 180° clockwise. The energy source is permanent ceramic magnets, which ensure constant clamping force throughout the entire service life.
Processing of workpieces can be done with or without coolant.
Slab model
| PM-300T | |
| Nominal grip force | 80 N/s m³ |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 300x150x28 |
| Weight, kg | 11 |
| Availability | stock |
| vendor code | 25042004 |
| Price, rub. | 24 266 |
Slab model
| PM-175 | |
| Nominal grip force | 60 N/s m³ |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 175x100x60 |
| Weight, kg | 6 |
| Availability | stock |
| vendor code | 25042002 |
| Price, rub. | 14 066 |
A magnetic table with an inclination (Sine magnetic plate) is designed for securing workpieces made of ferrimagnetic materials when processed on metal-cutting machines at various angles. The sine magnetic plate has wide versatility, since it has rotating parts in the longitudinal and transverse planes.
Slab model
| PM-300N | |
| Nominal grip force | 80 N/s m³ |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 300x150x120 |
| Tilt angle degrees | 0-45 |
| Weight, kg | 30 |
| Availability | stock |
| vendor code | 25042003 |
| Price, rub. | 42 147 |
MAGNETIC ROUND PLATE RM-160
Slab model
| PM-160 | PM-200 | |
| Nominal grip force | 90 N/s m³ | 90 N/cm³ |
| Overall dimensions, mm | Ø160 | Ø200 |
| ABIC Dimensions | 160x115x58x2.8 | 200x155x58x2.8 |
| Weight, kg | 8.4 | 14 |
| Availability | stock | stock |
| vendor code | P 44683 | P 54683 |
| Price, rub. | 11 066 | 18 010 |
PMS PLATE
Slab model
| PMS-100 | PMS-125 | |
| Nominal grip force | 90 N/s m³ | 90 N/cm³ |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 100×175 | 125×250 |
| Overall dimensions C-B-DE | 85x75x44 | 175x252x85 |
| Tilt angle .degree | 0-45 | 0-45 |
| Weight, kg | 11.5 | 21 |
| Availability | stock | stock |
| vendor code | P 74683 | P 94683 |
| Price, rub. | 19 529 | 21 500 |
Slab model
| PMS-150 | PMS-150-3 | |
| Nominal grip force | 90 N/s m³ | 90 N/cm³ |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 150×150 | 150×300 |
| Dimensions A-B-DE | 200x152x85 | 350x152x85 |
| Tilt angle .degree | 0-45 | 0-45 |
| Weight, kg | 14.8 | 28 |
| Availability | stock | stock |
| vendor code | P 84683 | P 05683 |
| Price, rub. | 22 824 | 28 700 |
MAGNETIC FLAT PLATE PMP
C=254mm D=20mm E=4.8mm(1+3.8) Handle in the form of a hex key.
A plate based on permanent magnets has the following advantages compared to electromagnetic plates and hydraulic or pneumatic devices: - does not require connection to energy sources; — provides more accurate processing of workpieces; — ensures absolute clamping reliability; — maintains basic technical characteristics throughout the entire service life; - does not require repair and maintenance costs
Slab model
| PMP-150-3 | PMP-150-35 | |
| Nominal grip force | 90 N/s m³ | 90 N/cm³ |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 150×300 | 200×400 |
| Dimensions ABC | 254x20x58x4.8 | 353x20xx4.8 |
| Weight, kg | 19 | 35 |
| Availability | stock | stock |
| vendor code | P 73504 | P 83504 |
| Price, rub. | 14 266 | 18 910 |
Slab model
| PMP-200-4 | PMP-150-11 | |
| Nominal grip force | 110 N/s m³ | 110 N/cm³ |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 254×300 | 200×400 |
| Dimensions ABC | 254x20x58x4.8 | 353x20xx4.8 |
| Weight, kg | 19 | 35 |
| Availability | stock | stock |
| vendor code | P 73504 | P 83504 |
| Price, rub. | 16 266 | 19 910 |
MAGNETIC ELECTRIC FLAT COOKER
Requires external power supply
Slab model
| PP-300-3 | PP-150-35 | PP-500-10 | |
| Nominal grip force | 160 N/cm³ | 160 N/cm³ | 160 N/cm³ |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 680×400 | 800×400 | 500×1000 |
| Dimensions ABC | 635x144x20 | 735x132xx18 | 941x142x20 |
| Weight, kg | 35 | 255 | 375 |
| Availability | stock | stock | stock |
| vendor code | P 15683 | P 03835 | P 13853 |
| Price, rub. | 66 266 | 112 910 | 161 000 |
How do surface grinding machines work?
The vast majority of parts made of metal undergo a technological operation such as grinding. To perform this with high efficiency and accuracy, surface grinding machines are used.
A rather difficult to manufacture banding machine with excellent functionality
Surface grinding machines of serial models can process both flat and profile parts. The surface processing accuracy that can be achieved using such devices is 0.16 microns. Of course, it is almost impossible to achieve such a result when processing on machines made by yourself. However, even the accuracy that homemade machines allow to obtain is quite sufficient for many metal products.
The load-bearing structural element of the machines of this group (as well as any other equipment) is the bed. Its dimensions directly determine what size parts can be processed on the machine. The most common material for manufacturing beds of surface grinding equipment is cast iron, since this metal, due to its characteristics, perfectly dampens vibrations, which is especially important for devices of this type.
Work table and controls of the 3G71M grinding machine
The structural element of surface grinding machines on which the workpiece is fixed is a work table having a round or rectangular shape. Its dimensions can vary significantly depending on the specific model of surface grinding equipment. The workpieces can be fixed on such a work table due to its magnetized surface or using special clamping elements. During processing, the work table makes reciprocating and circular movements.
Article on the topic: DIY table with infinity effect
In mass-produced surface grinding machines, the work tables are driven by a hydraulic system. In self-assembled equipment, mechanical transmissions are used for this.
Grinding a steel workpiece fixed on the working surface of the machine using a magnetic field
Important elements of the design of surface grinding equipment, which ensure the accuracy and smooth movement of the work table, are guides. In addition to high precision manufacturing, the guides must have exceptional strength, since in the process of almost constant movements of the desktop they are subject to active wear.
To achieve high processing accuracy, the guides must ensure accurate, smooth (without jerking) movement of the worktable with minimal friction of the contacting elements. That is why high-strength steel is used for the manufacture of these structural elements, which is hardened after the guides are made from it.
Option for manufacturing guides using angles and bearings
The working tool of a surface grinding machine, which can be a grinding wheel or an abrasive belt, is mounted on the spindle of the headstock. Rotation of the working tool, for which the main electric motor is responsible, can be transmitted through a gearbox or belt drive.
For do-it-yourself surface grinding machines, you can choose a simpler option: select the diameter of the grinding wheel so that it can be mounted directly on the electric motor shaft. This will eliminate the need to use a gear or belt drive.
Do-it-yourself electromagnetic table - Metalist's Handbook
Magnetic plates for grinding machines are a special class of metalworking equipment that is designed to hold steel workpieces on the working surface under the influence of electromagnetic attraction forces.
It would seem, why use such a sophisticated design when you can use traditional cams as a clamp, which reliably clamp the workpiece and provide maximum rigidity during processing? In fact, electromagnetic fixation using magnetic plates for grinding machines has a number of advantages, which we will discuss below.
The key advantage is the ability to operate the equipment in multi-threaded mode. The master can simultaneously fix several workpieces on one installation, thereby increasing the productivity of his work by an order of magnitude. In addition, the magnetic plate for the grinding machine can ensure extreme precision in machining the workpiece.
This is due to the fact that during the grinding process the metal part heats up and, accordingly, expands. In this case, the workpiece clamped in a vice is deformed, while the workpiece mounted on the electromagnetic plane expands freely on the working surface.
It is worth remembering that the plate is not capable of providing as much force as the locking cams.
In addition, if an emergency interruption of the power supply occurs, the workpiece will fall off the working surface.
That is why the scope of application of magnetic plates for grinding machines excludes work that requires high cutting forces.
Another disadvantage of such installations is the phenomenon of residual magnetism inherent in steel workpieces that were processed in this way. Fortunately, you can cope with the problem using a demagnetizer, which in most cases allows you to close your eyes to the above-described drawback.
Magnetic levitation at home
In the 90s of the 20th century, the Levitron toy, based on the influence of a magnetic field, became very popular.
This is a levitating top hovering in the air. A similar toy can be assembled at home to understand the essence of magnetic levitation. How to make Levitron - we will present detailed instructions.
List of materials:
- wooden board;
- a simple pencil;
- insulating tape;
- washers made of plastic or brass;
- cardboard;
- 13 neodymium disk magnets brand N52, size 12*3 mm;
- wide ring magnet with an outer diameter of 20, an inner diameter of 10 mm, brand N42.
Article on the topic: DIY kitchen cabinet
Description of the assembly process step by step:
- Making a layout. Initially, the top was assembled on two ceramic ring magnets. In our design we will use standard neodymium magnets. First, let's print out a diagram of the marking holes for installing magnets. Before starting work, check the conformity of the dimensions in the printed diagram and those indicated in the source code. If everything matches, then cut out the layout.
- Preparing the foundation. Attach a paper diagram to the board and mark according to it. Please note that the thickness of the wooden blank must be 6mm or more.
- Transfer of all circuit blocks to the base. Glue the paper carrier to the resulting base. Using a Forstner drill (d=12mm), punch the center of the circles. This will ensure further drilling accuracy.
- We drill holes. Using a Forstner drill (d=12mm), we make holes in the workpiece so that the bottom of the hole extends 3 mm into the top of the block. The magnets should be positioned as close to the top as possible.
- Installation of magnets. When the holes are ready, you have double-checked their dimensions, install the magnets with one pole facing up, for example the south one. To determine the polarity, you can use the marked D68PC-RB magnet. Place the block on a steel plate to make it easier for the magnets to move to the bottom of the holes. Let's take N52 magnets and place them in the holes, one at a time, as deep as possible. If you need to push the magnet through, you can use a wooden dowel.
- How to make a top. Take a pencil 40 mm long with a pointed end. We wrap electrical tape around it to increase the diameter to fit the central part of the ring magnet. Insert the pencil into the magnet so that the south pole is at the bottom, like the pointy part of the pencil. To add weight to the top, use plastic or brass washers: put several on top. To ensure proper operation, it is necessary to determine the acceptable number of washers using the selection method.
- Let's start the system. Cut cardboard or plastic for the platform. Place it on a magnetic base. On the platform, the top begins to spin and gradually rises with the platform until it falls into the magnetic field well.
Article on the topic: Do-it-yourself shower cabin made of tiles
If everything is done correctly, the top will freeze. Debugging the mechanism may take a long time.
Tips for adjusting the top:
- Try to ensure the base is balanced. Use pieces of cardboard or paper to raise the sides of the base and level it. If it deviates from the center to some side, lift it by placing pieces of paper under it.
- Apply three-point leveling.
- Consider the weight of the top: the device assumes the presence of a magnetic pit - the strength of the magnet in the center is weaker than near the edge. To keep the magnet in the center, you should add weight (when the top flies out) or decrease it (if the top does not rise from the platform).
- Another significant indicator is the height of the platform: a low platform does not allow the top to spin sufficiently. Therefore, you need to place paper or cardboard under it.
- If you have a 3D printer at hand, you can print a toy on it.
Thus, it is possible to make Levitron with your own hands at home. Based on the presented materials, you can design various souvenirs and interior items that can please you and your friends. In addition, you can show all kinds of tricks with magnets and levitation to children.
User manual
The magnetic plate should be re-opened and the equipment passport should be examined.
- Place it on the machine table.
- Check that the mounting is correct and start working.
- A workpiece made of ferromagnetic material must be placed on the working surface in the required position and the lever must be rotated 180 degrees. Check the reliability of the fastening.
- Start processing the workpiece.
- Metal shavings generated during operation can be removed with a brush after turning the handle 180 degrees. Then, after cleaning the surface, you need to fix the workpiece again using the handle.
- Upon completion of work, turn the handle and remove the workpiece.
Specifications
Technical conditions for the production of magnetic plates are regulated by GOST 16528-87 . It describes all the characteristics of stoves with different types of control.
The main parameters affecting the operation of magnetic plates are:
- Overall dimensions – minimum starting from 10x25 cm and maximum up to 32x100 cm. The final dimensions of the workpiece depend on this value. Also, the significant size of the plate increases the load on the machine’s work table.
- Magnetic force - acts constantly and when not in working position it is prevented by blocks of non-magnetic material. The range of action of this value is 50–120 N/cm².
- The distance between magnetic poles or coils. The smallest size available for the part being manufactured depends on it.
Purpose
The effectiveness of this simulator has long been proven by experts. Such tables are intended for the treatment of various diseases of the musculoskeletal system .
Article on the topic: Do-it-yourself upholstered furniture patterns and diagrams
Inversion tables are effective for the following diseases and pathologies:
- moderate postural disorders (initial stage scoliosis);
- chronic spasms in the muscles of the back or neck;
- as a prevention of varicose veins on the legs;
- for training people who lead a sedentary lifestyle;
- chronic stress as relaxation;
- to strengthen the back muscles.
Keep in mind that you shouldn’t expect any special miracles from using an inversion table .
Although it is used for the treatment and prevention of various pathologies, as a separate treatment method, it has little effect. Since the simulator treats existing diseases and does not in any way affect the cause of their formation.
Therefore, exercises on an inversion table must be combined with other treatment methods, for example, lifestyle changes.
You can buy a finished product in a store, or you can make it yourself. If you have little experience in manufacturing and assembling furniture items, you can resort to the second option.
Making a tabletop with lighting from New Year's garland
There is an easier way to make your own table with an infinity effect. In this case, instead of an LED strip, a regular New Year's garland is used. First, a square or rectangular frame is made from bars, then the number of light bulbs on the garland is counted.
After this, marks are placed on the frame in the places where the light bulbs will be located. It is recommended to place them at a distance of about 2 cm from each other. At the next stage of work, holes for light bulbs are drilled in the frame of the future table.
Then light bulbs are inserted into these holes and secured there. Then you need to glue the frame onto the mirror with your own hands, and glue glass with a mirror film on top of the frame.
What is the difference between a homemade and factory vacuum table?
Working equipment created independently allows you to adapt the device to the needs of a specific production process. Do-it-yourself vacuum tables allow you to take into account all the nuances of processing parts related to their size, as well as include all functions - from milling to molding work. A vacuum table for a CNC machine, assembled independently, saves the user money and simplifies further maintenance of the device.
Article on the topic: DIY standing desk
Vacuum tables can significantly improve the efficiency of the production process and improve the quality of manufactured products. This is achieved by creating the powerful clamping force needed to achieve consistent quality. If the CNC machine does not come with a ready-made table, you can make it yourself. This is a simple process, and diagrams and drawings of devices can be found freely available on the Internet.
- November 15, 2020
- 1218
Electromagnetic plates
The part is held on the plates by the forces of the magnetic field created by electromagnets.
The specific traction force of modern electromagnetic plates ranges from 20 to 130 N/cm2.
This plate for a rectangular table is made of low-carbon steel. It contains coils placed on cores, connected in series and connected to a direct current source. The plate is placed in a diamagnetic casing, which is mounted on the machine table and closed with a lid with inserts made of non-magnetic material (for example, brass) located above the coil cores.
If you place a part on top, the resulting field will reliably attract the part to be ground to the plate.
Before removing the part, the coils are disconnected from the source and shorted to a discharge resistor, the magnetic field disappears, and the part is released.
Electromagnetic tables.
Round tables are usually used on surface grinding machines and semi-automatic machines with continuous processing of products mounted on a rotating electromagnetic table.
The supply and removal of products is carried out continuously.
By design, such a table consists of fixed and movable parts.
Demagnetizers are used to remove residual magnetism from parts removed from electromagnetic plates and tables.
The demagnetizer consists of a magnetic core (made of sheet steel) with pole shoes (made of soft magnetic steel) and a coil connected to an alternating current network with a frequency of 50 Hz. The shoes are separated by non-magnetic spacers. The part is placed on the pole shoes, moved back and forth several times and demagnetized under the influence of an alternating magnetic field.
Plates with permanent magnets are used in precision (high-precision) grinding machines to secure parts.
They do not require a power source, have a long service life, and are more reliable in operation, since they eliminate the possibility of parts falling off the surface of the plate in the event of a power failure.
The average traction force of the plates is from 60 to 70 N/cm2.
The part is held on the plates by the forces of the magnetic field created by electromagnets.
The specific traction force of modern electromagnetic plates ranges from 20 to 130 N/cm2.
This plate for a rectangular table is made of low-carbon steel. It contains coils placed on cores, connected in series and connected to a direct current source. The plate is placed in a diamagnetic casing, which is mounted on the machine table and closed with a lid with inserts made of non-magnetic material (for example, brass) located above the coil cores.
If you place a part on top, the resulting field will reliably attract the part to be ground to the plate.
Before removing the part, the coils are disconnected from the source and shorted to a discharge resistor, the magnetic field disappears, and the part is released.
Electromagnetic tables.
Round tables are usually used on surface grinding machines and semi-automatic machines with continuous processing of products mounted on a rotating electromagnetic table.
The supply and removal of products is carried out continuously.
By design, such a table consists of fixed and movable parts.
Demagnetizers are used to remove residual magnetism from parts removed from electromagnetic plates and tables.
The demagnetizer consists of a magnetic core (made of sheet steel) with pole shoes (made of soft magnetic steel) and a coil connected to an alternating current network with a frequency of 50 Hz. The shoes are separated by non-magnetic spacers. The part is placed on the pole shoes, moved back and forth several times and demagnetized under the influence of an alternating magnetic field.
Plates with permanent magnets are used in precision (high-precision) grinding machines to secure parts.
They do not require a power source, have a long service life, and are more reliable in operation, since they eliminate the possibility of parts falling off the surface of the plate in the event of a power failure.
The average traction force of the plates is from 60 to 70 N/cm2.