Connection sizes for plumbing fixtures, taps, ½ and ¾ hoses - how do I know which one I need?
For example, the connecting size of the mixer is ¾.
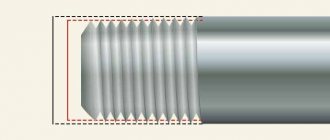
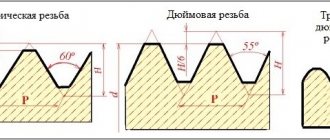
For pipes and other plumbing components, the measurement taken as a basis is from an inch to 25.4 mm. And it’s not so easy to express everything in millimeters. For example, ½ is a 15 mm pipe, and ¾ is 20 mm, an inch is clear 25 mm, an inch and a quarter is 32 mm. All this is along the flow section of the pipe. Even more complexities in carvings. There is a count of the number of threads per inch of length - 12, 14, 16, 18, depending on the diameter.
But there is no need to bother you with these difficulties. On faucets and other fittings it is written: ( 15 ) is ½ inch, (20) is ¾ inch.
For me, like for everyone, it was absolutely not clear what these fractions were in the notation, I had to figure it out.
For our country, sometimes designations of connections such as ½ and ¾ are sometimes not clear to everyone, but here everything depends on experience and general development, since these sizes have long taken root in the country in various areas of production, from plumbing structures to complex devices.
So, in Russia, the metric measure is mainly used in connecting structures, so the most common connection - bolts and nuts, have sizes M6, M8, M10, M12, M14, etc. The letter M indicates that measurements are in the Metric system, and the number indicates the diameter in millimeters.
But in addition to the metric system, which by the way is used in most countries (about 90%), there is also an inch unit of measurement. In Russia, this system is allowed in industry indefinitely.
It is the inch system that is widely used in plumbing, namely in designating connections and measuring the diameter of pipes. The most common designations are ½", ¾", 1″.
½ pipes are installed throughout the house/apartment, ¾ pipes are usually used to the apartment, and 1″ pipes to the house (if it is not large).
But still, let's figure out what exactly these numbers mean.
So, the designation ½ means that the thread size is ½", but in fact the nominal diameter of the pipe in metric measure will be equal to 15 millimeters, the external thread, or rather its outer diameter, is 20.955 millimeters, and the outer diameter of the pipe is 21.3 millimeters, but People commonly refer to ½ pipe as 20 (twenty), i.e. our craftsmen rounded this size to 20.
Now about the designation ¾, this means that the size of the threaded connection on the pipe is ¾", but in fact the nominal diameter of the pipe in metric measure will be equal to 20 millimeters, the external thread, or rather its outer diameter, is 26.441 millimeters, and the outer diameter of the pipe is 26, 8 millimeters.
But absolutely no one needs all these conversions into millimeters, and no one uses them, these numbers do not express either the internal or external diameters of the pipe, the only thing they are tied to is the nominal diameter.
Yes, by the way, ½ and ¾ are not even an inch, and they don’t even translate into an inch, it’s, to put it more clearly, a pipe inch.
Documentation that regulates threaded connections on pipes under the numbers: GOST 3262, GOST 6357.
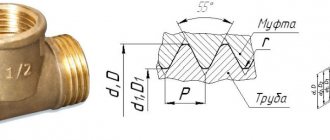
Connection device to the outlet and its designation
Steel couplings with or without zinc coating, having double-sided threads, are intended for connecting water and gas pipes in heating systems, gas pipelines, water pipelines and other lines with a non-aggressive working fluid at temperatures up to +175 C. and pressure less than 1, 6 MPa. (16 atm. or bar.). To connect the pipeline with plumbing and gas equipment, the fitting includes a coupling (has lateral longitudinal ribs for engagement with a gas wrench) and a lock nut with standard dimensions corresponding to the external pipe thread of the fitting in accordance with GOST 8969-75.
The fitting marking according to GOST 8969-75 includes the name of the part (squeeze), nominal diameter, material of manufacture (letter C for galvanized steel) and an indication of the above standard. An example of marking is Sgon 25-Ts GOST 8969-75.
Rice. 4 Installation of the drive
Where are squeegees used and installed?
Squeegees are used in water supply systems, heating systems, gas pipelines, they are installed:
- In water supply and heating lines after the valve on the riser. This allows the shut-off valves to be removed from the pipeline in the event of a malfunction for repair or replacement.
- When connecting old-style cast iron pipes to a heating radiator, their use also allows you to clean the pipeline from lime deposits and rust.
- For the supply line when connecting autonomous equipment for heating water - gas boilers, boilers, expansion tanks and plumbing fittings (faucets with a herringbone connector).
- On the pipeline for supplying gas to household and water heating equipment - stoves, boilers.
- Sometimes surges are used in sections of the system to obtain additional outlet, while the coupling is replaced with a tee, and the distance between the pipes is increased.
Table of water pipe diameters
Pipes are qualified according to their external size, which is specified by the manufacturer. To determine the internal diameter, you will need to subtract twice the wall thickness from the external value. However, products made of cast iron and steel are marked by internal diameter, taking into account their throughput. This should be remembered when using products made from different materials in the same system. Let's look at a few examples.
Steel pipe 76x3 means:
- outer diameter of the product 76 mm;
- wall thickness 3 mm;
- the internal passage will be 70 mm.
The calculation was as follows: 76 - (3x2) = 70 mm.
2 example. 1" copper pipe implies an outer thickness of 1 inch, or 25.4 mm.
Fittings are used to join products made of different materials. To connect a metal and plastic pipe, the fittings will have plastic on one side, which will allow for high-quality soldering, and on the other, threads for a reliable threaded connection
To do this, you need to pay attention to the thread size and pitch. When connecting to cast iron, sockets and special seals are used
Plastic can be soldered together, metal can be welded using electric or gas welding.
Steel
Table of sizes of steel pipes
When installed with steel products, their selection is made according to the outer diameter of the pipe of the water supply system. According to the requirements of GOST 10704–91, they are divided into groups:
- large diameter - from 508 mm;
- medium – 114-530 mm;
- small – up to 114 mm.
In home plumbing, the most popular products are those with small sizes. Medium - in the city water supply. Large - for main oil and gas pipelines. The most popular products include:
- ½” - 12.7 mm;
- ¾” - 19.0 mm;
- 1” - 25.4 mm;
- 1½” - 38.1 mm.
Specialists who are involved in laying and repairing water pipes on a daily basis know these values by heart, while others look them up in tables.
Cast iron
Cast Iron Pipe Size Chart
These products are used when laying street water supply networks. Their use indoors is limited. They have long-lasting operation and increased strength. However, they are fragile and are susceptible to impact. Disadvantages include significant weight and high cost. The size of the pipe for such a water supply system is calculated according to the internal throughput of the product.
Plastic
Modern technologies make it possible to produce high-quality plastic that is sufficiently durable, lightweight, does not corrode, and is an environmentally friendly material. Thanks to these characteristics, it displaces metal and cast iron from the construction market; its cost is significantly lower than these materials. The most popular materials are:
Plastic pipe size chart
- polyethylene - is the cheapest option, used for technical water supply in utility rooms;
- polypropylene - requires special equipment for soldering, well suited for cold water supply in the house;
- metal-plastic - one of the highest quality in this segment, used in cold and hot water supply indoors.
The size of these products leaves much to be desired. The problem is that each manufacturer sets its own sizing chart. Therefore, when assembling a plastic water supply system, it is advisable to purchase all components from one manufacturer. Or you will have to take measurements of each product. Despite this, plastic pipelines are distinguished by their performance characteristics and are very popular, especially when laying water distribution indoors.